路径规划
图搜索
- Dijkstra
- A*
- D*
- LPA*
- D* lite
- Theta*
- Lazy Theta*
- MLA*(Multi-Label A*)
- 跳点搜索算法(jps)
- Contraction Hierarchies(graphhopper中有)
- HCBS,SMT-HCBS 多目标MAPF算法
A*算法及其变种
A*变体WHCA
BCP-MAPF
MAPF-LNS, MAPF-LNS2, MAPF-PBS, EECBS
大牛mapf
RHCR:实现了ID(Independence Detection),ECBS, LRA*, PBS WHCA*,单智能体规划实现了SIPP,SpaceTimeA*,其中PBS底层使用SIPP
libMultiRobotPlanning
mapf
mapf相关算法
anytime cbs
ECBS多机器人路径规划
Multi-Agent Path Finding java实现
采样搜索
- 概率路线图(PRM)
- 快速随机探索树(RRT)(Rapidly-exploring Random Trees)
- RRT* 算法
- RRT-Connect
- Informed RRT*
智能算法
- 蚁群算法
- 粒子群算法
- 遗传算法
轨迹规划
- 路径跟踪PID算法
- 最优控制LQR算法
- 模型预测控制MPC算法
- 动态窗口算法DWA
- 人工势场算法APF
- 社会力模型SFM
- TEB算法
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/44040710
x ∈ X , u ∈ U ( x ) 有 x ′ = f ( x , u ) x \in X, u \in U(x)有 x'=f(x,u) x∈X,u∈U(x)有x′=f(x,u)初始状态 x I ∈ X x_I \in X xI∈X目标集 X G ⊊ X X_G \subsetneq X XG⊊X
其中x表示状态,X表示状态集,u表示状态为x时的操作集中的元素,f表示状态转移函数。
库
- STOMP(Stochastic Trajectory Optimization for Motion Planning)(基于概率优化)
- SBPL(Search-based planning library)(基于搜索的规划库)
其包含ARA*, Anytime D*,ANA* ,R和Multi-Heuristic A - CHOMP(Covariant Hamiltonian optimization for motion planning)(基于梯度的轨迹优化)
- OMPL(The Open Motion Planning Library)(基于RRT和PRM)
- MoveIt
- OptaPlanner
- 移动机器人领域相关C++库的综述
- Flexible Collision Library
- cbs-mapf python
- car-like cbs c++实现
- ccbs c++实现
- AA-SIPP(m)
- ORCA
- 路径规划
- Geatpy python遗传算法库
- scip 线性规划库
- Ipopt 非线性最优化问题求解器
- PettingZoo强化学习库
- Google OR-Tools 路线。安排、规划、分配、打包、求解
- jsprit 专注于物流领域的车辆路径规划(VRP)和货物装载优化
- valhalla:开源路径规划库valhalla
- OSRM:开源路径规划库OSRM
机器人学基础
- 《Principles of Robot Motion Theory, Algorithms, and Implementations》
- 《Robotics: Computational Motion Planning》
- 《 Planning Algorithms》
- Optimal and Efficient Path Planning for Unknown and Dynamic Environments
- Lifelong Planning A*
Contraction Hierarchies
《Contraction Hierarchies: Faster and Simpler Hierarchical Routing in Road Networks》
overlay graph:指的是删除伸缩点,保留最短路径的图
edge difference:收缩点v时引用的 shortcut数减去原图中v相连的边数
CH 表示为
(
G
=
(
V
,
E
)
,
<
)
(G=(V,E), <)
(G=(V,E),<)
upward graph:
G
↑
:
=
(
V
,
E
↑
)
,
E
↑
:
=
{
(
u
,
v
)
∈
E
:
u
<
v
}
G_{\uparrow} := (V, E_{\uparrow}), E_{\uparrow} := \{(u,v) \in E: u \lt v \}
G↑:=(V,E↑),E↑:={(u,v)∈E:u<v}
downward graph:
G
↓
:
=
(
V
,
E
↓
)
,
E
↓
:
=
{
(
u
,
v
)
∈
E
:
u
>
v
}
G_{\downarrow} := (V, E_{\downarrow}), E_{\downarrow} := \{ (u, v) \in E: u \gt v\}
G↓:=(V,E↓),E↓:={(u,v)∈E:u>v}
witness path:
P
=
⟨
v
,
.
.
.
,
w
⟩
≠
⟨
v
,
u
,
w
⟩
P=\left\langle v, ..., w\right\rangle \neq \left\langle v, u, w\right\rangle
P=⟨v,...,w⟩=⟨v,u,w⟩
在v,w之间,
w
(
P
)
≤
w
(
⟨
v
,
u
,
w
⟩
)
w\left( P\right) \le w(\left\langle v, u, w\right\rangle)
w(P)≤w(⟨v,u,w⟩)
remaining graph:
以点u为参考,将大于u的点叫做remaining nodes,相边的边叫remaining edges, 由remaining nodes构造的图叫remaing graph
点收缩算法
f
o
r
e
a
c
h
u
∈
V
(
根据点从小到大排序
)
d
o
f
o
r
e
a
c
h
(
v
,
u
)
∈
E
(
v
>
u
)
d
o
f
o
r
e
a
c
h
(
u
,
w
)
(
w
>
u
)
d
o
i
f
⟨
v
,
u
,
w
⟩
是从
v
到
w
的最短路径
E
:
=
E
∪
{
(
v
,
w
)
}
foreach u \in V (根据点从小到大排序) do \\ foreach \left(v, u\right) \in E( v \gt u) do \\ foreach \left(u, w\right)(w \gt u) do \\ if \left\langle v, u, w\right\rangle 是从v到w的最短路径 \\ E := E \cup\{\left(v, w\right)\}
foreachu∈V(根据点从小到大排序)doforeach(v,u)∈E(v>u)doforeach(u,w)(w>u)doif⟨v,u,w⟩是从v到w的最短路径E:=E∪{(v,w)}
SBPL
包含两个抽象类SBPLPlanner和DiscreteSpaceInformation
其结构为
SBPLPlanner结构
ARAPlanner :膨胀系数
e
(
s
)
e(s)
e(s)开始很大,迭代过程中减小
anaPlanner :
e
(
s
)
=
G
−
g
(
s
)
h
(
s
)
e(s)=\frac{G -g(s)}{h(s)}
e(s)=h(s)G−g(s)
DiscreteSpaceInformation结构
LPA*
是正向搜索
r
h
s
(
s
)
=
{
0
s
=
s
t
a
r
t
m
i
n
s
′
∈
p
r
e
d
(
s
)
(
g
(
s
′
)
+
c
(
s
′
,
s
)
)
s
≠
s
t
a
r
t
rhs(s) = \begin{cases} 0 & s = start \\ min_{s' \in pred(s)}(g(s') + c(s', s)) & s \ne start\end{cases}
rhs(s)={0mins′∈pred(s)(g(s′)+c(s′,s))s=starts=start
g(s)与A*中的一致
k
(
s
)
=
[
k
1
(
s
)
k
2
(
s
)
]
=
[
m
i
n
(
g
(
s
)
,
r
h
s
(
s
)
)
+
h
(
s
)
m
i
n
(
g
(
s
)
,
r
h
s
(
s
)
)
]
k(s) =[\begin{matrix} k_1(s) \\\ k_2(s)\end{matrix}] = [\begin{matrix} min(g(s), rhs(s)) + h(s) \\\ min(g(s), rhs(s)) \end{matrix}]
k(s)=[k1(s) k2(s)]=[min(g(s),rhs(s))+h(s) min(g(s),rhs(s))]
D*
属于增量搜索算法
维护两个代价值h(x)和k(x),其中h(x)表示从x到目标的路径的估值,k(x)表示从x到目标的最短路径的估值
{
k
(
x
)
<
h
(
x
)
r
a
i
s
e
s
t
a
t
e
k
(
x
)
=
h
(
x
)
l
o
w
e
r
e
d
s
t
a
t
e
\begin{cases} k(x) < h(x) & raise state \\ k(x) = h(x) & lowered state \end{cases}
{k(x)<h(x)k(x)=h(x)raisestateloweredstate
t
(
X
)
=
{
N
E
W
X
从未在
o
p
e
n
列表中
O
P
E
N
X
在
o
p
e
n
列表中
C
L
O
S
E
D
X
曾在
o
p
e
n
列表中,现在不在
t(X) = \begin{cases} NEW & X从未在open列表中 \\ OPEN & X在open列表中 \\ CLOSED & X曾在open列表中,现在不在 \end{cases}
t(X)=⎩
⎨
⎧NEWOPENCLOSEDX从未在open列表中X在open列表中X曾在open列表中,现在不在
D* Lite
是反向搜索
与LPA*差异在k(s)的
k
1
(
s
)
k_1(s)
k1(s)增加了实际运动距离
k
m
k_m
km
k
(
s
)
=
[
k
1
(
s
)
k
2
(
s
)
]
=
[
m
i
n
(
g
(
s
)
,
r
h
s
(
s
)
)
+
h
(
s
)
+
k
m
m
i
n
(
g
(
s
)
,
r
h
s
(
s
)
)
]
k(s) =[\begin{matrix} k_1(s) \\\ k_2(s)\end{matrix}] = [\begin{matrix} min(g(s), rhs(s)) + h(s) + k_m\\\ min(g(s), rhs(s)) \end{matrix}]
k(s)=[k1(s) k2(s)]=[min(g(s),rhs(s))+h(s)+km min(g(s),rhs(s))]
书籍
《移动机器人路径规划与轨迹跟踪》
《基于增强学习和ART2神经网络的移动机器人路径规划研究》
《不确定因素下物流配送车辆路径规划问题的建模及优化方法》
《Robot Path Planning and Cooperation. Foundations, Algorithms and Experimentations 》
《Advances in Practical Applications of Agents, Multi-Agent Systems, and Complex Systems Simulation》
《Programming Multi-Agent Systems 4th International Workshop》
论文
《ICBS: Improved Conflict-Based Search Algorithm for Multi-Agent Pathfinding》
icbs增加了节点类型,cardinal,semi-cardinal,no-cardinal,优先处理cardinal,semi-cardinal,可以减小节点数,同时使用MDD(multi-value decision diagram)来快速送别节点类型
《Branch-and-Cut-and-Price for Multi-Agent Pathfinding》
《Priority inheritance with backtracking for iterative multi-agent path finding》
《LaCAM:Search-Based Algorithm for Quick Multi-Agent Pathfinding》
两层搜索算法,高层使用DFS,低层使用bfs
其中priorities,order和search_tree用于低层搜索
《Push and Rotate:a Complete Multi-agent Pathfinding Algorithm》
《Searching with Consistent Prioritization for Multi-Agent Path Finding》
《SIPP:Safe Interval Path Planning for Dynamic Environments》
《M*: A Complete Multirobot Path Planning Algorithm with Optimality Bounds》
《Optimal and Bounded-Suboptimal Multi-Goal Task Assignment and Path Finding》
《MGCBS: An Optimal and Efficient Algorithm for Solving Multi-Goal Multi-Agent Path Finding Problem》
github对应代码
《Multi-Goal Multi-Agent Pickup and Delivery》
《Symmetry Breaking for k-Robust Multi-Agent Path Finding》
对称性分三类
- Rectangle Symmetries
- Corridor Symmetries
- Target Symmetries
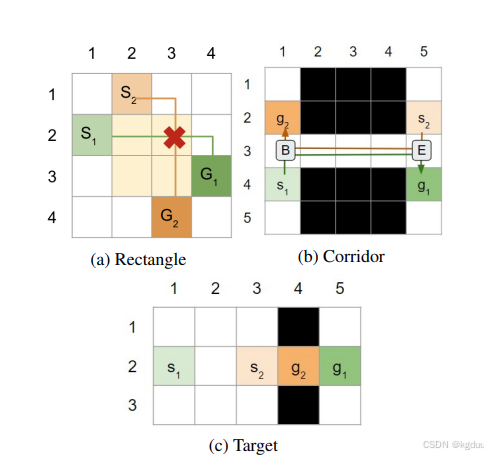
B ( a x , V , p , w ) 为约束 ⟨ a x , v , [ o t ( p , v ) , o t ( p , v ) + w ] ⟩ ,其中 v ∈ V B(a_x, V, p, w)为约束\langle a_x, v, [ot(p,v), ot(p,v)+w] \rangle,其中v \in V B(ax,V,p,w)为约束⟨ax,v,[ot(p,v),ot(p,v)+w]⟩,其中v∈V
o t ( p , v ) = t + ∣ v x − u x ∣ + ∣ v y − u y ∣ , p = ( u , t ) ot(p,v)=t+|v_x-u_x| +|v_y-u_y|, p=(u,t) ot(p,v)=t+∣vx−ux∣+∣vy−uy∣,p=(u,t)
《Symmetry Breaking Constraints for Grid-based Multi-Agent Path Finding》
《Independence Detection for Multi-Agent Pathfinding Problems》
《The Increasing Cost Tree Search for Optimal Multi-Agent Pathfinding》
Large Neighborhood Serach(LNS)
同一个搜索中使用多个destroy和repair方法来获得当前解的邻域
自适应大邻域搜索(Adaptive Large Neighborhood Search)入门到精通超详细解析-概念篇
任务分配调度算法
算法有
- Hungarian
- Large Neighborhood Search
- H-value-Based Heuristic(HBH)
问题 - TSP:算法有LKH3
- VRP
多机器人分配技术
算法学习收集
遗传算法求解VRPTW教案
大规模多智能体路径规划
AITIME论道
多智能体强化学习代码汇总
35篇最值得读的图神经网络经典论文
知乎强化学习博文
机器人路径规划
路径规划






















 7205
7205

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










