- 🍨 本文为🔗365天深度学习训练营 中的学习记录博客
- 🍖 原作者:K同学啊
👉 学习目标:
●
学习使用LSTM对糖尿病进行探索预测
●
本文的预测准确率,请尝试将其提升到70%以上(下一周更新我的解决方案)
1数据预处理
1.1设置GPU
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torchvision,torch
# 设置硬件设备,如果有GPU则使用,没有则使用cpu
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
device
1.2数据导入
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['savefig.dpi'] = 500 #图片像素
plt.rcParams['figure.dpi'] = 500 #分辨率
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 用来正常显示中文标签
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
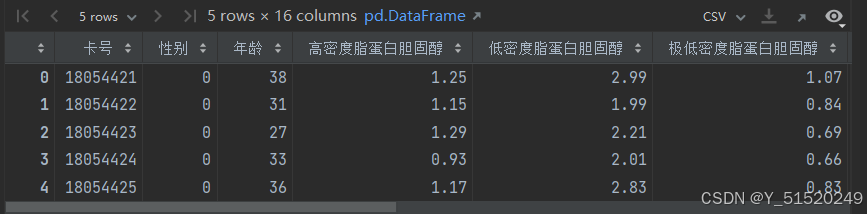
DataFrame=pd.read_excel(r'/home/aiusers/space_yjl/深度学习训练营/进阶/第R6周:LSTM实现糖尿病探索与预测/dia.xls')
DataFrame.head()
DataFrame.shape
1.3数据检查
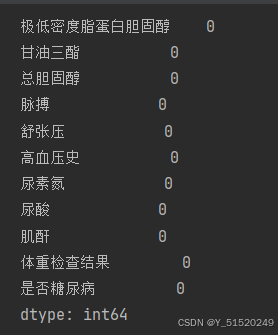
# 查看数据是否有缺失值
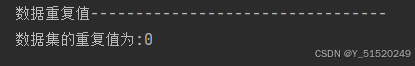
print('数据缺失值---------------------------------')
print(DataFrame.isnull().sum())
# 查看数据是否有重复值
print('数据重复值---------------------------------')
print('数据集的重复值为:'f'{DataFrame.duplicated().sum()}')
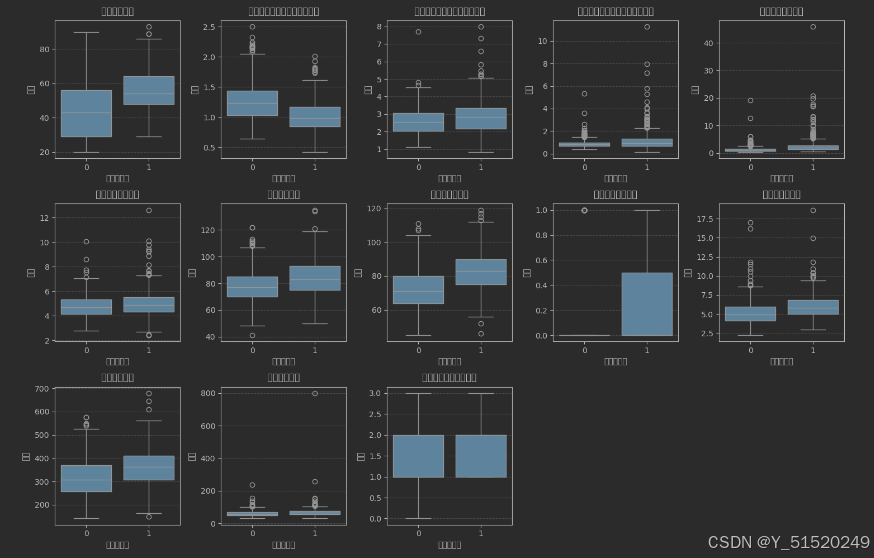
1.4数据分布分析
feature_map = {
'年龄': '年龄',
'高密度脂蛋白胆固醇': '高密度脂蛋白胆固醇',
'低密度脂蛋白胆固醇': '低密度脂蛋白胆固醇',
'极低密度脂蛋白胆固醇': '极低密度脂蛋白胆固醇',
'甘油三酯': '甘油三酯',
'总胆固醇': '总胆固醇',
'脉搏': '脉搏',
'舒张压':'舒张压',
'高血压史':'高血压史',
'尿素氮':'尿素氮',
'尿酸':'尿酸',
'肌酐':'肌酐',
'体重检查结果':'体重检查结果'
}
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 10))
for i, (col, col_name) in enumerate(feature_map.items(), 1):
plt.subplot(3, 5, i)
sns.boxplot(x=DataFrame['是否糖尿病'], y=DataFrame[col])
plt.title(f'{col_name}的箱线图', fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel('数值', fontsize=12)
plt.grid(axis='y', linestyle='--', alpha=0.7)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
这个因为或者环境的问题,导致图片不能正常可视化 后续会补充解决的。
2.LSTM 模型
2.1数据集构建
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
# '高密度脂蛋白胆固醇'字段与糖尿病负相关,故而在 X 中去掉该字段
X = DataFrame.drop(['卡号','是否糖尿病','高密度脂蛋白胆固醇'],axis=1)
y = DataFrame['是否糖尿病']
# sc_X = StandardScaler()
# X = sc_X.fit_transform(X)
X = torch.tensor(np.array(X), dtype=torch.float32)
y = torch.tensor(np.array(y), dtype=torch.int64)
train_X, test_X, train_y, test_y = train_test_split(X, y,
test_size=0.2,
random_state=1)
train_X.shape, train_y.shape

from torch.utils.data import TensorDataset, DataLoader
train_dl = DataLoader(TensorDataset(train_X, train_y),
batch_size=64,
shuffle=False)
test_dl = DataLoader(TensorDataset(test_X, test_y),
batch_size=64,
shuffle=False)
2.2定义模型
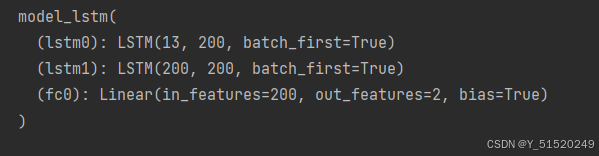
class model_lstm(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(model_lstm, self).__init__()
self.lstm0 = nn.LSTM(input_size=13 ,hidden_size=200,
num_layers=1, batch_first=True)
self.lstm1 = nn.LSTM(input_size=200 ,hidden_size=200,
num_layers=1, batch_first=True)
self.fc0 = nn.Linear(200, 2)
def forward(self, x):
out, hidden1 = self.lstm0(x)
out, _ = self.lstm1(out, hidden1)
out = self.fc0(out)
return out
model = model_lstm().to(device)
model
3.训练模型
3.1定义训练函数
# 训练循环
def train(dataloader, model, loss_fn, optimizer):
size = len(dataloader.dataset) # 训练集的大小
num_batches = len(dataloader) # 批次数目, (size/batch_size,向上取整)
train_loss, train_acc = 0, 0 # 初始化训练损失和正确率
for X, y in dataloader: # 获取图片及其标签
X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
# 计算预测误差
pred = model(X) # 网络输出
loss = loss_fn(pred, y) # 计算网络输出和真实值之间的差距,targets为真实值,计算二者差值即为损失
# 反向传播
optimizer.zero_grad() # grad属性归零
loss.backward() # 反向传播
optimizer.step() # 每一步自动更新
# 记录acc与loss
train_acc += (pred.argmax(1) == y).type(torch.float).sum().item()
train_loss += loss.item()
train_acc /= size
train_loss /= num_batches
return train_acc, train_loss
3.2定义测试函数
def test (dataloader, model, loss_fn):
size = len(dataloader.dataset) # 测试集的大小
num_batches = len(dataloader) # 批次数目, (size/batch_size,向上取整)
test_loss, test_acc = 0, 0
# 当不进行训练时,停止梯度更新,节省计算内存消耗
with torch.no_grad():
for imgs, target in dataloader:
imgs, target = imgs.to(device), target.to(device)
# 计算loss
target_pred = model(imgs)
loss = loss_fn(target_pred, target)
test_loss += loss.item()
test_acc += (target_pred.argmax(1) == target).type(torch.float).sum().item()
test_acc /= size
test_loss /= num_batches
return test_acc, test_loss
3.3训练模型
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # 创建损失函数
learn_rate = 1e-4 # 学习率
opt = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(),lr=learn_rate)
epochs = 30
train_loss = []
train_acc = []
test_loss = []
test_acc = []
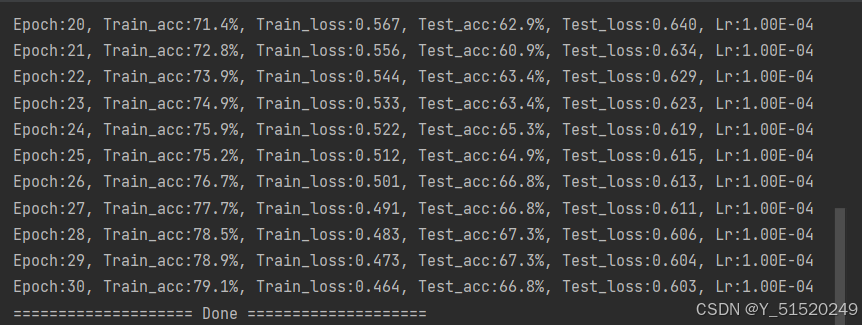
for epoch in range(epochs):
model.train()
epoch_train_acc, epoch_train_loss = train(train_dl, model, loss_fn, opt)
model.eval()
epoch_test_acc, epoch_test_loss = test(test_dl, model, loss_fn)
train_acc.append(epoch_train_acc)
train_loss.append(epoch_train_loss)
test_acc.append(epoch_test_acc)
test_loss.append(epoch_test_loss)
# 获取当前的学习率
lr = opt.state_dict()['param_groups'][0]['lr']
template = ('Epoch:{:2d}, Train_acc:{:.1f}%, Train_loss:{:.3f}, Test_acc:{:.1f}%, Test_loss:{:.3f}, Lr:{:.2E}')
print(template.format(epoch+1, epoch_train_acc*100, epoch_train_loss,
epoch_test_acc*100, epoch_test_loss, lr))
print("="*20, 'Done', "="*20)
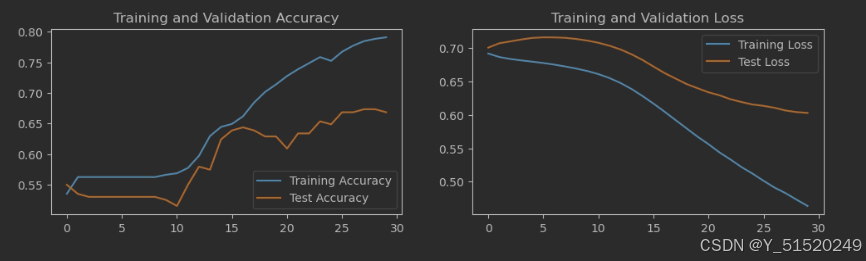
4模型评估
4.1Loss与Accuracy图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#隐藏警告
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore") #忽略警告信息
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 用来正常显示中文标签
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 用来正常显示负号
plt.rcParams['figure.dpi'] = 100 #分辨率
epochs_range = range(epochs)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 3))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(epochs_range, train_acc, label='Training Accuracy')
plt.plot(epochs_range, test_acc, label='Test Accuracy')
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.title('Training and Validation Accuracy')
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(epochs_range, train_loss, label='Training Loss')
plt.plot(epochs_range, test_loss, label='Test Loss')
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.title('Training and Validation Loss')
plt.show()
5.个人总结
通过结合多层 LSTM 网络、残差连接、以及注意力机制(Attention),提高对序列数据的建模能力。
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class EnhancedLSTM(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(EnhancedLSTM, self).__init__()
# 第一层 LSTM
self.lstm0 = nn.LSTM(input_size=13, hidden_size=256,
num_layers=2, batch_first=True, dropout=0.2)
# 第二层 LSTM
self.lstm1 = nn.LSTM(input_size=256, hidden_size=256,
num_layers=2, batch_first=True, dropout=0.2)
# 残差连接的全连接层
self.fc_residual = nn.Linear(13, 256)
# Attention 层
self.attention = nn.Linear(256, 1)
# 最后的全连接层
self.fc0 = nn.Linear(256, 2)
def forward(self, x):
# 残差连接
residual = self.fc_residual(x)
# 第一层 LSTM
out, _ = self.lstm0(x)
# 第二层 LSTM
out, _ = self.lstm1(out)
# 添加残差
out = out + residual
# 确保 out 是三维张量 (batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)
if out.dim() == 2:
out = out.unsqueeze(1) # 增加一个时间步维度 (batch_size, 1, hidden_size)
# 选择最后一个时间步的输出
out = out[:, -1, :] # (batch_size, hidden_size)
# Attention 机制
attn_weights = torch.softmax(self.attention(out.unsqueeze(1)), dim=1)
out = torch.sum(attn_weights * out.unsqueeze(1), dim=1)
# 输出层
out = self.fc0(out)
return out
# 设备选择
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
model = EnhancedLSTM().to(device)
print(model)
关键特点:
多层 LSTM:
通过多层的 LSTM 网络,模型能够更好地捕捉序列中的长程依赖关系。
残差连接:
残差连接有助于缓解深层网络中的梯度消失问题,使得信息在网络中能够更好地传递。
注意力机制:
通过引入注意力机制,模型能够根据输入序列的不同部分赋予不同的权重,从而提升对关键信息的捕捉能力。
灵活的输入处理:
如果 out 的维度被压缩为二维,模型会通过 unsqueeze(1) 将其转换回三维,确保可以处理不同形状的输入。




















 1110
1110

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








