先大概说说我是如何解决rs485(uart4)&rs233(uart5)的通信问题。
首先,在kernel-AGV/drivers/tty/serial/omap-serial.c中确定串口的默认时钟频率。
![]()
接着,在kernel/arch/arm/mach-omap2/board-ipc335x.c和kernel/arch/arm/mach-omap2/mux33xx.c中查看uart4(和流控脚)&uart5的配置;说明一下,board-ipc335x.c这个文件是根据evm板进行的更改,与各位的板级配置文件名可能不一致。
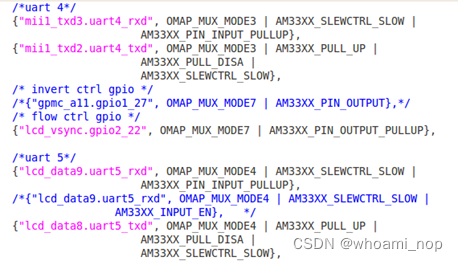
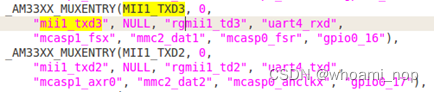
![]()
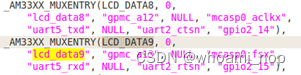
从而确认板级配置没有问题。
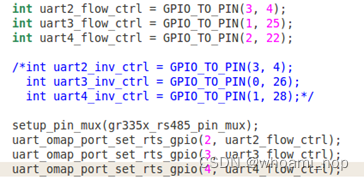
进一步的,查看uart_omap_port_set_rts_gpio函数的定义,将gpio设置成rts_gpio;
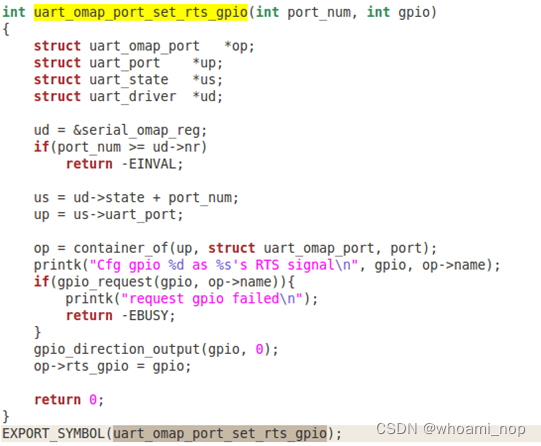
重点查看drivers/tty/serial目录,找到8250.c文件。通过更改nr_uarts的赋值达成目的,
/*static unsigned int nr_uarts = CONFIG_SERIAL_8250_RUNTIME_UARTS;*/
static unsigned int nr_uarts = 5; //支持uart0~5
static void __init serial8250_isa_init_ports(void)
{
struct uart_8250_port *up;
static int first = 1;
int i, irqflag = 0;
if (!first)
return;
first = 0;
for (i = 0; i < nr_uarts; i++) {
struct uart_8250_port *up = &serial8250_ports[i];
up->port.line = i;
spin_lock_init(&up->port.lock);
init_timer(&up->timer);
up->timer.function = serial8250_timeout;
/*
* ALPHA_KLUDGE_MCR needs to be killed.
*/
up->mcr_mask = ~ALPHA_KLUDGE_MCR;
up->mcr_force = ALPHA_KLUDGE_MCR;
up->port.ops = &serial8250_pops;
}
if (share_irqs)
irqflag = IRQF_SHARED;
for (i = 0, up = serial8250_ports;
i < ARRAY_SIZE(old_serial_port) && i < nr_uarts;
i++, up++) {
up->port.iobase = old_serial_port[i].port;
up->port.irq = irq_canonicalize(old_serial_port[i].irq);
up->port.irqflags = old_serial_port[i].irqflags;
up->port.uartclk = old_serial_port[i].baud_base * 16;
up->port.flags = old_serial_port[i].flags;
up->port.hub6 = old_serial_port[i].hub6;
up->port.membase = old_serial_port[i].iomem_base;
up->port.iotype = old_serial_port[i].io_type;
up->port.regshift = old_serial_port[i].iomem_reg_shift;
set_io_from_upio(&up->port);
up->port.irqflags |= irqflag;
if (serial8250_isa_config != NULL)
serial8250_isa_config(i, &up->port, &up->capabilities);
}
}
此时uart4&uart5虽然可以正常使用,但是rs485(uart4)仍然不能正常通讯,最后查阅documentation目录下的serial-rs485.txt;如下:
RS485 SERIAL COMMUNICATIONS
1. INTRODUCTION
EIA-485, also known as TIA/EIA-485 or RS-485, is a standard defining the
electrical characteristics of drivers and receivers for use in balanced
digital multipoint systems.
This standard is widely used for communications in industrial automation
because it can be used effectively over long distances and in electrically
noisy environments.
2. HARDWARE-RELATED CONSIDERATIONS
Some CPUs/UARTs (e.g., Atmel AT91 or 16C950 UART) contain a built-in
half-duplex mode capable of automatically controlling line direction by
toggling RTS or DTR signals. That can be used to control external
half-duplex hardware like an RS485 transceiver or any RS232-connected
half-duplex devices like some modems.
For these microcontrollers, the Linux driver should be made capable of
working in both modes, and proper ioctls (see later) should be made
available at user-level to allow switching from one mode to the other, and
vice versa.
3. DATA STRUCTURES ALREADY AVAILABLE IN THE KERNEL
The Linux kernel provides the serial_rs485 structure (see [1]) to handle
RS485 communications. This data structure is used to set and configure RS485
parameters in the platform data and in ioctls.
The device tree can also provide RS485 boot time parameters (see [2]
for bindings). The driver is in charge of filling this data structure from
the values given by the device tree.
Any driver for devices capable of working both as RS232 and RS485 should
provide at least the following ioctls:
- TIOCSRS485 (typically associated with number 0x542F). This ioctl is used
to enable/disable RS485 mode from user-space
- TIOCGRS485 (typically associated with number 0x542E). This ioctl is used
to get RS485 mode from kernel-space (i.e., driver) to user-space.
In other words, the serial driver should contain a code similar to the next
one:
static struct uart_ops atmel_pops = {
/* ... */
.ioctl = handle_ioctl,
};
static int handle_ioctl(struct uart_port *port,
unsigned int cmd,
unsigned long arg)
{
struct serial_rs485 rs485conf;
switch (cmd) {
case TIOCSRS485:
if (copy_from_user(&rs485conf,
(struct serial_rs485 *) arg,
sizeof(rs485conf)))
return -EFAULT;
/* ... */
break;
case TIOCGRS485:
if (copy_to_user((struct serial_rs485 *) arg,
...,
sizeof(rs485conf)))
return -EFAULT;
/* ... */
break;
/* ... */
}
}
4. USAGE FROM USER-LEVEL
From user-level, RS485 configuration can be get/set using the previous
ioctls. For instance, to set RS485 you can use the following code:
#include <linux/serial.h>
/* Driver-specific ioctls: */
#define TIOCGRS485 0x542E
#define TIOCSRS485 0x542F
/* Open your specific device (e.g., /dev/mydevice): */
int fd = open ("/dev/mydevice", O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0) {
/* Error handling. See errno. */
}
struct serial_rs485 rs485conf;
/* Enable RS485 mode: */
rs485conf.flags |= SER_RS485_ENABLED;
/* Set logical level for RTS pin equal to 1 when sending: */
rs485conf.flags |= SER_RS485_RTS_ON_SEND;
/* or, set logical level for RTS pin equal to 0 when sending: */
rs485conf.flags &= ~(SER_RS485_RTS_ON_SEND);
/* Set logical level for RTS pin equal to 1 after sending: */
rs485conf.flags |= SER_RS485_RTS_AFTER_SEND;
/* or, set logical level for RTS pin equal to 0 after sending: */
rs485conf.flags &= ~(SER_RS485_RTS_AFTER_SEND);
/* Set rts delay before send, if needed: */
rs485conf.delay_rts_before_send = ...;
/* Set rts delay after send, if needed: */
rs485conf.delay_rts_after_send = ...;
/* Set this flag if you want to receive data even whilst sending data */
rs485conf.flags |= SER_RS485_RX_DURING_TX;
if (ioctl (fd, TIOCSRS485, &rs485conf) < 0) {
/* Error handling. See errno. */
}
/* Use read() and write() syscalls here... */
/* Close the device when finished: */
if (close (fd) < 0) {
/* Error handling. See errno. */
}
5. REFERENCES
[1] include/linux/serial.h
[2] Documentation/devicetree/bindings/serial/rs485.txt
根据serial-rs485.txt给出的提示,在Linux下编译下面的代码,将生成的二进制可执行文件放入AM335x内核的文件系统中,执行它即可实现rs485通信(之所以需要执行该程序,是因为底层驱动配置中没有配置对应uart作为rs485的功能)。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <linux/serial.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <termios.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#define FALSE -1
#define TRUE 0
/* Driver-specific ioctls: */
#define TIOCGRS485 0x542E
#define TIOCSRS485 0x542F
void set_speed(int fd, int speed){
int speed_arr[] = { B115200, B38400, B19200, B9600, B4800, B2400, B1200, B300,B38400, B19200, B9600, B4800, B2400, B1200, B300, };
int name_arr[] = { 115200, 38400, 19200, 9600, 4800, 2400, 1200, 300, 38400, 19200, 9600, 4800, 2400, 1200, 300, };
int i;
int status;
struct termios Opt;
tcgetattr(fd, &Opt);
for ( i= 0; i < sizeof(speed_arr) / sizeof(int); i++) {
if (speed == name_arr[i]) {
tcflush(fd, TCIOFLUSH);
cfsetispeed(&Opt, speed_arr[i]);
cfsetospeed(&Opt, speed_arr[i]);
status = tcsetattr(fd, TCSANOW, &Opt);
if (status != 0) {
perror("tcsetattr fd1");
return;
}
tcflush(fd,TCIOFLUSH);
}
}
}
int set_Parity(int fd,int databits,int stopbits,int parity)
{
struct termios options;
if ( tcgetattr( fd,&options) != 0) {
perror("SetupSerial 1");
return(FALSE);
}
options.c_cflag &= ~CSIZE;
switch (databits)
{
case 7:
options.c_cflag |= CS7;
break;
case 8:
options.c_cflag |= CS8;
break;
default:
fprintf(stderr,"Unsupported data size\n"); return (FALSE);
}
switch (parity)
{
case 'n':
case 'N':
options.c_cflag &= ~PARENB; /* Clear parity enable */
options.c_iflag &= ~INPCK; /* Enable parity checking */
break;
case 'o':
case 'O':
options.c_cflag |= (PARODD | PARENB);
options.c_iflag |= INPCK; /* Disnable parity checking */
break;
case 'e':
case 'E':
options.c_cflag |= PARENB; /* Enable parity */
options.c_cflag &= ~PARODD;
options.c_iflag |= INPCK; /* Disnable parity checking */
break;
case 'S':
case 's': /*as no parity*/
options.c_cflag &= ~PARENB;
options.c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB;break;
default:
fprintf(stderr,"Unsupported parity\n");
return (FALSE);
}
switch (stopbits)
{
case 1:
options.c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB;
break;
case 2:
options.c_cflag |= CSTOPB;
break;
default:
fprintf(stderr,"Unsupported stop bits\n");
return (FALSE);
}
/* Set input parity option */
if (parity != 'n')
options.c_iflag |= INPCK;
tcflush(fd,TCIFLUSH);
options.c_cc[VTIME] = 150;
options.c_cc[VMIN] = 0; /* Update the options and do it NOW */
if (tcsetattr(fd,TCSANOW,&options) != 0)
{
perror("SetupSerial 3");
return (FALSE);
}
return (TRUE);
}
int read_datatty(int fd, unsigned char *rcv_buf, int TimeOut, int Len)
{
int retval;
fd_set rfds;
struct timeval tv;
int ret, pos;
tv.tv_sec = TimeOut / 1000; //set the rcv wait time
tv.tv_usec = TimeOut % 1000 * 1000; //100000us = 0.1s
pos = 0;
while (1)
{
FD_ZERO(&rfds);
FD_SET(fd, &rfds);
retval = select(fd + 1, &rfds, NULL, NULL, &tv);
if (retval == -1)
{
perror("select()");
break;
}
else if (retval)
{
ret = read(fd, rcv_buf + pos, 1);
if (-1 == ret)
{
printf("read error\n");
break;
}
pos++;
if (Len <= pos)
{
break;
}
}
else
{
printf("select_timeout\n");
break;
}
}
return




 本文详细介绍了在AM335x Linux系统下解决UART串口(RS485和RS232)通信问题的过程。通过分析kernel源码,调整uart_omap_port_set_rts_gpio函数,设置RS485参数,使用TIOCSRS485和TIOCGRS485 ioctls进行配置,并提供用户空间的示例代码。文章还探讨了串口初始化流程,包括uart_driver、uart_port和uart_ops结构体,以及串口驱动的注册和配置过程。
本文详细介绍了在AM335x Linux系统下解决UART串口(RS485和RS232)通信问题的过程。通过分析kernel源码,调整uart_omap_port_set_rts_gpio函数,设置RS485参数,使用TIOCSRS485和TIOCGRS485 ioctls进行配置,并提供用户空间的示例代码。文章还探讨了串口初始化流程,包括uart_driver、uart_port和uart_ops结构体,以及串口驱动的注册和配置过程。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 3140
3140










