1.9字符串常量池
1.9.1 创建对象的思考
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "hello";
String s2 = "hello";
String s3 = new String("hello");
String s4 = new String("hello");
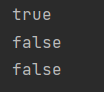
System.out.println(s1 == s2);
System.out.println(s1 == s3);
System.out.println(s3 == s4);
}输出:
常量池的由来:在Java中,类似于1,2,3,3.14,"hello"等字面类型的常量经常被使用,为了是程序的运行速度更快、更节省内存,Java为八种基本数据类型和String都提供了常量池。
1.9.2 字符串常量池(StringTable)
不同jdk版本下字符串常量池的位置是不同的
1.9.3 再谈String对象创建
//1.直接用字符串常量进行赋值
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "hello";
String s2 = "hello";
System.out.println(s1 == s2);
}图层解析(简图):

s2创建时,现在字符串常量池中找“hello”,找到了,返回赋值给s1,并没有创建一个新的对象;
//2.用new创建String对象
//使用new创建的对象,都是唯一的!!!简图:

由上可得:使用常量串创建的String对象的效率更高也更省空间.
intern方法:native方法,作用为手动将创建的String对象添加到常量池中.
代码示例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] ch = new char[]{'a','b','c'};
String s = new String(ch); //此时的s对象并不在常量池中
s.intern(); //加了intern()后便存在常量池中
String s1 = "abc"; //由于常量池中已经存在abc了,此时并不会开辟新的空间,而是s1直接引用abc
System.out.println(s == s1); //true 若注释s.intern(),则为false
}1.10 字符串的不可变性
String类的字符实际保存在内部维护的value字符数组中
String类被final修饰,不可被继承
所有涉及到修改字符串内容的操作修改的都是新对象:如replace
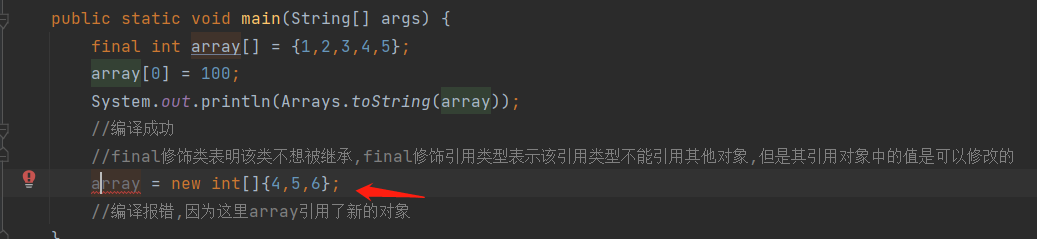
1.11 字符串修改
注:避免直接对String对象进行修改,String无法修改,只会产生一个新的对象,效率低;
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "hello";
s += "world";
System.out.println(s);
}
//尽量避免直接对String进行修改,而是通过StringBuilder和StringBuffer2. StringBuilder 和StringBuffer
2.1 StringBuilder
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuilder sb1 = new StringBuilder("hello");
StringBuilder sb2 = sb1;
sb1.append("world");
System.out.println(sb1); //helloworld
sb1.append(123);
System.out.println(sb1); //helloworld123
System.out.println(sb1 == sb2); //true
System.out.println(sb1.charAt(0)); //h
System.out.println(sb1.length()); //
System.out.println(sb1.capacity()); //获取底层数组的总大小
sb1.setCharAt(0,'H'); //Helloworld123
sb1.insert(0,666); //666Helloworld123
System.out.println(sb1);
sb1.deleteCharAt(0); //删除首字符 66Helloworld123
System.out.println(sb1);
sb1.delete(0,7); //删除[0,7)的字符 world123
System.out.println(sb1);
String str = sb1.substring(0,5); //截取[0,5)
System.out.println(str); //world
sb1.reverse(); //321dlrow
System.out.println(sb1);
str = sb1.toString(); //321dlrow
System.out.println(str);
}String和StringBuilder最大的区别在于StringBuilder的内容可以修改,而String的内容无法修改.
注:String和StringBuilder之间要相互转化:
String转变为StringBuilder:利用StringBuilder的构造方法或者append()方法
StringBuilder转变为String:调用toString()方法
2.1.1 String StringBuilder StringBuffer三者之间的区别
String的内容无可修改,另外两个可以修改
StringBuilder和StringBuffer的大部分功能是相同的
StringBuffer采用同步处理,是线程安全操作,而StringBuilder不安全







 文章讨论了Java中的字符串常量池,解释了如何通过直接赋值或`new`关键字创建`String`对象,指出常量池对提升效率和节省内存的作用。`intern()`方法用于将字符串手动加入常量池。同时,文章强调了`String`的不可变性以及推荐使用`StringBuilder`或`StringBuffer`进行字符串修改,因为它们在性能上更优,特别是在多线程环境下。
文章讨论了Java中的字符串常量池,解释了如何通过直接赋值或`new`关键字创建`String`对象,指出常量池对提升效率和节省内存的作用。`intern()`方法用于将字符串手动加入常量池。同时,文章强调了`String`的不可变性以及推荐使用`StringBuilder`或`StringBuffer`进行字符串修改,因为它们在性能上更优,特别是在多线程环境下。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








