经过日日夜夜的代码改进,现已完善了网络爬虫之爬取ts分片视频并批量合并的代码,只不过这次的代码和之前写的文章里的代码不同。它以一集为单位进行爬取,以下就是改进版代码的工作原理和讲解。
还是和以前一样,首先是代码展示,代码如下所示:
#spider.py
import os
import random
import threading
import time
import requests
from multiprocessing import Queue,Process
headers = {'Accept': '*/*',
'Accept-Encoding': 'identity',
'Accept-Language': 'zh-CN,zh;q=0.9,en;q=0.8,en-GB;q=0.7,en-US;q=0.6',
'Origin': 'https://www.XXXXX.com/',
'Referer': 'https://www.XXXXX.com/',
'Sec-Ch-Ua': '"Not.A/Brand";v="8", "Chromium";v="114", "Microsoft Edge";v="114"',
'Sec-Ch-Ua-Mobile': '?0',
'Sec-Ch-Ua-Platform': '"Windows"',
'Sec-Fetch-Dest': 'empty',
'Sec-Fetch-Mode': 'cors',
'Sec-Fetch-Site': 'cross-site',
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/114.0.0.0 Safari/537.36 Edg/114.0.1823.43'}
class video_msg:
def __init__(self, file_url, no, path):
self.__no__ = no
self.__file_url__ = file_url
self.__pa__ = path
if not str(path) in os.listdir():
os.mkdir(str(path))
def get_no(self):
return self.__no__
def get_file_url(self):
return self.__file_url__
def get_path(self):
return self.__pa__
def files_objective(path):
import re
file_lists = []
url_msg = open(f'{path}.txt', 'r')
urls = url_msg.read()
url_msg.close()
base_url = re.findall(r"https[A-Za-z0-9/:.]{0,80}", urls)
for i in range(1,len(base_url)+1,1):
file_lists.append(video_msg(file_url=base_url[i-1],no="%04d"%i,path=path))
print(f"{len(file_lists)}:{path}",end='\n')
return file_lists
class down_thread(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self,no,path,url):
super().__init__()
self.no=no
self.pa=path
self.url=url
def run(self):
super().run()
proxy={'http':'115.218.212.53'}
if not str("%s.ts"%self.no) in os.listdir():
time.sleep(random.randint(1, 5))
response=requests.get(url=self.url,verify=False,proxies=proxy,headers=headers)
if response.status_code==404:
os.system(f"echo 错误文件:{self.pa}.ts,地址:{self.url}>>error.txt")
print(f"当前文件:{self.pa}/{self.no}.ts,地址:{self.url}",end='\n')
with open(f"{self.no}.ts",'wb+')as fe:
fe.write(response.content)
fe.close()
class read_process(Process):
def __init__(self,file_queue,file_nums):
super().__init__()
self.__queue__=file_queue
self.__file_nums__=file_nums
def run(self) -> None:
super().run()
for files in range(1,self.__file_nums__,1):
self.__queue__.put(obj=files_objective(files))
class write_process(Process):
def __init__(self,file_queue):
super().__init__()
self.__queue__ = file_queue
def run(self) -> None:
super().run()
video_msgs=self.__queue__.get()
downs=[]
for sub_video in video_msgs:
downs.append(down_thread(path=sub_video.get_path(),no=sub_video.get_no(),url=sub_video.get_file_url()))
print(f"{sub_video.get_path()}:{sub_video.get_no()}:{sub_video.get_file_url()}")
os.chdir(str(video_msgs[0].get_path()))
for sub_thread in downs:
sub_thread.start()
sub_thread.join()
os.chdir("../")
class divide_process(Process):
def __init__(self,path,begin,end):
super().__init__()
self.__pa__=path
self.__begin__=begin
self.__end__=end
def run(self) -> None:
super().run()
instance=files_objective(self.__pa__)
thread_pool=[]
for counter in range(self.__begin__,self.__end__,1):
thread_pool.append(down_thread(url=instance[counter].get_file_url(),no=instance[counter].get_no(),path=instance[counter].get_path()))
os.chdir(str(instance[0].get_path()))
for sub_thread in thread_pool:
sub_thread.start()
sub_thread.join()
os.chdir("../")
def once(nums):
for i in range(0,int(nums/10)+1,1):
os.system(r"copy /b %03d?.ts %03d.ts"%(i,i))
def twice(nums):
for i in range(0,int(nums/100)+1,1):
os.system(r"copy /b %02d?.ts %02d.ts"%(i,i))
def third(nums):
for i in range(0,int(nums/1000)+1,1):
os.system(r"copy /b %01d?.ts %01d.ts"%(i,i))
def final(no):
os.system(r"copy /b ?.ts %s.ts"%no)
os.system(r"move %s.ts C:\Users\12952\Desktop\fetch"%no)
time.sleep(5)
os.system(r"del *.ts")
class comband_process(Process):
def __init__(self,counts,file_name,file_path):
super().__init__()
self.__nums__=counts
self.__file_name__=file_name
self.__pa__=file_path
def run(self) -> None:
super().run()
os.chdir(str(self.__pa__))
once(self.__nums__)
twice(self.__nums__)
third(self.__nums__)
final(str(self.__file_name__))
os.chdir("../")
def fetch_partition(file_nums):
# 爬取文件部分,也可用于检查文件缺陷(去掉#注释)。
q = Queue(maxsize=file_nums)
read_proc = read_process(file_queue=q,file_nums=file_nums+1)
write_proc = [write_process(file_queue=q) for i in range(0, file_nums, 1)]
read_proc.start()
for sub in write_proc:
sub.start()
q.close()
def assembly_partition(path,divided_nums):
# 集中爬取部分,逻辑上把一个视频分为多个小段进行爬取。path表示目录名,divided_nums表示分割视频数。
process_pool = [divide_process(path=path, begin=int(i * len(files_objective(path=path)) / divided_nums),end=int((i + 1) * len(files_objective(path=path)) / divided_nums)) for i in range(0, divided_nums, 1)]
for sub_process in process_pool:
sub_process.start()
def data_partition(video_nums):
# 数据处理部分,把爬取得到的碎片文件进行合并。
process_pool = []
for i in range(1, video_nums+1, 1):
os.chdir(str(i))
nums = len(os.listdir())
print(f"{i}:{nums}", end='\n')
process_pool.append(comband_process(counts=nums, file_name=str(i), file_path=str(i)))
os.chdir("../")
for sub_process in process_pool:
sub_process.start()
if __name__=='__main__':
#fetch_partition(file_nums=48)
#assembly_partition(path=48,divided_nums=100)
data_partition(48)
其次是代码工作原理的讲解,和之前的文章工作的原理差不多,只不过多了目录的操作以及使用了进程通信机制之一:消息队列。就好比是消费者与生产者问题,我在这里设置了一个生产者进程(read_process)和多个消费者进程(write_process),消费者进程的数目与爬取的集数有关。生产者进程负责向队列中添加某一集的视频信息(也就是大约1000多个ts视频文件的编号,爬取地址等等),消费者进程负责取出队列中的某一集信息并交给多个线程进行爬取。每个消费者进程对应着一部剧的某一集。因此就存在了操作系统的目录操作,即先生成某一集对应编号的文件夹,再向该文件夹里批量下载分片视频并在控制台上显示正在下载的文件,最后返回父目录。最后阶段的视频合成部分也是用到了多进程进行合成。假如一部剧有48集,那么最后阶段的合成部分将会开启大约100个进程,一半进程是python程序的合成进程(comband_process),另一半为每个合成进程调用的Windows命令处理程序(批处理命令如copy、move等)。我把爬取数据的几个部分分别写成了函数调用的形式方便进行操作。
最后展示一下代码工作的目录吧!目录结构如下:
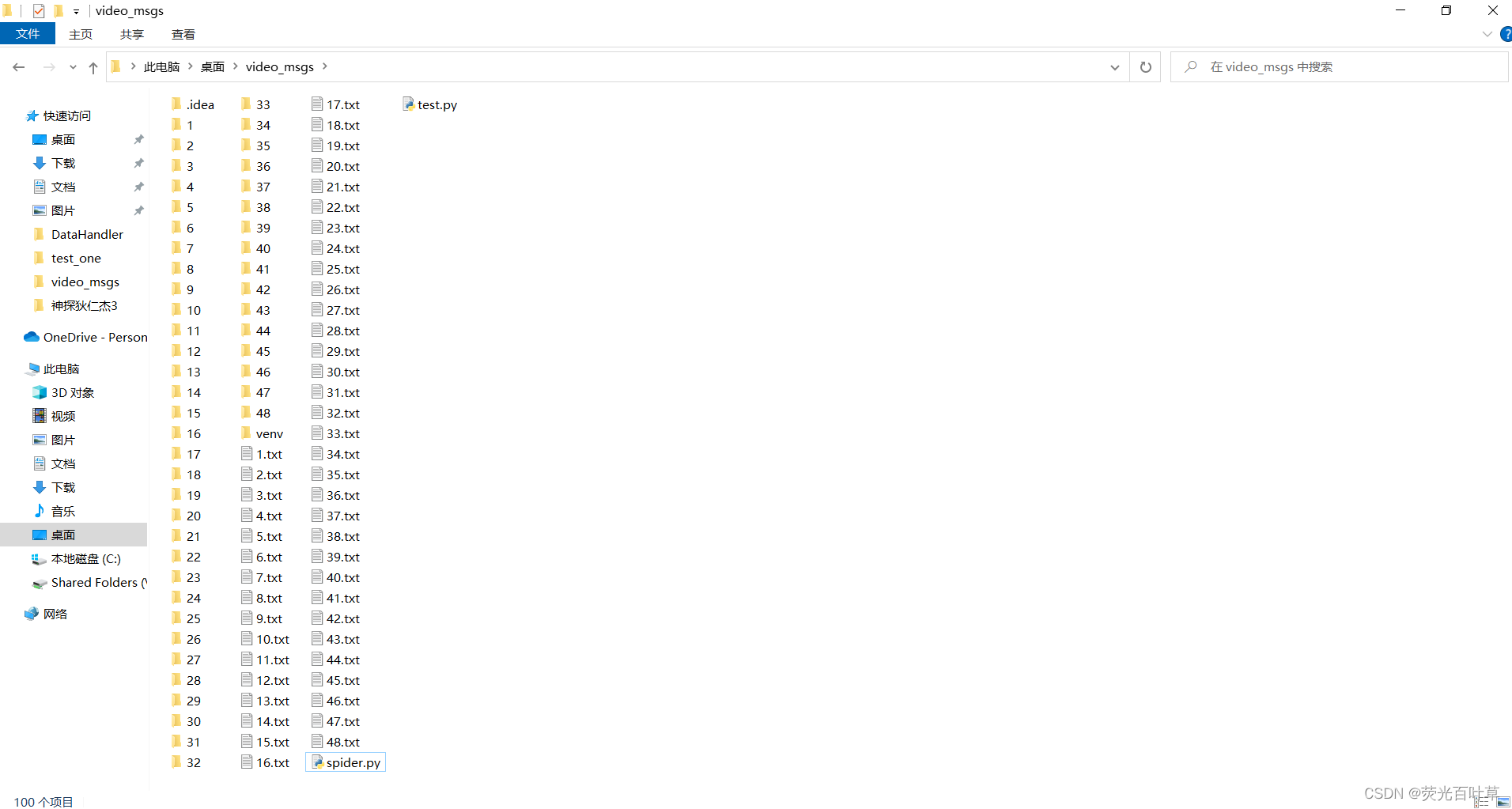
其中带有编号的文件夹是一部剧对应编号的集编号(如文件夹44表示第44集),带有编号的文本文件是从m3u8里获取的ts文件信息。





















 4065
4065

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










