目录
- Java实现队列
- 队列的经典题目
1.Java实现队列
1.1.概念
因为Queue是一个接口,所以不能自己实例化,所以需要通过链表和数组两种方式来实现它,,,
链表实现(较简单):
public class MyLinkedList {
static class Node {
public int val;
public Node next;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
public Node head;
public Node last;
public int usedSize;
/**
* 入队
*/
public void offer(int val) {
Node node = new Node(val);
if(this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
this.last = node;
} else {
this.last.next = node;
this.last = node;
}
this.usedSize++;
}
/**
* 出队
*/
public int poll() {
if(isEmpty()) {
throw new MyLinkedListIsEmpty("队列为空!");
}
int val = this.head.val;
this.head = this.head.next;
//处理一个结点的情况
if(this.head == null) {
this.last = null;
}
this.usedSize--;
return val;
}
/**
* 出队,,但是不删除
*/
public int peek() {
if(isEmpty()) {
throw new MyLinkedListIsEmpty("队列为空!");
}
return this.head.val;
}
public int size() {
return this.usedSize;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return usedSize == 0;
}
}
数组实现(比上面那个难):
public class MyCircularQueue {
private int elem[];
private int front;
private int rear;
public static final int DEFAULT_SIZE = 5;
public MyCircularQueue() {
this.elem = new int[DEFAULT_SIZE];
}
/**
* 入队
*/
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
if(isFull()) {
return false;
}
this.elem[this.rear] = value;
this.rear = (this.rear + 1) % this.elem.length;
return true;
}
/**
* 出队
*/
public int deQueue() {
if(isEmpty()) {
throw new MyCircularQueueIsEmpty("对列为空");
}
int val = this.elem[this.front];
this.front = (this.front + 1) % this.elem.length;
return val;
}
/**
* 获取对头元素
*/
public int Front() {
if(isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
return this.elem[this.front];
}
/**
* 得到队尾元素
*/
public int Rear() {
if(isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
return this.rear == 0 ? this.elem[this.elem.length - 1] : this.elem[rear - 1];
}
public Boolean isEmpty() {
return this.rear == this.front;
}
public Boolean isFull() {
return (this.rear+1)%this.elem.length == this.front;
}
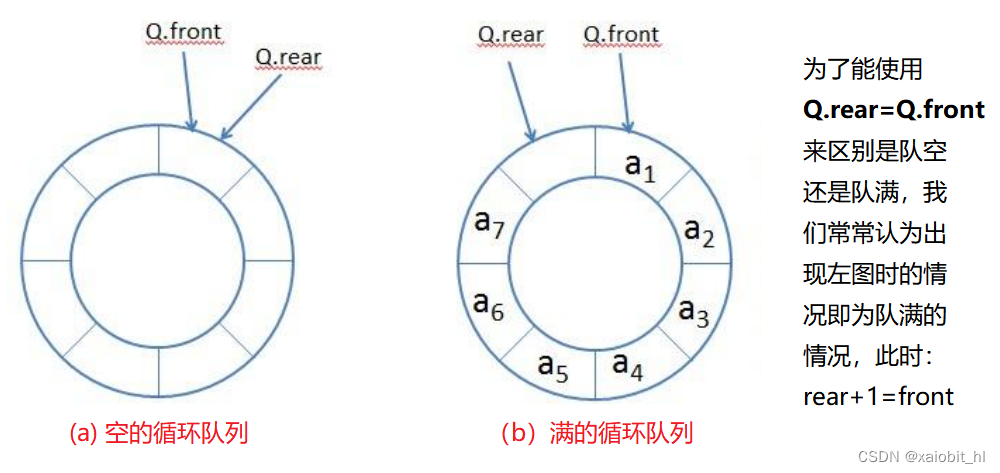
}这里要注意两个点:
1.就是图中文字描述:我们为了让 rear == front 用来判断队空,所以我们在循环队列里空一个位置;当然不止有这一种方法可以区别,我们还可以用计数器来判断:rear == front时,count或usedSize不为0,则队列不为空;
2.我们这里要用到一个公式:下图中 a7 下标如何走到 a1 下标,也就是说正常情况我们的 a7 下标为 6 ,走到下一个元素一般是 ++ ,但是这里 a1 下标为 0,这样就做不到了,所以rear -> front 就有这样一个公式:(rear+1) % array.length ; 当然对头往后走一步,也需要这样处理才合理,,
2.队列的经典题目
2.1.用队列实现栈

class MyStack {
private Queue<Integer> queue1;
private Queue<Integer> queue2;
public MyStack() {
queue1 = new LinkedList<>();
queue2 = new LinkedList<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
if(!queue1.isEmpty()) {
queue1.offer(x);
} else if(!queue2.isEmpty()){
queue2.offer(x);
} else {
queue1.offer(x);
}
}
public int pop() {
if(queue1.isEmpty() && queue2.isEmpty()) return -1;
if(!queue1.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue1.size();
for(int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++) {
int tmp = queue1.poll();
queue2.offer(tmp);
}
return queue1.poll();
} else {
int size = queue2.size();
for(int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++) {
int tmp = queue2.poll();
queue1.offer(tmp);
}
return queue2.poll();
}
}
public int peek() {
if(empty()) return -1;
if(!queue1.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue1.size();
int tmp = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
tmp = queue1.poll();
queue2.offer(tmp);
}
return tmp;
} else {
int size = queue2.size();
int tmp = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
tmp = queue2.poll();
queue1.offer(tmp);
}
return tmp;
}
}
public boolean empty() {
return queue1.isEmpty() && queue2.isEmpty();
}
}用队列实现栈,我们是需要准备两个队列的,不然无法做到;
1.push函数: 我们把元素都放在一个队列里头,也就是谁不为空就放谁,这里规定一下都为空的时候放queue1,当然,你也可以放queu2;
2.pop函数:先把不为空的队列 queue1 倒出 size-1 个元素 到 queue2 中,然后弹出剩下的那个元素;
3.peek函数:将不为空的队列 queue1 中的所有元素倒入 queue2 队列中,然后返回 queue.peek();当然,我这里是把每一个倒出来的元素都存在了一个 tmp 变量中,所以我只需要返回 tmp 变量;
4.empty函数:两个队列都为空就返回true;
2.2.用栈实现队列

class MyQueue {
private Stack<Integer> stack1;
private Stack<Integer> stack2;
public MyQueue() {
stack1 = new Stack<>();
stack2 = new Stack<>();
}
public void offer(int x) {
stack1.push(x);
}
public int poll() {
if(isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
if(!stack2.empty()) {
return stack2.pop();
} else {
int size = stack1.size();
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
int tmp = stack1.pop();
stack2.push(tmp);
}
return stack2.pop();
}
}
public int peek() {
if(isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
if(!stack2.empty()) {
return stack2.peek();
} else {
int size = stack1.size();
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
int tmp = stack1.pop();
stack2.push(tmp);
}
return stack2.peek();
}
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
if(stack1.empty() && stack2.empty()) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
}同样的,用栈实现队列,我们也需要两个栈,实现起来也是很相似的;
1.offer函数:我们规定一下入队都入在在stack1中,出队都出stack2中的元素;
2.poll函数:我们有两种情况:如果stack2中无元素,则把stack1中的元素全部倒入stack2中;
如果stack2中有元素,则直接出stack2中的元素;
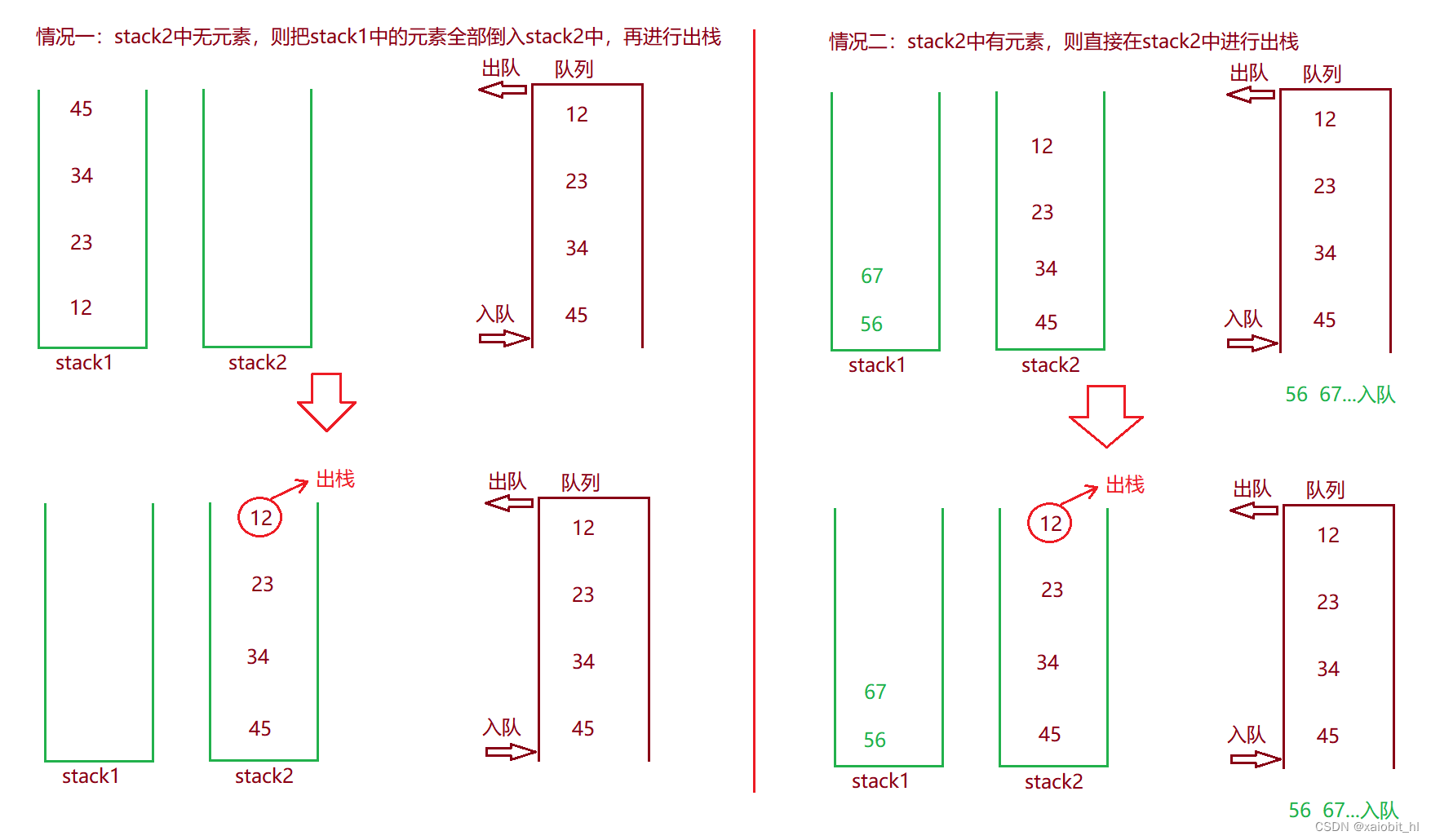
3.peek函数: 稍稍改动一下poll函数即可,poll函数是弹出栈,peek只需要返回stack2的栈顶即可;
4.isEmpty:当两个栈同时为空,才可以判断队列为空;
2.3.最小栈

class MinStack {
private Stack<Integer> stack1;
private Stack<Integer> MinStack;
public MinStack() {
stack1 = new Stack<>();
MinStack = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int val) {
stack1.push(val);
if(MinStack.empty()) {
MinStack.push(val);
} else {
if(val <= MinStack.peek()) {
MinStack.push(val);
}
}
}
//题目规定了栈不为空,所以这里没判断
public void pop() {
int tmp = stack1.pop();
if(tmp == MinStack.peek()) {
MinStack.pop();
}
}
//题目规定了栈不为空
public int top() {
return stack1.peek();
}
public int getMin() {
return MinStack.peek();
}
}
题目的目的是想让我们在O(1)时间复杂度内拿到栈的最小值,所以这里我们不能去遍历栈,而是需要用到两个栈,下面用画图的形式分析一下如何做到:

谢谢观看!!!








 本文详细讲解了Java中如何通过链表和数组实现队列,并展示了队列在栈模拟、队列实现栈和最小栈问题中的应用。深入理解了队列的先进先出特性及其在数据结构中的关键作用。
本文详细讲解了Java中如何通过链表和数组实现队列,并展示了队列在栈模拟、队列实现栈和最小栈问题中的应用。深入理解了队列的先进先出特性及其在数据结构中的关键作用。


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










