前言
本文通过Springboot启动方法分析SpringApplication逻辑。从静态run方法执行到各个阶段发布不同事件完成整个应用启动。
SpringApplication 源码注释中说明了该类的主要作用,如下所示

其他Spingboot 原理相关文章请参考
手把手分析Springboot @EnableScheduling原理
SpringCloud FeignClient底层实现原理(一)
启动逻辑详解
springboot应用在启动时存在两种方式:
第一种通过静态run方法直接启动
SpringApplication.run(MyApplication.class, args);第二种通过创建对象后执行run方法启动
SpringApplication application = new SpringApplication(MyApplication.class);
application.run(args)第二种方法其实就是第一种方法背后实现逻辑。
在run方法执行过程中大量使用事件机制完成日志,配置文件,激活profile等工作,下图为整体执行流程图。

- 通过SpringApplication静态run方法启动
- 初始化SpringApplication对象
- 设置资源加载器 (用于加载class文件,spring.factories文件)
- 设置primarysource
- 推断主类
- 通过SPI加载初始化器&监听器(稍后分析SPI实现逻辑)
- 执行run方法
- 加载SpringApplicationListner监听器,该监听器是是所有启动事件的发布者。此处与构造方法中加载的监听器作用不同
- SpringApplicationListner发布starting事件代表应用开始启动
- 包装应用启动参数
- 还在配置文件激活spring.active.profile对应的profile(感觉像是废话)发布enviromentPrepared事件
- 打印banner 默认是springboot ASCII编码
- 创建spring容器上下文
- 获取异常分析工厂类
- prepareContext 设置容器上下文
- 刷新容器获取工厂bean,工厂后置处理器,初始化单例bean
- 调用afterResfresh方法
- 发布启动完成事件
- 回调callRunner方法
- 发布应用运行中事件
Springboot SPI 分析
在初始化SpringApplication对象时通过springboot SPI方式对classpath下所有jar包中 META-INF/spring.factories文件进行加载,这也是springboot自动装配中使用到的逻辑。

在构造方法中 通过getSpringFactoriesInstances完成工厂类加载与初始化。
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type) {
return getSpringFactoriesInstances(type, new Class<?>[] {});
}
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
ClassLoader classLoader = getClassLoader();
// Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates
Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<>(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);
return instances;
}getSpringFactoriesInstances方法中通过一个单例类SpringFactoriesLoader完成所有META-INF/spring.factories文件的读取。通过classLoader.getResources方法读取classpath下所有jar包后队文件进行解析。
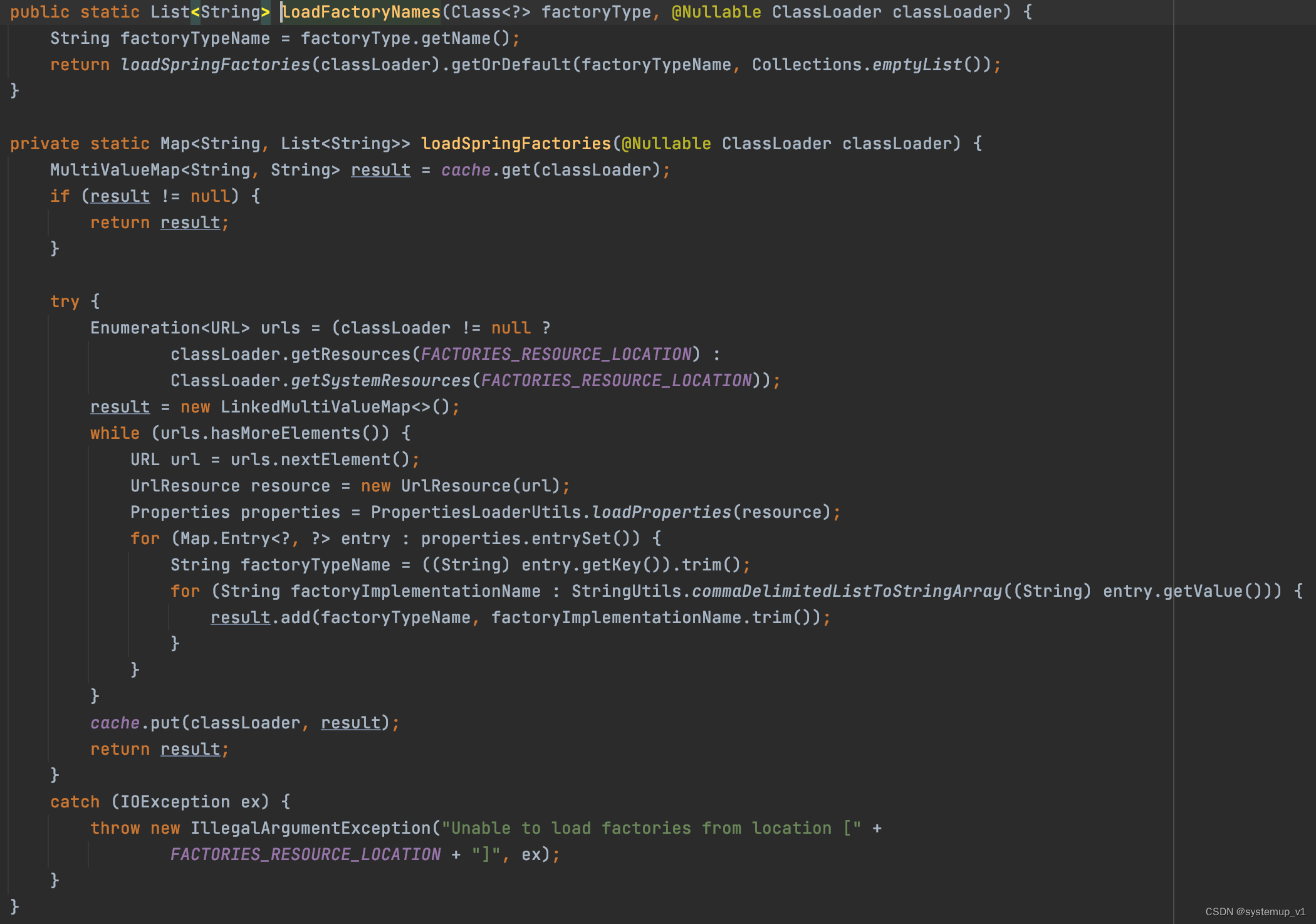
spring.factories文件内容为key value对,多个value用逗号分隔,如下所示
# Spring Test ContextCustomizerFactories
org.springframework.test.context.ContextCustomizerFactory=\
org.springframework.boot.test.context.ImportsContextCustomizerFactory,\
org.springframework.boot.test.context.filter.ExcludeFilterContextCustomizerFactory,\
org.springframework.boot.test.json.DuplicateJsonObjectContextCustomizerFactory,\
org.springframework.boot.test.mock.mockito.MockitoContextCustomizerFactory,\
org.springframework.boot.test.web.client.TestRestTemplateContextCustomizerFactory,\
org.springframework.boot.test.web.reactive.server.WebTestClientContextCustomizerFactory
# Test Execution Listeners
org.springframework.test.context.TestExecutionListener=\
org.springframework.boot.test.mock.mockito.MockitoTestExecutionListener,\
org.springframework.boot.test.mock.mockito.ResetMocksTestExecutionListener
# Environment Post Processors
org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessor=\
org.springframework.boot.test.web.SpringBootTestRandomPortEnvironmentPostProcessor
接下来是启动逻辑的重点run方法。本文重点分析run方法中事件触发逻辑。
事件机制详解
在run方法中通过getRunListeners方法加载事件监听器,该监听器负责发布应用启动中各个阶段的状态
- starting 阶段
- environmentPrepare阶段 负责配置文件,系统环境变量,激活profile等逻辑
- contextPrepared 阶段负责初始化applicationContext
- contextLoaded 阶段 applicationContext加载所有单例bean
- started 阶段 应用启动完成
- running 阶段 应用运行中状态

getRunListeners通过getSpringFactoriesInstances方法加载 SpringApplicationRunListener所有实现类,该接口默认实现类为 EventPublishingRunListener,该类包含如下方法

这下方法中通过 SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster类发送通知,该类名也能表示其作用:简单应用事件多播器,翻译出来总感觉差点意思。

在run 方法中存在以上6个listener方法调用的逻辑。具体发动哪些事件请看下图

上图中列出了监听器处理的部分事件,其他事件感兴趣的话可以通过源码进行分析。
总结
通过整体启动分析将整个启动流程进行梳理,有助于大家在阅读源码前掌握正义的概要避免陷入局部逻辑无法自拔。
后面将会针对不同逻辑进行深入分析。
























 851
851

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








