11-3 Java集合---- Iterator迭代器接口
一、说明
1.Iterator对象称为迭代器(设计模式的一种),主要用于遍历 Collection 集合中的元素。
2.GOF给迭代器模式的定义为:提供一种方法访问一个容器(container)对象中各个元素,而又不需暴露该对象的内部细节。迭代器模式,就是为容器而生。类似于“公交车上的售票员”、“火车上的乘务员”、“空姐”。
3.Collection接口继承了java.lang.Iterable接口,该接口有一个iterator()方法,那么所有实现了Collection接口的集合类都有一个iterator()方法,用以返回一个实现了Iterator接口的对象。
4.Iterator 仅用于遍历集合,Iterator 本身并不提供承装对象的能力。如果需要创建
Iterator 对象,则必须有一个被迭代的集合。
5.集合对象每次调用iterator()方法都得到一个全新的迭代器对象,默认游标都在集合
的第一个元素之前。
二、集合元素的遍历操作
1.内部的方法:hashNecxt()和next()
(1)hashNext()-----》判断是否还有元素
(2)next()-----》①指针下移②将下移以后的集合位置上的元素返回
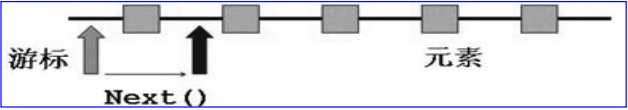
注意:在调用it.next()方法之前必须要调用it.hasNext()进行检测。若不调用,且下一条记录无效,直接调用it.next()会抛出NoSuchElementException异常。
2.集合对象每次调用
iterator()方法都得到一个全新的迭代器对象,默认游标都在集合的第一个元素之前。
三、Iterator接口remove()方法
1.内部定义了remove(),可以在遍历的时候,删除集合中的元素,此方法不同于集合直接调用remove()。
2.注意:
(1)Iterator可以删除集合的元素,但是是遍历过程中通过迭代器对象的remove方法,不是集合对象的remove方法。
(2)如果还未调用next()或在上一次调用 next 方法之后已经调用了 remove 方法,再调用remove都会报IllegalStateException。
代码:
package java1;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class IteratorTest {
@Test
public void test1() {
//集合元素的遍历:使用迭代器Iterator接口
// 9.itterator():返回Integer接口的实例,用于遍历集合元素。
Collection coll = new ArrayList();
coll.add(123);
coll.add(456);
coll.add(new Person("Jerry", 20));
coll.add(new String("Tom"));
coll.add(false);
Iterator iterator = coll.iterator();
//方式一:不推荐
// System.out.println(iterator.next());
// System.out.println(iterator.next());
// System.out.println(iterator.next());
// System.out.println(iterator.next());
// System.out.println(iterator.next());
//报异常:NoSuchElementException
// System.out.println(iterator.next());
//方式二:不推荐
// for (int i = 0;i < coll.size();i++){
// System.out.println(iterator.next());
// }
//方式三:推荐,hasNext判断当前指针所指元素的下一位是否有元素,有则返回true
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
@Test
public void test2() {
Collection coll = new ArrayList();
coll.add(123);
coll.add(456);
coll.add(new Person("Jerry", 20));
coll.add(new String("Tom"));
coll.add(false);
//错误方式一:跳动输出
// Iterator iterator = coll.iterator();
// while((iterator.next())!= null){
// System.out.println(iterator.next());
// }
//错误方式二:
//集合对象每次调用iterator()方法都得到一个全新的迭代器对象,默认游标都在集合的第一个元素之前。
// while(coll.iterator().hasNext()){
// System.out.println(coll.iterator().next());
// }
}
@Test
public void test3() {
Collection coll = new ArrayList();
coll.add(123);
coll.add(456);
coll.add(new Person("Jerry", 20));
coll.add(new String("Tom"));
coll.add(false);
//删除集合中“Tom”
Iterator iterator = coll.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Object obj = iterator.next();
if("Tom".equals(obj)){
iterator.remove();
}
}
//遍历集合
iterator = coll.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
}
输出:
123
456
Person{name='Jerry', age=20}
Tom
false
123
456
Person{name='Jerry', age=20}
false





 本文介绍了Java集合中的Iterator迭代器接口,包括其定义、用途、遍历操作和remove方法的使用。通过实例演示了如何正确遍历和删除集合元素,以及常见错误用法。
本文介绍了Java集合中的Iterator迭代器接口,包括其定义、用途、遍历操作和remove方法的使用。通过实例演示了如何正确遍历和删除集合元素,以及常见错误用法。

















 493
493












