遗传算法辅助异构改进的动态多群粒子群优化算法(GA-HIDMS-PSO)是一种将最先进的粒子群优化算法(PSO)与遗传算法(GA)相结合的元启发式优化算法。该混合模型利用了HIDMS-PSO的异构特性和遗传算法的进化特性。在遗传算法-HIDMS-PSO体系结构中,HIDMS-PSO作为主要搜索引擎,遗传算法作为辅助方法,对HIDMS-PSO算法的同质和异质亚群的选定比例进行辅助和减缓多样性的丧失。这两种方法连续运行。作为主要的搜索方法,HIDMS-PSO比遗传算法运行时间更长。HIDMS-PSO从同质和异质亚群中为遗传算法提供初始解,遗传算法返回的最终解取代了HIDMS-PSO中的先前解,从而恢复了搜索过程,并可能使用更多样化的粒子来引导群体。
该成果于2021年发表在IEEE会议期刊“IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation”上。目前GA-HIDMS-PSO方法被引6次。

1、算法原理
(1)标准粒子群算法
PSO是一种基于被称为粒子的代理群体的运动的随机搜索算法。该群由N个粒子组成,每个粒子的速度为v(t)i,在时间t的位置为x(t)i,个人最熟悉的位置为p best。粒子在n维搜索空间中通过使用三个向量,v(t−1)i,p best和g best,即群中全局最佳粒子的位置来移动。标准PSO算法使用以下两个方程来更新粒子的速度和位置:
其中ω是用于控制先前速度的影响的惯性权重,常数c1和c2控制认知(p best)和社会(g best)吸引的吸引率/水平,r1和r2是随机向量∈ [0,1]。
区分从粒子的类型允许异质粒子行为,限制快速信息交换,以防止过早收敛和人口多样性的损失。下图示出了单个单元的拓扑结构。
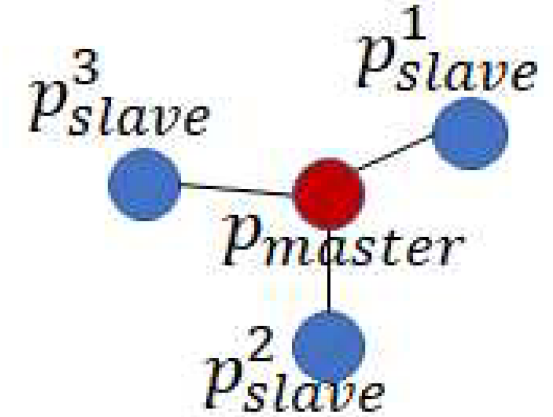
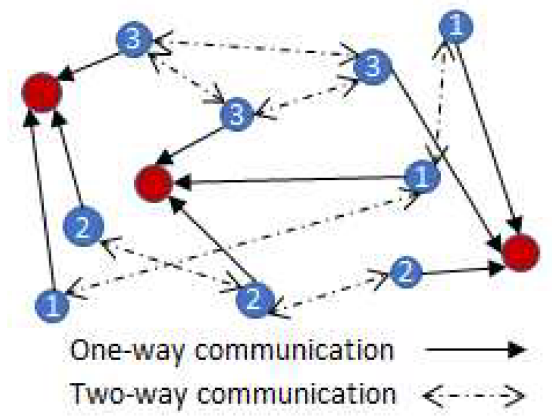
HIDMS-PSO算法采用通信模型来管理粒子之间的信息交换和交互。通信模型限制了信息流,并允许粒子通过主到主和从到从的通信交换信息(见下图)。主要通信受以下规则管辖:
(2)搜索行为
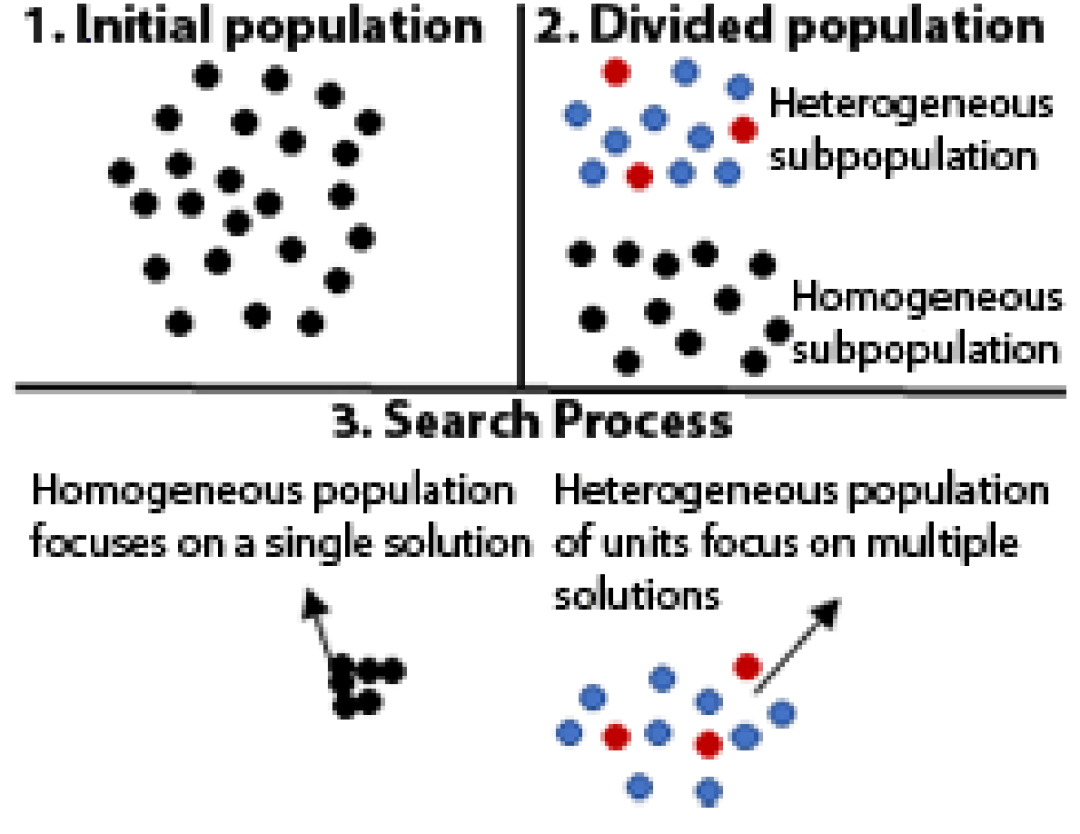
在HIDMS-PSO算法中,初始种群被划分为两个相等的子种群,一个是同质的,一个是异质的,每个子种群采用不同的运动策略。同质子种群使用经典PSO算法的更新方程,而异质亚种群则形成N个单位结构,并采取向内和向外的策略。面向内部的策略旨在将粒子引导到同一单元中的其他成员。相反,向外定向策略使用来自不同单位的样本来引导粒子。
向内移动策略:向内移动策略利用从所有单位成员获得的位置信息为粒子提供指导。对于向内运动,具有主角色的粒子随机选择公式中的一个来更新它们的速度:
其中v(t)m为速度,pbest m为个人最佳位置,xm为主粒子在时刻t的位置,xdis s为第n个单元中位置相似度最小的从粒子。主粒子的位置对从粒子有显著的影响。因此,单位的目标是通过引导主粒子走向xdis s来保持它们的多样性。
其中xbest s是第n个单元最适合的从属粒子的位置。通过将主粒子向最适从粒子的方向移动,主粒子进行局部探索。
其中xavg s是所有副粒子在主粒子当前单位内的平均位置。使用下式,从粒子指向从粒子个人最知名的位置和主粒子的位置。
其中v(t) s为速度,p bests为粒子在时刻t找到的最佳位置,xs为从粒子位置,xm为第n个单元的主粒子位置。
b)向外移动策略:与向内移动策略相比,向外移动策略为粒子提供来自群体中不同单位的引导。对于这种运动策略,具有主角色的粒子随机选择下列方程中的任意一个来更新它们的速度:
其中v(t) m为速度,p bestm为个人最佳位置,xm为主粒子在时刻t的位置,xavgunit为第n个单位粒子的平均位置。
其中xmunit为主粒子相对于随机选择的单位的位置。
其中xavg为粒子自身单元成员的平均位置,xmunit为随机选择单元的主粒子位置。与向内运动方案中从粒子的引导一样,向外运动策略中,从粒子使用以下速度更新方程从随机选择的单元中选择一个(相同类型的)从粒子的方向移动。
其中v(t) s为速度,p bests为个人最佳位置,xs为从粒子的位置,xrndunit为随机选择的同类从粒子。
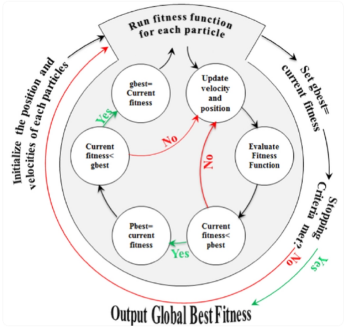
GA-HIDMS-PSO所对应的伪代码过程如下图所示


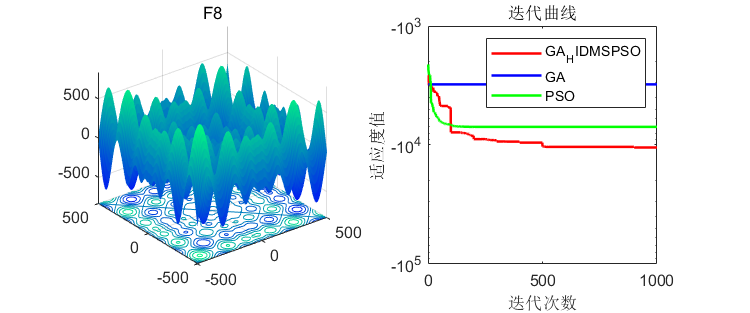
2、结果展示
在23个经典函数进行测试,并和经典粒子群算法、遗传算法进行比较,结果如下:
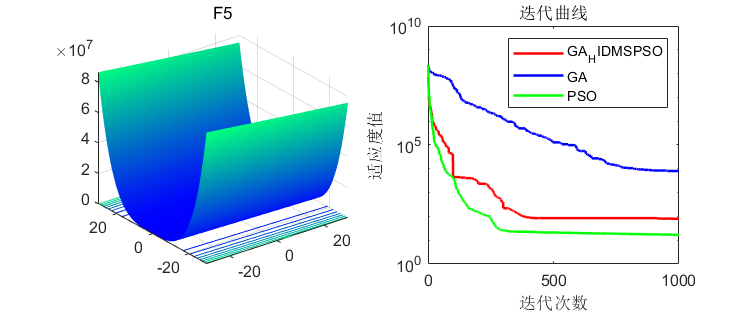
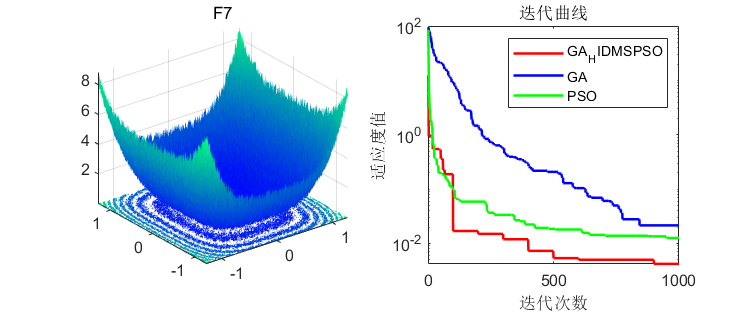
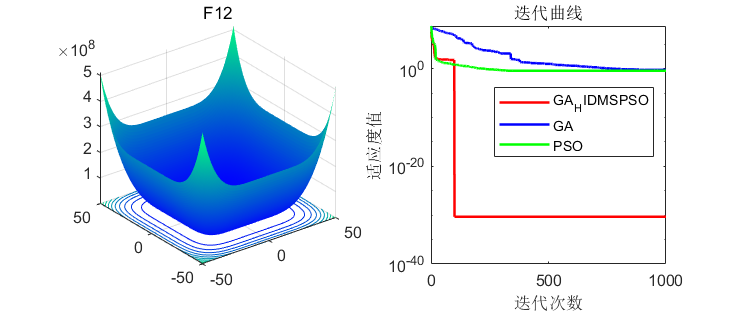
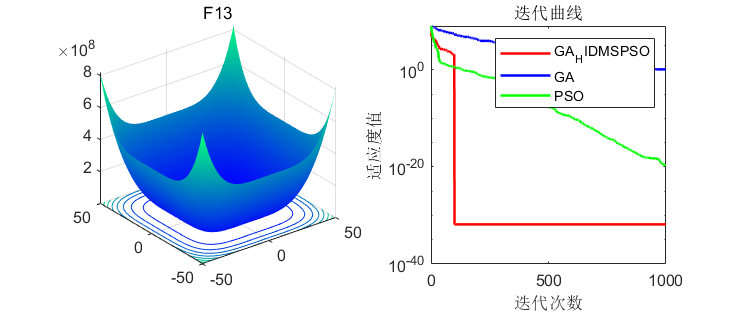
3、MATLAB核心代码
% 遗传算法辅助的HIDMS-PSO(GA-HIDMS-PSO)
function [fmin] = GA_HIDMSPSO(fhd,fId,n,d,range)
if rem(n,4)~=0, error("** Input Error: Swarm population must be divisible by 4 **"), end
rand('seed',sum(100*clock));
fevalCount=0;
LB=range(1);
UB=range(2);
Fmax=10^4*d; %maximum number function evaluations
Tmax=Fmax/n; %maximum number of iterations
%{
if d==10, Tmax=Tmax-289;
elseif d==30, Tmax=Tmax-900;
elseif d==50, Tmax=Tmax-1500;
elseif d==100, Tmax=Tmax-3000;
end
%}
ShowProgress=false;
%% Parameters of HIDMS-PSO
w1 = 0.99+(0.2-0.99)*(1./(1+exp(-5*(2*(1:Tmax)/Tmax-1)))); %nonlinear decrease inertia weight - Sigmoid function
c1 = 2.5-(1:Tmax)*2/Tmax; %personal acceleration coefficient
c2 = 0.5+(1:Tmax)*2/Tmax; %social acceleration coefficient
COM = false; %Communication model enabled/disabled
alpha_min = Tmax*0.01;
alpha_max = Tmax*0.1;
alpha = alpha_max; %initial alpha value, determines units' reshape interval
UPn = 4; %unit pop size (constant)
U_n = (n/2)/UPn; %number of units (constant)
U = reshape(randperm(n/2),U_n,UPn); %units (U_n-by-UPn matrix)
[master,slave1,slave2,slave3] = feval(@(x) x{:}, num2cell([1,2,3,4])); %unit members' codes (constant)
%Velocity clamp
MaxV = 0.15*(UB-LB);
MinV = -MaxV;
GA = false; %controls the switch between HIDMS-PSO and GA
PSO_phase = 100; %number of iterations HIDMS-PSO will run before switching back to GA
GA_phase = 50; %number of iterations GA will run before switching back to HIDMS-PSO
%% Initialisation
V = zeros(n,d); %initial velocities
X = unifrnd(LB,UB,[n,d]); %initial positions
PX = X; %initial pbest positions
F = feval(fhd,X',fId); %function evaluation
PF = F; %initial pbest cost
GX = []; %gbest solution vector
GF = inf; %gbest cost
%update gbest
for i=1:n
if PF(i)<GF, GF=PF(i); GX=PX(i,:); end
end
%% Main Loop of GA-HIDMS-PSO
for t=1:Tmax
%control the switch between GA and HIDMS-PSO
if t<=Tmax*0.9
if mod(t,PSO_phase)==0
GA = true;
end
end
%reshape units
if mod(t,round(alpha))==0
[~,idx] = sort(rand(U_n,UPn));
U = U(sub2ind([U_n,UPn],idx,ones(U_n,1)*(1:UPn)));
end
for i=1:n
if F(i) >= mean(F), w = w1(t) + 0.15; if w > 0.99, w = 0.99;end
else, w = w1(t) - 0.15; if w < 0.20, w = 0.20;end
end
if t <= Tmax*0.9
if ~isempty(find(U==i)) %if agent belongs to the heterogeneous subpop
if randi([0 1]) == 0 %inward-oriented movement
if ~isempty(find(U(:,master)==i)) %agent is master
behaviour = randi([1 3]);
[uId,~] = find(U(:,master)==i); %unit id of the ith (master) particle
if behaviour==1 %move towards the most dissimilar slave
sList = U(uId,slave1:slave3); %get slaves of the master
similarities = zeros(1,length(sList)); %
for ii=1:length(sList) %calculate similarities between master and slave particles
similarities(ii) = immse(PF(i),PF(sList(ii))); %immse is used instead of mae and mse for faster performance
end
[~,dsId] = max(similarities); %find the most dissimilar agent
dsId = sList(dsId); %idx of the dissimilar slave
V(i,:) = w*V(i,:)+c1(t)*rand([1 d]).*(PX(i,:) - X(i,:)) + c2(t)*rand([1 d]).*(PX(dsId,:) - X(i,:));
elseif behaviour == 2 %move towards the best slave
sList = U(uId,slave1:slave3); %idx of slaves in the unit
slave_costs = [F(sList(1)) F(sList(2)) F(sList(3))];
[~,bsId] = min(slave_costs); %best slave's idx
V(i,:) = w*V(i,:)+c1(t)*rand([1 d]).*(PX(i,:) - X(i,:)) + c2(t)*rand([1 d]).*(PX(sList(bsId),:) - X(i,:));
elseif behaviour == 3 %move towards average of slaves
sList = U(uId,slave1:slave3); %get slaves of the master
slaves_pos = [X(sList(1),:); PX(sList(2),:); X(sList(3),:);];
V(i,:) = w*V(i,:)+c1(t)*rand([1 d]).*(PX(i,:) - X(i,:)) + c2(t)*rand([1 d]).*(mean(slaves_pos) - X(i,:));
end
else %agent is slave, move towards the master particle
[uId,~] = find(U(:,slave1:slave3)==i); %find the unit particle belongs to
V(i,:) = w*V(i,:)+c1(t)*rand([1 d]).*(PX(i,:) - X(i,:)) + c2(t)*rand([1 d]).*(PX(U(uId,master),:) - X(i,:));
end
else %outward-oriented movement
if ~isempty(find(U(:,master)==i)) %agent is master
behaviour = randi([1 3]); %randomly selected behaviour
if behaviour==1 %if 1, move towards the avg pos of another unit
rndU = randi([1,U_n],1,1); %select a unit randomly
sList = U(rndU,slave1:slave3); %get slaves of a random unit
uX = [PX(U(rndU,master),:); X(sList(1),:); PX(sList(2),:); X(sList(3),:)]; %all positions of the unit
V(i,:) = w*V(i,:)+c1(t)*rand([1 d]).*(PX(i,:) - X(i,:)) + c2(t)*rand([1 d]).*(mean(uX) - X(i,:));
elseif behaviour==2 %move towards the master of another unit
V(i,:) = w*V(i,:)+c1(t)*rand([1 d]).*(PX(i,:) - X(i,:)) + c2(t)*rand([1 d]).*(PX(U(randi([1 U_n]),master),:) - X(i,:));
elseif behaviour==3 %move towards avg of self unit and master of another unit
sList = U(find(U(:,master)==i),slave1:slave3); %get all slaves of the unit
sList(4) = U(randi([1 U_n]),master); %add a master particle from a random unit
V(i,:) = w*V(i,:)+c1(t)*rand([1 d]).*(mean(X(sList,:)) - X(i,:)) + c2(t)*rand([1 d]).*(PX(U(randi([1 U_n]),master),:) - X(i,:));
end
else %agent is slave
[~,sType] = find(U==i); %find self slave type
Slist = U(:,sType); %get list of all slaves of the same type
[selfId,~] = find(Slist==i);
Slist(selfId) = []; %remove self from the list
rndSlave = randperm(length(Slist)); %shuffle the list
rndSlave = Slist(rndSlave(1)); %select the first one
V(i,:) = w*V(i,:)+c1(t)*rand([1 d]).*(PX(i,:) - X(i,:)) + c2(t)*rand([1 d]).*(X(rndSlave,:) - X(i,:));
end
end
else %velocity update for particles in the homogeneous subpop
V(i,:) = w*V(i,:)+c1(t)*rand([1 d]).*(PX(i,:) - X(i,:)) + c2(t)*rand([1 d]).*(GX - X(i,:));
end
else %final phase of the search process (exploitation)
V(i,:) = w*V(i,:)+c1(t)*rand([1 d]).*(PX(i,:) - X(i,:)) + c2(t)*rand([1 d]).*(GX - X(i,:));
end
V(i,:) = max(V(i,:),MinV); V(i,:) = min(V(i,:),MaxV); %velocity clamp
X(i,:) = X(i,:) + V(i,:); %update position
X(i,:) = max(X(i,:), LB); X(i,:) = min(X(i,:), UB); %apply lower and upper bound limits
%particle communication
if COM==true
if ~isempty(find(U==i)) %if particle belongs to the heterogeneous subpop
[~,sIdx] = find(U==i); %find the slave type of the ith particle
if sIdx == slave1 || sIdx == slave2 || sIdx == slave3 %if ith agent is a slave
sList = U(:,sIdx); %pool of same type of slaves from all units
rndSlave = randperm(length(sList),1); %select a random slave from the pool
%positional info exchange between the ith particle and a random slave of the same type
if PF(i) < PF(sList(rndSlave)), PF(sList(rndSlave)) = PF(i); PX(sList(rndSlave),:) = PX(i,:);
else, PF(i) = PF(sList(rndSlave)); PX(i,:) = PX(sList(rndSlave),:);
end
end
end
end
end
F = feval(fhd,X',fId); %function evaluation
fevalCount = fevalCount + n;
for j=1:n
if F(j) < PF(j), PF(j) = F(j); PX(j,:) = X(j,:); end %update pbests
if PF(j) < GF, GF = PF(j); GX = PX(j,:); end %update gbest
end
alpha = round(alpha_max-(alpha_max-alpha_min)*t/Tmax);
if GA==true
GA_pop_ids = [randi([1 n],1,n/2)]; %randomly select half of the population from both homogeneous and heterogeneous populations
GA_pop = X(GA_pop_ids,:); %create a new population for GA
[new_X,new_F,new_best,new_GF,fevalCount] = GeneticAlgorithm(fhd,fId,n/2,[LB UB],d,GA_pop,GA_phase,fevalCount);
X(GA_pop_ids,:) = new_X; %update particles with returned positions from GA
F(GA_pop_ids) = new_F; %update particle fitness with returned fitness from GA
%update gbest position and cost
if new_GF < GF
GX = new_best.Position;
GF = new_GF;
end
GA = false;
end
if ShowProgress==true, disp(['Iteration ' num2str(t) ' | Best cost = ' num2str(GF)]); end
end
fmin=GF;
end
参考文献
[1]Varna F T, Husbands P. Genetic algorithm assisted HIDMS-PSO: a new hybrid algorithm for global optimisation[C]//2021 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC). IEEE, 2021: 1304-1311.
完整代码获取
后台回复关键词:
点击下方卡片关注,获取更多代码





















 291
291

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










