本博客仅供学习交流使用,请勿用于作弊以及用于应付作业,珍惜每一个学习的机会
实验题目
以一个 m×n 的长方阵表示迷宫,0 和1分别表示迷宫中的通路和障碍。设计一个程序,对任意设定的迷宫,求出一条从入口到出口的通路,或得出没有通路的结论。要求实现以下功能:
- 以链表作存储结构的栈类型,编写一个求解迷宫的非递归程序。求得的通路以 (i,j) 的形式按通路顺序输出,其中(i,j) 为迷宫中的一个坐标。
- 求得迷宫中所有可能的通路,并输出最短路径。
以下是仅为一条测试数据:左上角 (0,1)为入口,右下角 (11,12)为出口。
|
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 | |
|
0 |
入 | ||||||||||||
|
1 | |||||||||||||
|
2 | |||||||||||||
|
3 | |||||||||||||
|
4 | |||||||||||||
|
5 | |||||||||||||
|
6 | |||||||||||||
|
7 | |||||||||||||
|
8 | |||||||||||||
|
9 | |||||||||||||
|
10 | |||||||||||||
|
11 |
出 | ||||||||||||
|
12 |
|
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 | |
|
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
|
2 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
|
3 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
|
4 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
5 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
|
6 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
|
7 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
|
8 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
|
9 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
|
10 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
|
11 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
|
12 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
题目分析与算法设计
题目性质
由于要输出所有路径,所以要用深搜。又因为要非递归,所以这是一道用栈模拟深搜的题目。
难点
在我做的过程中,发现这个题目主要有这么几个难点:
1.要以链表作为栈
不能调用STL,这就需要我们自己建立栈的数据类型了 。所以这题还考差了我们对链表和栈知识 的掌握。
2.要用非递归来实现。
以前我们总是用dfs()函数来写这种题目,然后每次调用函数结束的时候,总是会回到上次搜索的位置(比如说,按顺时针搜索,上次是搜索这个节点的上方,那当dfs()结束时,会自动搜索右方),相当于有个记录,避免下次从头开始。而用非递归来实现,则做不到“记录上次状态”的功能。这会导致在回溯时,会走一遍和原来一模一样的路径。
3.如何将路径正序输出
由于是起点先入栈,然后依次入栈,终点最后入栈。所以,如果直接pop的话,会得到一个倒序的序列。因此,我们需要找到方法来让他正序输出。
解决方案
以链表作为栈的实现
首先,我定义了一个栈的类。
class Stack
{
private:
Node*top=NULL;
int size=0;
public:
void Push(int row,int col);
void Pop();
Node*Top();
bool Empty();
int Size();
};
void Stack::Push(int row,int col)//节点入栈的函数
{
Node*p=new Node;
p->row=row;
p->col=col;
p->next=top;
top=p;
size++;
}
void Stack::Pop()//节点出栈的函数
{
//这里注意要对空指针进行特判,不然会报错
if(top!=NULL)
{
top=top->next;
}
size--;
}
bool Stack::Empty()//判断栈是否为空的函数
{
//这里也要注意空指针的特判
if(top==NULL)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}
Node* Stack::Top()//返回栈顶的指针
{
return top;
}
int Stack::Size()//返回栈的大小
{
return size;
}
这部分比较常规,在此就不再赘述了。唯一需要注意的是对于空指针的特判。
然后,我建立了几个栈的实例(下面会用到)
Stack pathStack;
//建立一个存储栈类型的vector,用来存储所有路径
vector<Stack> allPaths;
//存储最短的路径
Stack shortestPath;
//记录总共路径数的变量的
非递归的实现(重点)
struct Node
{
int row;
int col;
Node*next;
//建立一个di,来记录方向,以解决非递归没办法记录上次搜索方向的问题
int di;
};
首先,为了能记录上次这个节点搜遍了哪些方向,我建立了一个di=0.di=0,1,2,3分别代表搜过了上下左右。每次搜索让di++。
搜索算法的思路:
1.让起点入栈
2.当栈不为空的时候,循环
2.1如果到达终点,打印出路径。比较这条路径和最短路径的长度,如果更小,就覆盖最短路径。并且将终点标为未访问,回溯。
2.2如果到达终点,对这个节点向四个方向搜索。如果找到下一个可以走的节点,就把下一个节点入栈;如果没找到,回溯。
具体的搜索算法:
void Search()//核心:搜索算法
{
//首先将起点入栈
now_row=begin_row;
now_col=begin_col;
visited[begin_row][begin_col]=1;
pathStack.Push(begin_row,begin_col);
//当栈不为空的时候,搜索,启动!
while(!pathStack.Empty())
{
//记录下现在的位置
now_row=pathStack.Top()->row;
now_col=pathStack.Top()->col;
now_di=pathStack.Top()->di;
if (now_row == end_row && now_col == end_col) //如果走到了终点
{
//将这条路径存进放路径的vector中
allPaths.push_back(pathStack);
countPaths++;
//比较路径长短。如果更短,就把shortestPath覆盖掉
if (shortestPath.Empty() || pathStack.Size() < shortestPath.Size())
{
shortestPath = pathStack;
}
//重新让终点变得可达
visited[now_row][now_col]=0;
//回溯到上一个节点
pathStack.Pop();
now_row=pathStack.Top()->row;
now_col=pathStack.Top()->col;
now_di=pathStack.Top()->di;
}
//表示是否找到下一个可达的节点
bool found=0;
while(now_di<4&&found==0)
{
now_di++;
//对四个方向进行搜索
switch(now_di)
{
case 0:
now_row=pathStack.Top()->row-1;
now_col=pathStack.Top()->col;
break;//向上搜索
case 1:
now_row=pathStack.Top()->row;
now_col=pathStack.Top()->col+1;
break;//向右搜索
case 2:
now_row=pathStack.Top()->row+1;
now_col=pathStack.Top()->col;
break;//向下搜索
case 3:
now_row=pathStack.Top()->row;
now_col=pathStack.Top()->col-1;
break;//向左搜索
}
if(isValid(now_row,now_col))
{
found=1;
}
}
if(found==1)//如果找到了可以走的节点
{
//将新的节点入栈,接着搜索
pathStack.Top()->di=now_di;
pathStack.Push(now_row,now_col);
pathStack.Top()->row=now_row;
pathStack.Top()->col=now_col;
pathStack.Top()->di=-1;
visited[now_row][now_col]=1;
}
//如果没有找到,就回溯
else
{
visited[pathStack.Top()->row][pathStack.Top()->col]=0;//将这个地点标为可达
pathStack.Pop();//出栈
}
}
}
正序输出的实现
实现思路:
新建一个叫“reversedPath”的栈,然后把原栈复制过来。
之后,将原栈清空。
将“reversedPath”中的栈依次移到原栈中。
最后,将原栈输出,就得到了正序的路径。
void PrintPath(Stack &path) //打印路径
{
memset(visited,0,sizeof(visited));
cout<<"Step:"<<path.Size()<<endl;
//接下来这段代码是为了将栈翻转,来输出正确的路径
Stack reversedPath = path;//首先建立一个新的栈,将原来的栈拷贝过去
while(!path.Empty())//然后,将原来的栈清空
{
path.Pop();
}
while (!reversedPath.Empty())//然后将翻转的栈全部出栈,并以此加入到原栈中
{
path.Push(reversedPath.Top()->row,reversedPath.Top()->col);
reversedPath.Pop();
}
//这样我们将原栈输出,就得到了一个顺序正常的栈了!
cout << "Path: "<<endl;
if(path.Top()!=NULL)
{
cout << "(" << path.Top()->row<< ", " << path.Top()->col << ")";
visited[path.Top()->row][path.Top()->col]=1;//这个是为了最后打印出可视化路径用的
}
path.Pop();
while(!path.Empty())
{
cout << "-> (" << path.Top()->row<< ", " << path.Top()->col << ")";
visited[path.Top()->row][path.Top()->col]=1;
path.Pop();
}
cout<<endl;
//可视化路径(用“#”来表示路)
cout << "Visualize:('#'represents the path)"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<row;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<col;j++)
{
if(visited[i][j]==1)
{
cout<<"|#";
}
else
{
cout<<"|"<<map[i][j]<<"";
}
}
cout<<"|"<<endl;
}
}
其他函数的声明(可略看)
bool isValid(int next_row,int next_col)//判断走的节点是否合法
{
if(next_row>=0&&next_row<row&&next_col>=0&&next_col<col&&map[next_row][next_col]==0&&visited[next_row][next_col]==0)
{
return 1;
}
//合法的是哪个条件:1.节点仍然在迷宫中(不越界)2.没有走到墙里面3.节点没有被访问过
return 0;
}
上面这个函数是用来判断搜索的下一步是否合法的。额外写一个函数只是为了好看,做到“一个函数一个功能”,比较好维护。
void Initialize()
{
memset(visited,0,sizeof(visited));
memset(map,1,sizeof(map));
}
上面这个函数是将数组初始化的函数。同样也是为了好看。。。
void Input()//输入模块的函数
{
//这里用英文的原因是:中文有时候会输出乱码
cout<<"Please input the number of the row:"<<endl;
cin>>row;
cout<<"The maze has "<<row<<" rows."<<endl;
cout<<"Please input the number of the column:"<<endl;
cin>>col;
cout<<"The maze has "<<col<<" columns."<<endl;
cout<<"Please input the maze(from left to right,from top to down):"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<row;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<col;j++)
{
cin>>map[i][j];
}
}
//这里做了一个确认的环节
cout<<"The maze you input is:"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<row;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<col;j++)
{
cout<<"|"<<map[i][j];
}
cout<<"|";
cout<<endl;
}
//输入起点和终点的位置
cout<<"Please input where to start:"<<endl;
cout<<"row:"<<endl;
cin>>begin_row;
cout<<"column:"<<endl;
cin>>begin_col;
cout<<"Please input where to end:"<<endl;
cout<<"row:"<<endl;
cin>>end_row;
cout<<"column:"<<endl;
cin>>end_col;
cout<<"Input finish!Please wait for the result......"<<endl;
}
上面这个函数是用来输入的。因为进行了输入的确认,所以看起来比较长。
void InputTsetMap()//输入测试地图
{
row=13;
col=13;
begin_row=0;
begin_col=1;
end_row=11;
end_col=12;
for(int i=0;i<row;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<col;j++)
{
map[i][j]=TestMap[i][j];
}
}
cout<<"The test maze is:"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<row;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<col;j++)
{
cout<<"|"<<map[i][j];
}
cout<<"|";
cout<<endl;
}
cout<<"Input finish!Please wait for the result......"<<endl;
}
上面这个函数是用来输入初始化的迷宫的。
完整代码
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int row;
int col;
Node*next;
//建立一个di,来记录方向,以解决非递归没办法记录上次搜索方向的问题
int di;
};
//建立一个栈的类(因为接下来会用到两个栈的实例,所以我就建了一个类)
class Stack
{
private:
Node*top=NULL;
int size=0;
public:
void Push(int row,int col);
void Pop();
Node*Top();
bool Empty();
int Size();
};
int row,col,begin_row,begin_col,end_row,end_col;//这几个变量是用来存储起点和终点的坐标的
int now_row,now_col,now_di;//这几个变量是用来存储现在的坐标的
bool map[110][110];//记录迷宫
bool visited[110][110];//记录节点是否被访问过
bool TestMap[13][13]={
1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,
1,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,1,
1,1,1,1,1,0,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,
1,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1,
1,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,
1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,
1,0,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,
1,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,
1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,
1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,
1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0,1,0,1,
1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,
1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1
};//测试地图(从老师那里来的)
Stack pathStack;
//建立一个存储栈类型的vector,用来存储所有路径
vector<Stack> allPaths;
//存储最短的路径
Stack shortestPath;
//记录总共路径数的变量的
int countPaths=0;
void Initialize()//初始化数组的函数
{
memset(visited,0,sizeof(visited));
memset(map,1,sizeof(map));
}
void Input()//输入模块的函数
{
//这里用英文的原因是:中文有时候会输出乱码
cout<<"Please input the number of the row:"<<endl;
cin>>row;
cout<<"The maze has "<<row<<" rows."<<endl;
cout<<"Please input the number of the column:"<<endl;
cin>>col;
cout<<"The maze has "<<col<<" columns."<<endl;
cout<<"Please input the maze(from left to right,from top to down):"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<row;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<col;j++)
{
cin>>map[i][j];
}
}
//这里做了一个确认的环节
cout<<"The maze you input is:"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<row;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<col;j++)
{
cout<<"|"<<map[i][j];
}
cout<<"|";
cout<<endl;
}
//输入起点和终点的位置
cout<<"Please input where to start:"<<endl;
cout<<"row:"<<endl;
cin>>begin_row;
cout<<"column:"<<endl;
cin>>begin_col;
cout<<"Please input where to end:"<<endl;
cout<<"row:"<<endl;
cin>>end_row;
cout<<"column:"<<endl;
cin>>end_col;
cout<<"Input finish!Please wait for the result......"<<endl;
}
void InputTsetMap()//输入测试地图
{
row=13;
col=13;
begin_row=0;
begin_col=1;
end_row=11;
end_col=12;
for(int i=0;i<row;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<col;j++)
{
map[i][j]=TestMap[i][j];
}
}
cout<<"The test maze is:"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<row;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<col;j++)
{
cout<<"|"<<map[i][j];
}
cout<<"|";
cout<<endl;
}
cout<<"Input finish!Please wait for the result......"<<endl;
}
void Stack::Push(int row,int col)//节点入栈的函数
{
Node*p=new Node;
p->row=row;
p->col=col;
p->next=top;
top=p;
size++;
}
void Stack::Pop()//节点出栈的函数
{
//这里注意要对空指针进行特判,不然会报错
if(top!=NULL)
{
top=top->next;
}
size--;
}
bool Stack::Empty()//判断栈是否为空的函数
{
//这里也要注意空指针的特判
if(top==NULL)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}
Node* Stack::Top()//返回栈顶的指针
{
return top;
}
int Stack::Size()//返回栈的大小
{
return size;
}
bool isValid(int next_row,int next_col)//判断走的节点是否合法
{
if(next_row>=0&&next_row<row&&next_col>=0&&next_col<col&&map[next_row][next_col]==0&&visited[next_row][next_col]==0)
{
return 1;
}
//合法的是哪个条件:1.节点仍然在迷宫中(不越界)2.没有走到墙里面3.节点没有被访问过
return 0;
}
void PrintPath(Stack &path) //打印路径
{
memset(visited,0,sizeof(visited));
cout<<"Step:"<<path.Size()<<endl;
//接下来这段代码是为了将栈翻转,来输出正确的路径
Stack reversedPath = path;//首先建立一个新的栈,将原来的栈拷贝过去
while(!path.Empty())//然后,将原来的栈清空
{
path.Pop();
}
while (!reversedPath.Empty())//然后将翻转的栈全部出栈,并以此加入到原栈中
{
path.Push(reversedPath.Top()->row,reversedPath.Top()->col);
reversedPath.Pop();
}
//这样我们将原栈输出,就得到了一个顺序正常的栈了!
cout << "Path: "<<endl;
if(path.Top()!=NULL)
{
cout << "(" << path.Top()->row<< ", " << path.Top()->col << ")";
visited[path.Top()->row][path.Top()->col]=1;//这个是为了最后打印出可视化路径用的
}
path.Pop();
while(!path.Empty())
{
cout << "-> (" << path.Top()->row<< ", " << path.Top()->col << ")";
visited[path.Top()->row][path.Top()->col]=1;
path.Pop();
}
cout<<endl;
//可视化路径(用“#”来表示路)
cout << "Visualize:('#'represents the path)"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<row;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<col;j++)
{
if(visited[i][j]==1)
{
cout<<"|#";
}
else
{
cout<<"|"<<map[i][j]<<"";
}
}
cout<<"|"<<endl;
}
}
void Search()//核心:搜索算法
{
//首先将起点入栈
now_row=begin_row;
now_col=begin_col;
visited[begin_row][begin_col]=1;
pathStack.Push(begin_row,begin_col);
//当栈不为空的时候,搜索,启动!
while(!pathStack.Empty())
{
//记录下现在的位置
now_row=pathStack.Top()->row;
now_col=pathStack.Top()->col;
now_di=pathStack.Top()->di;
if (now_row == end_row && now_col == end_col) //如果走到了终点
{
//将这条路径存进放路径的vector中
allPaths.push_back(pathStack);
countPaths++;
//比较路径长短。如果更短,就把shortestPath覆盖掉
if (shortestPath.Empty() || pathStack.Size() < shortestPath.Size())
{
shortestPath = pathStack;
}
//重新让终点变得可达
visited[now_row][now_col]=0;
//回溯到上一个节点
pathStack.Pop();
now_row=pathStack.Top()->row;
now_col=pathStack.Top()->col;
now_di=pathStack.Top()->di;
}
//表示是否找到下一个可达的节点
bool found=0;
while(now_di<4&&found==0)
{
now_di++;
//对四个方向进行搜索
switch(now_di)
{
case 0:
now_row=pathStack.Top()->row-1;
now_col=pathStack.Top()->col;
break;//向上搜索
case 1:
now_row=pathStack.Top()->row;
now_col=pathStack.Top()->col+1;
break;//向右搜索
case 2:
now_row=pathStack.Top()->row+1;
now_col=pathStack.Top()->col;
break;//向下搜索
case 3:
now_row=pathStack.Top()->row;
now_col=pathStack.Top()->col-1;
break;//向左搜索
}
if(isValid(now_row,now_col))
{
found=1;
}
}
if(found==1)//如果找到了可以走的节点
{
//将新的节点入栈,接着搜索
pathStack.Top()->di=now_di;
pathStack.Push(now_row,now_col);
pathStack.Top()->row=now_row;
pathStack.Top()->col=now_col;
pathStack.Top()->di=-1;
visited[now_row][now_col]=1;
}
//如果没有找到,就回溯
else
{
visited[pathStack.Top()->row][pathStack.Top()->col]=0;//将这个地点标为可达
pathStack.Pop();//出栈
}
}
}
int main()
{
Initialize();
cout<<"If you want to input your own maze,input 1."<<endl
<<"If you want to see the test maze,input 2."<<endl;
cout<<"Your choice:"<<endl;
int choice;
cin>>choice;
if(choice==1)
{
Input();
Search();
cout<<"All paths:"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<countPaths;i++)
{
cout<<i+1<<":"<<endl;
PrintPath(allPaths[i]);
cout<<endl;
}
cout<<"The shortest path:"<<endl;
PrintPath(shortestPath);
}
if(choice==2)
{
InputTsetMap();
Search();
cout<<"All paths:"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<countPaths;i++)
{
cout<<i+1<<":"<<endl;
PrintPath(allPaths[i]);
cout<<endl;
}
cout<<"The shortest path:"<<endl;
PrintPath(shortestPath);
}
system("pause");
}
程序复杂度分析
空间复杂度
该程序的空间开销主要是存地图,以及存是否有被访问过。复杂度为为O(n^2)。
bool map[110][110];
bool visited[110][110];
bool TestMap[13][13]={
1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,
1,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,1,
1,1,1,1,1,0,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,
1,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1,
1,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,1,
1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,
1,0,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,
1,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,
1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,1,1,0,1,
1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,
1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0,1,0,1,
1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,
1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1
};
这里我做了优化。不同于传统的int型存地图,然后用例如-1来标记访问过(开销4字节),我全部用bool型来存,另外开了个bool型的visited数组标记是否有被走过。这样节省了一半的空间开销。
此外的空间开销就是两个栈和一个vector。复杂度为O(n)。
Stack pathStack;
//建立一个存储栈类型的vector,用来存储所有路径
vector<Stack> allPaths;
//存储最短的路径
Stack shortestPath;
//记录总共路径数的变量的
时间复杂度
时间复杂度主要在于DFS。查找所有点的邻接点所需时间为O(n^2),访问顶点的邻接点所花时间为O(1),此时,总的时间复杂度为O(n^2)。
程序运行结果展示
我还做了一下迷宫的可视化,用“#”来表示路径。
选择自己输入迷宫
输入
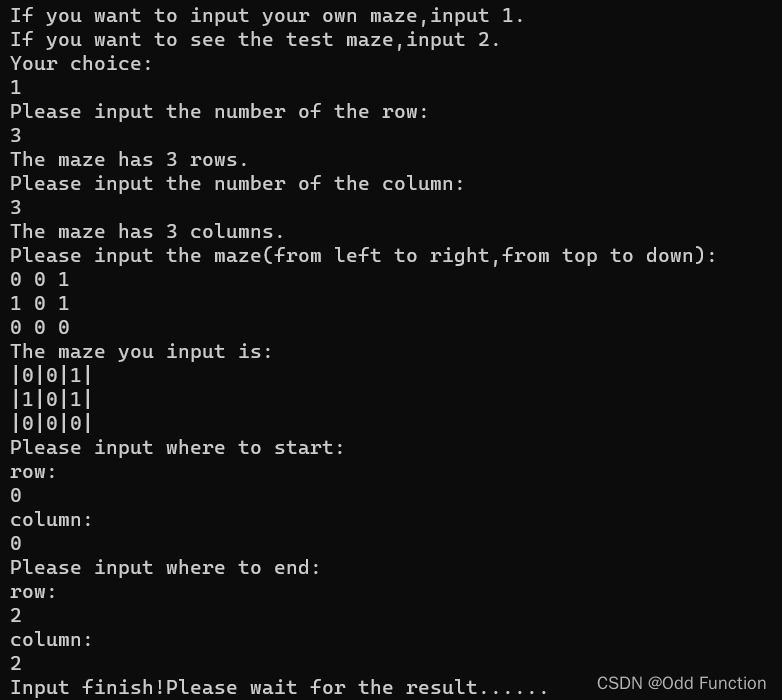
输出

选择运行测试例
输入
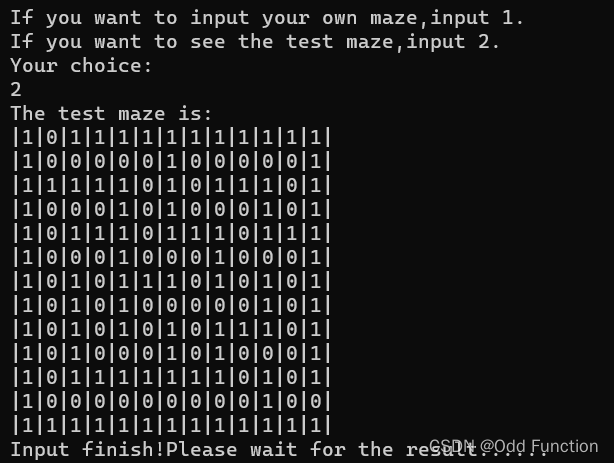
输出
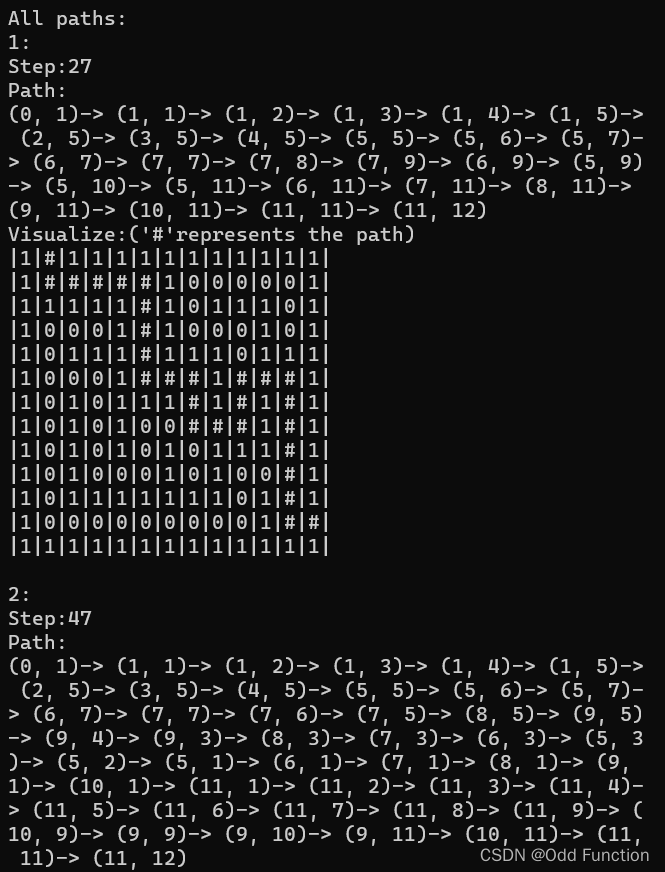
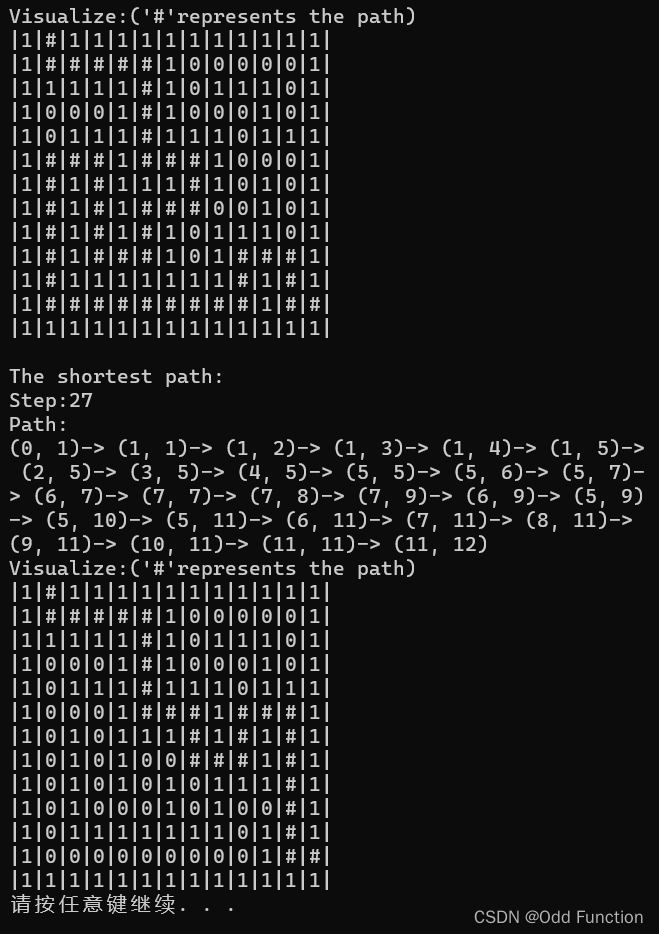
碎碎念
一开始,我只做出来了一个栈,并没有定义栈这个数据类型。
后来,由于要输出所有的路径,以及最短的路径,需要用到多个栈,我才定义了栈的数据类型。
在最后输出路径的时候,我遇到了一个问题:由于栈是先进后出的,所以如果我从上到下pop,输出来的是反向的路径。
为此,我的解决方法是:
1.再建立一个栈,叫reversedPath,并且把path赋值给它。
2.让path的元素弹出
3.将reversedPath的元素依次弹出,并且加入到新的栈中。
4.最后再把新的栈pop。
这样子,就得到了正序输出的路径。
在输出最短路径的时候,我又遇到了个问题:
如何比较路径的长短?
为了解决这个问题,我在栈这个类里面定义了一个private的元素size=0;并且开了个public的接口函数Size()来访问这个元素。之后,我在Push函数中加了size++;,在Pop函数中加了size--。这样,不同的栈就可以通过比较size来确定最短路径了。




















 3080
3080

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








