代码入口
ServiceConfig类
private static final Protocol protocol = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Protocol.class).getAdaptiveExtension();
最终返回的结果:
Protocol$Adaptive
方法调用流程图
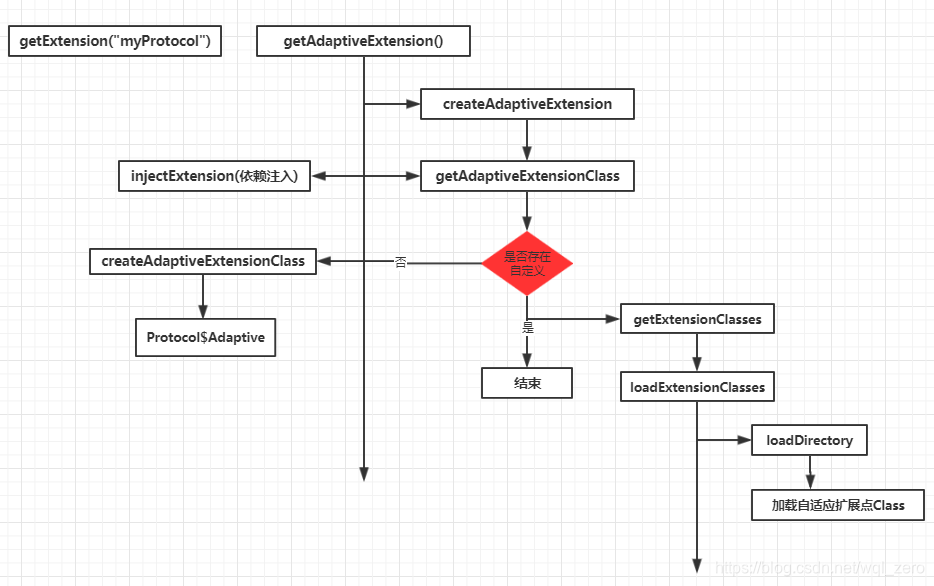
getExtensionLoader源码
//初始化一个ExtensionLoader
//type=com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol
public static <T> ExtensionLoader<T> getExtensionLoader(Class<T> type) {
//type进行合法性校验,包括是否为空,是否为一个接口,以及该接口是否带有SPI的注解
if (type == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Extension type == null");
if(!type.isInterface()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Extension type(" + type + ") is not interface!");
}
if(!withExtensionAnnotation(type)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Extension type(" + type +
") is not extension, because WITHOUT @" + SPI.class.getSimpleName() + " Annotation!");
}
//private static final ConcurrentMap<Class<?>, ExtensionLoader<?>> EXTENSION_LOADERS = new ConcurrentHashMap<Class<?>, ExtensionLoader<?>>();
//从EXTENSION_LOADERS缓存中取type
//loader = com.alibaba.dubbo.common.extension.ExtensionLoader[com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol]
ExtensionLoader<T> loader = (ExtensionLoader<T>) EXTENSION_LOADERS.get(type);
if (loader == null) {
//新建ExtensionLoader
EXTENSION_LOADERS.putIfAbsent(type, new ExtensionLoader<T>(type));
loader = (ExtensionLoader<T>) EXTENSION_LOADERS.get(type);
}
return loader;
}
private ExtensionLoader(Class<?> type) {
this.type = type;
//新建一个ExtensionFactory, 如果本身该load就是ExtensionFactory类型, 则objectFactory置为null
objectFactory = (type == ExtensionFactory.class ? null : ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(ExtensionFactory.class).getAdaptiveExtension());
}
AdaptiveExtension源码
public T getAdaptiveExtension() {
Object instance = cachedAdaptiveInstance.get();
if (instance == null) {
if(createAdaptiveInstanceError == null) {
synchronized (cachedAdaptiveInstance) {
instance = cachedAdaptiveInstance.get();
if (instance == null) {
try {
//创建一个自适应扩展点
instance = createAdaptiveExtension();
cachedAdaptiveInstance.set(instance);
} catch (Throwable t) {
createAdaptiveInstanceError = t;
throw new IllegalStateException("fail to create adaptive instance: " + t.toString(), t);
}
}
}
}
else {
throw new IllegalStateException("fail to create adaptive instance: " + createAdaptiveInstanceError.toString(), createAdaptiveInstanceError);
}
}
return (T) instance;
}
createAdaptiveExtension()方法
private T createAdaptiveExtension() {
try {
//先是调用getAdaptiveExtensionClass获得自适应扩展点的class对象,再进行注入操作
return injectExtension((T) getAdaptiveExtensionClass().newInstance());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Can't create adaptive extension " + type + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
getAdaptiveExtensionClass()方法
private Class<?> getAdaptiveExtensionClass() {
//getAdaptiveExtensionClass 方法同样包含了三个逻辑,如下:
//1:调用 getExtensionClasses 获取所有的拓展类
//2:检查缓存,若缓存不为空,则返回缓存
//3:若缓存为空,则调用 createAdaptiveExtensionClass 创建自适应拓展类
//ExtensionLoader的核心部分——getExtensionClasses()函数,
//该函数的作用就是扫描classpath底下的配置文件,加载该interface对应的所有的扩展点,并将扩展点进行分类(Adaptive,Activate),以及生成包装类等。
//在扫描的过程中,如果发现该扩展类为Adaptive类型,则将该class缓存到cachedAdaptiveClass中。
//如果所有的扩展类均不是Adaptive类型,则调用createAdaptiveExtensionClass生成一个Adaptive类型的扩展类。
getExtensionClasses();
if (cachedAdaptiveClass != null) {
return cachedAdaptiveClass;
}
//如果在调用后,cachedAdaptiveClass没有被赋值,则自动生成一个自适应的扩展点
return cachedAdaptiveClass = createAdaptiveExtensionClass();
}
getExtensionClasses()方法
//加载扩展点的实现类
private Map<String, Class<?>> getExtensionClasses() {
//map存储数据结构:
//com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol => [com.itheima.dubbo.DefineProtocol]
//如果cachedClasses缓存中没有,则调用loadExtensionClasses去加载
Map<String, Class<?>> classes = cachedClasses.get();
if (classes == null) {
synchronized (cachedClasses) {
classes = cachedClasses.get();
if (classes == null) {
classes = loadExtensionClasses();
cachedClasses.set(classes);
}
}
}
return classes;
}
// 此方法已经getExtensionClasses方法同步过。
private Map<String, Class<?>> loadExtensionClasses() {
//type = protocol.class
//得到SPI注解
final SPI defaultAnnotation = type.getAnnotation(SPI.class);
if(defaultAnnotation != null) {
//这里根据注解的值,缓存default的扩展点
String value = defaultAnnotation.value();
if(value != null && (value = value.trim()).length() > 0) {
String[] names = NAME_SEPARATOR.split(value);
if(names.length > 1) {
throw new IllegalStateException("more than 1 default extension name on extension " + type.getName()
+ ": " + Arrays.toString(names));
}
if(names.length == 1) cachedDefaultName = names[0];
}
}
//调用loadDirectory函数根据不同的路径去加载扩展点
//loadDirectory函数会去DUBBO_INTERNAL_DIRECTORY、DUBBO_DIRECTORY,和SERVICES_DIRECTORY等六个路径下去寻找配置文件,
//类似于jdk的SPI中放在META-INF/services目录下的文件,这里给出protocol的配置文件com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol
Map<String, Class<?>> extensionClasses = new HashMap<String, Class<?>>();
loadFile(extensionClasses, DUBBO_INTERNAL_DIRECTORY);
loadFile(extensionClasses, DUBBO_DIRECTORY);
loadFile(extensionClasses, SERVICES_DIRECTORY);
return extensionClasses;
}
loadFile()的方法
//加载文件
private void loadFile(Map<String, Class<?>> extensionClasses, String dir) {
String fileName = dir + type.getName();
try {
Enumeration<java.net.URL> urls;
ClassLoader classLoader = findClassLoader();
if (classLoader != null) {
urls = classLoader.getResources(fileName);
} else {
urls = ClassLoader.getSystemResources(fileName);
}
if (urls != null) {
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
java.net.URL url = urls.nextElement();
try {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(url.openStream(), "utf-8"));
try {
String line = null;
//line = [adaptive=org.apache.dubbo.common.extension.factory.AdaptiveExtensionFactory]
//line = [spi=org.apache.dubbo.common.extension.factory.SpiExtensionFactory]
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
final int ci = line.indexOf('#');
if (ci >= 0) line = line.substring(0, ci);
line = line.trim();
if (line.length() > 0) {
try {
String name = null;
int i = line.indexOf('=');
if (i > 0) {
name = line.substring(0, i).trim();
line = line.substring(i + 1).trim();
}
if (line.length() > 0) {
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(line, true, classLoader);
//加载对应的实现类,并且判断实现类是当前的加载的扩展点的实现
//判断clazz是否为type的子类,如果不是,抛异常
if (! type.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Error when load extension class(interface: " +
type + ", class line: " + clazz.getName() + "), class "
+ clazz.getName() + "is not subtype of interface.");
}
//判断是否有定义的适配器,如果有则在前面讲过的获取适配器的时候,直接返回当前自定义的适配类,不需要再自动创建
//是否为Adaptive种类的扩展类
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Adaptive.class)) {
if(cachedAdaptiveClass == null) {
cachedAdaptiveClass = clazz;
} else if (! cachedAdaptiveClass.equals(clazz)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("More than 1 adaptive class found: "
+ cachedAdaptiveClass.getClass().getName()
+ ", " + clazz.getClass().getName());
}
} else {
try {
clazz.getConstructor(type);
Set<Class<?>> wrappers = cachedWrapperClasses;
if (wrappers == null) {
cachedWrapperClasses = new ConcurrentHashSet<Class<?>>();
wrappers = cachedWrapperClasses;
}
wrappers.add(clazz);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
//检查是否有拷贝构造函数
clazz.getConstructor();
if (name == null || name.length() == 0) {
name = findAnnotationName(clazz);
if (name == null || name.length() == 0) {
if (clazz.getSimpleName().length() > type.getSimpleName().length()
&& clazz.getSimpleName().endsWith(type.getSimpleName())) {
name = clazz.getSimpleName().substring(0, clazz.getSimpleName().length() - type.getSimpleName().length()).toLowerCase();
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException("No such extension name for the class " + clazz.getName() + " in the config " + url);
}
}
}
String[] names = NAME_SEPARATOR.split(name);
if (names != null && names.length > 0) {
//注解为Activate种类的class
Activate activate = clazz.getAnnotation(Activate.class);
if (activate != null) {
cachedActivates.put(names[0], activate);
}
for (String n : names) {
if (! cachedNames.containsKey(clazz)) {
cachedNames.put(clazz, n);
}
Class<?> c = extensionClasses.get(n);
if (c == null) {
extensionClasses.put(n, clazz);
} else if (c != clazz) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Duplicate extension " + type.getName() + " name " + n + " on " + c.getName() + " and " + clazz.getName());
}
}
}
}
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
IllegalStateException e = new IllegalStateException("Failed to load extension class(interface: " + type + ", class line: " + line + ") in " + url + ", cause: " + t.getMessage(), t);
exceptions.put(line, e);
}
}
} // end of while read lines
} finally {
reader.close();
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.error("Exception when load extension class(interface: " +
type + ", class file: " + url + ") in " + url, t);
}
} // end of while urls
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.error("Exception when load extension class(interface: " +
type + ", description file: " + fileName + ").", t);
}
}
//这个函数非常长,而且各种if else的缩进也很深,大概的处理流程是对配置文件中的各个扩展点进行如下操作
//1. 判断该扩展点是否是要加载的interface的子类,如果不是则忽略
//2. 如果该class带有Adaptive的注解,则缓存到cachedAdaptiveClass中
//3. 如果该class具有拷贝构造函数,则缓存到cachedWrapperClasses中
//4. 如果该class带有Activate注解,则缓存到cachedActivates中
//5. 将所有的扩展点缓存到cachedClasses中
getAdaptiveExtensionClass()方法中的(createAdaptiveExtensionClass()方法)
//创建适配器扩展点的过程(创建一个动态的字节码文件)
//一个type对应的所有扩展点均已加载完毕,我们再回到getAdaptiveExtensionClass中,看一下如果没有自适应的扩展点,调用createAdaptiveExtensionClass是如何生成一个自适应的类的。
private Class<?> createAdaptiveExtensionClass() {
//构建自适应拓展代码
String code = new AdaptiveClassCodeGenerator(type, cachedDefaultName).generate();
ClassLoader classLoader = findClassLoader();
//获取编译器实现类
org.apache.dubbo.common.compiler.Compiler compiler = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(org.apache.dubbo.common.compiler.Compiler.class).getAdaptiveExtension();
//动态编译字节码
return compiler.compile(code, classLoader);
}
先调用createAdaptiveExtensionClassCode函数生成一段文本代码,然后再获取Compiler类型的扩展点去编译这段代码。
Compiler的扩展点加载也是通过ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader进行的。
Protocol$Adaptive(String extName = (url.getProtocol() == null ? "dubbo" : url.getProtocol() )可以看出dubbo是默认协议)
package com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.extension.ExtensionLoader;
public class Protocol$Adaptive implements com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol {
public void destroy() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("method public abstract void com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol.destroy() of interface com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol is not adaptive method!");
}
public int getDefaultPort() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("method public abstract int com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol.getDefaultPort() of interface com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol is not adaptive method!");
}
public com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invoker refer(java.lang.Class arg0, com.alibaba.dubbo.common.URL arg1) throws com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.RpcException {
if (arg1 == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("url == null");
com.alibaba.dubbo.common.URL url = arg1;
String extName = (url.getProtocol() == null ? "dubbo" : url.getProtocol() );
if(extName == null) throw new IllegalStateException("Fail to get extension(com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol) name from url(" + url.toString() + ") use keys([protocol])");
com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol extension = (com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol)ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol.class).getExtension(extName);
return extension.refer(arg0, arg1);
}
public com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Exporter export(com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invoker arg0) throws com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.RpcException {
if (arg0 == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invoker argument == null");
if (arg0.getUrl() == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Invoker argument getUrl() == null");com.alibaba.dubbo.common.URL url = arg0.getUrl();
String extName = ( url.getProtocol() == null ? "dubbo" : url.getProtocol() );
if(extName == null) throw new IllegalStateException("Fail to get extension(com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol) name from url(" + url.toString() + ") use keys([protocol])");
com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol extension = (com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol)ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.Protocol.class).getExtension(extName);
return extension.export(arg0);
}
}
private T createAdaptiveExtension() {
try {
return injectExtension((T) getAdaptiveExtensionClass().newInstance());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Can not create adaptive extension " + type + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
private T injectExtension(T instance) {
try {
if (objectFactory != null) {
for (Method method : instance.getClass().getMethods()) {
//寻找set方法
if (method.getName().startsWith("set")
&& method.getParameterTypes().length == 1
&& Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) {
/**
* Check {@link DisableInject} to see if we need auto injection for this property
*/
if (method.getAnnotation(DisableInject.class) != null) {
continue;
}
Class<?> pt = method.getParameterTypes()[0];
try {
String property = method.getName().length() > 3 ? method.getName().substring(3, 4).toLowerCase() + method.getName().substring(4) : "";
//从objectFactory获取要注入的扩展点 objectFactory = AdaptiveExtensionFactory
Object object = objectFactory.getExtension(pt, property);
if (object != null) {
//注入到具体的类中
method.invoke(instance, object);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("fail to inject via method " + method.getName()
+ " of interface " + type.getName() + ": " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
return instance;
}
该方法不仅仅用在自适应扩展点的注入,也适用于其他类型的扩展点,我们来看一下注入的大致流程
1. 遍历该instance的所有方法,找到以set开头的方法,准备进行注入。
2. 调用objectFactory.getExtension()方式获取要注入的实例。
3. 调用method.invoke进行注入。
这里,我们又看到了前面出现的ExtensionFactory,前文提到每个扩展点的ExtensionLoader实例中均有一个objectFactory来存储ExtensionFactory实例,并且这个objectFactory也是通过getExtensionLoader方式产生的ExtensionFactory自适应的扩展点
构造方法:
private ExtensionLoader(Class<?> type) {
this.type = type;
objectFactory = (type == ExtensionFactory.class ? null : ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(ExtensionFactory.class).getAdaptiveExtension());
}
@SPI
public interface ExtensionFactory {
/**
* Get extension.
*
* @param type object type.
* @param name object name.
* @return object instance.
*/
<T> T getExtension(Class<T> type, String name);
}
ExtensionFactory扩展点分为SpiExtensionFactory、AdaptiveExtensionFactory和SpringExtensionFactory三种,下面我们来分析一下AdaptiveExtensionFactory的代码,看看调用objectFactory.getExtension的时候都发生了什么。
@Adaptive
public class AdaptiveExtensionFactory implements ExtensionFactory {
private final List<ExtensionFactory> factories;
public AdaptiveExtensionFactory() {
ExtensionLoader<ExtensionFactory> loader = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(ExtensionFactory.class);
List<ExtensionFactory> list = new ArrayList<ExtensionFactory>();
for (String name : loader.getSupportedExtensions()) {
list.add(loader.getExtension(name));
}
factories = Collections.unmodifiableList(list);
}
@Override
public <T> T getExtension(Class<T> type, String name) {
//factories = [adaptive=org.apache.dubbo.common.extension.factory.AdaptiveExtensionFactory,spi=org.apache.dubbo.common.extension.factory.SpiExtensionFactory]
for (ExtensionFactory factory : factories) {
T extension = factory.getExtension(type, name);
if (extension != null) {
return extension;
}
}
return null;
}
}
在AdaptiveExtensionFactory的构造函数中,将SpiExtensionFactory和SpringExtensionFactory实例化后存入factories中。在getExtension中,会依次调用SpiExtensionFactory和SpringExtensionFactory的方法来寻找扩展点,找到即返回。
以SpiExtensionFactory为例来看一下具体的getExtension函数:
public class SpiExtensionFactory implements ExtensionFactory {
@Override
public <T> T getExtension(Class<T> type, String name) {
if (type.isInterface() && type.isAnnotationPresent(SPI.class)) {
ExtensionLoader<T> loader = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(type);
if (!loader.getSupportedExtensions().isEmpty()) {
return loader.getAdaptiveExtension();
}
}
return null;
}
}
其实就是对相应的type生成对应的ExtensionLoader再找到Adaptive扩展点返回。至此,便完成了一个class实例化后,其内部所有的可注入的变量的注入操作。ExtensionFactory就相当于所有扩展点的工厂,提供相应的接口去取获取扩展点。
代码入口:(ExtensionLoader.java)
Protocol protocol = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Protocol.class).getExtension("myProtocol");
加载所有的扩展点
public T getExtension(String name) {
if (name == null || name.length() == 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Extension name == null");
// 如果name是"true",返回默认扩展点实现
if ("true".equals(name)) {
return getDefaultExtension();
}
Holder<Object> holder = cachedInstances.get(name);
if (holder == null) {
cachedInstances.putIfAbsent(name, new Holder<Object>());
holder = cachedInstances.get(name);
}
Object instance = holder.get();
if (instance == null) {
synchronized (holder) {
instance = holder.get();
if (instance == null) {
//如果不是默认实现,则先尝试从缓存中获取,如果缓存中没有,再t通过createExtension方法创建实例,最后再放入缓存。
instance = createExtension(name);
holder.set(instance);
}
}
}
return (T) instance;
}
private T createExtension(String name) {
//从SPI配置文件加载class
Class<?> clazz = getExtensionClasses().get(name);
if (clazz == null) {
throw findException(name);
}
try {
//根据得到class创建实例并缓存。
T instance = (T) EXTENSION_INSTANCES.get(clazz);
if (instance == null) {
EXTENSION_INSTANCES.putIfAbsent(clazz, clazz.newInstance());
instance = (T) EXTENSION_INSTANCES.get(clazz);
}
//依赖注入
injectExtension(instance);
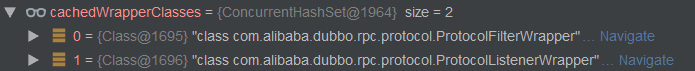
//filter=com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol.ProtocolFilterWrapper
//listener=com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol.ProtocolListenerWrapper
//进行包装
Set<Class<?>> wrapperClasses = cachedWrapperClasses;
if (wrapperClasses != null && !wrapperClasses.isEmpty()) {
for (Class<?> wrapperClass : wrapperClasses) {
instance = injectExtension((T) wrapperClass.getConstructor(type).newInstance(instance));
}
}
return instance;
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Extension instance(name: " + name + ", class: " +
type + ") could not be instantiated: " + t.getMessage(), t);
}
}
instance = injectExtension((T) wrapperClass.getConstructor(type).newInstance(instance));
ProtocolFilterWrapper类
public <T> Exporter<T> export(Invoker<T> invoker) throws RpcException {
if (Constants.REGISTRY_PROTOCOL.equals(invoker.getUrl().getProtocol())) {
return protocol.export(invoker);
}
return protocol.export(buildInvokerChain(invoker, Constants.SERVICE_FILTER_KEY, Constants.PROVIDER));
}
Protocol.export(invoker),这里是调用的DubboProtocol的export方法。
private static <T> Invoker<T> buildInvokerChain(final Invoker<T> invoker, String key, String group) {
Invoker<T> last = invoker;
List<Filter> filters = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Filter.class).getActivateExtension(invoker.getUrl(), key, group);
if (filters.size() > 0) {
for (int i = filters.size() - 1; i >= 0; i --) {
final Filter filter = filters.get(i);
final Invoker<T> next = last;
last = new Invoker<T>() {
public Class<T> getInterface() {
return invoker.getInterface();
}
public URL getUrl() {
return invoker.getUrl();
}
public boolean isAvailable() {
return invoker.isAvailable();
}
public Result invoke(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
return filter.invoke(next, invocation);
}
public void destroy() {
invoker.destroy();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return invoker.toString();
}
};
}
}
return last;
}





 本文深入剖析了Dubbo SPI(Service Provider Interface)机制的工作原理,详细介绍了如何通过SPI机制实现服务的扩展与自适应调用。从ExtensionLoader的初始化到AdaptiveExtension的生成,再到ExtensionFactory的使用,全面展示了Dubbo SPI的实现细节。
本文深入剖析了Dubbo SPI(Service Provider Interface)机制的工作原理,详细介绍了如何通过SPI机制实现服务的扩展与自适应调用。从ExtensionLoader的初始化到AdaptiveExtension的生成,再到ExtensionFactory的使用,全面展示了Dubbo SPI的实现细节。
















 1152
1152

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








