与在操作系统中的线程竞争相似,GPU编程各个线程之间也存在竞态条件,为了保证程序按照我们设计的逻辑运行,原子性操作必不可少。
本章以计算直方图为例,说明在GPU上使用原子操作的方法。
在CPU上计算直方图
这是平凡的
// 代码9.4.1在CPU上计算直方图
//时间:2019.07.30
#include "cuda_runtime.h"
#include "device_launch_parameters.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "book.h"
#define SIZE (10*1024*1024)
int main()
{
unsigned char *buffer = (unsigned char *)big_random_block(SIZE);
unsigned int histo[256];
//对直方图数组进行初始化
for(int i = 0; i < 256; i++)
{
histo[i] = 0;
}
//CPU统计直方图信息
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++)
{
histo[buffer[i]]++;
}
//验证直方图统计的正确性
long histoCount = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++)
{
histoCount += histo[i];
}
printf("Histogram Sum:%ld\n", histoCount);
free(buffer);
system("pause");
return 0;
}

显然,10485760 = 1024102410,验证通过!
在GPU上计算直方图
通过GPU的多个线程来处理输入缓冲区的不同部分,在这个过程中,多个线程可能同时对输出直方图的同一个元素进行递增。在这种情况下,我们需要通过原子递增操作来避免线程竞争问题。
一些重要函数及技巧
1. cudaMemset
类似于memset,cudaMemset对GPU上的内存初始化数值,如果初始化失败,将返回一个错误码,用法示例:
cudaMemset(dev_histo, 0, sizeof(int)* 256);//对GPU上的内存初始化数值
2. block数量的选择技巧
- 由于直方图包含了256个元素,因此threadsPerBlock可以设置成256,这样做方便又高效。
- block数量的选择
假设我们有100MB数据,也就是104857600个字节。我们可以用一个block,每个thread处理409600个数据元素;也可以用409600个block,每个thread处理一个数据元素。
通过一些性能实验,发现当block的数量为GPU中处理器数量的2倍时,将达到最优性能。
3. GPU原子递增操作
atomicAdd(addr,y)是CUDA提供的原子递增操作函数,它包含两个参数,第一个参数是要递增的变量地址,第二个参数是每次递增的步长。
这个函数将生成一个原子操作序列,这个操作序列包括读取地址addr处的值,将这个值增加y,以及将结果保存到addr。
底层硬件将确保执行这些操作时,其他任何线程都不会读取或者写入地址addr上的值,示例如下:
atomicAdd(&histo[buffer[i]], 1);//每次递增1
使用GPU全局内存原子操作计算直方图
// 代码9.4.2.1在GPU上计算直方图(全局内存)
//时间:2019.07.30
#include "cuda_runtime.h"
#include "device_launch_parameters.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "book.h"
#define SIZE (10*1024*1024)
__global__ void histo_kernal(unsigned char *buffer, long size, unsigned int *histo)
{
int i = threadIdx.x + blockIdx.x*blockDim.x;
int stride = gridDim.x*blockDim.x;
while (i < size)
{
atomicAdd(&histo[buffer[i]], 1);//原子性操作
i += stride;
}
}
int main()
{
unsigned char *buffer = (unsigned char *)big_random_block(SIZE);
//记录起始事件
cudaEvent_t start, stop;
cudaEventCreate(&start);
cudaEventCreate(&stop);
cudaEventRecord(start, 0);
//在GPU上为文件数据分配内存
unsigned char *dev_buffer;
unsigned int *dev_histo;
cudaMalloc((void **)&dev_buffer, SIZE);
cudaMemcpy(dev_buffer, buffer, SIZE, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
cudaMalloc((void **)&dev_histo, sizeof(int)* 256);
cudaMemset(dev_histo, 0, sizeof(int)* 256);//对GPU上的内存初始化数值
//执行kernal函数,经验发现当线程块的数量为GPU中处理器数量的2倍时,将达到最优性能
cudaDeviceProp prop;
cudaGetDeviceProperties(&prop, 0);
int blocks = prop.multiProcessorCount;
histo_kernal << <blocks * 2, 256 >> >(dev_buffer, SIZE, dev_histo);
//将GPU统计得到的直方图copy到CPU
unsigned int histo[256];
cudaMemcpy(histo, dev_histo, sizeof(int)* 256,cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
//得到停止时间并显示计时结果
cudaEventRecord(stop, 0);
cudaEventSynchronize(stop);
float elapsedTime;
cudaEventElapsedTime(&elapsedTime, start, stop);
printf("Time to generate:%3.1f ms\n", elapsedTime);
//验证直方图总和是否正确
long histoCount = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++)
{
histoCount += histo[i];
}
printf("Histogram Sum:%ld\n", histoCount);
//验证与CPU得到的是相同的计数值
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++)
{
histo[buffer[i]]--;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++)
{
if (histo[i] != 0)
printf("Failure ar %d!\n", i);
}
//释放CUDA事件,主机内存,GPU内存
cudaEventDestroy(start);
cudaEventDestroy(stop);
cudaFree(dev_histo);
cudaFree(dev_buffer);
free(buffer);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
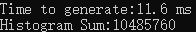
使用GPU共享内存原子操作计算直方图
全局内存dev_histo只有256个字节,当数千个线程尝试访问如此少量的内存位置时,将发生大量的竞争。为了保证递增操作的原子性,对相同内存位置的操作都将被硬件串行化,这是效率低下的。
使用共享内存可以有效解决以上问题,思路如下:
将直方图计算分为两个阶段,在第一个阶段,使用共享内存,每个并行block将独立计算它所处理数据的直方图,每个block中的所有线程在该block中对共享内存缓冲区的操作仍然需要保证原子性。显然,在一个block中只有256个线程在256个地址上发生竞争,这将极大地减少在使用全局内存时在数千个线程之间发生竞争的情况。在第二个阶段,将第一个阶段每个block产生的统计结果,加和到最终直方图相应的元素上,同时,必须要注意的是,第一个阶段完成之后需要线程同步,等到所有block都完成了局部计算之后,第二个阶段才可以进行。
// 代码9.4.2.2在GPU上计算直方图(共享内存)
//时间:2019.07.30
#include "cuda_runtime.h"
#include "device_launch_parameters.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "book.h"
#define SIZE (10*1024*1024)
__global__ void histo_kernal(unsigned char *buffer, long size, unsigned int *histo)
{
//每个block中都包含一个独立的共享内存temp,每个block中有256个thread
__shared__ unsigned int temp[256];
temp[threadIdx.x] = 0;//初始化为0
__syncthreads();
//每个block中计算一下计数值
int i = threadIdx.x + blockIdx.x*blockDim.x;
int stride = gridDim.x*blockDim.x;
while (i < size)
{
atomicAdd(&temp[buffer[i]], 1);//原子性操作
i += stride;
}
__syncthreads();
//将每个block中的temp内容汇总到histo
atomicAdd(&(histo[threadIdx.x]), temp[threadIdx.x]);
}
int main()
{
unsigned char *buffer = (unsigned char *)big_random_block(SIZE);
//记录起始事件
cudaEvent_t start, stop;
cudaEventCreate(&start);
cudaEventCreate(&stop);
cudaEventRecord(start, 0);
//在GPU上为文件数据分配内存
unsigned char *dev_buffer;
unsigned int *dev_histo;
cudaMalloc((void **)&dev_buffer, SIZE);
cudaMemcpy(dev_buffer, buffer, SIZE, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
cudaMalloc((void **)&dev_histo, sizeof(int)* 256);
cudaMemset(dev_histo, 0, sizeof(int)* 256);//对GPU上的内存初始化数值
//执行kernal函数,经验发现当线程块的数量为GPU中处理器数量的2倍时,将达到最优性能
cudaDeviceProp prop;
cudaGetDeviceProperties(&prop, 0);
int blocks = prop.multiProcessorCount;
histo_kernal << <blocks * 2, 256 >> >(dev_buffer, SIZE, dev_histo);
//将GPU统计得到的直方图copy到CPU
unsigned int histo[256];
cudaMemcpy(histo, dev_histo, sizeof(int)* 256, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
//得到停止时间并显示计时结果
cudaEventRecord(stop, 0);
cudaEventSynchronize(stop);
float elapsedTime;
cudaEventElapsedTime(&elapsedTime, start, stop);
printf("Time to generate:%3.1f ms\n", elapsedTime);
//验证直方图总和是否正确
long histoCount = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++)
{
histoCount += histo[i];
}
printf("Histogram Sum:%ld\n", histoCount);
//验证与CPU得到的是相同的计数值
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++)
{
histo[buffer[i]]--;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++)
{
if (histo[i] != 0)
printf("Failure ar %d!\n", i);
}
//释放CUDA事件,主机内存,GPU内存
cudaEventDestroy(start);
cudaEventDestroy(stop);
cudaFree(dev_histo);
cudaFree(dev_buffer);
free(buffer);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
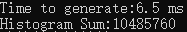
显然,性能是确有提升的。





 本文详细介绍了在GPU上使用原子操作计算直方图的方法,包括使用全局内存和共享内存两种方式,以及如何选择block数量以达到最优性能。
本文详细介绍了在GPU上使用原子操作计算直方图的方法,包括使用全局内存和共享内存两种方式,以及如何选择block数量以达到最优性能。
















 824
824

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








