在我自学C++过程中,我选择了C++Primer这本书,并对部分代码习题进行了求解以及运行结果。接下来几个月我将为大家定时按章节更新习题答案与运行结果,运行环境(Visual Studio Code,windows 11):
C++ Primer (第五版)习题答案总目录:
目录
9.1 对于下面的程序任务,vector、deque和list哪种容器最为适合?解释你的选择的理由。如果没有哪一种容器优于其他容器,也请解释理由。
9.2 定义一个list对象,其元素类型是int的deque。
9.4 编写函数,接受一对指向vector的迭代器和一个int值。在两个迭代器指定的范围中查找给定的值,返回一个布尔值来指出是否找到。
9.5 重写上一题的函数,返回一个迭代器指向找到的元素。注意,程序必须处理未找到给定值的情况。
9.7 为了索引 int 的 vector 中的元素,应该使用什么类型?
9.8 为了读取string 的list 中的元素,应该使用什么类型?如果写入list,又应该使用什么类型?
9.11 对6种创建和初始化 vector 对象的方法,每一种都给出一个实例。解释每个vector包含什么值。
9.13 如何从一个list初始化一个vector?从一个vector又该如何创建?编写代码验证你的答案。
9.14 编写程序,将一个list中的char * 指针元素赋值给一个vector中的string。
9.16 重写上一题的程序,比较一个list中的元素和一个vector中的元素。
9.18 编写程序,从标准输入读取string序列,存入一个deque中。编写一个循环,用迭代器打印deque中的元素。
9.19 重写上一题的程序,用list替代deque。列出程序要做出哪些改变。
9.20 编写程序,从一个list拷贝元素到两个deque中。值为偶数的所有元素都拷贝到一个deque中,而奇数值元素都拷贝到另一个deque中。
9.22 假定iv是一个int的vector,下面的程序存在什么错误?你将如何修改?
9.24 编写程序,分别使用 at、下标运算符、front 和 begin 提取一个vector中的第一个元素。在一个vector上测试你的程序。
9.26 使用下面代码定义的ia,将ia 拷贝到一个vector和一个list中。是用单迭代器版本的erase从list中删除奇数元素,从vector中删除偶数元素。
9.27 编写程序,查找并删除forward_list中的奇数元素。
9.31 第316页中删除偶数值元素并复制奇数值元素的程序不能用于list或forward_list。为什么?修改程序,使之也能用于这些类型。
9.33 在本节最后一个例子中,如果不将insert的结果赋予begin,将会发生什么?编写程序,去掉此赋值语句,验证你的答案。
9.37 为什么list或array没有capacity成员函数?
9.41 编写程序,从一个vector初始化一个string。
9.42 假定你希望每次读取一个字符存入一个string中,而且知道最少需要读取100个字符,应该如何提高程序的性能?
9.44 重写上一题的函数,这次使用一个下标和replace。
9.46 重写上一题的函数,这次使用位置和长度来管理string,并只使用insert。
9.50 编写程序处理一个vector,其元素都表示整型值。计算vector中所有元素之和。修改程序,使之计算表示浮点值的string之和。
9.1 对于下面的程序任务,vector、deque和list哪种容器最为适合?解释你的选择的理由。如果没有哪一种容器优于其他容器,也请解释理由。
-
(a) 读取固定数量的单词,将它们按字典序插入到容器中。我们将在下一章中看到,关联容器更适合这个问题。
-
answer:list,因为需要频繁的插入操作。
-
(b) 读取未知数量的单词,总是将单词插入到末尾。删除操作在头部进行。
-
answer:deque,总是在头尾进行插入、删除操作。
-
(c)从一个文件读取未知数量的整数。将这些数排序,然后将它们打印到标准输出。
-
answer:vector,没有特别的需求选vector
9.2 定义一个list对象,其元素类型是int的deque。
list<deque<int>> l;9.4 编写函数,接受一对指向vector的迭代器和一个int值。在两个迭代器指定的范围中查找给定的值,返回一个布尔值来指出是否找到。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
bool FindInt(vector<int>::const_iterator begin1, vector<int>::const_iterator end1, int n)
{
while (begin1 != end1)
{
if (*begin1 == n)
{
return true;
}
++begin1;
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
vector<int> v1 = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 };
cout << FindInt(v1.begin(), v1.end(), 99) << endl;
return 0;
}
9.5 重写上一题的函数,返回一个迭代器指向找到的元素。注意,程序必须处理未找到给定值的情况。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
vector<int>::const_iterator FindInt(vector<int>::const_iterator begin1, vector<int>::const_iterator end1, int n)
{
while (begin1 != end1)
{
if (*begin1 == n)
{
return begin1;
}
++begin1;
}
return begin1;
}
int main()
{
vector<int> v1 = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 };
FindInt(v1.begin(), v1.end(), 99);
return 0;
}9.6 下面的程序有何错误?你应该如何修改它?
list<int> lst1;
list<int>::iterator iter1 = lst1.begin(),
iter2 = lst1.end();
while (iter1 < iter2) /* ... */
list<int> lst1;
list<int>::iterator iter1 = lst1.begin(),
iter2 = lst1.end();
while (iter1 != iter2) /* ... */
9.7 为了索引 int 的 vector 中的元素,应该使用什么类型?
vector<int>::size_type
9.8 为了读取string 的list 中的元素,应该使用什么类型?如果写入list,又应该使用什么类型?
list<string>::const_iterator //read
list<string>::iterator //write
9.10 下面4个对象分别是什么类型?
vector<int> v1;
const vector<int> v2;
auto it1 = v1.begin(), it2 = v2.begin();
auto it3 = v1.cbegin(), it4 = v2.cbegin();
it1:vector<int>::iterator,it2:vector<int>::const_iterator;
it3:vector<int>::const_iterator,it4:vector<int>::const_iterator。
9.11 对6种创建和初始化 vector 对象的方法,每一种都给出一个实例。解释每个vector包含什么值。
vector<int> v1; //v1为空
vector<int> v2 = v1; //v2为空
vector<int> v3(v2); //v3为空
vector<int> v4(10); //10个0
vector<int> v5(10,1); //10个1
vector<int> v6{1,2,3}; //1 2 3
vector<int> v7 = {1,2,3}; //1 2 3
vector<int> v8(v7.begin(),v7.end()); //1 2 3
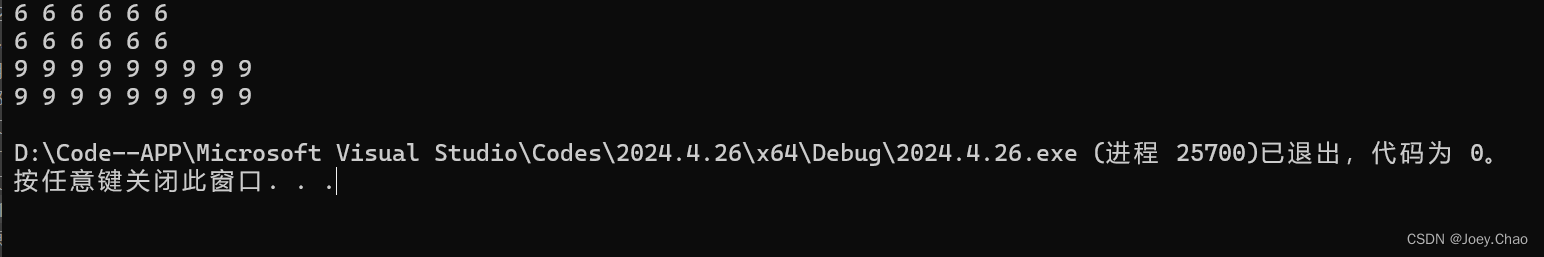
9.13 如何从一个list初始化一个vector?从一个vector又该如何创建?编写代码验证你的答案。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include <sstream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> ilst(6, 6);
vector<int> ivc(9, 9);
vector<double> dvc(ilst.begin(), ilst.end());
for (auto i : ilst)
cout << i << " ";
cout << endl;
for (auto i1 : dvc)
cout << i1 << " ";
cout << endl;
vector<int> dvc1 = ivc;
for (auto i : dvc1)
cout << i << " ";
cout << endl;
for (auto i1 : ivc)
cout << i1 << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
9.14 编写程序,将一个list中的char * 指针元素赋值给一个vector中的string。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include <sstream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char c1[6] = { 'a','a','a','a','a','a' };
char c2[6] = { 'b','b','b','b','b','b' };
char c3[6] = { 'c','c','c','c','c','c' };
list<char*> l = { c1,c2,c3 };
vector<string> v1(l.begin(), l.end());
for (auto s : v1)
cout << s << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;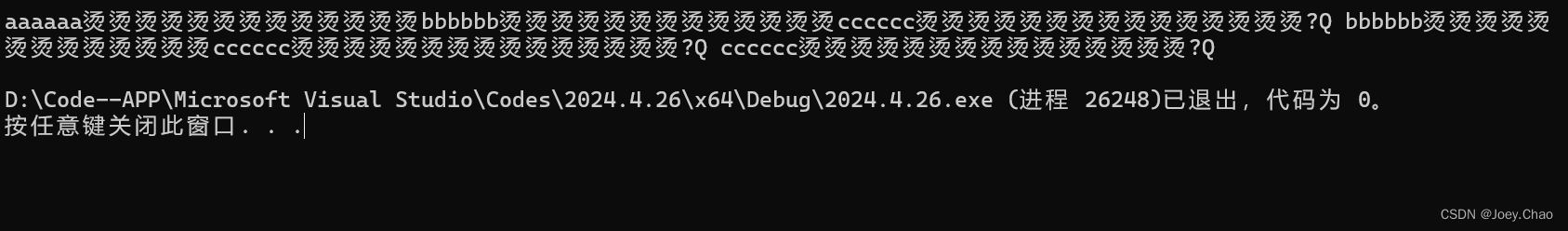
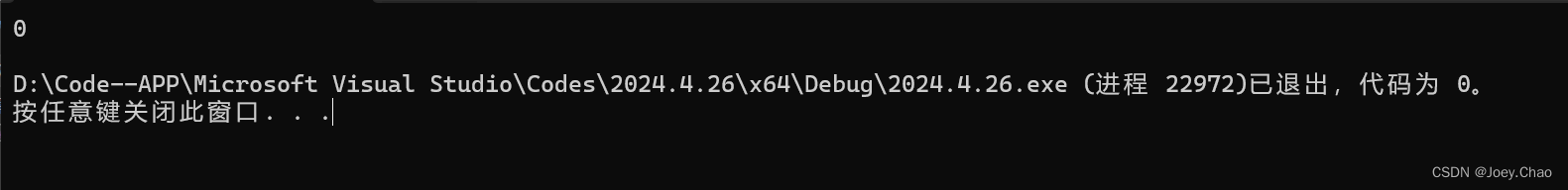
9.15 编写程序,判定两个vector<int>是否相等。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include <sstream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v1 = { 1,2,3,4,5,6 };
vector<int>v2 = { 1,2,6 };
cout << (v1 == v2) << endl;
return 0;
}
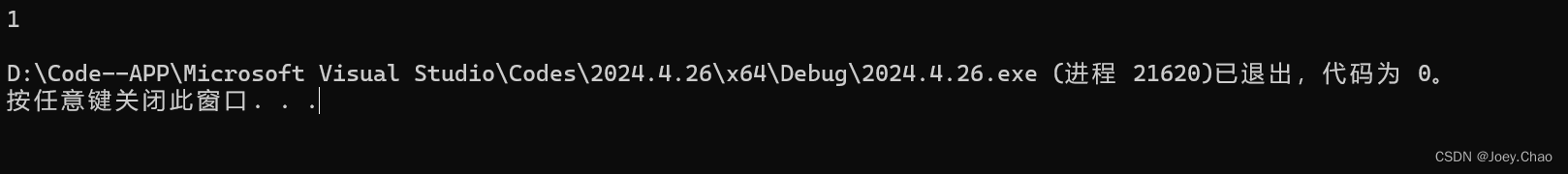
9.16 重写上一题的程序,比较一个list中的元素和一个vector中的元素。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include <sstream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v1 = { 1,2,6 };
list<int> v2 = { 1,2,6 };
cout << (v1 == (vector<int>(v2.begin(),v2.end()))) << endl;
return 0;
}
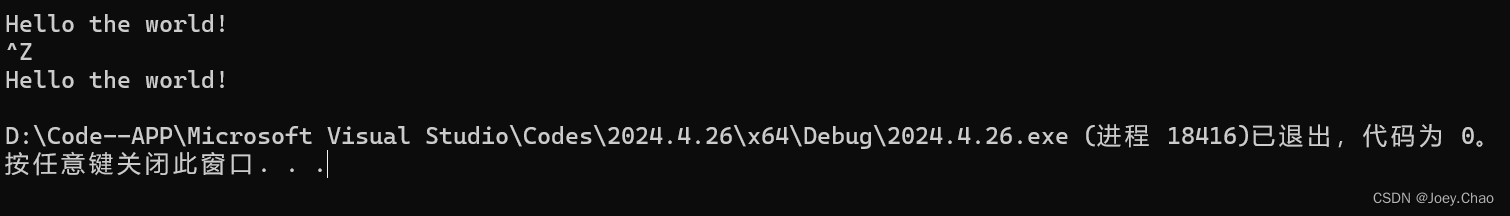
9.18 编写程序,从标准输入读取string序列,存入一个deque中。编写一个循环,用迭代器打印deque中的元素。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include <sstream>
#include <deque>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
deque<string> d1;
while (cin >> s)
{
d1.push_back(s);
}
for (deque<string>::const_iterator it = d1.begin(); it != d1.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
9.19 重写上一题的程序,用list替代deque。列出程序要做出哪些改变。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <deque>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
list<string> d1;
while (cin >> s)
{
d1.push_back(s);
}
for (list<string>::const_iterator it = d1.begin(); it != d1.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
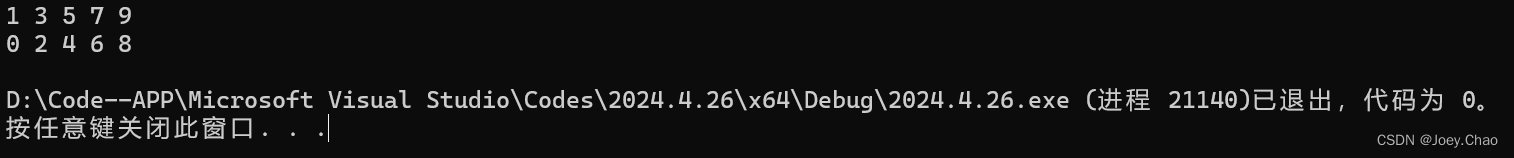
9.20 编写程序,从一个list拷贝元素到两个deque中。值为偶数的所有元素都拷贝到一个deque中,而奇数值元素都拷贝到另一个deque中。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <deque>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> l = { 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 };
deque<int> d_odd, d_even;
for (const auto& i : l)
{
if (i % 2)
{
d_odd.push_back(i);
}
else
{
d_even.push_back(i);
}
}
for (const auto& i1 : d_odd)
{
cout << i1 << " ";
}
cout << endl;
for (const auto& i2 : d_even)
{
cout << i2 << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
9.22 假定iv是一个int的vector,下面的程序存在什么错误?你将如何修改?
vector<int>::iterator iter = iv.begin(),
mid = iv.begin() + iv.size() / 2;
while (iter != mid)
if (*iter == some_val)
iv.insert(iter, 2 * some_val);
1.循环不会停止;
2.迭代器在插入操作后会变化。
while (iter != mid)
{
if (*iter == some_val)
{
iter = v.insert(iter, 2 * some_val);
++iter;
}
++iter;
}
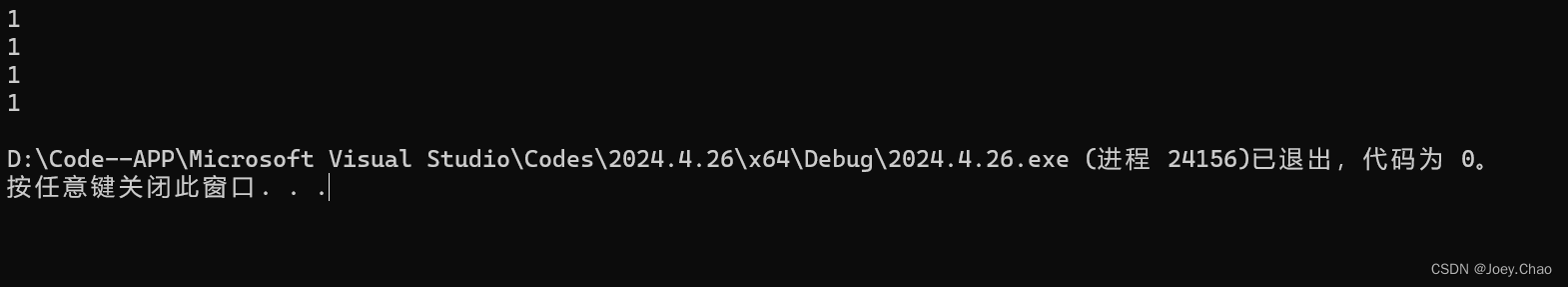
9.24 编写程序,分别使用 at、下标运算符、front 和 begin 提取一个vector中的第一个元素。在一个vector上测试你的程序。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <deque>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v1 = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 };
cout << v1.at(0) << endl;
cout << v1[0] << endl;
cout << v1.front() << endl;
cout << *v1.begin() << endl;
return 0;
}
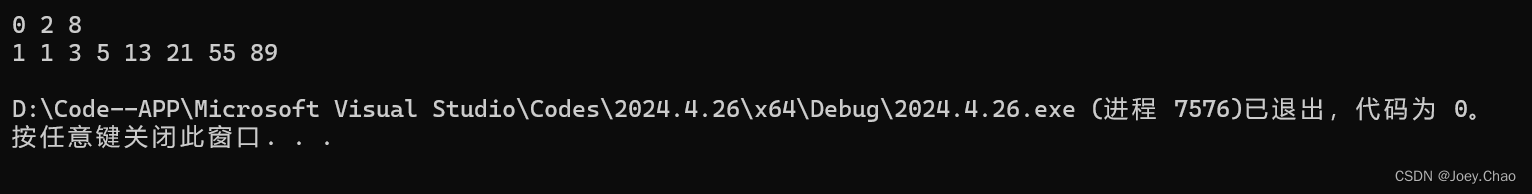
9.26 使用下面代码定义的ia,将ia 拷贝到一个vector和一个list中。是用单迭代器版本的erase从list中删除奇数元素,从vector中删除偶数元素。
int ia[] = { 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 55, 89 };
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <deque>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int ia[] = { 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 55, 89 };
list<int> l(ia, end(ia));
vector<int> v(ia, end(ia));
for (auto i = l.begin(); i != l.end();)
{
if (*i % 2)
{
i = l.erase(i);
}
else
{
i++;
}
}
for (auto i = v.begin(); i != v.end();)
{
if (*i % 2 == 0)
{
i = v.erase(i);
}
else
{
i++;
}
}
for (const auto& i : l)
{
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << endl;
for (const auto& i : v)
{
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
9.27 编写程序,查找并删除forward_list<int>中的奇数元素。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <deque>
#include <forward_list>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
forward_list<int> f = { 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 };
auto prev = f.before_begin();
auto curr = f.begin();
while (curr != f.end())
{
if (*curr % 2)
{
curr = f.erase_after(prev);
}
else
{
prev = curr;
curr++;
}
}
for (const auto& f0 : f)
{
cout << f0 << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
9.28 编写函数,接受一个forward_list和两个string共三个参数。函数应在链表中查找第一个string,并将第二个string插入到紧接着第一个string之后的位置。若第一个string未在链表中,则将第二个string插入到链表末尾。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <deque>
#include <forward_list>
using namespace std;
void insertString(forward_list<string> &f, const string& f1, const string& f2)
{
auto prev = f.before_begin();
auto curr = f.begin();
while (curr != f.end())
{
if (*curr == f1)
{
f.insert_after(curr, f2);
return;
}
else
{
prev = curr;
curr++;
}
}
f.insert_after(curr, f2);
}
int main()
{
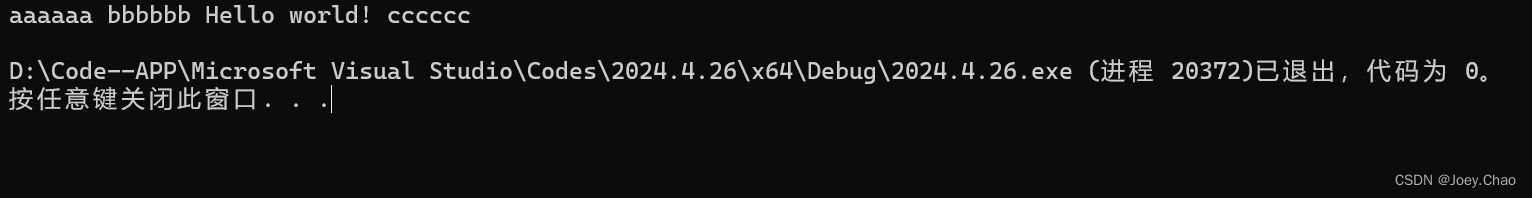
forward_list<string> fs = { "aaaaaa","bbbbbb","cccccc" };
insertString(fs, "bbbbbb", "Hello world!");
for (const auto& s : fs)
{
cout << s << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
9.31 第316页中删除偶数值元素并复制奇数值元素的程序不能用于list或forward_list。为什么?修改程序,使之也能用于这些类型。
不能直接用于list或forward_list,list 和 forward_list 。与其他容器的一个不同是,迭代器不支持加减运算,究其原因,链表中元素并非在内存中连续存储,因此无法通过地址的加减在元素间远距离移动。因此,应多次调用++来实现与迭代器加法相同的效果。
list:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <deque>
#include <forward_list>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> l = { 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 };
auto it = l.begin();
while (it != l.end())
{
if (*it % 2)
{
it = l.insert(it, *it);
it++;
it++;
}
else
{
it = l.erase(it);
}
}
for (const auto& s : l)
{
cout << s << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
forward_list:
对于 forward_list ,由于是单向链表结构,删除元素时,需将前驱指针调整为指向下一个节点,因此需维护“前驱”、“后驱”两个迭代器。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <deque>
#include <forward_list>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
forward_list<int> l = { 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 };
auto it = l.begin();
auto prev = l.before_begin();
while (it != l.end())
{
if (*it % 2)
{
it = l.insert_after(it, *it);
prev = it;
it++;
}
else
{
it = l.erase_after(prev);
}
}
for (const auto& s : l)
{
cout << s << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
9.33 在本节最后一个例子中,如果不将insert的结果赋予begin,将会发生什么?编写程序,去掉此赋值语句,验证你的答案。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <deque>
#include <forward_list>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> l = { 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 };
auto begin = l.begin();
while (begin != l.end())
{
++begin;
l.insert(begin, 66);
++begin;
}
for (const auto& s : l)
{
cout << s << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}Aborted!
9.37 为什么list或array没有capacity成员函数?
list所占的空间不是连续的;array是固定size的。
9.39 解释下面程序片段做了什么:
vector<string> svec;
svec.reserve(1024);
string word;
while (cin >> word)
svec.push_back(word);
svec.resize(svec.size() + svec.size() / 2);
为svec预留1024的空间,将输入添加到svec中,将svec的size增加当前size的一半。
9.41 编写程序,从一个vector初始化一个string。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <deque>
#include <forward_list>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<char> v1 = { 'a','b','c','d','e' };
string s1(v1.begin(), v1.end());
for (const auto c : v1)
cout << c << " ";
cout << endl;
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
9.42 假定你希望每次读取一个字符存入一个string中,而且知道最少需要读取100个字符,应该如何提高程序的性能?
string s;
s.reserve(100);
9.43 编写一个函数,接受三个string参数是s、oldVal 和newVal。使用迭代器及insert和erase函数将s中所有oldVal替换为newVal。测试你的程序,用它替换通用的简写形式,如,将"tho"替换为"though",将"thru"替换为"through"。
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void replace_with_str(string& s, const string& oldVal, const string& newVal)
{
auto iter = s.begin();
while (iter != s.end())
{
if ((s.end() - iter) < (oldVal.end() - oldVal.begin()))
{
return;
}
if (oldVal == string(iter, iter + oldVal.size()))
{
iter = s.erase(iter, iter + oldVal.size());
iter = s.insert(iter, newVal.begin(), newVal.end());
iter += newVal.size();
}
else
++iter;
}
}
int main()
{
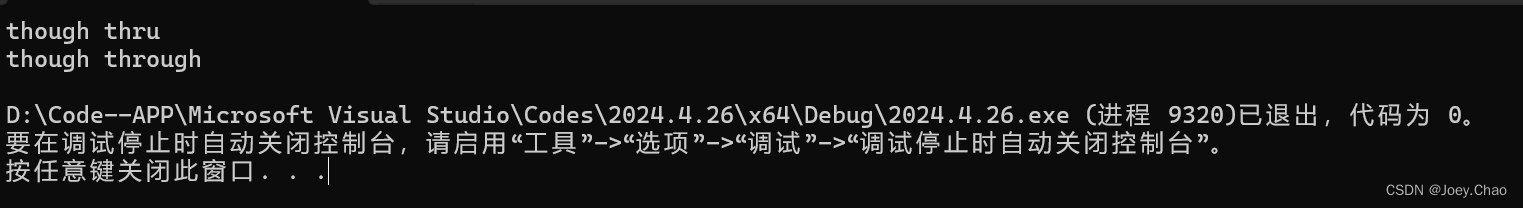
string s("tho thru");
replace_with_str(s, "tho", "though");
cout << s << endl;
replace_with_str(s, "thru", "through");
cout << s << endl;
return 0;
}

9.44 重写上一题的函数,这次使用一个下标和replace。
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void replace_with_str(string& s, const string& oldVal, const string& newVal)
{
string::size_type index = 0;
while (index != s.size())
{
if (oldVal == string(s, index,oldVal.size()))
{
s.replace(index, oldVal.size(), newVal);
}
index++;
}
}
int main()
{
string s("tho thru");
replace_with_str(s, "tho", "though");
cout << s << endl;
replace_with_str(s, "thru", "through");
cout << s << endl;
return 0;
}
9.45 编写一个函数,接受一个表示名字的string参数和两个分别表示前缀(如"Mr.“或"Mrs.”)和后缀(如"Jr.“或"III”)的字符串。使用迭代器及insert和append函数将前缀和后缀添加到给定的名字中,将生成的新string返回。
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
string addname(const string& name, const string& pre, const string& post)
{
string s = name;
s.insert(s.begin(), pre.cbegin(), pre.cend());
return s.append(post);
}
int main()
{
cout << addname("Andy", "Mr.", "Jr.") << endl;
cout << addname("Janice", "Ms.", "Js.") << endl;
return 0;
}
9.46 重写上一题的函数,这次使用位置和长度来管理string,并只使用insert。
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
string addname(const string& name, const string& pre, const string& post)
{
string s = name;
s.insert(0,pre);
return s.insert(s.size(),post);
}
int main()
{
cout << addname("Andy", "Mr.", "Jr.") << endl;
cout << addname("Janice", "Ms.", "Js.") << endl;
return 0;
}
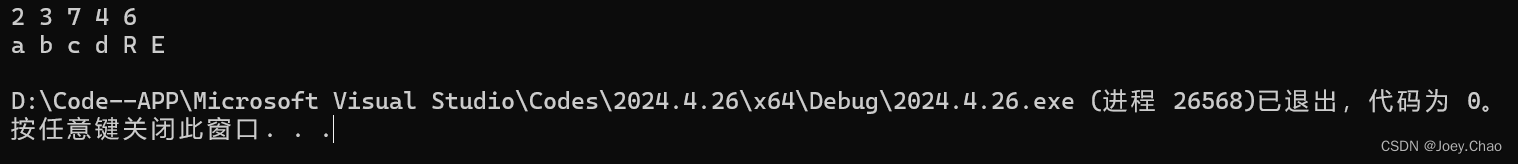
9.47 编写程序,首先查找string"ab2c3d7R4E6"中每个数字字符,然后查找其中每个字母字符。编写两个版本的程序,第一个要使用find_first_of,第二个要使用find_first_not_of。
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string numbers("0123456789");
string s("ab2c3d7R4E6");
for (int pos = 0; (pos = s.find_first_of(numbers, pos)) != string::npos; ++pos)
{
cout << s[pos] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
for (int pos = 0; (pos = s.find_first_not_of(numbers, pos)) != string::npos; ++pos)
{
cout << s[pos] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
9.49 如果一个字母延伸到中线之上,如d 或 f,则称其有上出头部分(ascender)。如果一个字母延伸到中线之下,如p或g,则称其有下出头部分(descender)。编写程序,读入一个单词文件,输出最长的既不包含上出头部分,也不包含下出头部分的单词。
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
void find_longest_word(ifstream &in)
{
string s, longest_word;
int max_length = 0;
while (in >> s)
{
if (s.find_first_of("bdfghjklpqty") != string::npos)
continue;
cout << s << " ";
if (max_length < s.size())
{
max_length = s.size();
longest_word = s;
}
}
cout << endl;
cout << longest_word << endl;
}
int main()
{
ifstream ifs("D:/1.txt");
if (!ifs)
return -1;
find_longest_word(ifs);
return 0;
}

9.50 编写程序处理一个vector,其元素都表示整型值。计算vector中所有元素之和。修改程序,使之计算表示浮点值的string之和。
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<string> v1(6, "6");
int sum_int = 0;
for (const auto s : v1)
{
sum_int += stoi(s);
}
cout << sum_int << endl;
vector<string> v2(8, "8.88");
double sum_double = 0;
for (const auto s : v2)
{
sum_double += stod(s);
}
cout << sum_double << endl;
return 0;
}

9.51 设计一个类,它有三个unsigned成员,分别表示年、月和日。为其编写构造函数,接受一个表示日期的string参数。你的构造函数应该能处理不同的数据格式,如January 1,1900、1/1/1990、Jan 1 1900 等。
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class my_date
{
public:
my_date(const string&);
private:
unsigned int year;
unsigned int month;
unsigned int day;
};
my_date::my_date(const string& s)
{
string date_str = s;
string::size_type index1 = 0;
string::size_type index2 = 0;
if (s.find(',') != string::npos)
{
index1 = s.find(' ');
index2 = s.find(',', index1 + 1);
cout << "year: " << s.substr(index2 + 1, s.size()) << "; month: " << s.substr(0, index1) << "; day: " << s.substr(index1 + 1, index2 - index1 - 1) << endl;
if (s.find("Jan") < s.size()) month = 1;
if (s.find("Feb") < s.size()) month = 2;
if (s.find("Mar") < s.size()) month = 3;
if (s.find("Apr") < s.size()) month = 4;
if (s.find("May") < s.size()) month = 5;
if (s.find("Jun") < s.size()) month = 6;
if (s.find("Jul") < s.size()) month = 7;
if (s.find("Aug") < s.size()) month = 8;
if (s.find("Sep") < s.size()) month = 9;
if (s.find("Oct") < s.size()) month = 10;
if (s.find("Nov") < s.size()) month = 11;
if (s.find("Dec") < s.size()) month = 12;
day = stoi(s.substr(index1 + 1, index2 - index1 - 1));
year = stoi(s.substr(index2 + 1, s.size()));
}
else if (s.find('/') != string::npos)
{
index1 = s.find('/');
index2 = s.find('/', index1 + 1);
cout << "year: " << s.substr(index2 + 1, s.size()) << "; month: " << s.substr(0, index1) << "; day: " << s.substr(index1 + 1, index2 - index1 - 1) << endl;
month = stoi(s.substr(0, index1));
day = stoi(s.substr(index1 + 1, index2 - index1 - 1));
year = stoi(s.substr(index2 + 1, s.size()));
}
else
{
index1 = s.find(' ');
index2 = s.find(' ', index1 + 1);
cout << "year: " << s.substr(index2 + 1, s.size()) << "; month: " << s.substr(0, index1) << "; day: " << s.substr(index1 + 1, index2 - index1 - 1) << endl;
if (s.find("Jan") < s.size()) month = 1;
if (s.find("Feb") < s.size()) month = 2;
if (s.find("Mar") < s.size()) month = 3;
if (s.find("Apr") < s.size()) month = 4;
if (s.find("May") < s.size()) month = 5;
if (s.find("Jun") < s.size()) month = 6;
if (s.find("Jul") < s.size()) month = 7;
if (s.find("Aug") < s.size()) month = 8;
if (s.find("Sep") < s.size()) month = 9;
if (s.find("Oct") < s.size()) month = 10;
if (s.find("Nov") < s.size()) month = 11;
if (s.find("Dec") < s.size()) month = 12;
day = stoi(s.substr(index1 + 1, index2 - index1 - 1));
year = stoi(s.substr(index2 + 1, s.size()));
}
cout << "year:" << year << ";month:" << month << ";day:" << day << endl;
}
int main()
{
my_date my_date1("January 1,1900");
my_date my_date2("1/1/1900");
my_date my_date3("Jan 1 1900");
return 0;
}
9.52 使用stack处理括号化的表达式。当你看到一个左括号,将其记录下来。当你在一个左括号之后看到一个右括号,从stack中pop对象,直至遇到左括号,将左括号也一起弹出栈。然后将一个值(括号内的运算结果)push到栈中,表示一个括号化的(子)表达式已经处理完毕,被其运算结果所替代。
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
#include <cctype>
using namespace std;
string calc(string n1, string n2, string n3)
{
string s;
if (n2 == "+")
{
s = to_string(stoi(n1) + stoi(n3));
}
else
{
s = to_string(stoi(n1) - stoi(n3));
}
return s;
}
int main()
{
string s("100+888*(9-3)");
stack<string> stack;
for (auto iter = s.begin(); iter != s.end();)
{
if (*iter == '(')
{
stack.push(string(1, *iter));
++iter;
while (*iter != ')')
{
stack.push(string(1, *iter));
++iter;
}
}
else if(*iter==')')
{
string f1 = stack.top();
stack.pop();
string f2 = stack.top();
stack.pop();
string f3 = stack.top();
stack.pop();
stack.pop();
stack.push(calc(f3, f2, f1));
++iter;
}
else
{
++iter;
}
}
while (!stack.empty())
{
cout << stack.top() << endl;
stack.pop();
}
return 0;
}



























 8218
8218

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










