A. Shuffle Party
Problem Statement
You are given an array a 1 , a 2 , … , a n a_1, a_2, \ldots, a_n a1,a2,…,an. Initially, a i = i a_i=i ai=i for each 1 ≤ i ≤ n 1 \le i \le n 1≤i≤n.
The operation swap ( k ) \texttt{swap}(k) swap(k) for an integer k ≥ 2 k \ge 2 k≥2 is defined as follows:
- Let d d d be the largest divisor † ^\dagger † of k k k which is not equal to k k k itself. Then swap the elements a d a_d ad and a k a_k ak.
Suppose you perform swap ( i ) \texttt{swap}(i) swap(i) for each i = 2 , 3 , … , n i=2,3,\ldots, n i=2,3,…,n in this exact order. Find the position of 1 1 1 in the resulting array. In other words, find such j j j that a j = 1 a_j = 1 aj=1 after performing these operations.
† ^\dagger † An integer x x x is a divisor of y y y if there exists an integer z z z such that y = x ⋅ z y = x \cdot z y=x⋅z.
Input
Each test contains multiple test cases. The first line contains the number of test cases t t t ( 1 ≤ t ≤ 1 0 4 1 \le t \le 10^4 1≤t≤104). The description of the test cases follows.
The only line of each test case contains one integer n n n ( 1 ≤ n ≤ 1 0 9 1 \le n \le 10^9 1≤n≤109) — the length of the array a a a.
Output
For each test case, output the position of 1 1 1 in the resulting array.
Example
Example
| input |
|---|
| 4 |
| 1 |
| 4 |
| 5 |
| 120240229 |
| output |
|---|
| 1 |
| 4 |
| 4 |
| 67108864 |
Note
In the first test case, the array is [ 1 ] [1] [1] and there are no operations performed.
In the second test case, a a a changes as follows:
- Initially, a a a is [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 ] [1,2,3,4] [1,2,3,4].
- After performing swap ( 2 ) \texttt{swap}(2) swap(2), a a a changes to [ 2 ‾ , 1 ‾ , 3 , 4 ] [\underline{2},\underline{1},3,4] [2,1,3,4] (the elements being swapped are underlined).
- After performing swap ( 3 ) \texttt{swap}(3) swap(3), a a a changes to [ 3 ‾ , 1 , 2 ‾ , 4 ] [\underline{3},1,\underline{2},4] [3,1,2,4].
- After performing swap ( 4 ) \texttt{swap}(4) swap(4), a a a changes to [ 3 , 4 ‾ , 2 , 1 ‾ ] [3,\underline{4},2,\underline{1}] [3,4,2,1].
Finally, the element 1 1 1 lies on index 4 4 4 (that is, a 4 = 1 a_4 = 1 a4=1). Thus, the answer is 4 4 4.
Solution
具体见文后视频。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;
void solve()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
int i = 1;
while (i * 2 <= n) i *= 2;
cout << i << endl;
}
signed main()
{
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
int Data;
cin >> Data;
while (Data --)
solve();
return 0;
}
B. Binary Path
Problem Statement
You are given a 2 × n 2 \times n 2×n grid filled with zeros and ones. Let the number at the intersection of the i i i-th row and the j j j-th column be a i j a_{ij} aij.
There is a grasshopper at the top-left cell ( 1 , 1 ) (1, 1) (1,1) that can only jump one cell right or downwards. It wants to reach the bottom-right cell ( 2 , n ) (2, n) (2,n). Consider the binary string of length n + 1 n+1 n+1 consisting of numbers written in cells of the path without changing their order.
Your goal is to:
- Find the lexicographically smallest † ^\dagger † string you can attain by choosing any available path;
- Find the number of paths that yield this lexicographically smallest string.
† ^\dagger † If two strings s s s and t t t have the same length, then s s s is lexicographically smaller than t t t if and only if in the first position where s s s and t t t differ, the string s s s has a smaller element than the corresponding element in t t t.
Input
Each test contains multiple test cases. The first line contains the number of test cases t t t ( 1 ≤ t ≤ 1 0 4 1 \le t \le 10^4 1≤t≤104). The description of the test cases follows.
The first line of each test case contains a single integer n n n ( 2 ≤ n ≤ 2 ⋅ 1 0 5 2 \le n \le 2 \cdot 10^5 2≤n≤2⋅105).
The second line of each test case contains a binary string a 11 a 12 … a 1 n a_{11} a_{12} \ldots a_{1n} a11a12…a1n ( a 1 i a_{1i} a1i is either 0 0 0 or 1 1 1).
The third line of each test case contains a binary string a 21 a 22 … a 2 n a_{21} a_{22} \ldots a_{2n} a21a22…a2n ( a 2 i a_{2i} a2i is either 0 0 0 or 1 1 1).
It is guaranteed that the sum of n n n over all test cases does not exceed 2 ⋅ 1 0 5 2 \cdot 10^5 2⋅105.
Output
For each test case, output two lines:
- The lexicographically smallest string you can attain by choosing any available path;
- The number of paths that yield this string.
Example
Example
| input |
|---|
| 3 |
| 2 |
| 00 |
| 00 |
| 4 |
| 1101 |
| 1100 |
| 8 |
| 00100111 |
| 11101101 |
| output |
|---|
| 000 |
| 2 |
| 11000 |
| 1 |
| 001001101 |
| 4 |
Note
In the first test case, the lexicographically smallest string is 000 \mathtt{000} 000. There are two paths that yield this string:
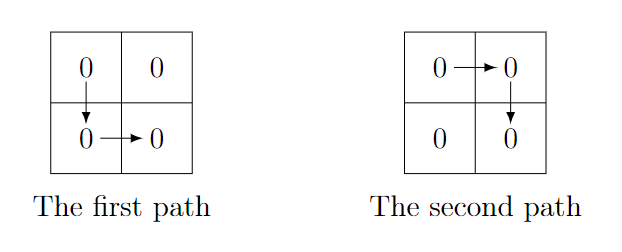
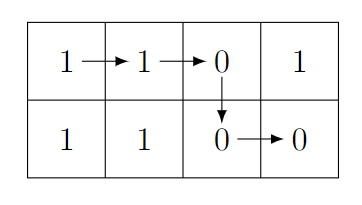
In the second test case, the lexicographically smallest string is 11000 \mathtt{11000} 11000. There is only one path that yields this string:
Solution
具体见文后视频。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;
void solve()
{
int n;
string s[2];
cin >> n >> s[0] >> s[1];
int p = n - 1;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i ++)
if (s[0][i] != '0' && s[1][i - 1] == '0')
{
p = i - 1;
break;
}
string res;
for (int i = 0; i <= p; i ++)
res += s[0][i];
res += s[1][p];
for (int i = p + 1; i < n; i ++)
res += s[1][i];
int lst = 0;
for (int i = n - 1, j = n; i >= 0; i --, j --)
if (res[j] != s[1][i])
{
lst = i + 1;
break;
}
cout << res << endl;
cout << p - lst + 1 << endl;
}
signed main()
{
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
int Data;
cin >> Data;
while (Data --)
solve();
return 0;
}
C. Bitwise Operation Wizard
Problem Statement
There is a secret sequence p 0 , p 1 , … , p n − 1 p_0, p_1, \ldots, p_{n-1} p0,p1,…,pn−1, which is a permutation of { 0 , 1 , … , n − 1 } \{0,1,\ldots,n-1\} { 0,1,…,n−1}.
You need to find any two indices i i i and j j j such that p i ⊕ p j p_i \oplus p_j pi⊕pj is maximized, where ⊕ \oplus ⊕ denotes the bitwise XOR operation.
To do this, you can ask queries. Each query has the following form: you pick arbitrary indices a a a, b b b, c c c, and d d d ( 0 ≤ a , b , c , d < n 0 \le a,b,c,d < n 0≤a,b,c,d<n). Next, the jury calculates x = ( p a ∣ p b ) x = (p_a \mid p_b) x=(pa∣pb) and y = ( p c ∣ p d ) y = (p_c \mid p_d) y=(pc∣pd), where ∣ | ∣ denotes the bitwise OR operation. Finally, you receive the result of comparison between x x x and y y y. In other words, you are told if x < y x < y x<y, x > y x > y x>y, or x = y x = y x=y.
Please find any two indices i i i and j j








 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
















 765
765

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








