public class MyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new MyServerInitializer());
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(8899).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}-
创建两个事件循环组
EventLoopGroup,即bossGroup和workerGroup。 -
bossGroup接收事件后,转发给workerGroup。
NioEventLoopGroup
构造函数如下:bossGroup的线程数通常指定为1
public NioEventLoopGroup() {
this(0);
}
//指定线程个数
public NioEventLoopGroup(int nThreads) {
this(nThreads, (Executor) null);
}NioEventLoopGroup实现了 EventLoopGroup接口, EventLoopGroup文档说明:
// 提供将Channel可以注册到EventLoopGroup中的若干方法
public interface EventLoopGroup extends EventExecutorGroup {
//返回下一个即将被使用的EventLoop
@Override
EventLoop next();
//将Channel注册到EventLoop中,注册完成后,返回的ChannelFuture对象会得到通知
ChannelFuture register(Channel channel);
//传入的ChannelPromise对象在注册完成后也会得到通知
ChannelFuture register(ChannelPromise promise);
}-
ChannelPromise接口继承了ChannelFuture接口。
- 构造函数中的其他参数的默认值:
selectorProvider: SelectorProvider.provider()selectStrategyFactory:DefaultSelectStrategyFactory.INSTANCErejectedExecutionHandler:RejectedExecutionHandlers.reject()
-
NioEventLoopGroup的父类MultithreadEventLoopGroup: 当传入的
nThreads线程数为0时,会使用默认线程数字段DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS,它的计算逻辑如下:public abstract class MultithreadEventLoopGroup extends MultithreadEventExecutorGroup implements EventLoopGroup { private static final int DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS; static { DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS = Math.max(1, SystemPropertyUtil.getInt( "io.netty.eventLoopThreads", NettyRuntime.availableProcessors() * 2)); } protected MultithreadEventLoopGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor, Object... args) { super(nThreads == 0 ? DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS : nThreads, executor, args); } }
2.线程工厂ThreadFactory和执行器Executor
MultithreadEventLoopGroup是之前提到的NioEventLoopGroup的父类,是一个抽象类。在上节中提到它有一套计算线程数量的逻辑。
它继承自MultithreadEventExecutorGroup,而且真正的构造函数逻辑就在它的父类中。
MultithreadEventExecutorGroup
protected MultithreadEventExecutorGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor,
EventExecutorChooserFactory chooserFactory, Object... args) {
......
//创建一个‘线程任务执行器’,传入一个线程工厂作为参数
if (executor == null) {
executor = new ThreadPerTaskExecutor(newDefaultThreadFactory());
}
......
}ThreadFactory是一个接口,只定义了一个newThread 方法如下:
public interface ThreadFactory {
Thread newThread(Runnable r);
}
线程工厂使得线程的创建和线程的执行逻辑得到解耦,线程工厂可以设置线程的优先级、名字、是否后台线程、所属的ThreadGroup等信息。例如常用的工具类Executors的内部类DefaultThreadFactory就是接口ThreadFactory的一个实现类:
static class DefaultThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory {
private static final AtomicInteger poolNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
private final ThreadGroup group;
private final AtomicInteger threadNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
private final String namePrefix;
DefaultThreadFactory() {
SecurityManager s = System.getSecurityManager();
group = (s != null) ? s.getThreadGroup() :
Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup();
namePrefix = "pool-" +
poolNumber.getAndIncrement() +
"-thread-";
}
//创建新线程,设置是否后台运行,所属的ThreadGroup,优先级
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread t = new Thread(group, r,
namePrefix + threadNumber.getAndIncrement(),
0);
if (t.isDaemon())
t.setDaemon(false);
if (t.getPriority() != Thread.NORM_PRIORITY)
t.setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY);
return t;
}
}
执行器接口--Executor
Executor接口是一个函数式接口,定义了一个execute方法:
public interface Executor {
void execute(Runnable command);
}
上面的ThreadPerTaskExecutor就是Executor接口的实现类:
public final class ThreadPerTaskExecutor implements Executor {
private final ThreadFactory threadFactory;
public ThreadPerTaskExecutor(ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
if (threadFactory == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("threadFactory");
}
this.threadFactory = threadFactory;
}
@Override
public void execute(Runnable command) {
threadFactory.newThread(command).start();
}
}
它持有一个线程工厂ThreadFactory对象,使用代理模式,执行时使用线程工厂创建了一个新的线程,并启动。
Executor接口提供了一种执行任务的新方式,不是直接新建线程并运行new Thread(Runnable).start()。创建Executor接口的实现类,将Runnable对象传入执行器中执行。
Executor executor = new XXXExeutor();
executor.execute(new RunnableTask1());
executor.execute(new RunnableTask2());
具体例如:
-
直接执行
Runnable对象class DirectExecutor implements Executor { public void execute(Runnable r) { r.run(); } }} -
ThreadPerTaskExecutor的例子是新建了一个线程执行任务。 -
将任务按照一定的顺序执行,如
io.grpc.internal.SerializingExecutor, 它将任务首先添加到队列中,然后按序执行。public final class SerializingExecutor implements Executor, Runnable { private final Queue<Runnable> runQueue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<Runnable>(); public SerializingExecutor(Executor executor) { Preconditions.checkNotNull(executor, "'executor' must not be null."); this.executor = executor; } //将任务添加到队列中,按序执行 @Override public void execute(Runnable r) { runQueue.add(checkNotNull(r, "'r' must not be null.")); schedule(r); } }
1. ServerBootstrap的使用:
通过链式的方式逐个调用group、channel、handler、childHandler方法,本质上是对需要的变量进行赋值。
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))
.childHandler(new MyServerInitializer());ServerBootStrap继承了抽象类AbstractBootstrap,作用是启动ServerChannel。一些重要的变量定义位于父类AbstractBootStrap中,而另一些位于子类ServerBootStrap中,下面会提到。
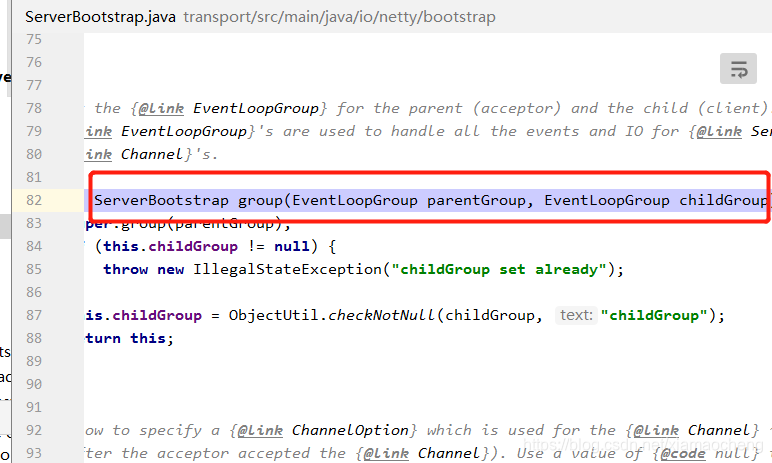
分解之后:
82:将参数 parentGroup 也就是bossGroup对象传入父类的group方法。
父类AbstractBootStrap的group方法如下:可以看到是将bossGroup对象赋值给父类的成员变量group。
2.channel 方法:
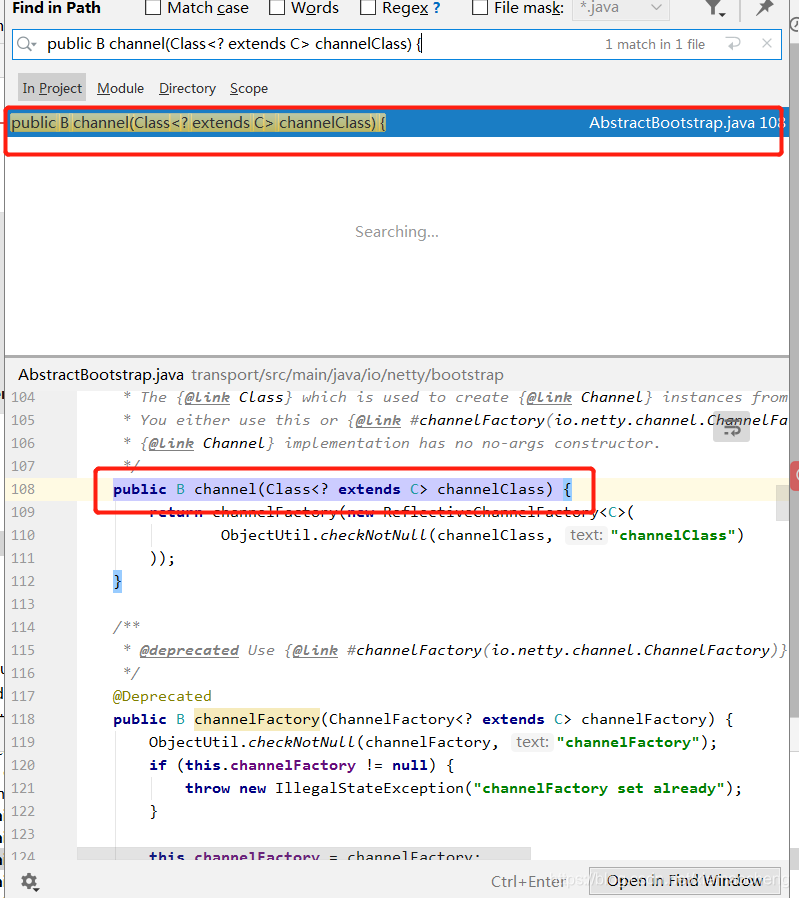
channel方法位于父类中,本质是new一个ReflectiveChannelFactory,并赋值给父类的成员变量channelFactory。 在需要的时候,使用持有的channelFactory变量来创建channel。
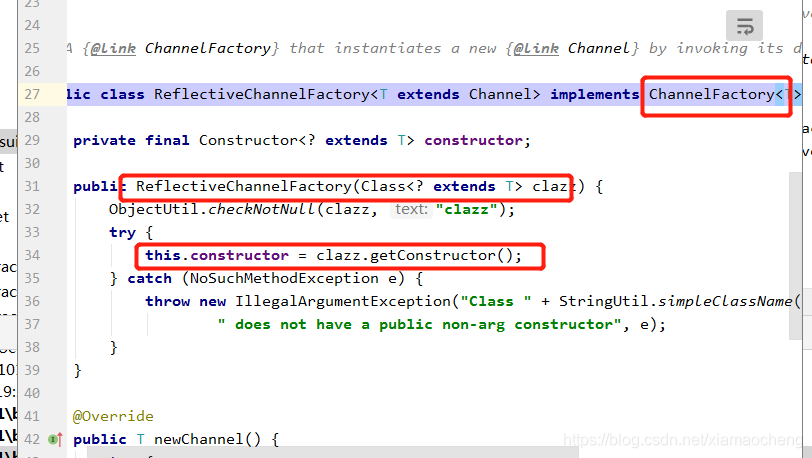
ReflectiveChannelFactory实现了ChannelFactory接口,它的newChannel方法调用传入的Class对象的
构造函数创建实例:
3. childHandler方法:
public ServerBootstrap childHandler(ChannelHandler childHandler) {
if (childHandler == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("childHandler");
}
this.childHandler = childHandler;
return this;
}调用的堆栈:
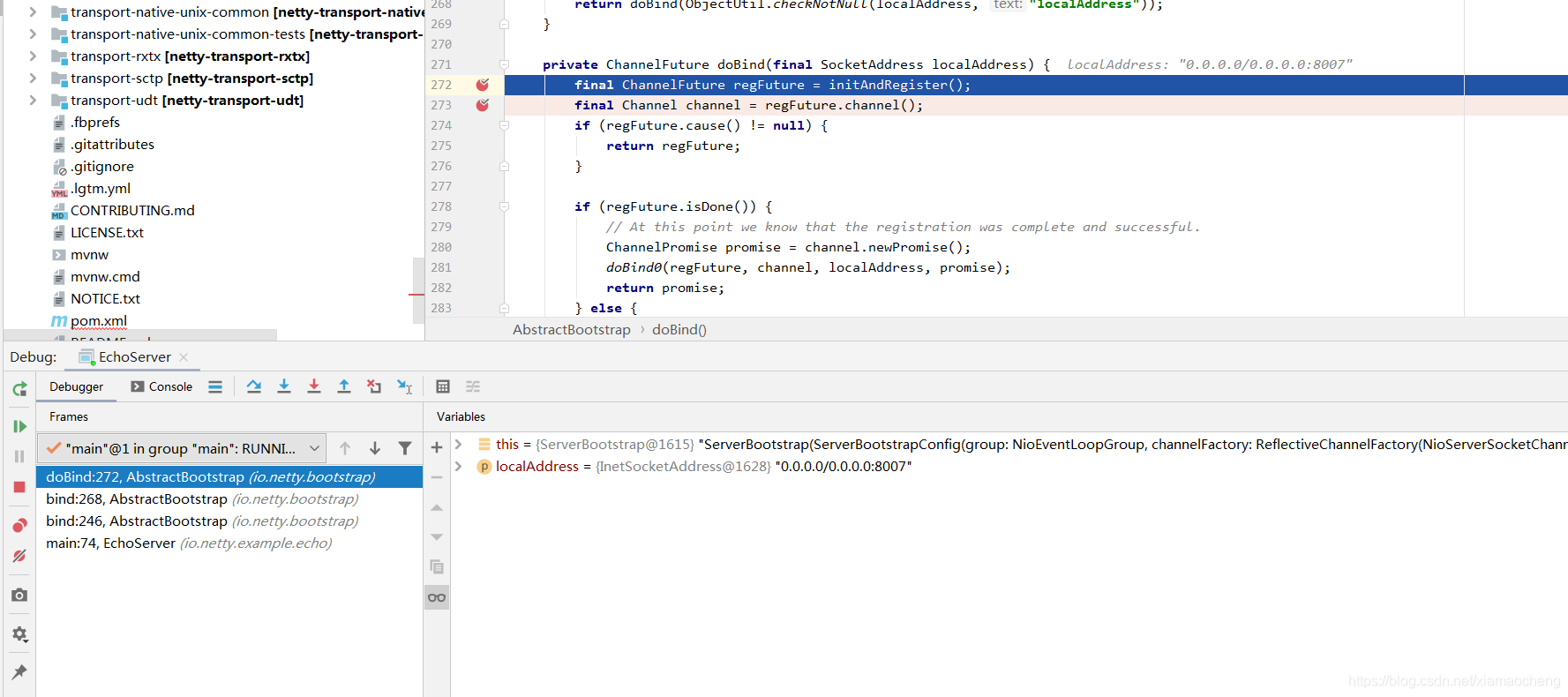
总结1:
group, channel, childHandler方法对变量group, childGroup, channelFactory, childHandler变量进行了赋值。
总结2:
selector 是在new NioEventoop()时创建的。
selectionKey=javaChaneele().register(eventLoop,0,this);
最终监听OP_ACCEPT是通过bind完成后的firechnelACtivate 来出发的。
NioEventLOOP 是通过register操作的执行来完成的
相关log:
参考文档





 本文详细解析了Netty服务端的启动流程,包括事件循环组(EventLoopGroup)的创建与配置,NioEventLoopGroup的工作原理,ServerBootstrap的使用方法以及关键组件如Channel、Handler的注册过程。
本文详细解析了Netty服务端的启动流程,包括事件循环组(EventLoopGroup)的创建与配置,NioEventLoopGroup的工作原理,ServerBootstrap的使用方法以及关键组件如Channel、Handler的注册过程。

















 794
794

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










