提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、继承uvm_component的几大组件
-
- 1. uvm_driver
- 2. uvm_monitor
- 3. uvm_sequencer
- 4. uvm_scoreboard
- 5. reference model
- 6. uvm_agent
- 6. uvm_env
- 6. uvm_test
- 二、UVM的树形结构
-
- 1. 为什么要有parent参数
- 2. get_parent、get_child等函数
- 三、field automation机制
-
- 1. field automation机制相关的宏
- 2. field automation机制的常用函数
- 3. field automation机制中标志位(UVM_ALL_ON)
- 4. field automation中也可以加if条件
- 四、UVM打印信息的控制
-
- 1. 设置/查看打印信息的冗余度阈值
- 2. 打印信息的重载
- 3. UVM_ERROR达到一定数量结束仿真
- 五、config_db机制
-
- 1. set和get函数的参数
- 2. get语句也可以省略?
- 3. 寄信多次,收信一次,以哪个为准?
- 4. config_db机制支持通配符
- 4. check_config_usage
- 总结
前言
本篇主要介绍UVM的几大组件,以及一些基础的知识
一、继承uvm_component的几大组件
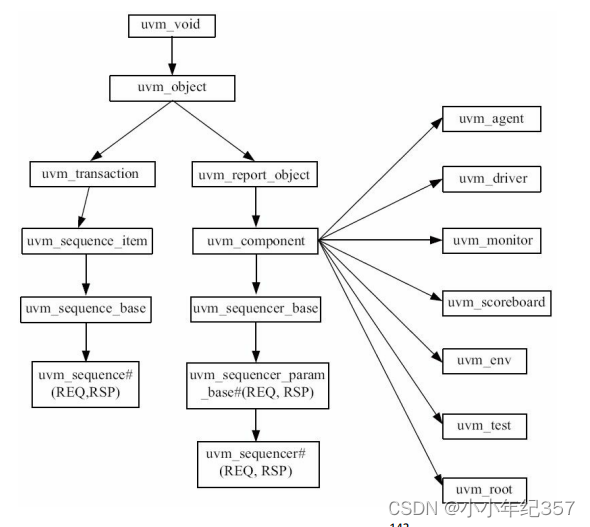
如上图,继承uvm_component的组件有uvm_agent/driver/monitor/scoreboard/env/test
1. uvm_driver
所有的driver都要派生自uvm_driver。driver的功能主要就是向sequencer索要sequence_item(transaction),并且将sequence_item里的信息驱动到DUT的端口上,这相当于完成了从transaction级别到DUT能够接受的端口级别信息的转换。
相关代码如下:
class my_driver extends uvm_driver#(my_transaction);
virtual my_if vif;
`uvm_component_utils(my_driver)//加入factory机制,把my_driver注册在UVM内部的一张表中
function new(string name = "my_driver", uvm_component parent = null);//每一个派生自uvm_component在new函数中都要指明两个参数:name和parent
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
if(!uvm_config_db#(virtual my_if)::get(this, "", "vif", vif))
`uvm_fatal("my_driver", "virtual interface must be set for vif!!!")
endfunction
extern task main_phase(uvm_phase phase);//driver所做的事情几乎都在main_phase中完成
extern task drive_one_pkt(my_transaction tr);
endclass
task my_driver::main_phase(uvm_phase phase);
vif.data <= 8'b0;
vif.valid <= 1'b0;
while(!vif.rst_n)
@(posedge vif.clk);
while(1) begin
seq_item_port.get_next_item(req);//得到一个新的req,并且驱动它
drive_one_pkt(req);
seq_item_port.item_done();//驱动完req后,通知sequencer
end
endtask
2. uvm_monitor
所有的monitor都要派生自uvm_monitor。monitor做的事情与driver相反,driver向DUT的pin上发送数据,而monitor则是从DUT的pin上接收数据,并且把接收到的数据转换成transaction级别的sequence_item,再把转换后的数据发送给scoreboard或者reference model,供其比较。
class my_monitor extends uvm_monitor;
virtual my_if vif;
uvm_analysis_port #(my_transaction) ap;
`uvm_component_utils(my_monitor)
function new(string name = "my_monitor", uvm_component parent = null);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
if(!uvm_config_db#(virtual my_if)::get(this, "", "vif", vif))
`uvm_fatal("my_monitor", "virtual interface must be set for vif!!!")
ap = new("ap", this);
endfunction
extern task main_phase(uvm_phase phase);
extern task collect_one_pkt(my_transaction tr);
endclass
task my_monitor::main_phase(uvm_phase phase);
my_transaction tr;
while(1) begin
tr = new("tr");
collect_one_pkt(tr);
ap.write(tr);
end
endtask
DUT的输入口设置一个monitor有必要吗?
第一,在一个大型的项目中,driver根据某一协议发送数据,而monitor根据这种协议收集数据,如果driver和monitor由不同的人员实现,那么可以大大减少其中任何一方对协议理解的错误;
第二,在实现代码重用时,使用monitor是非常有必要的。
3. uvm_sequencer
所有的sequencer都要派生自uvm_sequencer。sequencer的功能就是组织管理sequence,当driver要求数据时,它就把sequence生成的sequence_item转发给driver。
class my_sequencer extends uvm_sequencer #(my_transaction);
function new(string name, uvm_component parent);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
`uvm_component_utils(my_sequencer)
endclass
4. uvm_scoreboard
一般的scoreboard都派生自uvm_scoreboard。scoreboard的功能就是比较reference model和monitor分别发送来的数据,根据比较结果判断DUT是否正确工作。
class my_scoreboard extends uvm_scoreboard;
my_transaction expect_queue[$];
uvm_blocking_get_port #(my_transaction) exp_port;
uvm_blocking_get_port #(my_transaction) act_port;
`uvm_component_utils(my_scoreboard)
extern function new(string name, uvm_component parent = null);
extern virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
extern virtual task main_phase(uvm_phase phase);
endclass
function my_scoreboard::new(string name, uvm_component parent = null);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
function void my_scoreboard::build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
exp_port = new("exp_port", this);
act_port = new("act_port", this);
endfunction
task my_scoreboard::main_phase(uvm_phase phase);
my_transaction get_expect, get_actual, tmp_tran;
bit result;
bit cmp_en = 1'b1;
super.main_phase(phase);
fork
while(1) begin
uvm_config_db#(bit)::wait_modified(this, "", "cmp_en");//这里是什么意思?后续在看
void'(uvm_config_db#(bit)::get(this, "", "cmp_en", cmp_en));
`uvm_info("my_scoreboard", $sformatf("cmp_en value modified, the new value is %0d", cmp_en), UVM_LOW)
end
while (1) begin
exp_port.get(get_expect);
expect_queue.push_back(get_expect);
end
while (1) begin
act_port.get(get_actual);
if(expect_queue.size() > 0) begin
tmp_tran = expect_queue.pop_front();
result = get_actual.compare(tmp_tran);
if(result) begin
`uvm_info("my_scoreboard", "Compare SUCCESSFULLY", UVM_LOW);
end
else begin
`uvm_error("my_scoreboard", "Compare FAILED");
$display("the expect pkt is");
tmp_tran.print()




 本文详细介绍了UVM验证方法论的基础组件,包括uvm_driver、uvm_monitor、uvm_sequencer、uvm_scoreboard、uvm_agent、uvm_env和uvm_test的职责与用法。此外,还探讨了UVM的树形结构、field automation机制、打印信息控制以及config_db机制,为理解和应用UVM提供基础指导。
本文详细介绍了UVM验证方法论的基础组件,包括uvm_driver、uvm_monitor、uvm_sequencer、uvm_scoreboard、uvm_agent、uvm_env和uvm_test的职责与用法。此外,还探讨了UVM的树形结构、field automation机制、打印信息控制以及config_db机制,为理解和应用UVM提供基础指导。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 7718
7718

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








