简介
树这种数据结构在前端日常开发中是比较常见的,诸如经常接触的DOM树、级联选择、树形控件等等,都是利用树这种数据结构实现的。
在JS中一般是通过Object和Array这两家数据类型来构建树结构的。结构如下图
深度优先遍历
口诀:顾名思义就是尽可能深入的去搜索树的分支并且访问他们。用图看一下就比较好理解了。

算法实现:这个算法实现也比较简单,通过forEach去递归遍历子节点就可以了,代码如下
const tree = {
val: 'a',
children: [
{
val: 'b',
children: [
{
val: 'd',
children: []
},
{
val: 'e',
children: []
}
]
},
{
val: 'c',
children: [
{
val: 'f',
children: []
},
{
val: 'g',
children: []
}
]
}
]
}
const dfs = (root) => {
console.log(root.val);
root.children.forEach(dfs)
}
dfs(tree)
结果如下

广度优先遍历
口诀:先访问离根节点最近的节点,也可以理解成先访问完自己的子节点,再去访问子节点的子节点,概念图如下。

算法实现:主要思路就是通过一个队列,1.将根节点入队,2.把队头出队并且访问,3.最后把队头的子节点依次入队,重复 2、3点直到队列为空为止。
const tree = {
val: 'a',
children: [
{
val: 'b',
children: [
{
val: 'd',
children: []
},
{
val: 'e',
children: []
}
]
},
{
val: 'c',
children: [
{
val: 'f',
children: []
},
{
val: 'g',
children: []
}
]
}
]
}
const bfs = (root) => {
const q = [root] // 创建队列
while (q.length > 0) {
const n = q.shift() // 队头出队
console.log(n.val); // 访问队头
n.children.forEach(child => q.push(child)) // 遍历队头子节点并依次入队
}
}
bfs(tree)

二叉树的先中后序遍历
二叉树概念:树中每个节点最多只能有两个子节点
JS中模拟二叉树可以通过Object来实现:

先序遍历
口诀:先访问根节点,再对根节点的左子树进行先序遍历,再对根节点的右子树进行先序遍历,简单来说就是 根 => 左 => 右 这么个顺序。遍历顺序如下
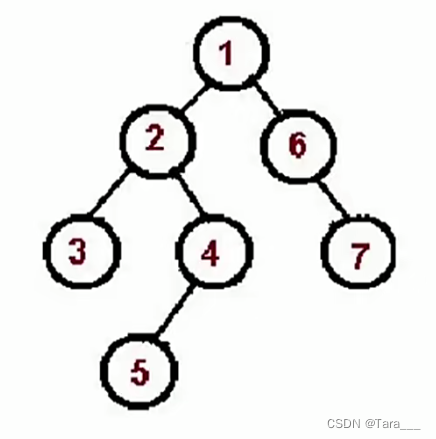
代码如下:
const binaryTree = {
val: 1,
left: {
val: 2,
left: {
val: 4,
left: null,
right: null
},
right: {
val: 5,
left: null,
right: null
}
},
right: {
val: 3,
left: {
val: 6,
left: null,
right: null
},
right: {
val: 7,
left: null,
right: null
}
}
}
const preOrder = (root) => {
if (!root) return // 拦截 null
console.log(root.val); // 访问根节点
preOrder(root.left); // 递归左子树
preOrder(root.right); // 递归右子树
}
preOrder(binaryTree)
结果如下

中序遍历
口诀:先访问根节点的左子树并对其进行中序遍历,再访问根节点,最后访问根节点的右子树并进行中序遍历,也就是 左子树 => 根 => 右子树
理解图如下:

代码如下:
const binaryTree = {
val: 1,
left: {
val: 2,
left: {
val: 4,
left: null,
right: null
},
right: {
val: 5,
left: null,
right: null
}
},
right: {
val: 3,
left: {
val: 6,
left: null,
right: null
},
right: {
val: 7,
left: null,
right: null
}
}
}
const inOrder = (root) => {
if (!root) return // 拦截 null
inOrder(root.left); // 递归左子树
console.log(root.val); // 访问根节点
inOrder(root.right); // 递归右子树
}
inOrder(binaryTree)
结果如下:

后序遍历
口诀:访问根节点左子树并进行后序遍历,再访问根节点右子树并进行后续遍历,最后访问根节点

代码:
const binaryTree = {
val: 1,
left: {
val: 2,
left: {
val: 4,
left: null,
right: null
},
right: {
val: 5,
left: null,
right: null
}
},
right: {
val: 3,
left: {
val: 6,
left: null,
right: null
},
right: {
val: 7,
left: null,
right: null
}
}
}
const postOrder = (root) => {
if (!root) return // 拦截 null
postOrder(root.left); // 递归左子树
postOrder(root.right); // 递归右子树
console.log(root.val); // 访问根节点
}
postOrder(binaryTree)
结果:

先中后序遍历 非递归版
(1)先序遍历
这里先将right入队,是因为我们用了数组的pop方法,拿到的是数组最后一个元素,先将right推入数组中再将left推入数组中,可以保证先将left出队并访问。
const preOrder = (root) => {
if (!root) return // 拦截 null
let stack = [root]
while (stack.length) {
let n = stack.pop()
console.log(n.val)
if (n.right) stack.push(n.right)
if (n.left) stack.push(n.left)
}
}
(2)中序遍历
const inOrder = (root) => {
if (!root) return // 拦截 null
let stack = []
let p = root
while (stack.length || p) {
while(p) {
stack.push(p)
p = p.left
}
let n = stack.pop()
console.log(n.val)
p = n.right
}
}
(3)后序遍历
这里的思路就是通过两个数组来记录出队的顺序,stack数组用来遍历树的节点,按照 根 => 右 => 左的顺序将节点树推入 outputStack 数组中,这样一来在 outputStack 数组中就可以通过pop方法来实现 左 => 右 => 根 的后序遍历顺序了。
const postOrder = (root) => {
if (!root) return // 拦截 null
let stack = [root]
let outputStack = []
while (stack.length) {
const n = stack.pop()
outputStack.push(n)
if (n.left) stack.push(n.left)
if (n.right) stack.push(n.right)
}
while (outputStack.length) {
const n = outputStack.pop()
console.log(n.val)
}
}
























 1243
1243

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








