Intervals on the Ring

题意
本题的意思是给出我们一个环,相当于一个长度为n的数轴,其中1和n是连在一起的,给我们数轴上的一些区间要求我们构造一些区间,使构造的区间的交集等于给定的区间的并集。
题解
将一个数组划为n个区间

假定给出的是这样的区间,那么我们构造的区间就可以每一个缺少其中的一个空隙,这样我们就交集一定不会含有这些空隙但是却会含有给定的区间
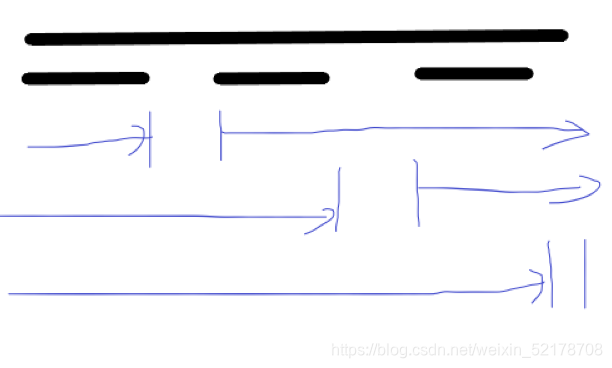
例如这样,所以我们只需要找到区间间的空隙就可以直接输出答案了
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 3010;
struct node {
int l, r;
}a[N];
int m,n;
bool cmp(node x, node y) {
return x.l < y.l;
}
void solve() {
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)cin>>a[i].l>>a[i].r;
sort(a,a+m,cmp);
cout<<m<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)cout<<a[i].l<<" "<<a[(m-1+i)%m].r<<endl;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin.exceptions(ios::badbit | ios::failbit);
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--)solve();
}
Hamburger Steak

题意
给了我们n个蟹黄堡和m口锅,要求我们输出总时间最短的方案,注意的是一个蟹黄堡可以在不同时间放在两口锅里面烤,但是不能用两口锅同时烤,所以困扰我们最久的就是这个怎样切割的问题;
题解
对于题目我们可以发现,我们所能够做到的最短时间就是所有蟹黄堡所需要的时间加起来除以锅的数量所得到的平均值,所以我们的目标应该是尽可能达到平均值,那么对于这个切割问题又要怎么思考呢
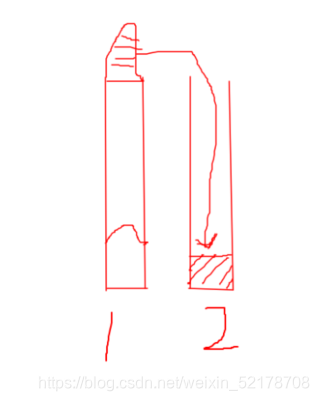
比如我们在第一口锅里面放面包,如果多出来一部分,那么我们就可以将多出来的时间放在第二口锅里面煎如果这个时间小于我们在第一口锅中第一个蟹黄堡所用的时间的话,就可以将多出来的时间放在第二口锅里面煎,这样不会对我们的结果产生影响,而如果放在第二口锅中的时间大于在第一口锅中所用的时间的话,说明这样放是不行的,我们就要把锅的最大时间延长到可以刚好煎完这个蟹黄堡并且不会对第一个蟹黄堡造成影响的时候,将第二口锅中剩下的汉堡和第一口锅中的第一个蟹黄堡对换位置,我们可以发现,我们所用的时间刚好就是这个大的蟹黄堡完全煎完的时间
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
//#define _ 0
//return ~~(0^_^0)~~
const int maxn = 1e5 + 10;
int a[maxn];
void solve() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
int sum = 0;
int maxn = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
sum += a[i];
maxn = max(maxn, a[i]);
}
maxn = max(maxn, (sum + m - 1) / m);
int now = 0;
int k = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (maxn - now > a[i]) {
cout << "1 " << k << " " << now << " ";
now += a[i];
cout << now << endl;
}
else if (maxn - now == a[i]) {
cout << "1 " << k << " " << now << " ";
now = 0;
k++;
cout << maxn << endl;
}
else {
cout << "2 " << k + 1 << " 0 " << a[i] - (maxn - now) << " " << k << " " << now << " " << maxn << endl;
now = a[i] - (maxn - now);
k++;
}
}
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
solve();
}
洛谷深搜补题
八皇后

题解
对行进行dfs 用三个数组分别表示主对角线,副对角线,每一列是否满足
注意主对角线处于是(i+j),副对角线的处于(n+j-i)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n;
const int N=20;
vector<int>a(N);
bool l[N],zdj[N],fdj[N];
vector<vector<int>>b;
void dfs(int d){
if(d==n){
b.push_back(a);
return;
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(l[i]==0&&zdj[d+i]==0&&fdj[n-d+i]==0){
a[d]=i;
l[i]=zdj[i+d]=fdj[i+n-d]=1;
dfs(d+1);
l[i]=zdj[i+d]=fdj[i+n-d]=0;
a[d]=0;
}
}
}
void solve(){
cin>>n;
dfs(0);
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)cout<<(b[i][j]+1)<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
cout<<b.size();
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
solve();
return 0;
}
马的遍历
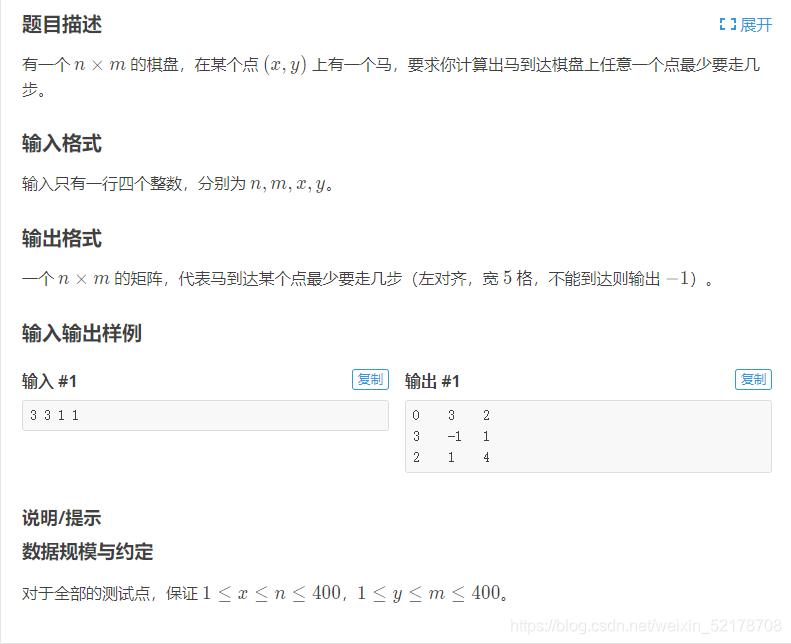
int dx[8] = { -2, -2, -1, -1, 1, 1, 2, 2 };
int dy[8] = { 1, -1, 2, -2, 2, -2, 1, -1 };
用这个来表示马的运动轨迹,如果经历过就标记,最后没有办法走的话就退出
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
//#define _ 0
//return ~~(0^_^0)~~
int n, m, x, y;
const int N = 410;
int g[N][N];
pair<int, int>q[N * N];
void bfs() {
g[x][y] = 0;
int flag = 1;
int tt = 0;
int hh = 0;
q[0] = { x,y };
int dx[8] = { -2, -2, -1, -1, 1, 1, 2, 2 };
int dy[8] = { 1, -1, 2, -2, 2, -2, 1, -1 };
int gta = 0;
while (hh <= tt) {
auto t = q[hh++];
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
int x = t.first + dx[i], y = t.second + dy[i];
if (g[x][y] == -1 && x > 0 && x <= n && y > 0 && y <= m) {
g[x][y] = g[t.first][t.second] + 1;
q[++tt] = { x,y };
}
}
}
}
void solve() {
cin >> n >> m >> x >> y;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)g[i][j] = -1;
}
bfs();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)cout << setw(5) << left << g[i][j];
cout << endl;
}
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
solve();
}
涂色问题
其实我们可以发现,只需要将没有包完的部分填成其他颜色就可以了
那我们可以将nn的矩阵扩大到(n+2)(n+2)的矩阵,外面全是零,用bfs将外面的全部染成一种另外的颜色,遇到最后输出就好了
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
//#define _ 0
//return ~~(0^_^0)~~
const int N = 45;
int g[N][N];
bool a[N][N];
int dx[4] = { 1,-1,0,0 };
int dy[4] = { 0,0,1,-1 };
int ans = 0;
int n;
pair<int, int>p[N * N];
void ss(int u, int v) {
g[u][v] = -1;
p[0] = { u,v };
int hh = 0, tt = 0;
while (hh <= tt) {
auto t = p[hh++];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int x = t.first + dx[i], y = t.second + dy[i];
if (x >= 0 && x <= n+1 && y >= 0 && y <= n+1 && g[x][y] == 0 && a[x][y] == 0) {
p[++tt] = { x,y };
a[x][y] = 1;
g[x][y] = -1;
}
}
}
}
void bfs() {
ss(0, 0);
}
void solve() {
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)cin >> g[i][j];
}
bfs();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (g[i][j] == -1)cout << 0 << " ";
else if (g[i][j] == 1)cout << 1 << " ";
else cout << 2 << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
solve();
}





















 349
349

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








