链表
链表与数组
存储多个元素,数组可能是最常用的数据结构
数组的缺点
- 数组的创建需要申请一段连续的内存空间,并且大小是固定的。(大多数语言数组是固定的)。当数组不能满足容量需求时,需要扩容。
- 数组的开头或中间位置插入数据的成本很高,需要进行大量元素的位移。
- javascriptd的Array类的方法背后的原理原理就是这样。
链表的优势
- 链表中的元素在内存中不必是连续的空间。
- 链表中的每个元素由一个存储元素本身的节点和一个**指向下一个元素的引用(指针或连接)**组成。
相对于数组的优点:
- 内存空间不连续,可以充分利用计算机的内存。实现灵活的内存动态管理。
- 创建链表时不必确定大小,并且可以无限延伸下去。
- 插入和删除数据时,时间复杂度可以达到O(1).相对数组效率高。
相对数组的缺点:
- 访问任何一个位置的元素,需要从头开始访问。
- 无法通过下标直接访问元素,需要从头访问。
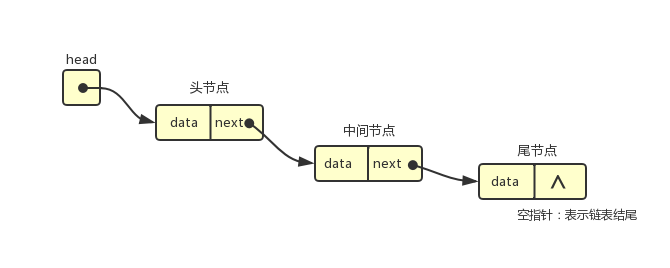
封装一个链表类
function LinkedList () {
//链表属性
this.head = null;
this.length = 0;
//内部类:节点类
function Node (data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
//1.链表尾部添加一项 append(data)
LinkedList.prototype.append = function (data) {
//1.1 创建一个新的节点对象
var newNode = new Node(data);
//1.2 如果添加的是第一个节点为空
if(this.length == 0) {
this.head = newNode;
}else{
//如果不是找到最后一个节点
var current = this.head;
while(current.next) {
current = current.next;
}
current.next = newNode;
}
//1.3链表长度+1
this.length += 1;
}
//2.toString方法
LinkedList.prototype.toString = function () {
var current = this.head;
var listString = '';
while(current) {
listString += current.data + ' ';
current = current.next;
}
return listString;
}
//3.在特定位置插入insert(position,data)
LinkedList.prototype.insert = function (position,data) {
//创建一个节点
var newNode = new Node(data);
//对position进项越界判断
if(position < 0 || position > this.length) {return false;}
//判断插入位置为第一个
if(position == 0) {
newNode.next = this.head;
this.head = newNode;
}else { //不为第一个
var index = 0;
//设置前一个节点
var previous = null;
//设置后一个节点
var current = this.head;
while(index < position) {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
index ++;
}
//插入节点
newNode.next = current;
previous.next = newNode;
}
//长度 +1
this.length += 1;
}
//4.获取对应位置元素 get(position)
LinkedList.prototype.get = function(position) {
if(position < 0 || position >= this.length ) {return null;}
var current = this.head;
var index = 0;
while(index < position) {
current = current.next;
index ++;
}
return current;
}
//5.返回元素在列表中的索引,否则返回-1 indexof(data)
LinkedList.prototype.indexof = function(data) {
var current = this.head;
var index = 0;
while(current) {
if(data == current.data) {
return index;
}
current = current.next;
index ++;
}
return -1;
}
//6.修改某个位置的元素 updata(position,data)
LinkedList.prototype.update = function(position,data) {
var newNode = new Node(data);
if(position < 0 || position >= this.length) {return false;}
var current = this.head;
var index = 0;
while(index++ < position) {
current = current.next;
}
current.data = newNode.data;
return true;
}
//7.移除特定位置的数据 removeAt(position)
LinkedList.prototype.removeAt = function(position) {
var current = this.head;
//越界判断
if(position < 0 || position >= this.length) {return null};
//删除的是第一个节点
if(position == 0) {
this.head = this.head.next;
}else{ //不是第一个节点
var index = 0;
var previous = null;
while(index++ < position){
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
//让前一个节点的next,指向curr的next
previous.next = current.next;
}
//长度-1
this.length --;
return current.data;
}
//8.移除链表中的一项 remove(data)
LinkedList.prototype.remove = function(data) {
//获取位置
var position = this.indexof(data);
//移除项
return this.removeAt(position);
}
//9.判断了链表元素个数 size()
LinkedList.prototype.size = function () {
return this.length;
}
//10.判断链表是否有元素 isEmpty()
LinkedList.prototype.isEmpty = function() {
return this.length == 0;
}
}
双向链表
单向链表:
- 只能从头遍历到尾
- 链表相连的过程是单向的
- 实现的原理是链表中上一个元素中有一个指向下一个的引用。
- 缺点:可以轻松到达下一个节点,但是到上一个节点需要从头遍历。
双向链表:
- 既可以从头遍历到尾,又可以从尾遍历到头。
- 链表相连的过程是双向的
- 实现的原理是一个节点既有向前连接的引用,又有向后连接的引用。
- 缺点:抽入和删除节点时需要四个引用,实现起来较困难,而且内存空间更大。但是这些缺点和我们实际应用的方便程度相比,微不足道。
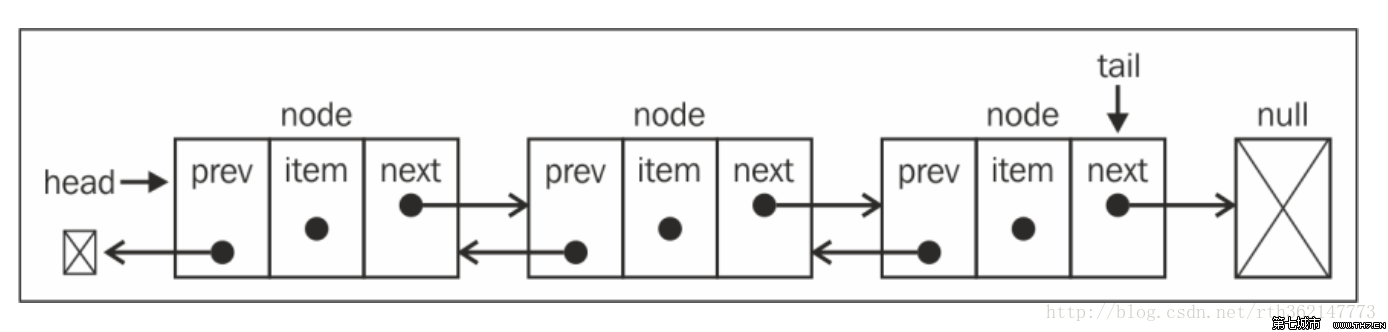
封装一个双向链表类
(可以对比单向链表,插入和删除方法改动较大)
//封装双向链表类
function DoublyLinkedList() {
//属性
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.length = 0;
//内部类:节点类
function Node(data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null;
}
//1.链表尾部添加一项append(data)
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.append = function(data) {
var newNode = new Node(data);
if(this.length == 0) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
}else {
newNode.prev = this.tail;//新节点指向原来的最后一项
this.tail.next = newNode;//原节点的next指向新节点
this.tail = newNode;//新节点作为tail
}
this.length ++;
}
//2.在特定位置插入insert(position,data)
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.insert = function (position,data) {
var newNode = new Node(data);
//2.1越界判断
if(position < 0 || position > this.length) {return false;}
//2.2链表为空时
if(this.length == 0) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
}else { //2.3链表不为空
if(position == 0) { //2.3.1新节点插入最前面
newNode.next = this.head;
this.head.prev = newNode;
this.head = newNode;
}else if(position == this.length) { //2.3.2新节点插入最后一位
newNode.prev = this.tail;
this.tail.next = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
}else { //2.3.3插入中间
var index = 0;
var current = this.head;
//找到插入节点位置
while(index < position) {
current = current.next;
index ++;
}
//修改指针
newNode.next = current;
newNode.prev = current.prev;
current.prev.next = newNode;
current.prev = newNode;
}
}
//长度 +1
this.length ++;
return true;
}
//3.toString方法(从头遍历和从尾遍历)
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.toString = function() {
return this.forwordString();
}
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.forwordString = function() {
var resultString = '';
var current = this.head;
while(current) {
resultString += current.data + " ";
current = current.next;
}
return resultString;
}
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.backwordString = function() {
var resultString = '';
var current = this.tail;
while(current) {
resultString += current.data + " ";
current = current.prev;
}
return resultString;
}
//4.获取对应位置元素 get
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.get = function(position) {
if(position < 0 || position >= this.length ) {return null;}
if(position < this.length / 2 ) { //当position较小时从头遍历
var current = this.head;
var index = 0;
while(index < position) {
current = current.next;
index ++;
}
return current;
}else {
var current = this.tail;
var index = this.length - 1;
while(index > position) { //当position较大时从尾遍历
current = current.prev;
index --;
}
return current;
}
}
//5.返回元素在列表中的索引,否则返回-1
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.indexof = function(data) {
var current =this.head;
var index = 0;
while(current) {
if(current.data == data) {
return index;
}
index ++;
current = current.next;
}
return -1;
}
//6.修改某个元素 update
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.update = function(position,data) {
if(position < 0 || position >= this.length ) {return false;}
if(position < this.length / 2) {
var current = this.head;
var index = 0;
while(index ++ < position) {
current = current.next;
}
current.data = data;
return true;
}else {
var current = this.tail;
var index = this.length - 1;
while(index -- > position) {
current = current.prev;
}
current.data = data;
return true;
}
}
//7.移除特定位置的数据 removeAt
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.removeAt = function(position) {
//越界判断
if(position < 0 || position >= this.length) {return null;}
var current = this.head;
//只有一个节点时
if(this.length == 1) {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
}else { //不只一个节点时
if(position == 0) { //在移除第一个节点
this.head.next.prev = null;
this.head = this.head.next;
}else if(position == this.length - 1) { //移除最后一个节点
current = this.tail;
this.tail.prev.next = null;
this.tail = this.tail.prev;
}else { //移除中间节点
var index = 0;
while(index ++ < position) {
current = current.next;
}
current.prev.next = current.next;
current.next.prev = current.prev;
}
}
this.length --;
return current.data;
}
//8.移除链表中的一项 remove
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.remove = function(data) {
var position = this.indexof(data);
return this.removeAt(position);
}
//9.isEmpy
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.isEmpty = function() {
return this.length == 0;
}
//10.size
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.size = function() {
return this.length;
}
}





















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








