C++内存分布
我们先来看一下下面的一段代码相关问题
int globalVar = 1;
static int staticGlobalVar = 1;
void Test()
{
static int staticVar = 1;
int localVar = 1;
int num1[10] = {1, 2, 3, 4};
char char2[] = "abcd";
char* pChar3 = "abcd";
int* ptr1 = (int*)malloc(sizeof (int)*4);
int* ptr2 = (int*)calloc(4, sizeof(int));
int* ptr3 = (int*)realloc(ptr2, sizeof(int)*4);
free (ptr1);
free (ptr3);
}
1. 选择题:
选项: A.栈 B.堆 C.数据段 D.代码段
globalVar在哪里?__c__ staticGlobalVar在哪里?__c__
staticVar在哪里?__c__ localVar在哪里?__a__
num1 在哪里?__a__
char2在哪里?__a__ *char2在哪里?__d__
pChar3在哪里?__a__ *pChar3在哪里?__d__
ptr1在哪里?__a__ *ptr1在哪里?__b__
2. 填空题:
sizeof(num1) = __40__;
sizeof(char2) = __5__; strlen(char2) = __4__;
sizeof(pChar3) = __8__; strlen(pChar3) = __4__;
sizeof(ptr1) = __8__;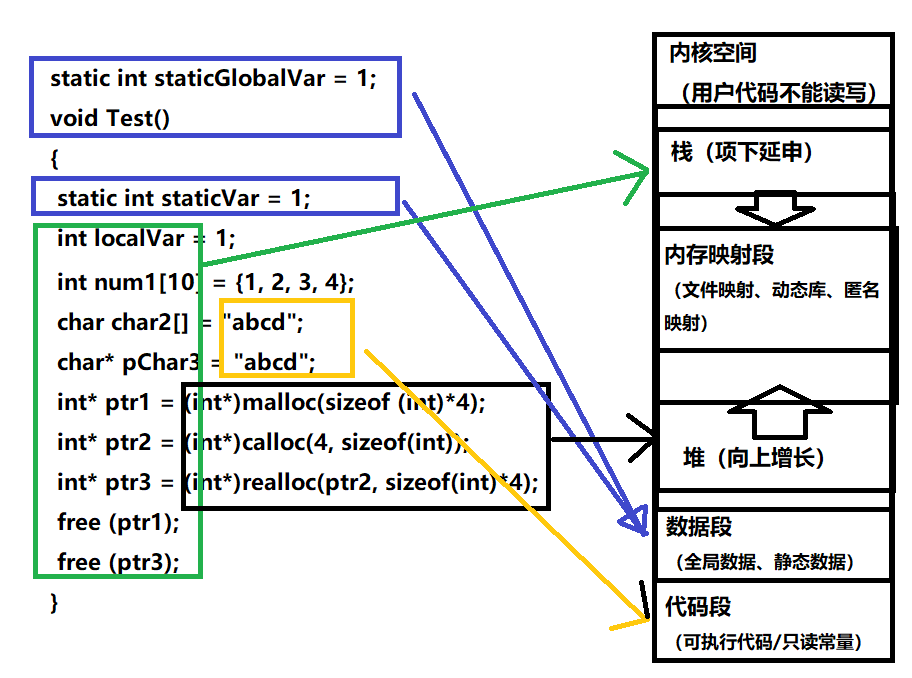
【说明】
堆又叫堆栈,非静态局部变量/函数参数/返回值等等,栈是向下增长的。
内存映射段是高效的I/O映射方式,用于装载一个共享的动态内存库。用户可使用系统接口创建共享共享内存,做进程间通信。(Linux课程如果没学到这块,现在只需要了解一下)。
堆用于程序运行时动态内存分配,堆是可以上增长的。
数据段--存储全局数据和静态数据。
代码段--可执行的代码/只读常量。
C语言当中动态内存管理方式
malloc/calloc/realloc/free
void Test ()
{
int* p1 = (int*) malloc(sizeof(int));
free(p1);
// 1.malloc/calloc/realloc的区别是什么?
int* p2 = (int*)calloc(4, sizeof (int));
int* p3 = (int*)realloc(p2, sizeof(int)*10);
// 这里需要free(p2)吗?
free(p3 );
}【面试题分享】
malloc/calloc/realloc的区别?
C++内存管理方式
C语言内存管理方式在C++当中可以继续使用,但是有些地方就无能为力而且使用起来比较繁琐,因此C++又提出了自己的内存管理方式:通过new和delete操作符来进行动态内存管理。
new/delete操作内置类型
void Test()
{
// 动态申请一个int类型的空间
int* ptr4 = new int;
// 动态申请一个int类型的空间并初始化为10
int* ptr5 = new int(10);
// 动态申请10个int类型的空间
int* ptr6 = new int[10];
delete ptr4;
delete ptr5;
delete[] ptr6;
}
【注意】申请和释放单个元素的空间,使用new和delete操作符,申请和释放连续的空间,使用new[]和delete[]。
new和delete操作自定义类型
class Test
{
public:
Test()
: _data(0)
{
cout<<"Test():"<<this<<endl;
}
~Test()
{
cout<<"~Test():"<<this<<endl;
}
private:
int _data;
};
void Test2()
{
// 申请单个Test类型的空间
Test* p1 = (Test*)malloc(sizeof(Test));
free(p1);
// 申请10个Test类型的空间
Test* p2 = (Test*)malloc(sizoef(Test) * 10);
free(p2);
}
void Test2()
{
// 申请单个Test类型的对象
Test* p1 = new Test;
delete p1;
// 申请10个Test类型的对象
Test* p2 = new Test[10];
delete[] p2;
}【注意】
在申请自定义类型的空间时,new会调用构造函数,delete会调用析构函数,而malloc和free不会。
operator new与operator delete函数(重要)
operator new与operator delete函数(重点)
new和delete是用户进行动态内存申请和释放的操作符,operator new 和operator delete是系统提供的全局函数,new在底层调用operator new全局函数来申请空间,delete在底层通过operator delete全局函数来释放空间。
/*
operator new:该函数实际通过malloc来申请空间,当malloc申请空间成功时直接返回;申请空间失败,
尝试执行空 间不足







 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








