首先,我们得清楚,为什么要对网络进行优化?这是基于什么样的场景下才需要考虑到的工作。
其次,需要知道,网络优化具体应该怎么做。
模型优化的目的:为了解决深度学习中的容易遇到的 过拟合、梯度爆炸、梯度消失,三类问题,提出的解决办法。
一、过拟合(overfitting)
模型在训练集上的表现非常好,但是在测试集上的表现很差。通常是由于网络的参数量太大而任务本身难度太小、数据量小,导致模型相对比任务本身来说,太过于聪明,出现模型过度学习到非目标特征本身的特征,使模型输入 x 和模型权重 w 产生了线性相关性,从而导致了过拟合的出现。
解决模型过拟合的办法①:模型搭建时中加入Dropout
通过使部分模型权重失活的方式,来减少模型的参数量,以此防止过拟合的出现,需要对任务难度评估和对应的模型参数搭配非常熟悉。
使用 demo如下,可以看见在0.5的权重失活下,有0.5范围左右的输出变为了0,且失活目标位是随机的。
import torch
from torch import nn
x = torch.randn(1,1,2,10)
dropout = nn.Dropout(0.5)
out = dropout(x)
print(out)
第一次运行 输出:
tensor([[[[ 0.0000, -1.1751, -1.0928, -0.6260, 0.0000, -0.0000, -0.0000,
-0.0000, 0.0000, -0.0000],
[-0.0000, 2.9594, -2.7653, -0.0000, -2.6314, 0.0000, -0.0000,
-0.0000, -3.9002, -0.0000]]]])
第二次运行 输出:
tensor([[[[ 1.2695, -2.5052, 0.0000, -0.0000, -1.9676, 0.0000, 0.0483,
-0.0000, 4.4935, -2.6391],
[ 0.0000, -0.0000, 4.3747, -4.0744, 0.5882, 0.0000, 0.0000,
-0.0000, -0.5639, 0.3098]]]])
可以看见,两次输出的结果失活目标存在变化,证实了Drpout的失活目标是根据失活范围随机选定的。
模型搭建中如何使用Droputout, 下面提供DNN和CNN的demo:
import torch
from torch import nn
class DnnNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.Linear_layers = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(784, 512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Linear(512, 256),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(256, 10),
nn.Dropout(0.5)
)
def forward(self, x):
h = self.Linear_layers(x)
return h
class CnnNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.conv2d_layers = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 3, 3),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout2d(0.5),
nn.Conv2d(3, 3, 3),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout2d(0.5),
nn.Conv2d(3, 3, 3),
nn.Dropout2d(0.5)
)
def forward(self, x):
h = self.conv2d_layers(x)
return h
if __name__ == '__main__':
x1 = torch.randn(1, 28*28)
net = DnnNet()
y1 = net(x1)
print("y1.shape: ", y1.shape)
print("y1: ", y1)
x2 = torch.randn(1, 3, 10, 10)
net = CnnNet()
y2 = net(x2)
print("y2.shape: ", y2.shape)
print("y2: ", y2)
注意:卷积使用的是:nn.Dropout2d() 而全连接使用的是: nn.Dropout()
输出结果如下:
y1.shape: torch.Size([1, 3, 10])
y1: tensor([[[ 0.0000, 0.1649, -0.0000, -0.0653, -0.0000, -0.0000, 0.0000,
-0.0000, 0.0709, 0.0000],
[ 0.0000, 0.0000, -0.1149, 0.0885, 0.0980, -0.0000, 0.0000,
-0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000],
[ 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, -0.0494, 0.2310, -0.0000, 0.0000,
-0.4139, -0.4306, 0.3792]]], grad_fn=<MulBackward0>)
y2.shape: torch.Size([1, 3, 4, 4])
y2: tensor([[[[-0.3224, -0.3224, -0.3224, -0.3224],
[-0.3224, -0.3224, -0.3224, -0.3224],
[-0.3224, -0.3224, -0.3224, -0.3224],
[-0.3224, -0.3224, -0.3224, -0.3224]],
[[ 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000],
[ 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000],
[ 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000],
[ 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000]],
[[ 0.1046, 0.1046, 0.1046, 0.1046],
[ 0.1046, 0.1046, 0.1046, 0.1046],
[ 0.1046, 0.1046, 0.1046, 0.1046],
[ 0.1046, 0.1046, 0.1046, 0.1046]]]], grad_fn=<MulBackward0>)
解决模型过拟合的办法②:正则化
L1正则化:会直接把数据压到0上, 更多用在模型的稀疏化处理,模型过于复杂,需要减小时使用。
L2正则化:L2正则化可以将数据限制到无限接近0的位置,但是并不会等于0
总结:如果是为了防止过拟合,就用L2,希望把W变小,减弱模型的学习能力就行了,但是不希望变成0,变成0,会导致模型的退化,Relu激活函数的缺陷就是,会把结果变为0.
如何给模型添加正则化?在模型的优化器中已经加入了正则化参数,如下:
from torchvision import models
import torch
m = models.inception_v3()
opt = torch.optim.Adam(m.parameters(), weight_decay=0.2)
print("torch.optim.Adam(weight_decay=0.2): ", opt)
默认使用L2正则化,默认给了一个值是0,可以给0-1之间的值 ,而在0 - 1之间的原因是:
1. 数值稳定性:过大的 weight_decay 值可能会导致数值不稳定或权重过快减小,从而影响模型训练的效果。小的 weight_decay 值能够平滑地调整权重,避免剧烈的权重变化。
2. 正则化效果:weight_decay 值过大可能会过度惩罚权重,使得模型的表达能力降低,导致欠拟合。适中的 weight_decay 值能够有效地防止过拟合,同时又不会过多地限制模型的表达能力。
3. 常见实践:在实践中,weight_decay 通常被设为一个较小的值(例如 0.0001 到 0.01),这已经证明在许多任务中能够有效地改善模型性能。
注意:测试模型的时候,一定要加net.eval()
二、梯度爆炸
链式法则:两个函数组合起来的复合函数,导数等于里面函数代入外函数值的导乘以里面函数之导数。
由于链式法则在计算梯度时的影响,在神经网络的层数较多时,意味着连乘越多,因此很容易导致其中某一个比较大的值在连乘过程中被快速放大,导致模型出现了梯度爆炸,也就是超出了计算机所能支持的最大计算精度。
解决梯度爆炸的办法:
BatchNomal:批归一化
在模型中加入BatchNomal的作用:
1.计算时压力就不会太大,就不容易精度溢出。
2.用sigmold举例,如果数据做了归一化在激活的时候,数据很容易落在梯度比较大的区间,增大学习梯度。
3.我们希望模型的输入、w、输出的h,都能在 -1 - 1之间,这样自始至终,计算都不会太大或太小,有利于计算机计算,且网络也会学的又快又好。
4.凸显数据的差异性,提升特征提取能力,加速学习。
5.可以解决梯度爆炸,梯度爆炸:是由于梯度过大导致的,为了保证不容易出现梯度消失和梯度爆炸,首先就是把梯度限定到某个范围之间,这个范围就是-1 - 1之间。因为把每一层的特征都抑制在了-1 - 1之间,权重初始化的时候也被限制在一定范围内,x和w都被限制到类似于做了归一化的分布中,得到的结果h就不会大,反向求导的梯度就不会大。因为BachNomal是把大的分布抑制在-1 - 1之间,有可能会出0,因此就会出现梯度消失,因此,BachNomal不会解决梯度消失。全连接或者卷积,推荐每一层网络都加上BachNomal。
注意:如果加了BachNomal,最好将网络中的bias设置为False,因为BachNomal中带了滑动系数,如果网络再进行偏移,有可能偏移会过大了。
模型设计中使用BatchNomal的demo如下:
import torch
from torch import nn
class DnnNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.Linear_layers = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(784, 512),
nn.BatchNorm1d(512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Linear(512, 256),
nn.BatchNorm1d(256),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(256, 10),
nn.BatchNorm1d(10),
nn.Dropout(0.5)
)
def forward(self, x):
h = self.Linear_layers(x)
return h
class CnnNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.conv2d_layers = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 16, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(16),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout2d(0.5),
nn.Conv2d(16, 32, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(32),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout2d(0.5),
nn.Conv2d(32, 64, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout2d(0.5)
)
def forward(self, x):
h = self.conv2d_layers(x)
return h
if __name__ == '__main__':
x1 = torch.randn(3, 784)
net = DnnNet()
y1 = net(x1)
print("y1.shape: ", y1.shape)
print("y1: ", y1)
x2 = torch.randn(1, 3, 10, 10)
net = CnnNet()
y2 = net(x2)
print("y2.shape: ", y2.shape)
print("y2: ", y2)
三、梯度消失
链式法则:两个函数组合起来的复合函数,导数等于里面函数代入外函数值的导乘以里面函数之导数。
由于链式法则在计算梯度时的影响,在神经网络的层数较多时,意味着连乘越多,因此很容易导致其中某一个比较小的值在连乘过程中被快速缩小,直至变为0,从而导致模型出现了梯度爆炸,也就是超出了计算机所能支持的最小计算精度。
抑制梯度消失的方法:
1.从激活函数角度出发,不要用sigold和tanh, 用ReLU和PReLU也可以延缓
2.模型中加BachNomal一定程度上也可以抑制梯度消失,因为缩小的没有那么快了
解决梯度爆炸的办法:
只有给模型加残差,将链式法则由原本的连乘变为连加,确保权重不会等于0.
残差网络:
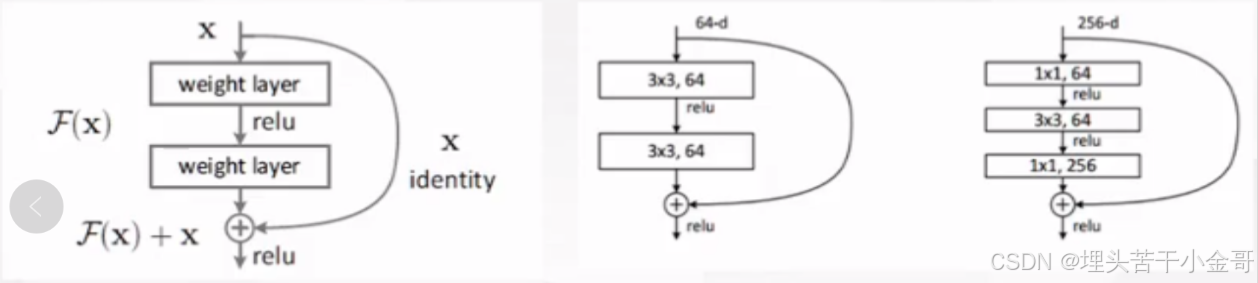
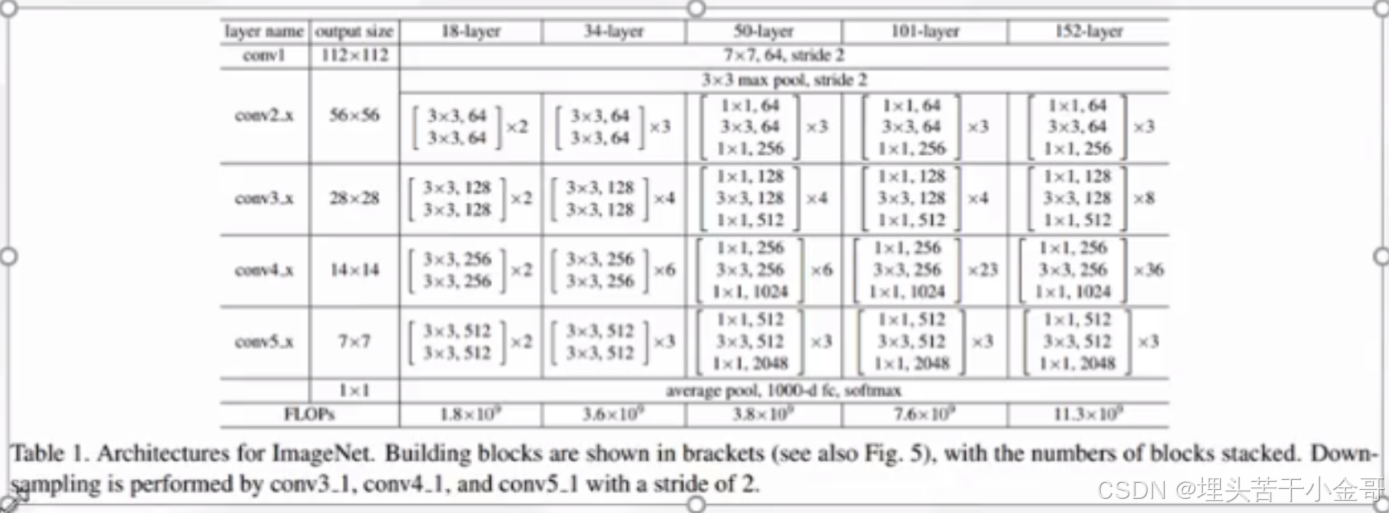 resnet18复现代码
resnet18复现代码
import torch
from torch import nn
class ResBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_c):
super().__init__()
self.layers = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_c, in_c, 3, 1, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(in_c),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(in_c, in_c, 3, 1, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(in_c)
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.layers(x) + x
class down_sample(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_c):
super().__init__()
self.layers = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_c, 2 * in_c, 3, 2, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(2 * in_c),
nn.ReLU()
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.layers(x)
class resNet18(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(3, 2, 1)
)
self.hidden_layer = nn.Sequential(
ResBlock(64),
ResBlock(64),
down_sample(64),
ResBlock(128),
ResBlock(128),
down_sample(128),
ResBlock(256),
ResBlock(256),
down_sample(256),
ResBlock(512),
ResBlock(512)
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.hidden_layer(self.conv1(x))
if __name__ == '__main__':
net = resNet18()
x = torch.randn(1,3,224, 224)
y = net(x)
print(y.shape)
resnet34复现代码:
from torch import nn
import torch
class ResBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_c):
super().__init__()
self.layer = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_c, in_c, 3, 1, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(in_c),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(in_c, in_c, 3, 1, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(in_c)
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.layer(x) + x
class down_sample(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_c):
super().__init__()
self.layer = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_c, 2 * in_c, 3, 2, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(2 * in_c),
nn.ReLU()
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.layer(x)
class resNet34(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 64, 7, 2, padding=3, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.hidden_layer = nn.Sequential(
ResBlock(64),
ResBlock(64),
ResBlock(64),
down_sample(64),
ResBlock(128),
ResBlock(128),
ResBlock(128),
ResBlock(128),
down_sample(128),
ResBlock(256),
ResBlock(256),
ResBlock(256),
ResBlock(256),
ResBlock(256),
ResBlock(256),
down_sample(256),
ResBlock(512),
ResBlock(512),
ResBlock(512),
)
def forward(self, x):
print(self.conv1(x).shape)
return self.hidden_layer(self.conv1(x))
if __name__ == '__main__':
net = resNet34()
x = torch.randn(1,3,228,228)
y = net(x)
print(y.shape)
总结:基于以上,结合Dropout 、 BatchNomal 、 残差三种方式,就可以完美的避免模型搭建经常遇到的三类问题,过拟合、梯度爆炸、梯度消失。
网络优化技巧:
1*1 和 3*3 的卷积对比:
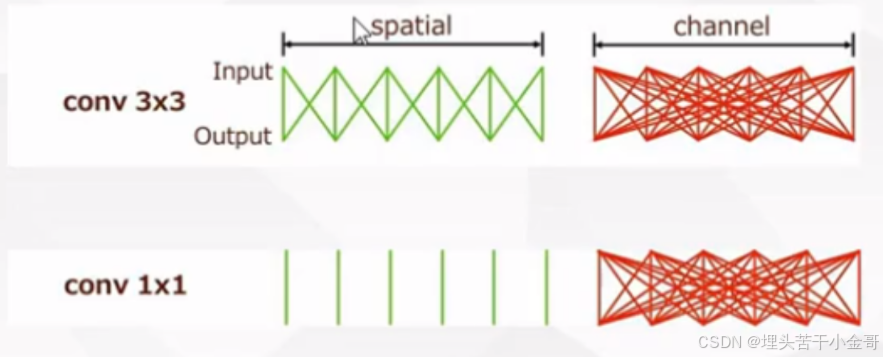
可以发现,1*1的卷积并不会做像素融合
分离卷积:
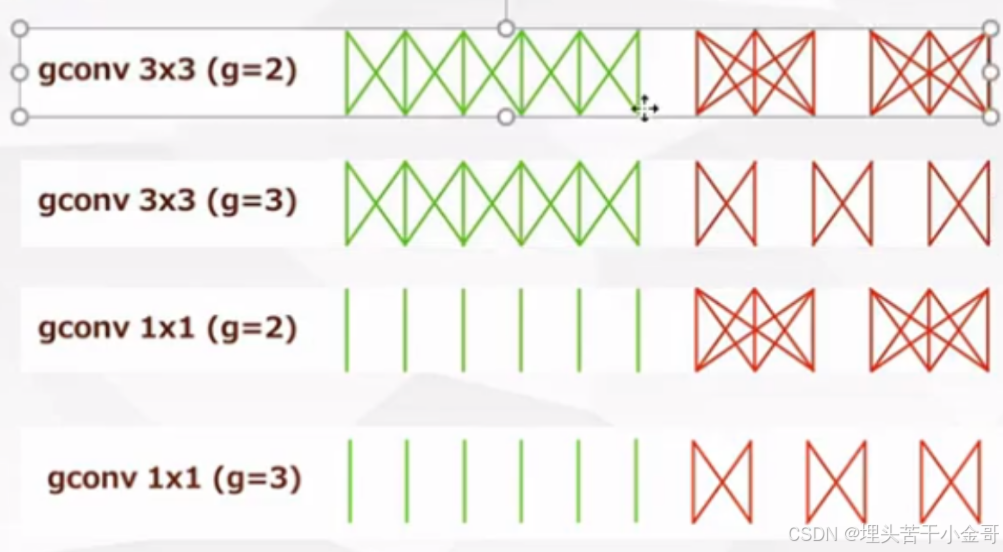
分离卷积的前提:
1.组数需要能被输入和输出通道整除
2.卷积至少要保证存在通道融合,否则通道完全分离,拿到的特征是十分片面的。
深度可分离卷积:输入通道,输出通道,分组,都一样
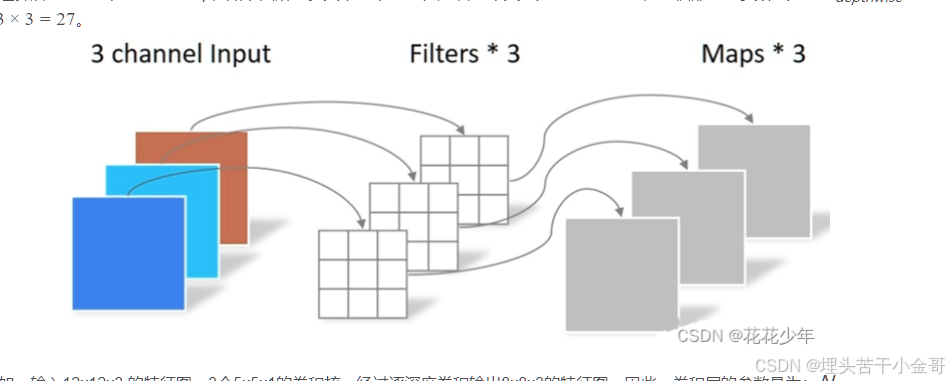
通道混洗:
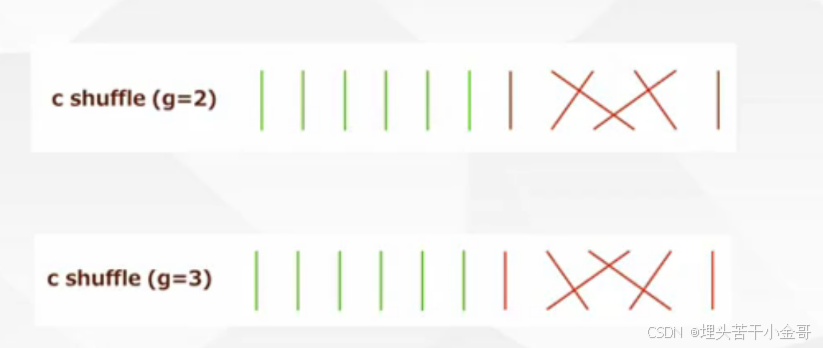
1.将通道转为深度可分离卷积,输入通道、输出通道、组数完全 一 一 对应
2.交叉的方法:①神经网络 ②reshape,一般第二种比较多,因为1*1的卷积也会有一个学习的过程,而通道混洗,只是为了改变位置,而不是特征本身,因此,reshape更合适。
高效的网络模块:
ResNet瓶颈结构: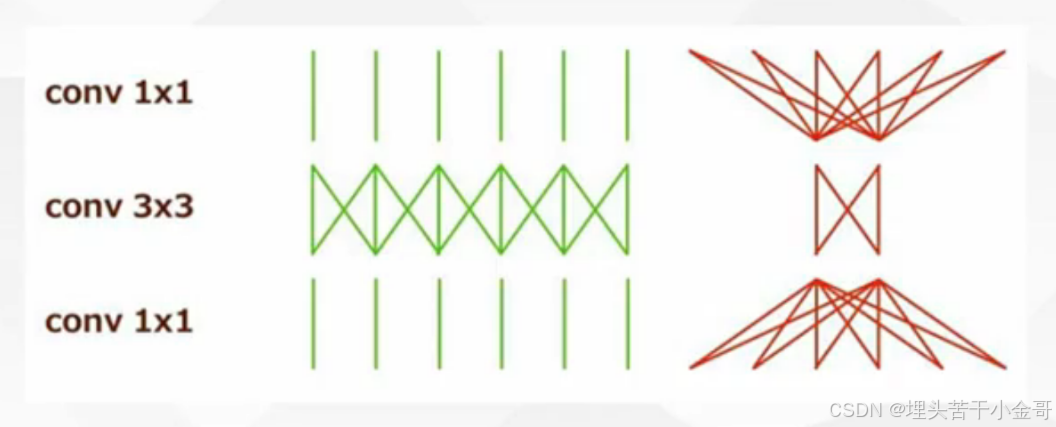
MobilenetV1: 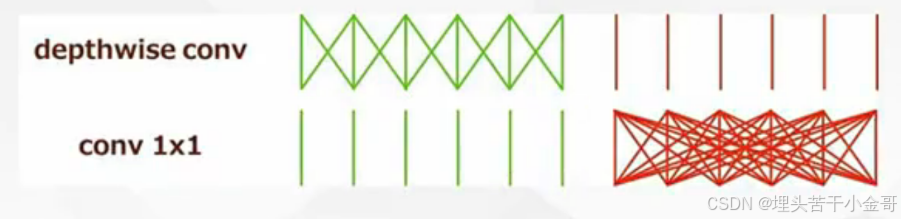
MobilenetV2:
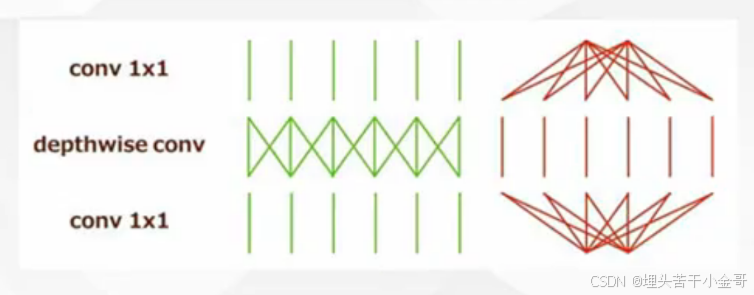
ShuffleNet:
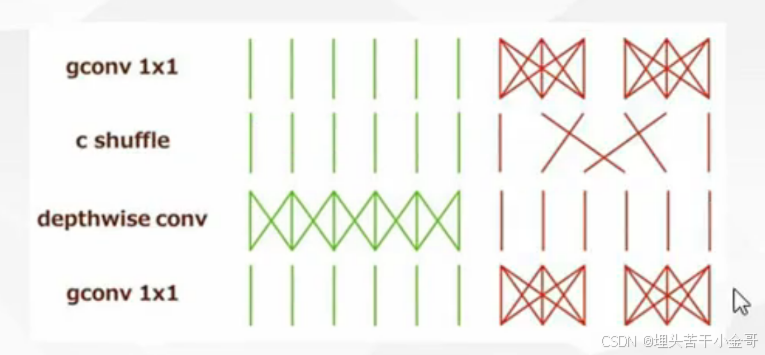
下面附上MobilenetV2的复现代码:
import torch
from torch import nn
config = [
[-1, 32, 1, 2],
[1, 16, 1, 1],
[6, 24, 2, 2],
[6, 32, 3, 2],
[6, 64, 4, 2],
[6, 96, 3, 1],
[6, 160, 3, 2],
[6, 320, 1, 1]
]
class Block(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, p_c, i, t, c, n, s): # i代表当前第几个block
super().__init__()
# 每个重复的最后一次负责下采样
# 所以i = n-1 的时候进行操作
self.i = i
self.n = n
_s = s if i == n-1 else 1 # 判断是否是最后一次重复的步长,是最后一次重复的步长为2
# 判断是否是最后一次重复,最后一次重复负责通道变换为下一层的输入
_c = c if i == n-1 else p_c
_p_c = p_c * t # 输入通道扩增倍数
self.layer = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(p_c, _p_c, 1, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(_p_c),
nn.ReLU6(),
nn.Conv2d(_p_c, _p_c, 3, _s, padding=1, groups=_p_c, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(_p_c),
nn.ReLU6(),
nn.Conv2d(_p_c, _c, 1, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(_c)
)
def forward(self, x):
if self.i == self.n-1:
return self.layer(x)
else:
return self.layer(x) + x
class MobilenetV2(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
super().__init__()
self.input_layer = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 32, 3, 2, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(32),
nn.ReLU6()
)
self.blocks = []
p_c = config[0][1]
for t, c, n, s in config[1:]:
for i in range(n):
self.blocks.append(Block(p_c, i, t, c, n, s))
p_c = c
self.hidden_layer = nn.Sequential(*self.blocks)
self.output_layer = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(320, 1280, 1, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(1280),
nn.ReLU6(),
nn.AvgPool2d(7, 1),
nn.Conv2d(1280, 10, 1, 1, bias=False)
)
def forward(self, x):
h = self.input_layer(x)
print(h.shape)
h = self.hidden_layer(h)
print(h.shape)
h = self.output_layer(h)
h = h.reshape(-1, 10)
return h
if __name__ == '__main__':
net = MobilenetV2(config)
x = torch.randn(1,3, 224, 224)
y = net(x)
print(y.shape)
还差使用复现的MobileNet网络实现小项目的训练、测试代码,后面抽空补上~





















 1572
1572

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










