求从迷宫左上角(0,0)到右下角(M-1,N-1)的路径。
M x N的迷宫如下:O代表可通行,X代表不可通行。每次只能往上下左右四个方向走一步。
{'O','X','X','X','X','X','X','X'
'O','O','O','O','O','X','X','X'
'X','O','X','X','O','O','O','X'
'X','O','X','X','O','X','X','O'
'X','O','X','X','O','X','X','X'
'X','O','X','X','O','O','O','X'
'X','O','O','O','O','X','O','O'
'X','X','X','X','X','X','X','O'}
一、深度优先算法求出所有到达出口的路径:
#include <iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
#define m 8//迷宫的长度
#define n 8//迷宫的宽度
int s=1;//答案个数记录
typedef struct location{
int xx,yy;
}location;//位置
void findpath(location L, int **map, vector<string>& path) {
// 越界检查
if (L.xx < 0 || L.yy < 0 || L.xx >= m || L.yy >= n || map[L.xx][L.yy] == 0) {
return;
}
// 到达终点
if (L.xx == m - 1 && L.yy == n - 1) {
s++;
string lo = "(" + to_string(L.xx) + "," + to_string(L.yy) + ")";
path.push_back(lo);
cout << "第" << s << "种路径为:";
for (const string& p : path) {
cout << p << " ";
}
cout << endl;
path.pop_back();
return;
}
// 标记为已访问
map[L.xx][L.yy] = 0;
// 四个方向进行搜索
vector<location> directions = {{1, 0}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}};
for (const auto& dir : directions) {
location next = {L.xx + dir.xx, L.yy + dir.yy};
string lo = "(" + to_string(L.xx) + "," + to_string(L.yy) + ")";
path.push_back(lo);
findpath(next, map, path);
path.pop_back();
}
// 回溯,恢复状态
map[L.xx][L.yy] = 1;
}
int main(){
location L;
L.xx=0;
L.yy=0;
int **map=new int*[m];
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
map[i]=new int[n];
}
int Map[m][n]={
{1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{1,1,1,1,1,0,0,0},
{0,1,0,0,1,1,1,0},
{0,1,0,0,1,0,0,1},
{0,1,0,0,1,0,0,0},
{0,1,0,0,1,1,1,0},
{0,1,1,1,1,0,1,1},
{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1}
};//迷宫地图使用二维数组存储
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
map[i][j]=Map[i][j];
}
}
if(map[0][0]==0){
cout<<"这个迷宫没有出路!";
return 0;
}
vector<string> path;
findpath(L,map,path);
if(s==0){
cout<<"没有找到这个迷宫的出路!";
}
return 0;
}
深度优先搜索运用递归遍历通路,并用栈存储正确的迷宫路径。
输出结果:
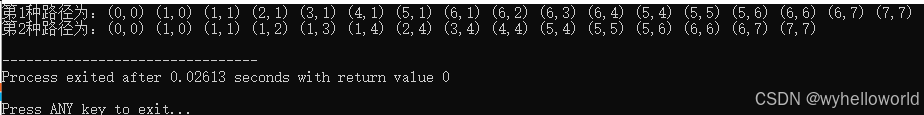
二、广度优先搜索找出最短路径:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include<queue>
#include <string>
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define m 8 // 迷宫的长度
#define n 8 // 迷宫的宽度
int s = 0; // 答案个数记录
using namespace std;
struct location{
int xx;//记录坐标(x,y)
int yy;
int f;//记录是由谁扩展而来,即父亲节点是谁
int h;//这个点在que里的位置
};
struct location que[2501];
const vector<location> directions = {{1, 0}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}};
void output(int x){
if(x==0){
cout<<"最短路径为:(0,0) ";
return;
}
output(que[x].f);
cout<<"("<<que[x].xx<<","<<que[x].yy<<") ";
}
void findpath(location L, int map[][n], queue<location>& path) {
int i=0;
if(L.xx>=m||L.yy>=n){
return;
}
path.push(L);
que[i]=L;
while(!path.empty()){
L=path.front();
map[L.xx][L.yy]=0;
if(L.xx==m-1&L.yy==n-1){
output(i);
break;
}
// 四个方向进行搜索
for (const auto& dir : directions) {
location next = {L.xx + dir.xx, L.yy + dir.yy};
if (map[next.xx][next.yy]==1){
next.f=L.h;
que[++i]=next;
next.h=i;
path.push(next);
}
}
path.pop();
}
}
int main() {
location L;
L.xx = 0;
L.yy = 0;
L.f=0;
L.h=0;
int Map[m][n] = {
{1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1},
{0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0},
{0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1}
}; // 迷宫地图使用二维数组存储
queue<location> path;
findpath(L, Map, path);
return 0;
}
广度优先搜索可以理解为许多人同时开始走迷宫,每个人都在同一时间内向上、下、左、右走一步,最先走到终点的路径就是最短路径。
从根节点开始找到所有能走的点进行入队,根节点出队。以此类推,最先到达终点的为最短路径。此时从终点使用递归寻找该节点的父节点进行逆向输出。
que中保存了所有可以走的路径节点。每个节点有坐标、自己的索引值以及父节点的索引值用来从结果逆向输出路径。
输出结果: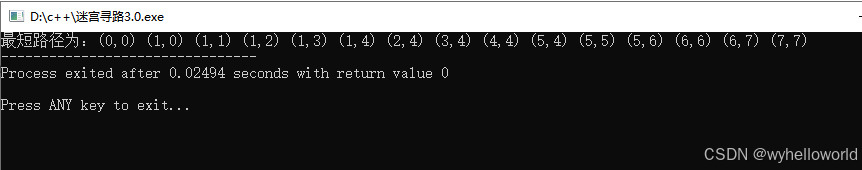
三、从文件中打开地图:
#include <iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;
int s=0;//答案个数记录
typedef struct location{
int xx,yy;
}location;//位置
int M,N;
int** readfile(){
fstream file;//创建fstream对象
file.open("map.txt",std::ios::in);
if (!file) {
std::cerr << "文件打开失败!" << std::endl;
return NULL;//文件打开失败
}
string line;
int i=0;
int j=0;
int **map=new int*[M];
while(getline(file,line)){
map[i]=new int[N];
for(char c:line){
if(c=='1'||c=='O'){
map[i][j++]=1;
}else if(c=='0'||c=='X'){
map[i][j++]=0;
}
}
i++;
j=0;
}
return map;
}
void findpath(location L,int **map,vector<string> path){
if (L.xx < 0 || L.yy < 0 || L.xx >= M || L.yy >= N || map[L.xx][L.yy] == 0) {
return;
}
string lo = "(" + to_string(L.xx) + "," + to_string(L.yy) + ")";
path.push_back(lo);
map[L.xx][L.yy]=0;
if(L.xx==M-1&&L.yy==N-1){
cout<<"第"<<++s<<"种路径为:";
for(string p:path){
cout<<p<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
path.pop_back();
}//如果到达终点,输出路径
location tmp=L;
L.xx += 1;
findpath(L, map, path);
L=tmp;
L.yy += 1;
findpath(L, map, path);
L=tmp;
L.xx -= 1;
findpath(L, map, path);
L=tmp;
L.yy -= 1;
findpath(L, map, path);
L=tmp;
path.pop_back();
map[L.xx][L.yy]=1;
}
int main(){
location L;
L.xx=0;
L.yy=0;
cout<<"请输入地图长宽:";
cin>>M>>N;
int **Map=readfile();
if(Map[0][0]==0){
cout<<"这个迷宫没有出路!";
return 0;
}
vector<string> path;
findpath(L,Map,path);
if(s==0){
cout<<"没有找到这个迷宫的出路!";
}
return 0;
}
这一问中添加了readfile()函数用来从文件中解析地图数据,并使用动态数组存储地图。
输出结果:





















 2657
2657

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








