什么是异步
异步(Asynchronous)是指在进行多任务处理时,各个任务的执行不依赖于其他任务的完成,无需等待一个操作完成后再开始下一个操作。与之相对的是同步(Synchronous),同步操作需要按顺序执行,每个步骤必须等待前一个步骤完成才能开始。
异步处理的优点包括但不限于:
提高效率:允许程序在等待某个慢操作(如I/O操作)完成的同时,继续执行其他任务,提高了系统的整体响应速度和吞吐量。
增强用户体验:在用户界面(UI)编程中,异步处理能防止界面冻结,保持应用的响应性。
解耦:通过事件驱动或消息队列的方式,异步处理有助于解耦系统组件,使它们可以独立地开发、部署和扩展。
可扩展性:对于大规模分布式系统,异步通信机制能够更容易地水平扩展,以应对高并发场景。
实现异步编程的技术和框架有很多,根据不同的应用场景和技术栈选择合适的方法,例如:
回调函数:是最基础的异步处理方式,通过传入一个函数作为参数,在异步操作完成时调用该函数。
Promise/Promise链(JavaScript中)或Future(Java中):提供了更加优雅的异步编程模型,可以链式调用来组织异步操作。
async/await(现代编程语言中广泛支持):进一步简化异步代码,使得异步代码看起来更像是同步代码,提高可读性和可维护性。
消息队列和事件总线:用于解耦系统组件,通过发布-订阅模式或命令模式处理异步消息。
线程池和并发库:如Java的Executor框架,用于管理线程资源,执行异步任务。
选择合适的异步处理策略,可以显著提升软件系统的性能和用户体验。
初始化线程的 4 种方式:
继承Thread
实现Runnable
实现Callable接口+FutureTask(可以拿到返回结果,可以处理异常)
线程池
创建“com.atguigu.gulimall.search.thread.ThreadTest”类,代码如下:
1、继承 Thread 类: 这是最简单的方式之一。你可以创建一个类,继承自 Thread 类,并重写它的 run() 方法来定义线程要执行的任务。然后通过创建该类的实例并调用 start() 方法来启动线程。
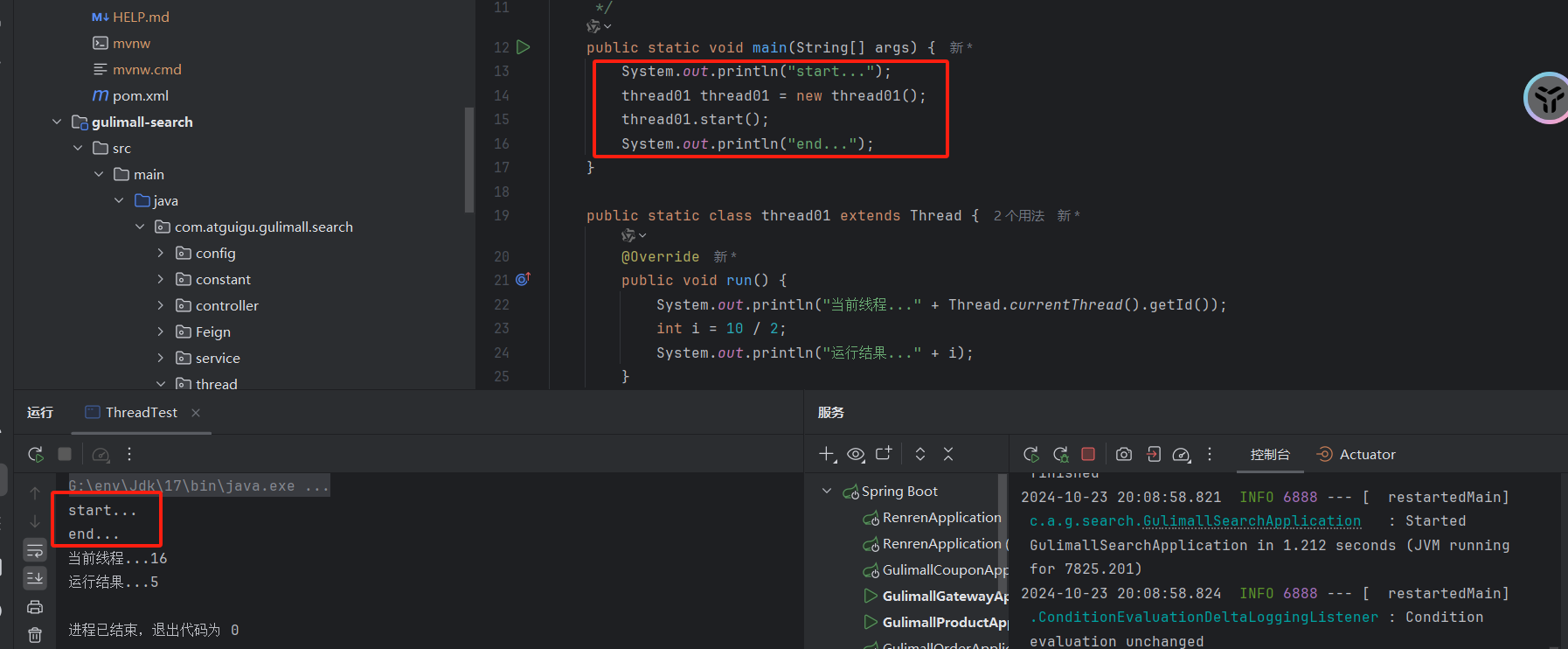
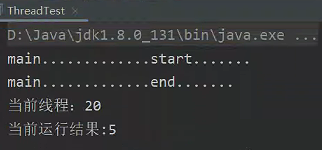
2、实现 Runnable 接口: 这种方式更加灵活,因为 Java 是单继承的,如果你的类已经继承了其他类,你仍然可以实现 Runnable 接口来实现多线程。
然后你可以通过创建 Thread 实例,传入 Runnable 对象来启动线程:
package com.atguigu.gulimall.search.thread;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class ThreadTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("main.............start.......");
// 2、实现Runnable
Runnable01 runnable01 = new Runnable01();
new Thread(runnable01).start();
System.out.println("main.............end.......");
}
public static class Runnable01 implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("当前线程:"+Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10/2;
System.out.println("当前运行结果:" + i);
}
}
}
结果
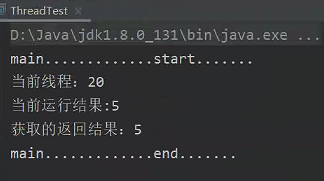
3、实现 Callable 接口 + FutureTask: Callable 接口允许线程返回结果,并且可以抛出异常。结合 FutureTask 可以异步获取线程执行结果。
使用 FutureTask 来获取线程执行结果:
package com.atguigu.gulimall.search.thread;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class ThreadTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException{
System.out.println("main.............start.......");
// 3、实现Callable接口+FutureTask
FutureTask<Integer> futureTask = new FutureTask<>(new Callable01());
new Thread(futureTask).start();
// 阻塞等待整个线程执行完成,获取返回结果
Integer integer = futureTask.get();
System.out.println("获取的返回结果:" + integer);
System.out.println("main.............end.......");
}
public static class Callable01 implements Callable<Integer>{
@Override
public Integer call() {
System.out.println("当前线程:"+Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10/2;
System.out.println("当前运行结果:" + i);
return i;
}
}结果
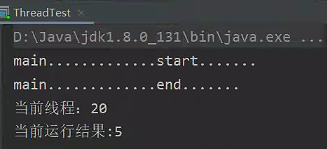
4、线程池: 使用线程池可以管理和复用线程,避免频繁地创建和销毁线程,提高了资源利用率。
// 当前系统中池只有一个,每个异步任务,提交给线程池让他自己去执行就行
package com.atguigu.gulimall.search.thread;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class ThreadTest {
// 方式一:初始化一个线程池
// public static ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
// 方式二:初始化一个线程池
public static ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
5,
200,
10,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(100000),
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("main.............start.......");
// 4、线程池
executor.execute(new Runnable01());
System.out.println("main.............end.......");
}
public static class Runnable01 implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("当前线程:"+Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10/2;
System.out.println("当前运行结果:" + i);
}
}
}结果
总结:
我们以后再业务代码里面,以上三种启动线程的方式都不用。将所有的多线程异步任务都交给线程池执行。
分析:
方式1 和 方式2:主进程无法获取线程的运算结果,不适合当前场景。
方式3:主进程可以获取线程的运算结果,但是不利于控制服务器中的线程资源。可以导致服务器资源耗尽。
方式4:可以控制资源,性能稳定。max
通过如下两种方式初始化线程池
Executors.newFiexedThreadPool(3);
//或者
new ThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, workQueue, threadFactory, handler);
通过线程池性能稳定,也可以获取执行结果,并捕获异常。但是,在业务复杂情况下,一个异步调用可能会依赖于另一个异步调用的执行结果。
1、线程池
1.1、七大参数
1.corePoolSize[5]:核心线程数[一直存在,除非(allowCoreThreadTimeOut)];线程池,创建好以后就准备就绪的线程数量,就等待接收异步任务去执行5个 Thread thread = new Thread(); thread.start();
2.maximumPoolSize[200]:最大线程数量;控制资源。
3.keepAlive Time:存活时间。如果当前正在运行的线程数量大于core数量,释放空闲的线程(maximumPoolSize-corePoolSize)。只要线程空闲大于指定的keepAliveTime。
4.unit:时间单位。
5.BlockingQueue workQueue:阻塞队列。如果任务有很多。就会将多的任务放在队列里面,只要有线程空闲,就会去队列里面取出新的任务继续执行。
6.ThreadFactory:线程创建的工厂。
7.RejectedExecutionHandler handler:如果队列满了,按照我们指定的拒绝策略,拒绝执行。
1.2、运行流程
1.线程池创建,准备好 core 数量的核心线程,准备接受任务。
2.新的任务进来,用 core 准备好的空闲线程执行。
2.1core 满了,就将再进来的任务放入阻塞队列中。空闲的 core 就会自己去阻塞队 列获取任务执行。
2.2阻塞队列满了,就直接开新线程执行,最大只能开到 max 指定的数量。
2.3max 都执行好了。Max-core 数量空闲的线程会在 keepAliveTime 指定的时间后自动销毁。最终保持到 core 大小。
2.4如果线程数开到了 max 的数量,还有新任务进来,就会使用 reject 指定的拒绝策 略进行处理。
3. 所有的线程创建都是由指定的 factory 创建的。
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
5,
200,
10,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(100000),
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());面试:
问题:一个线程池 core 7 ; max 20 , queue : 50 , 100 并发进来怎么分配的;
答案:先有 7 个能直接得到执行,接下来 50 个进入队列排队,在多开 13 个继续执行。现在 70 个 被安排上了。剩下 30 个默认拒绝策略。
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy()); 如果不想抛弃还要执行。CallerRunsPolicy;
1.3、常见的4种线程池
newCachedThreadPool :创建一个可缓存的线程池,如果线程池长度超过处理需要,可灵活回收空闲线程,若无可回收,则新建线程。 core=0,都可回收。
newFixedThreadPool:创建一个定长线程池,可控制线程最大并发数,超出的线程会在对垒中等待。core=max,都不可回收。
newScheduledThreadPool:创建一个定长线程池。支持定势及周期性人去执行,定时任务。
newSingleThreadExecutor:创建一个单线程化的线程池,他只会用唯一的工作线程来执行任务,保证所有任务。
Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
Executors.newFixedThreadPool();
Executors.newScheduledThreadPool();
Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();1.4、使用线程池的好处
1.降低资源的消耗
通过重复利用已经创建好的线程降低线程的创建和销毁带来的损耗 .
2.提高响应速度
因为线程池中的线程数没有超过线程池的最大上限时,有的线程处于等待分配任务的状态,当任务来时无需创建新的线程就能执行。
3.提高线程的可管理性
线程池会根据当前系统特点对池内的线程进行优化处理,减少创建和销毁线程带来的系统开销。无限的创建和销毁线程不仅消耗系统资源,还降低系统的稳定性,使用线程池进行统一分配。
2、CompletableFuture组合式异步编程
业务场景:
查询商品详情页的逻辑比较复杂,有些数据还需要远程调用,必然需要花费更多的时间。
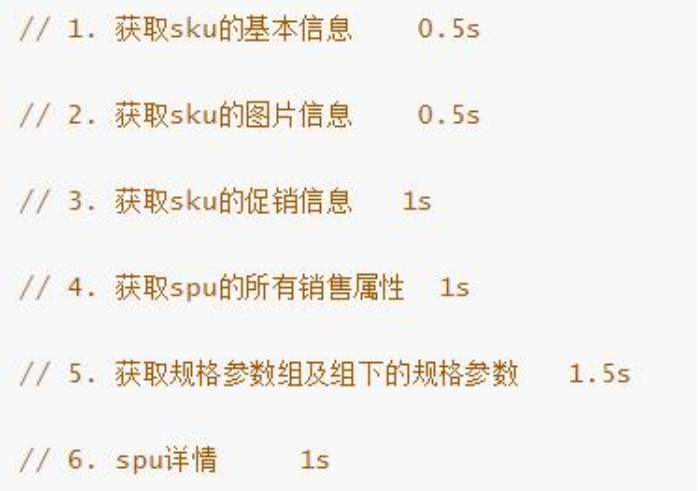
假如商品详情页的每个查询,需要如下标注的时间才能完成
那么,用户需要 5.5s 后才能看到商品详情页的内容。很显然是不能接受的。
如果有多个线程同时完成这 6 步操作,也许只需要 1.5s 即可完成响应。
2.1、创建异步对象
1)、runAsync 和 supplyAsync方法
CompletableFuture 提供了四个静态方法来创建一个异步操作。
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable)
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor)
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier)
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor)没有指定Executor的方法会使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool() 作为它的线程池执行异步代码。如果指定线程池,则使用指定的线程池运行。以下所有的方法都类同。
runXxxx 都是没有返回结果的,
supplyXxx 都是可以获取返回结果的
可以传入自定义的线程池,否则就用默认的线程池
创建“com.atguigu.gulimall.search.thread.CompletableFutureTest” 类,代码如下:
package com.atguigu.gulimall.search.thread;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
/**
* @Description: CompletableFutureTest
* @Author: wts
* @Date: 2024/5/13 13:50
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class CompletableFutureTest {
// 初始化一个线程池
public static ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
5,
200,
10,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(100000),
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
System.out.println("main.............start.......");
// 无返回值
CompletableFuture<Void> runAsyncFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("runAsync当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 2;
System.out.println("runAsync当前运行结果:" + i);
}, executor);
// 有返回值
CompletableFuture<Integer> supplyAsyncFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("supplyAsync当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 2;
System.out.println("supplyAsync当前运行结果:" + i);
return i;
}, executor);
Integer integer = supplyAsyncFuture.get();
System.out.println("supplyAsync获取当前运行结果:" + integer);
System.out.println("main.............end.......");
}
}结果
2.2、计算结果完成时的回调方法
当CompletableFuture的计算结果完成,或者抛出异常的时候,可以执行特定的Action。主要是下面的方法:
public CompletableFuture<T> whenComplete(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action)
public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action)
public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action, Executor executor)
public CompletableFuture<T> exceptionally(Function<Throwable,? extends T> fn)whenComplete 可以处理正常和异常的计算结果, exceptionally 处理异常情况。
whenComplete 和 whenCompleteAsync 的区别:
whenComplete:是执行当前任务的线程执行继续执行 whenComplete 的任务。 whenCompleteAsync:是执行把 whenCompleteAsync 这个任务继续提交给线程池来进行执行。
方法不以 Async 结尾,意味着 Action 使用相同的线程执行,而 Async 可能会使用其他线程 执行(如果是使用相同的线程池,也可能会被同一个线程选中执行)
可以看到Action的类型是BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable>它可以处理正常的计算结果,或者异常情况。
package com.atguigu.gulimall.search.thread;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class CompletableFutureTest {
// 方式二:初始化一个线程池
public static ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
5,
200,
10,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(100000),
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
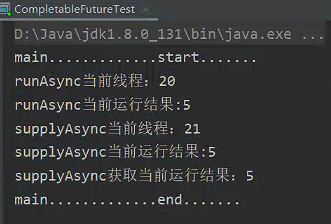
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
System.out.println("main.............start.......");
/**
* 方法成功完成后的感知
*/
CompletableFuture<Integer> supplyAsyncFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("supplyAsync当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 2;
System.out.println("supplyAsync当前运行结果:" + i);
return i;
}, executor).whenComplete((result, exception) -> {
// 虽然能得到异常信息,但是没法修改返回数据
System.out.println("异步任务完成了...结果是" + result + ";异常是" + exception);
// 可以感知异常,同时返回默认值
}).exceptionally(throwable -> 10);
Integer integer = supplyAsyncFuture.get();
System.out.println("supplyAsync获取当前运行结果:" + integer);
System.out.println("main.............end.......");
}
}结果
2.3、handle 方法
handle 是执行任务完成时对结果的处理。
handle 方法和 thenApply 方法处理方式基本一样。不同的是 handle 是在任务完成后再执行,还可以处理异常的任务。thenApply 只可以执行正常的任务,任务出现异常则不执行 thenApply 方法。
public <U> CompletionStage<U> handle(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn);
public <U> CompletionStage<U> handleAsync(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn);
public <U> CompletionStage<U> handleAsync(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn,Executcomplete 一样,可对结果做最后的处理(可处理异常),可改变返回值。
// 方法执行完成后的处理
CompletableFuture<Integer> handleFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("handleFuture当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 5;
System.out.println("handleFuture当前运行结果:" + i);
return i;
}, executor).handle((result, exception) -> {
if (result != null) {
return result * 2;
}
if (exception != null) {
return 0;
}
return 0;
});结果

2.4、线程串行化
public <U > completableFuture < U > thenApply(Function < ? super T, ? extends U > fn);
public <U > completableFuture < U > thenApplyAsync(Function < ? super T, ? extends U > fn);
public <U > CompletableFuture < U > thenApplyAsync(Function < ? super T, ? extends U > fn, Executor executor);
public completionStage<Void> thenAccept (consumer < ? super T > action);
public Completionstage<Void> thenAcceptAsync (Consumer < ? super T > action);
public Completionstage<Void> thenAcceptAsync (consumer < ? super T > action, Executor executor);
public CompletionStage<Void> thenRun (Runnable action);
public Completionstage<Void> thenRunAsync (Runnable action);
public Completionstage<Void> thenRunAsync (Runnable action, Executor executor);thenApply 方法:当一个线程依赖另一个线程时,获取上一个任务返回的结果,并返回当前任务的返回值。 返回两次
thenAccept 方法:消费处理结果。接收任务的处理结果,并消费处理,无返回结果。 返一次
thenRun 方法:只要上面的任务执行完成,就开始执行 thenRun,只是处理完任务后,执行 thenRun 的后续操作,不能获取上一步的执行结果。
带有 Async 默认是异步执行的。同之前线程公用一个线程。
以上都要前置任务成功完成。
Function<? super T,? extends U>
T:上一个任务返回结果的类型
U:当前任务的返回值类型
/**
* 4、线程串行化
*/
// 4.1、thenApplyAsync能接收上一步的返回结果,也有返回值
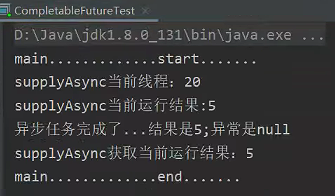
CompletableFuture<String> thenApplyAsync = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("thenApplyAsync当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 5;
System.out.println("thenApplyAsync当前运行结果:" + i);
return i;
}, executor).thenApplyAsync(res -> {
System.out.println("thenApplyAsync任务2启动了。。。。" + res);
return "hello" + res;
}, executor);
String thenApplyAsyncResult = thenApplyAsync.get();
System.out.println("thenApplyAsync返回结果:" + thenApplyAsyncResult);
// 4.2、thenAcceptAsync能接收上一步返回结果,但无返回值
CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptAsync = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("thenAcceptAsync当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 5;
System.out.println("thenAcceptAsync当前运行结果:" + i);
return i;
}, executor).thenAcceptAsync(res -> {
System.out.println("thenAcceptAsync任务2启动了。。。。" + res);
}, executor);
// 4.3、thenRun 不能获取得到上一步的执行结果
CompletableFuture<Void> thenRunAsync = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("thenRunAsync当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 5;
System.out.println("thenRunAsync当前运行结果:" + i);
return i;
}, executor).thenRunAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("thenRunAsync任务2启动了。。。。");
}, executor);结果
2.5、两任务组合-都要完成
两个任务必须都完成,触发该任务。
runAfterBoth
两个future不需要获取 future的结果,只需两个 future处理完任务后, 处理该任务。
public CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterBoth(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action);
public CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterBothAsync(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action);
public CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterBothAsync(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action,Executor thenAcceptBoth
组合两个 future,获取两个 future 任务的返回结果,然后处理任务,没有返回值。
public <U> CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptBoth(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action);
public <U> CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptBothAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action);
public <U> CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptBothAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action, Executor executor);thenCombine
组合两个 future,获取两个 future 的返回结果,并返回当前任务的返回值
public <U,V> CompletableFuture<V> thenCombine(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn);
public <U,V> CompletableFuture<V> thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn);
public <U,V> CompletableFuture<V> thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn,Executor executor); /**
* 5、两任务组合-都要完成
*/
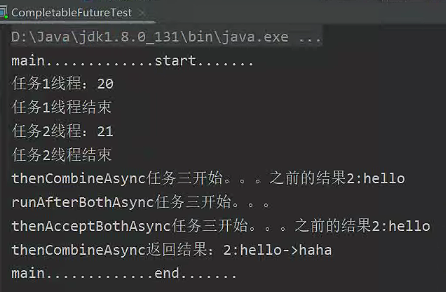
CompletableFuture<Object> future01 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("任务1线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 5;
System.out.println("任务1线程结束");
return i;
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<Object> future02 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("任务2线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("任务2线程结束");
return "hello";
}, executor);
// 5.1、不能得到两个任务的参数,也无返回结果
future01.runAfterBothAsync(future02, () -> {
System.out.println("runAfterBothAsync任务三开始。。。");
}, executor);
// 5.2、能得到两个任务的参数,无返回结果
future01.thenAcceptBothAsync(future02, (f1, f2) -> {
System.out.println("thenAcceptBothAsync任务三开始。。。之前的结果" + f1 + ":" + f2);
}, executor);
// 5.3、能得到两个任务的参数,并返回结果
CompletableFuture<String> thenCombineAsync = future01.thenCombineAsync(future02, (f1, f2) -> {
System.out.println("thenCombineAsync任务三开始。。。之前的结果" + f1 + ":" + f2);
return f1 + ":" + f2 + "->haha";
}, executor);
System.out.println("thenCombineAsync返回结果:" + thenCombineAsync.get());结果
2.6、两任务组合-只要有一个任务完成就执行第三个
当两个任务中,任意一个 future 任务完成的时候,执行任务。
runAfterEither 方法
两个任务有一个执行完成,不需要获取 future 的结果,处理任务,也没有返回值。
public CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterEither(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action);
public CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterEitherAsync(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action);
public CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterEitherAsync(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action,Executor executor);
acceptEither 方法
两个任务有一个执行完成,获取它的返回值,处理任务,没有新的返回值。
public CompletableFuture<Void> acceptEither(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Consumer<? super T> action);
public CompletableFuture<Void> acceptEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Consumer<? super T> action);
public CompletableFuture<Void> acceptEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Consumer<? supeapplyToEither 方法
两个任务有一个执行完成,获取它的返回值,处理任务并有新的返回值。
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> applyToEither(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Function<? super T, U> fn);
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> applyToEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Function<? super T, U> fn);
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> applyToEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Function<? sup /**
* 6、两个任务只要有一个完成,我们就执行任务3
*/
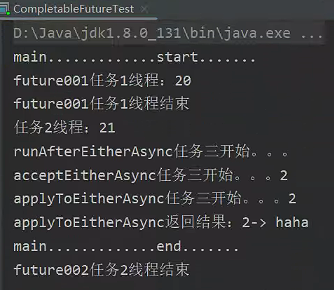
CompletableFuture<Object> future001 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("future001任务1线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 5;
System.out.println("future001任务1线程结束");
return i;
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<Object> future002 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("任务2线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("future002任务2线程结束");
return "hello";
}, executor);
// 6.1、runAfterEitherAsync 不感知结果,自己也无返回值
future001.runAfterEitherAsync(future002, () -> {
System.out.println("runAfterEitherAsync任务三开始。。。");
}, executor);
// 6.2、acceptEitherAsync 感知结果,自己没有返回值
future001.acceptEitherAsync(future002, (res) -> {
System.out.println("acceptEitherAsync任务三开始。。。" + res);
}, executor);
// 6.3、applyToEitherAsync 感知结果,自己没有返回值
CompletableFuture<String> applyToEitherAsync = future001.applyToEitherAsync(future002, (res) -> {
System.out.println("applyToEitherAsync任务三开始。。。" + res);
return res.toString() + "-> haha";
}, executor);
System.out.println("applyToEitherAsync返回结果:" + applyToEitherAsync.get());结果
thenCompose 方法
thenCompose 方法允许你对两个 CompletionStage 进行流水线操作,第一个操作完成时,将其结果作为参数传递给第二个操作。
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenCompose(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn);
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenComposeAsync(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn) ;
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenComposeAsync(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage2.7、多任务组合
public static completableFuture<Void> all0f(completableFuture<?>... cfs);
public static completableFuture<Obiect> anyof(completableFuture<?>... cfs);- allOf:等待所有任务完成
- anyOf:只要有一个任务完成
allOf
/**
* 7、多任务组合
*/
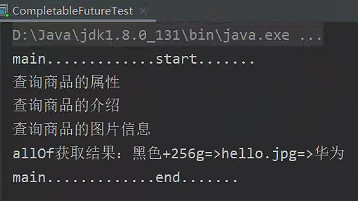
CompletableFuture<String> futureAttr = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("查询商品的属性");
return "黑色+256g";
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<String> futureImg = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println("查询商品的图片信息");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "hello.jpg";
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<String> futureDesc = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("查询商品的介绍");
return "华为";
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<Void> allOf = CompletableFuture.allOf(futureAttr, futureImg, futureDesc);
allOf.get(); //等待所有线程执行完
System.out.println("allOf获取结果:" + futureAttr.get() + "=>" + futureImg.get() + "=>" + futureDesc.get());结果
anyOf
/**
* 7、多任务组合
*/
CompletableFuture<String> futureAttr = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("查询商品的属性");
return "黑色+256g";
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<String> futureImg = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println("查询商品的图片信息");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "hello.jpg";
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<String> futureDesc = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("查询商品的介绍");
return "华为";
}, executor);
// CompletableFuture<Void> allOf = CompletableFuture.allOf(futureAttr, futureImg, futureDesc);
// allOf.get(); //等待所有线程执行完
// System.out.println("allOf获取结果:" + futureAttr.get() + "=>" + futureImg.get() + "=>" + futureDesc.get());
CompletableFuture<Object> anyOf = CompletableFuture.anyOf(futureAttr, futureImg, futureDesc);
anyOf.get();
System.out.println("anyOf获取结果:" + futureAttr.get() + "=>" + futureImg.get() + "=>" + futureDesc.get());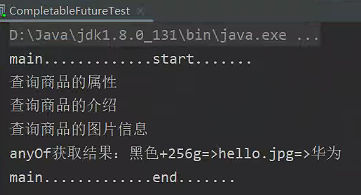
























 4669
4669

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








