文章目录
环境准备
这里我选用的是miniconda,下载安装,不论是在服务器还是在本地,都是非常简单的,这里就不过多赘述了,自行去官网 👉miniconda下载链接。如果你觉得这篇文章有帮助,别忘了关注B站帅小柏,点赞、评论和分享是对我最大的支持。
创建conda环境
由于如果是在本地创建环境的话,默认是在C盘。(当然,有个例外,base环境是和conda的安装路径是一致的)那么,这里我就演示一下指定路径创建环境的情况。
步骤 1: 打开终端
在 Windows 上,您可以使用 Anaconda Prompt 或 CMD。在 macOS 或 Linux 上,打开 Terminal。
步骤 2: 使用 --prefix 创建环境
使用以下命令在您希望的路径下创建虚拟环境:
conda create --prefix G:\env\AI_Basics python=3.11
G:\env\AI_Basics是希望创建虚拟环境的路径(可以根据需要更改)。
步骤 3: 激活环境
查看已有已创建的环境
conda env list
创建完成后,可以激活该环境:
conda activate G:\env\AI_Basics
激活后,就可以在该环境中安装包和运行 Python 脚本。
注意:如果是环境乱套了 ,需要删除该环境重新配置的话 ,可先退出该环境,进入base环境后,执行以下代码
conda env remove --prefix G:\env\AI_Basics
安装本系列实验所需的包
可以安以下这些库,文档里面的其他库因为版本原因安装失败或者是不存在 比如 mpl_toolkits 和 copy 都合并到其他库了或者就自带了。
pip install numpy matplotlib tensorflow tqdm
- 文档上tensorflow(推荐使用1.x版本),这里可以直接安tensorflow2.x, 后面的实验代码会做修改,大可放心
pip install tensorflow
实验1 产生式系统实验——决策树逻辑
- 这个实验通过简单的决策树逻辑,模拟了一个基础的动物识别系统,展示了如何利用特征进行分类和推理。
决策树的精髓
- 信息增益:决策树通过计算每个特征的信息增益来选择最佳分割点。信息增益衡量了一个特征在数据集中的分类效果。
- 递归分裂:决策树通过递归地分裂数据集,根据最佳特征将数据分成子集,直到达到停止条件(如节点包含的样本数小于某个阈值,或者没有特征可以分裂)。
- 叶节点:每个叶节点代表一个分类结果。
这个示例程序就是把所有的可能情况列举了一遍。也没用到决策树的精髓。
示例完整代码如下
# 动物识别系统
# 自定义函数,判断有无重复元素
def judge_repeat(value, list=[]):
for i in range(0, len(list)):
if (list[i] == value):
return 1
else:
if (i != len(list) - 1):
continue
else:
return 0
# 自定义函数,对已经整理好的综合数据库real_list进行最终的结果判断
def judge_last(list):
for i in list:
if i == '23': # 食肉类
for i in list:
if i == '12': # 黄褐色
for i in list:
if i == '21': # 哺乳类
for i in list:
if i == '13': # 有斑点
print("黄褐色,有斑点,哺乳类,食肉类->金钱豹\n")
print("所识别的动物为金钱豹")
return 0
elif i == '14': # 有黑色条纹
print("黄褐色,有黑色条纹,哺乳类,食肉类->虎\n")
print("所识别的动物为虎")
return 0
elif (i == '14'): # 有黑色条纹
for i in list:
if i == '24': # 蹄类
print("有黑色条纹,蹄类->斑马\n")
print("所识别的动物为斑马")
return 0
elif i == '24': # 蹄类
for i in list:
if i == '13': # 有斑点
for i in list:
if i == '15': # 长脖
for i in list:
if i == '16': # 长腿
print("有斑点,有黑色条纹,长脖,蹄类->长颈鹿\n")
print("所识别的动物为长颈鹿")
return 0
elif i == '20': # 善飞
for i in list:
if i == '22': # 鸟类
print("善飞,鸟类->信天翁\n")
print("所识别的动物为信天翁")
return 0
elif i == '22': # 鸟类
for i in list:
if i == '4': # 不会飞
for i in list:
if i == '15': # 长脖
for i in list:
if i == '16': # 长腿
print("不会飞,长脖,长腿,鸟类->鸵鸟\n")
print("所识别的动物为鸵鸟")
return 0
elif (i == '4'): # 不会飞
for i in list:
if (i == '22'): # 鸟类
for i in list:
if (i == '18'): # 会游泳
for i in list:
if (i == '19'): # 黑白二色
print("不会飞,会游泳,黑白二色,鸟类->企鹅\n")
print("所识别的动物企鹅")
return 0
else:
if (list.index(i) != len(list) - 1):
continue
else:
print("\n根据所给条件无法判断为何种动物")
dict_before = {'1': '有毛发', '2': '产奶', '3': '有羽毛', '4': '不会飞', '5': '会下蛋', '6': '吃肉', '7': '有犬齿',
'8': '有爪', '9': '眼盯前方', '10': '有蹄', '11': '反刍', '12': '黄褐色', '13': '有斑点', '14': '有黑色条纹',
'15': '长脖', '16': '长腿', '17': '不会飞', '18': '会游泳', '19': '黑白二色', '20': '善飞', '21': '哺乳类',
'22': '鸟类', '23': '食肉类', '24': '蹄类', '25': '金钱豹', '26': '虎', '27': '长颈鹿', '28': '斑马',
'29': '鸵鸟', '30': '企鹅', '31': '信天翁'}
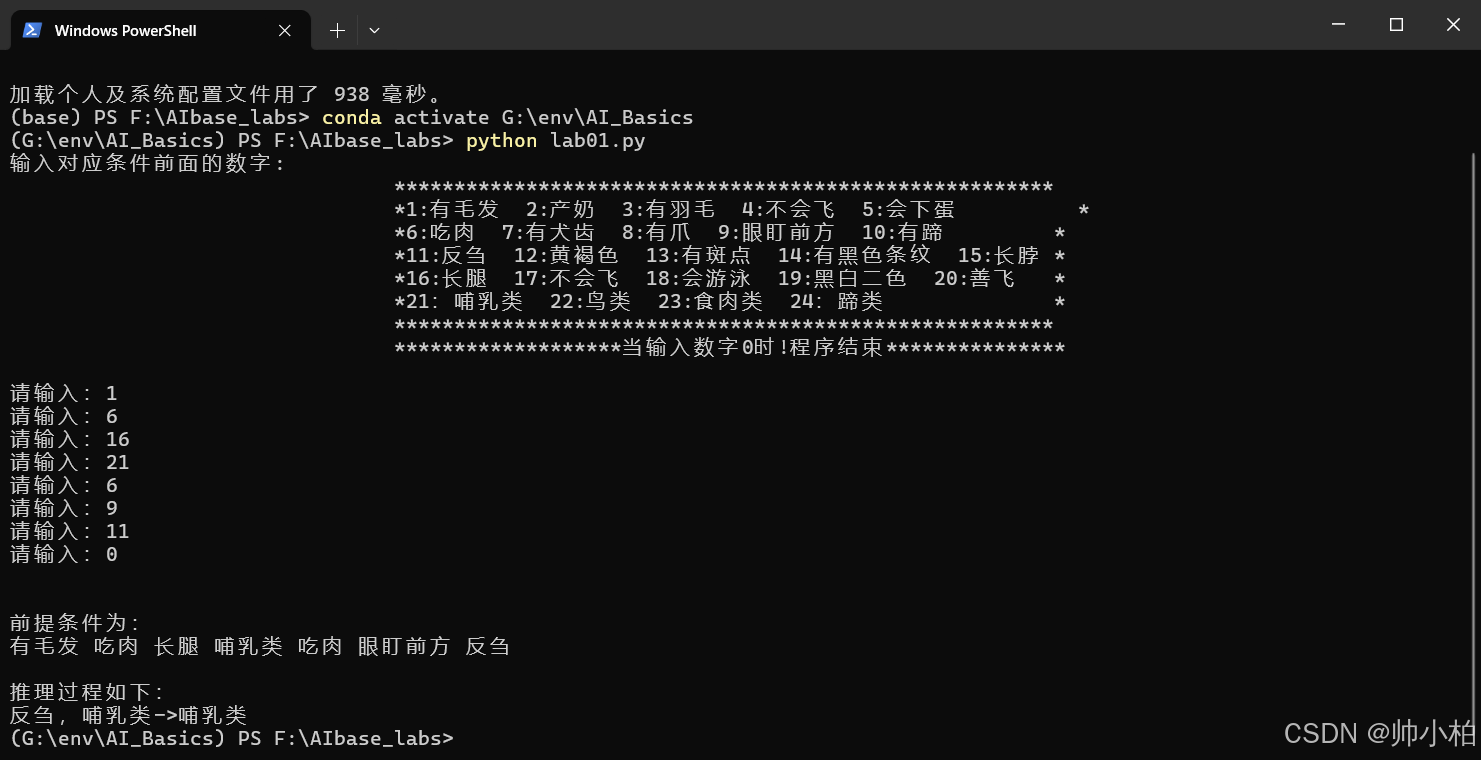
print("""输入对应条件前面的数字:
*******************************************************
*1:有毛发 2:产奶 3:有羽毛 4:不会飞 5:会下蛋 *
*6:吃肉 7:有犬齿 8:有爪 9:眼盯前方 10:有蹄 *
*11:反刍 12:黄褐色 13:有斑点 14:有黑色条纹 15:长脖 *
*16:长腿 17:不会飞 18:会游泳 19:黑白二色 20:善飞 *
*21:哺乳类 22:鸟类 23:食肉类 24:蹄类 *
*******************************************************
*******************当输入数字0时!程序结束***************
""")
# 综合数据库
list_real = []
while (1):
# 循环输入前提条件所对应的字典中的键
num_real = input("请输入:")
list_real.append(num_real)
if (num_real == '0'):
break
print("\n")
print("前提条件为:")
# 输出前提条件
for i in range(0, len(list_real) - 1):
print(dict_before[list_real[i]], end=" ")
print("\n")
print("推理过程如下:")
# 遍历综合数据库list_real中的前提条件
for i in list_real:
if i == '1':
if judge_repeat('21', list_real) == 0:
list_real.append('21')
print("有毛发->哺乳类")
elif i == '2':
if judge_repeat('21', list_real) == 0:
list_real.append('21')
print("产奶->哺乳类")
elif i == '3':
if judge_repeat('22', list_real) == 0:
list_real.append('22')
print("有羽毛->鸟类")
else:
if list_real.index(i) != len(list_real) - 1:
continue
else:
break
for i in list_real:
if i == '4':
for i in list_real:
if i == '5':
if judge_repeat('22', list_real) == 0:
list_real.append('22')
print("不会飞,会下蛋->鸟类")
elif i == '6':
for i in list_real:
if i == '21':
if judge_repeat('21', list_real) == 0:
list_real.append('21')
print("食肉->哺乳类")
elif i == '7':
for i in list_real:
if i == '8':
for i in list_real:
if i == '9':
if judge_repeat('23', list_real) == 0:
list_real.append('23')
print("有犬齿,有爪,眼盯前方->食肉类")
elif i == '10':
for i in list_real:
if i == '21':
if judge_repeat('24', list_real) == 0:
list_real.append('24')
print("有蹄,哺乳类->蹄类")
elif i == '11':
for i in list_real:
if i == '21':
if judge_repeat('24', list_real) == 0:
list_real.append('24')
print("反刍,哺乳类->哺乳类")
else:
if i != len(list_real) - 1:
continue
else:
break
judge_last(list_real)
跑通打卡 √
实验2 洗衣机模糊推理系统
模糊逻辑系统:
- 通过计算最大值和最小值来处理两个输入集合的组合,类似于模糊逻辑中的模糊集合操作。
sludge和grease可能代表两种不同的输入变量,time代表时间点。x1和y1可能是某种模糊规则的结果。result代表在不同时间点下的最大模糊输出。
import numpy as np
# 定义输入变量
sludge = [0, 0.5, 1]
grease = [0, 0.5, 1]
time = [0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1]
# 计算sludge和grease的组合最大值矩阵
sludgeandgrease = np.zeros((len(sludge), len(grease)))
for i in range(len(sludge)):
for j in range(len(grease)):
sludgeandgrease[i][j] = max(sludge[i], grease[j])
# 将矩阵重塑为向量
sludgeandgrease = sludgeandgrease.reshape(-1, 1)
# 计算最终矩阵R,存储最小值
R = np.zeros((len(sludgeandgrease), len(time)))
for i in range(len(sludgeandgrease)):
for j in range(len(time)):
R[i][j] = min(sludgeandgrease[i][0], time[j]) # 取单一元素
# 定义x1和y1输入向量
x1 = [0, 0.83, 0.6]
y1 = [0, 0.71, 0.7]
# 计算x1和y1的组合最大值矩阵
x1y1 = np.zeros((len(x1), len(y1)))
for i in range(len(x1)):
for j in range(len(y1)):
x1y1[i][j] = max(x1[i], y1[j])
# 将矩阵重塑为向量
x1y12 = x1y1.reshape(9)
# 初始化最终结果
result = np.zeros(5)
# 初始化临时存储矩阵
a = np.zeros(9)
# 计算结果向量
for i in range(5):
for j in range(9):
a[j] = x1y12[j] * R[j][i]
result[i] = max(a)
# 输出结果
print(result)
跑通打卡 √

实验3 缺失,暂无实验
实验4 AStar求解八数码问题
import numpy as np
class State:
def __init__(self, state, directionFlag=None, parent=None, f=0):
self.state = state
self.direction = ['up', 'down', 'right', 'left']
if directionFlag:
self.direction.remove(directionFlag)
self.parent = parent
self.f = f
def getDirection(self):
return self.direction
def setF(self, f):
self.f = f
return
# 打印结果
def showInfo(self):
for i in range(len(self.state)):
for j in range(len(self.state)):
print(self.state[i, j], end=' ')
print("\n")
print('->')
return
# 获取0点
def getZeroPos(self):
postion = np.where(self.state == 0)
return postion
# 曼哈顿距离 f = g + h,g=1,如果用宽度优先的评估函数可以不调用该函数
def getFunctionValue(self):
cur_node = self.state.copy()
fin_node = self.answer.copy()
dist = 0
N = len(cur_node)
for i in range(N):
for j in range(N):
if cur_node[i][j] != fin_node[i][j]:
index = np.argwhere(fin_node == cur_node[i][j])
x = index[0][0] # 最终x距离
y = index[0][1] # 最终y距离
dist += (abs(x - i) + abs(y - j))
return dist + 1
def nextStep(self):
if not self.direction:
return []
subStates = []
boarder = len(self.state) - 1
# 获取0点位置
x, y = self.getZeroPos()
# 向左
if 'left' in self.direction and y > 0:
s = self.state.copy()
tmp = s[x, y - 1]
s[x, y - 1] = s[x, y]
s[x, y] = tmp
news = State(s, directionFlag='right', parent=self)
news.setF(news.getFunctionValue())
subStates.append(news)
# 向上
if 'up' in self.direction and x > 0:
# it can move to upper place
s = self.state.copy()
tmp = s[x - 1, y]
s[x - 1, y] = s[x, y]
s[x, y] = tmp
news = State(s, directionFlag='down', parent=self)
news.setF(news.getFunctionValue())
subStates.append(news)
# 向下
if 'down' in self.direction and x < boarder:
# it can move to down place
s = self.state.copy()
tmp = s[x + 1, y]
s[x + 1, y] = s[x, y]
s[x, y] = tmp
news = State(s, directionFlag='up', parent=self)
news.setF(news.getFunctionValue())
subStates.append(news)
# 向右
if self.direction.count('right') and y < boarder:
# it can move to right place
s = self.state.copy()
tmp = s[x, y + 1]
s[x, y + 1] = s[x, y]
s[x, y] = tmp
news = State(s, directionFlag='left', parent=self)
news.setF(news.getFunctionValue())
subStates.append(news)
# 返回F值最小的下一个点
subStates.sort(key=compareNum)
return subStates[0]
# A* 迭代
def solve(self):
# openList
openTable = []
# closeList
closeTable = []
openTable.append(self)
while len(openTable) > 0:
# 下一步的点移除open
n = openTable.pop(0)
# 加入close
closeTable.append(n)
# 确定下一步点
subStates = n.nextStep()
path = []
# 判断是否和最终结果相同
if (subStates.state == subStates.answer).all():
while subStates.parent and subStates.parent != originState:
path.append(subStates.parent)
subStates = subStates.parent
path.reverse()
return path
openTable.append(subStates)
else:
return None, None
def compareNum(state):
return state.f
if __name__ == '__main__':
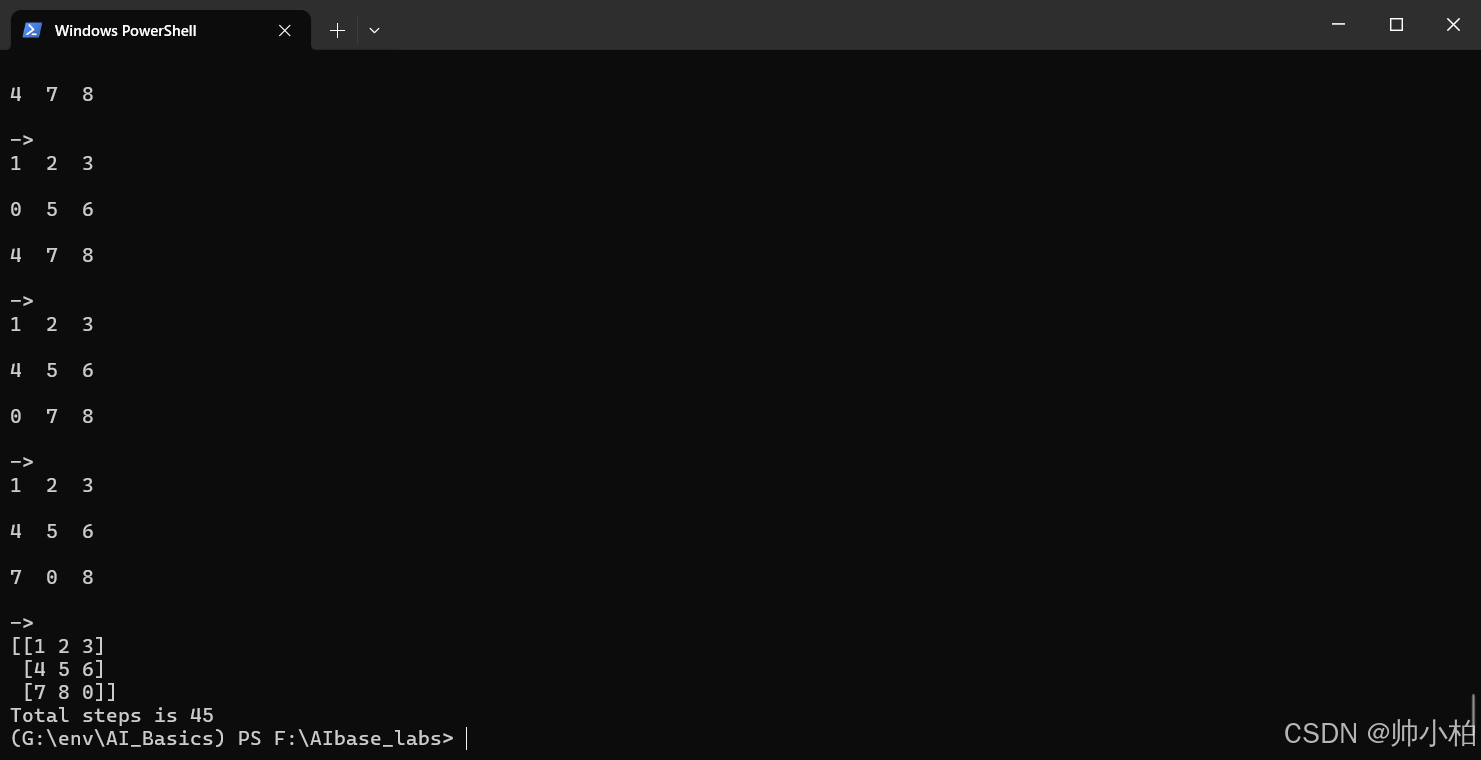
originState = State(np.array([[1, 5, 3], [2, 4, 6], [7, 0, 8]]))
State.answer = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 0]])
s1 = State(state=originState.state)
path = s1.solve()
if path:
for node in path:
node.showInfo()
print(State.answer)
print("Total steps is %d" % len(path))
跑通打卡√
实验5 AStar求解迷宫寻路问题
import numpy as np
class Point:
def __init__(self, x, y):
self.x = x
self.y = y
self.f = 0
def setF(self, f):
self.f = f
def __eq__(self, other):
return self.x == other.x and self.y == other.y
# 曼哈顿距离比较 f = g + h,g=1
def getFunctionValue(self, end):
dist = abs(self.x - end.x) + abs(self.y - end.y)
return dist + 1
class State:
def __init__(self, state, current_point=Point(0, 0), end_point=Point(0, 0)):
self.state = state
self.cP = current_point
self.eP = end_point
def __eq__(self, other):
return self.cP == other.cP
def setF(self, f):
self.f = f
def setCurrentPoint(self, x, y):
self.cP.x = x
self.cP.y = y
def getCurPoint(self):
return self.cP.x, self.cP.y
# 确定下一步的方法
def nextStep(map, openTable, closeTable, wrongTable):
subPoints = []
boarder = len(map.state) - 1
# 获取当前所在的点
x, y = map.getCurPoint()
# 往左走
if y > 0 and map.state[x][y - 1] == 0:
p = Point(x, y - 1)
if p not in closeTable and p not in wrongTable:
# 添加到可以走的list
openTable.append(p)
# new point
# 获取F函数值
p.setF(p.getFunctionValue(map.eP))
subPoints.append(p)
# 往上走
if x > 0 and map.state[x - 1][y] == 0:
p = Point(x - 1, y)
if p not in closeTable and p not in wrongTable:
openTable.append(p)
p.setF(p.getFunctionValue(map.eP))
subPoints.append(p)
# 往下走
if x < boarder and map.state[x + 1][y] == 0:
p = Point(x + 1, y)
if p not in closeTable and p not in wrongTable:
openTable.append(p)
p.setF(p.getFunctionValue(map.eP))
subPoints.append(p)
# 往右走
if y < boarder and map.state[x][y + 1] == 0:
p = Point(x, y + 1)
if p not in closeTable and p not in wrongTable:
openTable.append(p)
p.setF(p.getFunctionValue(map.eP))
subPoints.append(p)
# 根据F值排序,获取F值最近的
subPoints.sort(key=compareF)
if len(subPoints) < 1:
# 防止走到死路无法回头情况
wrongTable.append(Point(map.cP.x, map.cP.y))
closeTable.remove(map.cP)
next_point = closeTable[-1]
map.cP.x, map.cP.y = next_point.x, next_point.y
else:
next_point = subPoints[0]
map.cP.x, map.cP.y = next_point.x, next_point.y
closeTable.append(next_point)
openTable.remove(next_point)
# 迭代走下一步
def solve(map, openTable, closeTable, wrongTable):
# start the loop
while not map.cP == map.eP:
nextStep(map, openTable, closeTable, wrongTable)
def compareF(p):
return p.f
# 展示最后结果
def showInfo(map, path):
for i in range(len(map.state)):
for j in range(len(map.state)):
if Point(i, j) in path:
# 正确路径用‘*’表示
print('*', end=' ')
else:
print(map.state[i, j], end=' ')
print("\n")
return
if __name__ == '__main__':
# openList
openTable = []
# closeList
closeTable = []
# 走错路返回用的
wrongTable = []
state = np.array([[0, 0, 0, 0, 0], [1, 0, 1, 0, 1], [0, 0, 0, 0, 1], [0, 1, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 1, 0]])
# 起点终点
start_point = Point(0, 0)
end_point = Point(4, 4)
# 最终路径
path = [start_point]
Map = State(state, Point(0, 0), end_point)
solve(Map, openTable, closeTable, wrongTable)
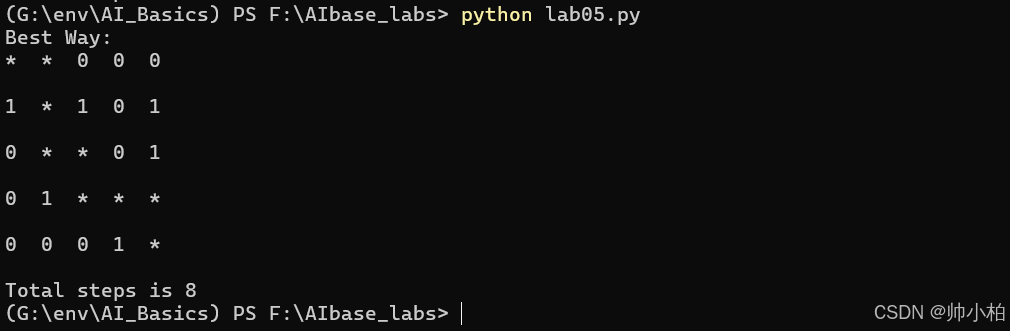
print('Best Way:')
path = path + closeTable
showInfo(Map, path)
print("Total steps is %d" % (len(path) - 1))
跑通打卡√
实验6 遗传算法求最值问题
求最大值
import numpy as np
from numpy import cos
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import cm
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
import datetime
DNA_SIZE = 24 # 编码长度
POP_SIZE = 100 # 种群大小
CROSS_RATE = 0.8 # 交叉率
MUTA_RATE = 0.15 # 变异率
Iterations = 1000 # 代次数
X_BOUND = [0, 10] # X区间
Y_BOUND = [0, 10] # Y区间
def F(x, y): # 适应度函数
return (6.452 * (x + 0.125 * y) * (cos(x) - cos(2 * y))**2) / (0.8 + (x - 4.2)**2 + 2 * (y - 7)**2) + 3.226 * y
def decodeDNA(pop): # 解码
x_pop = pop[:, 1::2] # 奇数列表示X
y_pop = pop[:, ::2] # 偶数列表示y
x = x_pop.dot(2**np.arange(DNA_SIZE)[::-1]) / float(2**DNA_SIZE - 1) * (X_BOUND[1] - X_BOUND[0]) + X_BOUND[0]
y = y_pop.dot(2**np.arange(DNA_SIZE)[::-1]) / float(2**DNA_SIZE - 1) * (Y_BOUND[1] - Y_BOUND[0]) + Y_BOUND[0]
return x, y
def getfitness(pop):
x, y = decodeDNA(pop)
temp = F(x, y)
return (temp - np.min(temp)) + 0.0001 # 减去最小的适应度是为了防止适应度出现负数
def select(pop, fitness): # 根据适应度选择
temp = np.random.choice(np.arange(POP_SIZE), size=POP_SIZE, replace=True, p=(fitness) / (fitness.sum()))
return pop[temp]
def crossmuta(pop, CROSS_RATE):
new_pop = []
for i in pop: # 遍历种群中的每一个个体,将该个体作为父代
temp = i.copy() # 子代先得到父亲的全部基因
if np.random.rand() < CROSS_RATE: # 以交叉概率发生交叉
j = pop[np.random.randint(POP_SIZE)] # 从种群中随机选择另一个个体,并将该个体作为母代
cpoints1 = np.random.randint(0, DNA_SIZE * 2 - 1) # 随机产生交叉的点
cpoints2 = np.random.randint(cpoints1, DNA_SIZE * 2)
temp[cpoints1:cpoints2] = j[cpoints1:cpoints2] # 子代得到位于交叉点后的母代的基因
mutation(temp, MUTA_RATE) # 后代以变异率发生变异
new_pop.append(temp)
return new_pop
def mutation(temp, MUTA_RATE):
if np.random.rand() < MUTA_RATE: # 以MUTA_RATE的概率进行变异
mutate_point = np.random.randint(0, DNA_SIZE) # 随机产生一个实数,代表要变异基因的位置
temp[mutate_point] = temp[mutate_point] ^ 1 # 将变异点的二进制为反转
def print_info(pop): # 用于输出结果
fitness = getfitness(pop)
maxfitness = np.argmax(fitness) # 返回最大值的索引值
print("max_fitness:", fitness[maxfitness])
x, y = decodeDNA(pop)
print("最优的基因型:", pop[maxfitness])
print("(x, y):", (x[maxfitness], y[maxfitness]))
print("F(x,y)_max = ", F(x[maxfitness], y[maxfitness]))
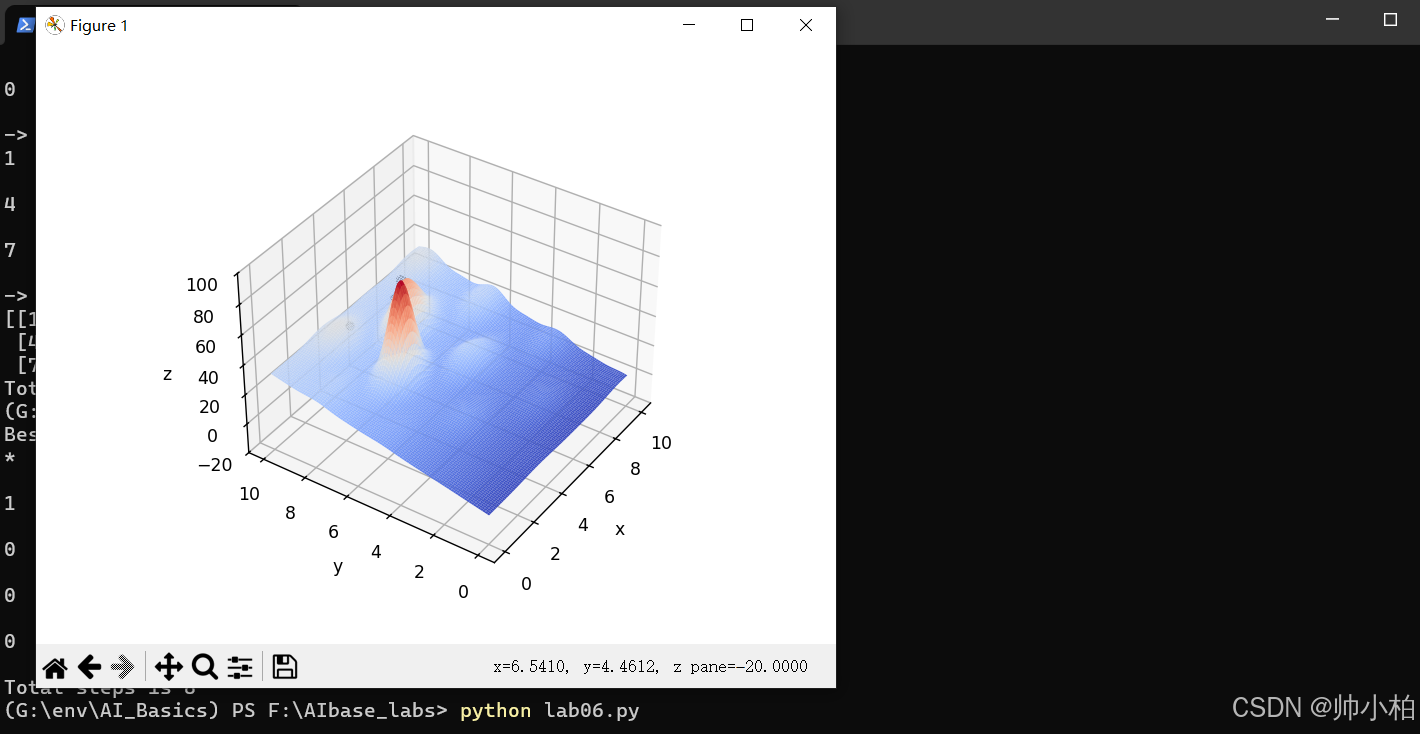
def plot_3d(ax):
X = np.linspace(*X_BOUND, 100)
Y = np.linspace(*Y_BOUND, 100)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(X, Y)
Z = F(X, Y)
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap=cm.coolwarm)
ax.set_zlim(-20, 100)
ax.set_xlabel('x')
ax.set_ylabel('y')
ax.set_zlabel('z')
start_t = datetime.datetime.now()
if __name__ == "__main__":
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
plt.ion()
plot_3d(ax)
pop = np.random.randint(2, size=(POP_SIZE, DNA_SIZE * 2))
for _ in range(Iterations): # 迭代N代
x, y = decodeDNA(pop)
if 'sca' in locals():
sca.remove()
sca = ax.scatter(x, y, F(x, y), c='black', marker='o')
plt.show()
plt.pause(0.1)
pop = np.array(crossmuta(pop, CROSS_RATE))
fitness = getfitness(pop)
pop = select(pop, fitness) # 选择生成新的种群
end_t = datetime.datetime.now()
print((end_t - start_t).seconds)
print_info(pop)
plt.ioff()
plt.show()
跑通打卡√
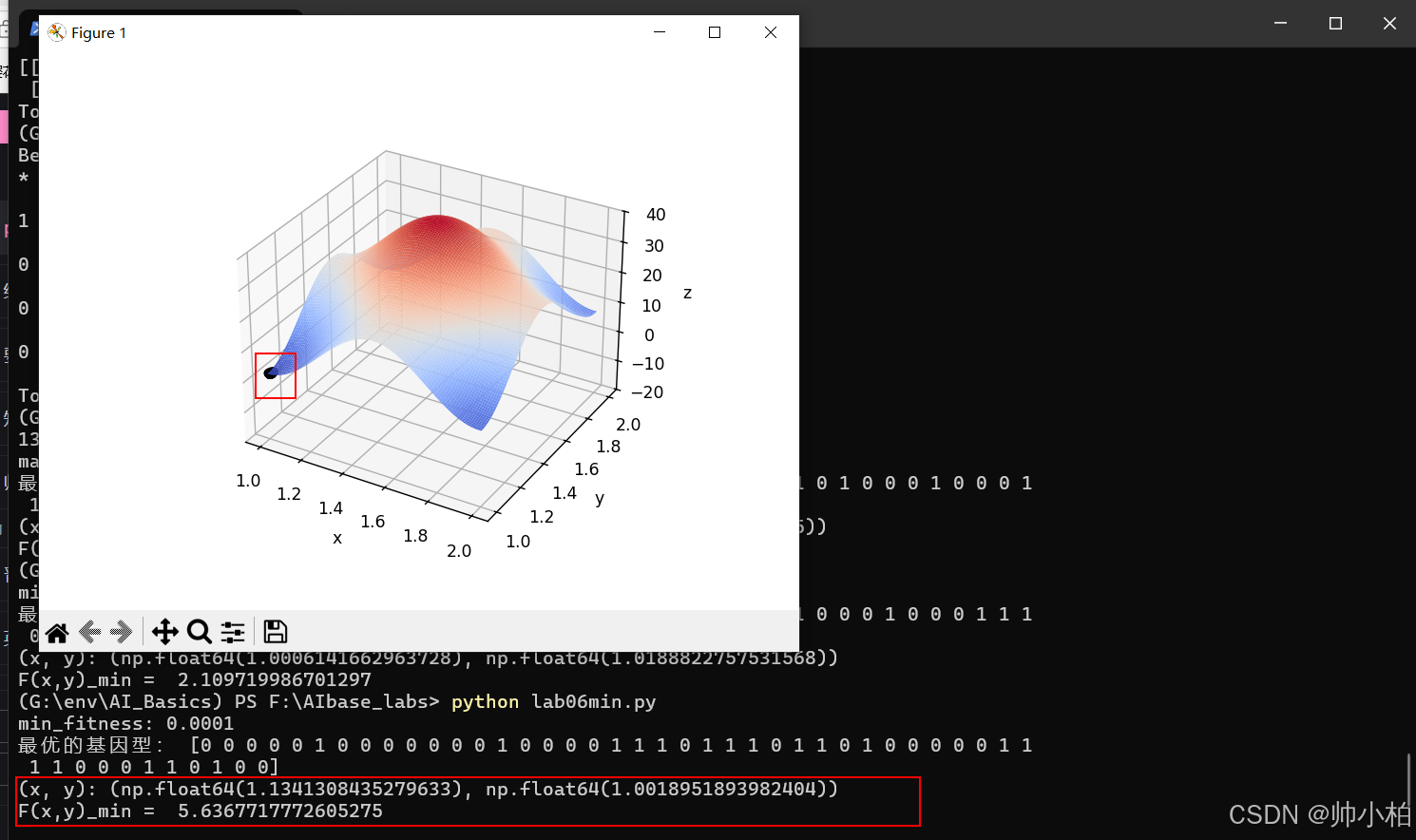
求最小值
import numpy as np
from numpy import cos
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import cm
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
DNA_SIZE = 24 # 编码长度
POP_SIZE = 200 # 种群大小
CROSS_RATE = 0.5 # 交叉率
MUTA_RATE = 0.015 # 变异率
Iterations = 50 # 迭代次数
X_BOUND = [1, 2] # X区间
Y_BOUND = [1, 2] # Y区间
def F(x, y): # 适应度函数
return 20 + x**2 + y**2 - 10 * (cos(2 * np.pi * x) + cos(2 * np.pi * y))
def decodeDNA(pop): # 解码
x_pop = pop[:, 1::2] # 奇数列表示X
y_pop = pop[:, ::2] # 偶数列表示y
x = x_pop.dot(2**np.arange(DNA_SIZE)[::-1]) / float(2**DNA_SIZE - 1) * (X_BOUND[1] - X_BOUND[0]) + X_BOUND[0]
y = y_pop.dot(2**np.arange(DNA_SIZE)[::-1]) / float(2**DNA_SIZE - 1) * (Y_BOUND[1] - Y_BOUND[0]) + Y_BOUND[0]
return x, y
def getfitness(pop):
x, y = decodeDNA(pop)
temp = F(x, y)
return -(temp - np.max(temp)) + 0.0001 # 减去最大的适应度是为了防止适应度出现负数
def select(pop, fitness): # 根据适应度选择
indices = np.random.choice(np.arange(POP_SIZE), size=POP_SIZE, replace=True, p=(fitness) / fitness.sum())
return pop[indices]
def crossmuta(pop, CROSS_RATE):
new_pop = []
for i in pop: # 遍历种群中的每一个个体,将该个体作为父代
temp = i.copy() # 子代先得到父亲的全部基因
if np.random.rand() < CROSS_RATE: # 以交叉概率发生交叉
j = pop[np.random.randint(POP_SIZE)] # 从种群中随机选择另一个个体,并将该个体作为母代
cpoints1 = np.random.randint(0, DNA_SIZE * 2 - 1) # 随机产生交叉的点
cpoints2 = np.random.randint(cpoints1, DNA_SIZE * 2)
temp[cpoints1:cpoints2] = j[cpoints1:cpoints2] # 子代得到位于交叉点后的母代的基因
mutation(temp, MUTA_RATE) # 后代以变异率发生变异
new_pop.append(temp)
return new_pop
def mutation(temp, MUTA_RATE):
if np.random.rand() < MUTA_RATE: # 以MUTA_RATE的概率进行变异
mutate_point = np.random.randint(0, DNA_SIZE * 2) # 随机产生一个实数,代表要变异基因的位置
temp[mutate_point] = temp[mutate_point] ^ 1 # 将变异点的二进制为反转
def print_info(pop): # 用于输出结果
fitness = getfitness(pop)
minfitness = np.argmin(fitness)
print("min_fitness:", fitness[minfitness])
x, y = decodeDNA(pop)
print("最优的基因型:", pop[minfitness])
print("(x, y):", (x[minfitness], y[minfitness]))
print("F(x,y)_min = ", F(x[minfitness], y[minfitness]))
def plot_3d(ax):
X = np.linspace(*X_BOUND, 100)
Y = np.linspace(*Y_BOUND, 100)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(X, Y)
Z = F(X, Y)
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap=cm.coolwarm)
ax.set_zlim(-20, 40)
ax.set_xlabel('x')
ax.set_ylabel('y')
ax.set_zlabel('z')
if __name__ == "__main__":
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
plt.ion()
plot_3d(ax)
pop = np.random.randint(2, size=(POP_SIZE, DNA_SIZE * 2))
for _ in range(Iterations): # 迭代N代
x, y = decodeDNA(pop)
if 'sca' in locals():
sca.remove()
sca = ax.scatter(x, y, F(x, y), c='black', marker='o')
plt.show()
plt.pause(0.1)
pop = np.array(crossmuta(pop, CROSS_RATE))
fitness = getfitness(pop)
pop = select(pop, fitness) # 选择生成新的种群
print_info(pop)
plt.ioff()
plt.show()
跑通打卡√
实验7 遗传算法求TSP问题
import numpy as np
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 各个城市的坐标
City_Map = 100 * np.random.rand(20, 2) # 随机产生20个城市
DNA_SIZE = len(City_Map) # 编码长度
POP_SIZE = 200 # 种群大小
CROSS_RATE = 0.6 # 交叉率
MUTA_RATE = 0.2 # 变异率
Iterations = 1000 # 迭代次数
def distance(DNA): # 根据DNA的路线计算距离
dis = 0
temp = City_Map[DNA[0]]
for i in DNA[1:]:
dis += np.sqrt((City_Map[i][0] - temp[0]) ** 2 + (City_Map[i][1] - temp[1]) ** 2)
temp = City_Map[i]
dis += np.sqrt((temp[0] - City_Map[DNA[0]][0]) ** 2 + (temp[1] - City_Map[DNA[0]][1]) ** 2)
return dis
def getfitness(pop): # 计算种群适应度,这里适应度用距离的倒数表示
fitness = np.array([1 / distance(DNA) for DNA in pop])
return fitness - np.min(fitness) + 1e-4 # 保证适应度为正数
def select(pop, fitness): # 根据适应度选择,以赌轮盘的形式
index = np.random.choice(np.arange(len(pop)), size=POP_SIZE, replace=True, p=fitness / fitness.sum())
return [pop[i] for i in index]
def mutation(DNA, MUTA_RATE): # 进行变异
if np.random.rand() < MUTA_RATE:
mutate_point1 = np.random.randint(0, DNA_SIZE)
mutate_point2 = np.random.randint(0, DNA_SIZE)
while mutate_point1 == mutate_point2:
mutate_point2 = np.random.randint(0, DNA_SIZE)
DNA[mutate_point1], DNA[mutate_point2] = DNA[mutate_point2], DNA[mutate_point1]
def crossmuta(pop, CROSS_RATE): # 交叉变异
new_pop = []
for parent in pop:
child = parent.copy()
if np.random.rand() < CROSS_RATE:
mate = pop[np.random.randint(POP_SIZE)].copy()
k1, k2 = sorted(random.sample(range(DNA_SIZE), 2))
fragment1 = child[k1:k2]
fragment2 = mate[k1:k2]
child[k1:k2] = fragment2
mate[k1:k2] = fragment1
child = resolve_conflict(child, fragment1, fragment2, k1, k2)
mutation(child, MUTA_RATE)
new_pop.append(child)
return new_pop
def resolve_conflict(child, fragment1, fragment2, k1, k2):
left_part = child[:k1]
right_part = child[k2:]
conflict_free = resolve_part(left_part, fragment1, fragment2) + fragment2 + resolve_part(right_part, fragment1, fragment2)
return conflict_free
def resolve_part(part, fragment1, fragment2):
result = []
for gene in part:
while gene in fragment2:
gene = fragment1[fragment2.index(gene)]
result.append(gene)
return result
def print_info(pop): # 用于输出结果
fitness = getfitness(pop)
maxfitness = np.argmax(fitness)
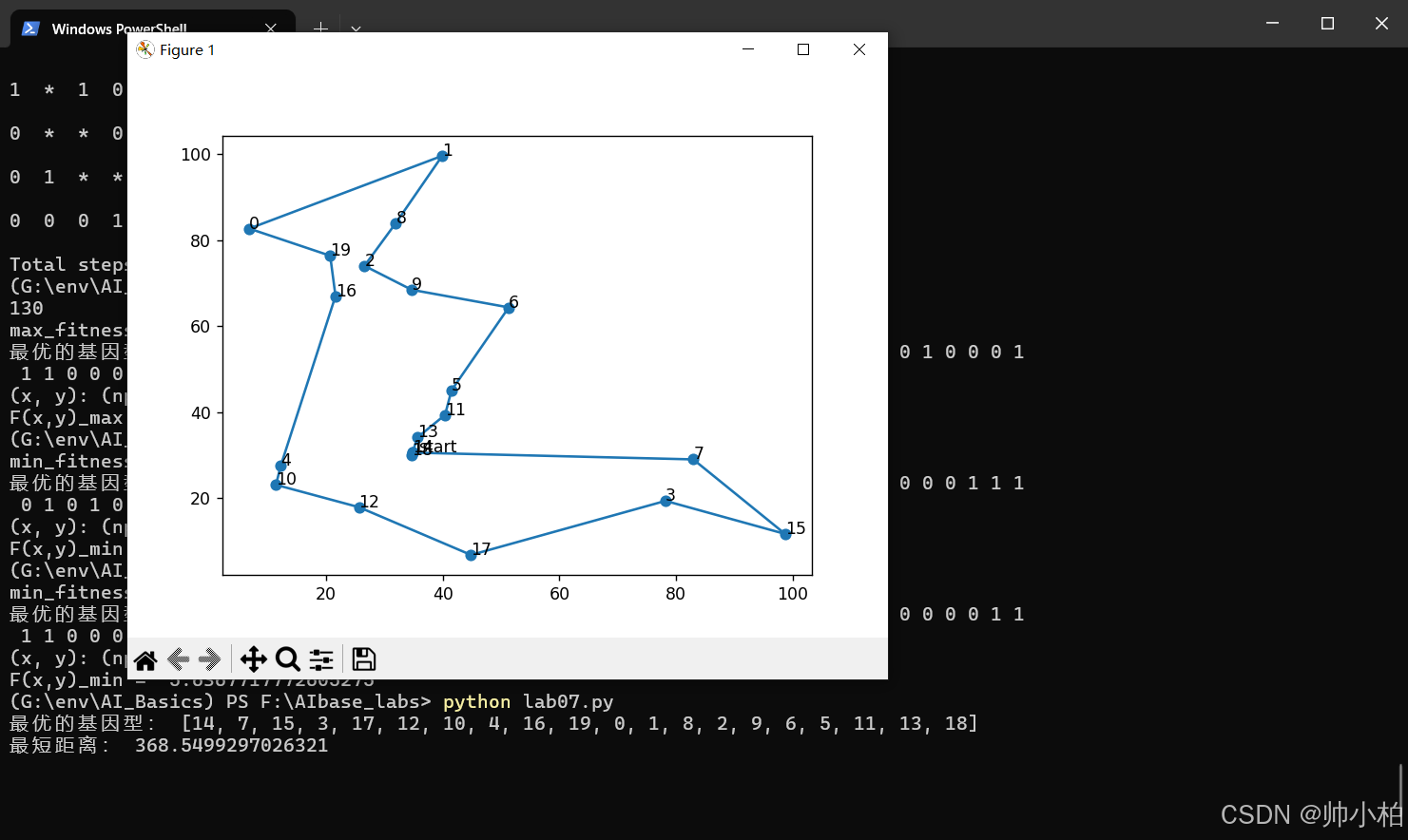
print("最优的基因型:", pop[maxfitness])
print("最短距离:", distance(pop[maxfitness]))
best_map = [City_Map[i] for i in pop[maxfitness]]
best_map.append(City_Map[pop[maxfitness][0]])
X = np.array(best_map)[:, 0]
Y = np.array(best_map)[:, 1]
plt.figure()
plt.scatter(X, Y)
for dot in range(len(X) - 1):
plt.annotate(pop[maxfitness][dot], xy=(X[dot], Y[dot]), xytext=(X[dot], Y[dot]))
plt.annotate('start', xy=(X[0], Y[0]), xytext=(X[0] + 1, Y[0]))
plt.plot(X, Y)
plt.show()
if __name__ == "__main__":
pop = [random.sample(range(DNA_SIZE), DNA_SIZE) for _ in range(POP_SIZE)]
best_dis = []
for i in range(Iterations):
pop = crossmuta(pop, CROSS_RATE)
fitness = getfitness(pop)
maxfitness = np.argmax(fitness)
best_dis.append(distance(pop[maxfitness]))
pop = select(pop, fitness)
print_info(pop)
plt.figure()
plt.plot(range(Iterations), best_dis)
plt.xlabel('Iteration')
plt.ylabel('Distance')
plt.title('Distance over Iterations')
plt.show()
跑通打卡√
实验8 BP神经网络分类MNIST数据集
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.utils import to_categorical
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist
# 加载 MNIST 数据集
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
x_train, x_test = x_train / 255.0, x_test / 255.0
y_train, y_test = to_categorical(y_train), to_categorical(y_test)
# 模型构建
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=(28, 28)),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(500, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.5),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(1000, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.5),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(300, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax')
])
# 编译模型
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss='categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
# 训练模型
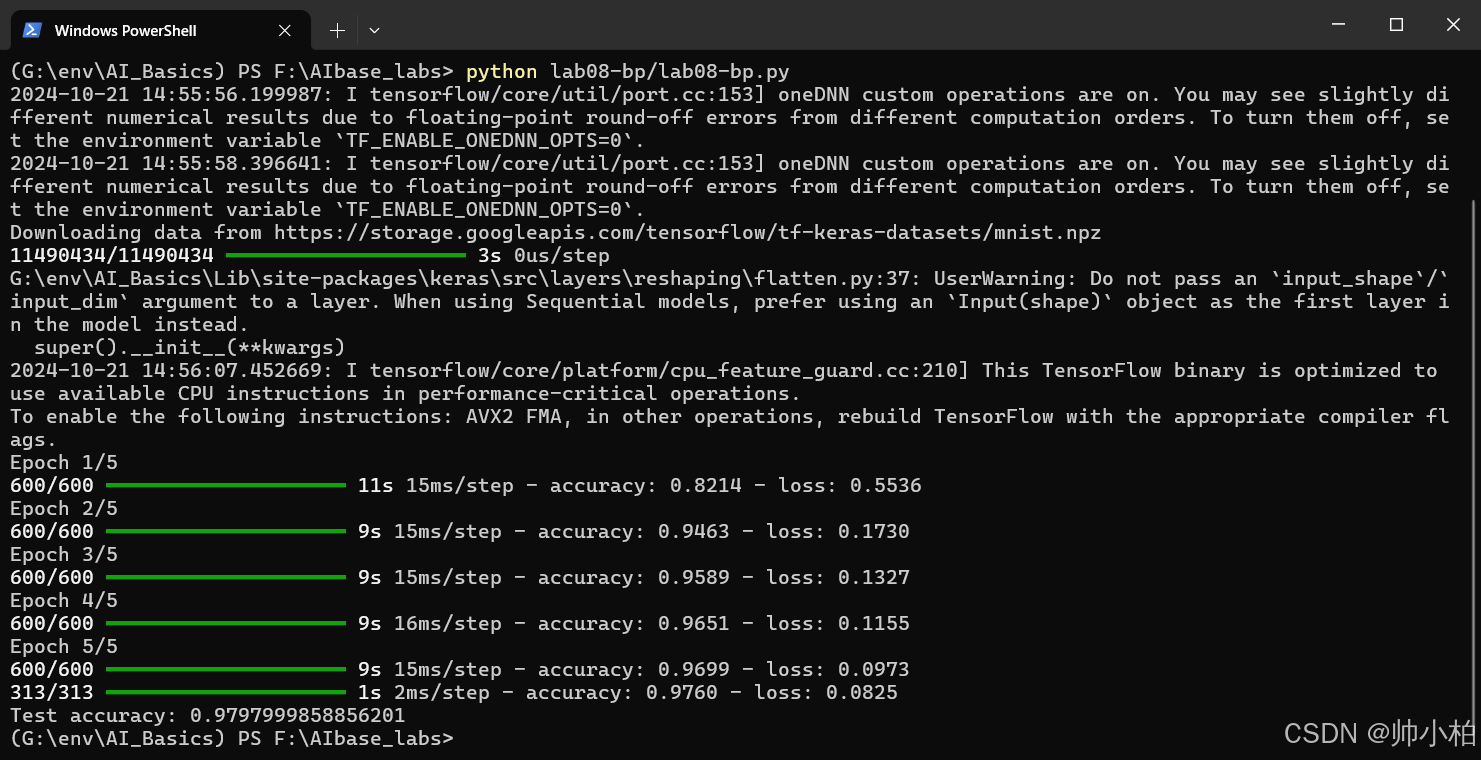
model.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs=5, batch_size=100)
# 评估模型
test_loss, test_acc = model.evaluate(x_test, y_test)
print('Test accuracy:', test_acc)
跑通打卡√
实验9 基于神经网络的优化计算
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
# 代价函数(具有三角不等式性质)
def price_cn(vec1, vec2):
return np.linalg.norm(np.array(vec1) - np.array(vec2))
# 计算该方案下,总的路径长度
def calc_distance(path):
dis = 0.0
for i in range(len(path) - 1):
dis += distance[path[i]][path[i + 1]]
return dis
# 得到城市之间的距离矩阵
def get_distance(citys):
N = len(citys)
distance = np.zeros((N, N))
for i, curr_point in enumerate(citys):
line = []
[line.append(price_cn(curr_point, other_point)) if i != j else line.append(0.0) for j, other_point in enumerate(citys)]
distance[i] = line
return distance
# 动态方程计算微分方程du
def calc_du(V, distance):
a = np.sum(V, axis=0) - 1
b = np.sum(V, axis=1) - 1
t1 = np.zeros((N, N))
t2 = np.zeros((N, N))
for i in range(N):
for j in range(N):
t1[i, j] = a[j]
for i in range(N):
for j in range(N):
t2[j, i] = b[j]
c_1 = V[:, 1:N]
c_0 = np.zeros((N, 1))
c_0[:, 0] = V[:, 0]
c = np.concatenate((c_1, c_0), axis=1)
c = np.dot(distance, c)
return -A * (t1 + t2) - D * c
# 更新神经网络的输入U
def calc_U(U, du, step):
return U + du * step
# 更新神经网络的输出V
def calc_V(U, U0):
return 1 / 2 * (1 + np.tanh(U / U0))
# 计算当前网络的能量
def calc_energy(V, distance):
t1 = np.sum(np.power(np.sum(V, axis=0) - 1, 2))
t2 = np.sum(np.power(np.sum(V, axis=1) - 1, 2))
idx = [i for i in range(1, N)]
idx = idx + [0]
Vt = V[:, idx]
t3 = distance * Vt
t3 = np.sum(np.sum(np.multiply(V, t3)))
e = 0.5 * (A * (t1 + t2) + D * t3)
return e
# 检查路径的正确性
def check_path(V):
newV = np.zeros([N, N])
route = []
for i in range(N):
mm = np.max(V[:, i])
for j in range(N):
if V[j, i] == mm:
newV[j, i] = 1
route += [j]
break
return route, newV
# 可视化画出哈密顿回路和能量趋势
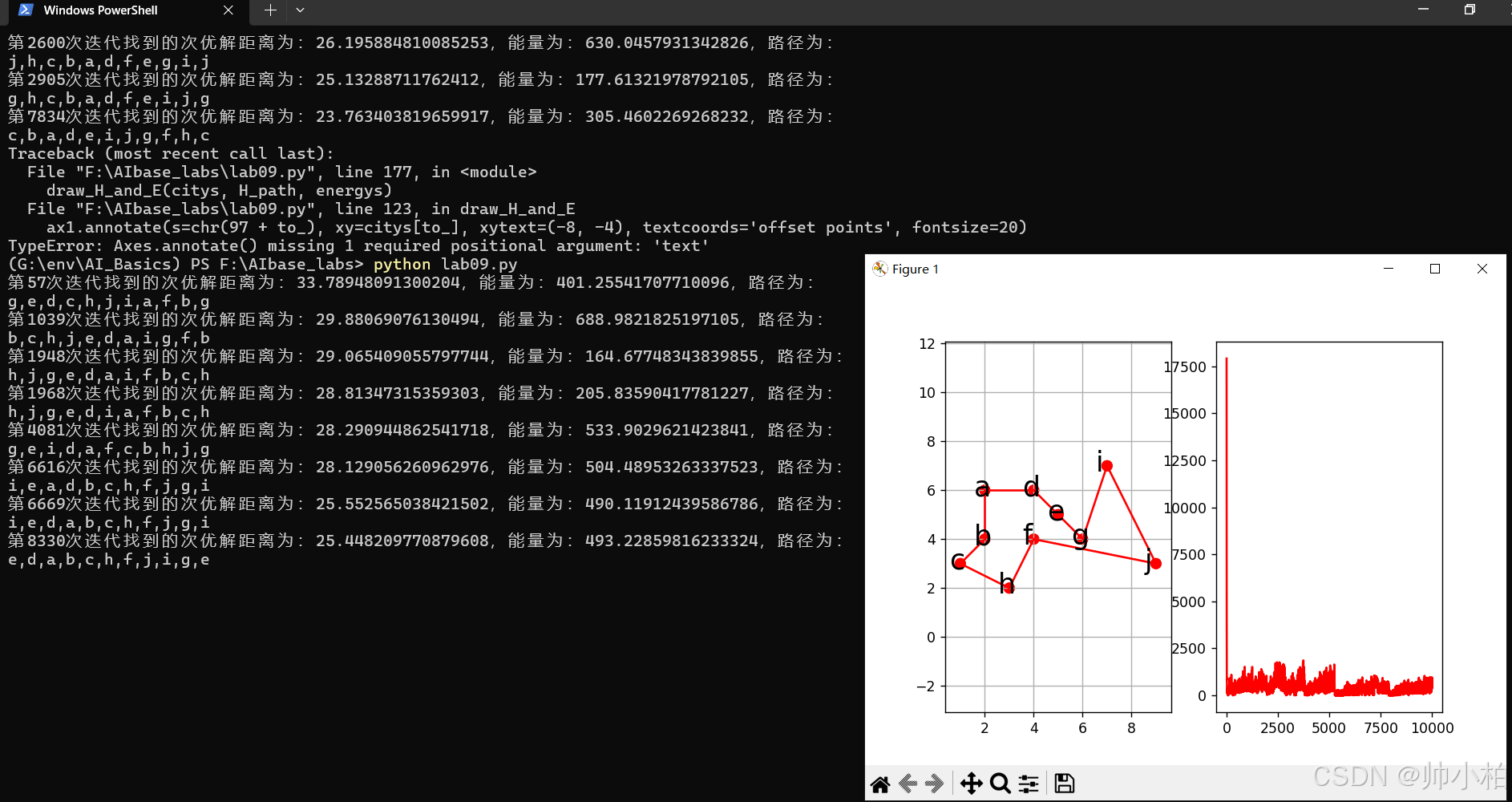
def draw_H_and_E(citys, H_path, energys):
fig = plt.figure()
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(121)
plt.xlim(0, 7)
plt.ylim(0, 7)
for (from_, to_) in H_path:
p1 = plt.Circle(citys[from_], 0.2, color='red')
p2 = plt.Circle(citys[to_], 0.2, color='red')
ax1.add_patch(p1)
ax1.add_patch(p2)
ax1.plot((citys[from_][0], citys[to_][0]), (citys[from_][1], citys[to_][1]), color='red')
ax1.annotate(text=chr(97 + to_), xy=citys[to_], xytext=(-8, -4), textcoords='offset points', fontsize=20)
ax1.axis('equal')
ax1.grid()
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(122)
ax2.plot(np.arange(0, len(energys), 1), energys, color='red')
plt.show()
# 定义城市坐标
citys = np.array([[2, 6], [2, 4], [1, 3], [4, 6], [5, 5], [4, 4], [6, 4], [3, 2], [7, 7], [9, 3]])
distance = get_distance(citys)
N = len(citys)
A = N * N
D = N / 2
U0 = 0.0009
step = 0.0001
num_iter = 10000
U = 1 / 2 * U0 * np.log(N - 1) + (2 * (np.random.random((N, N))) - 1)
V = calc_V(U, U0)
energys = np.array([0.0 for x in range(num_iter)])
best_distance = np.inf
best_route = []
H_path = []
for n in range(num_iter):
du = calc_du(V, distance)
U = calc_U(U, du, step)
V = calc_V(U, U0)
energys[n] = calc_energy(V, distance)
route, newV = check_path(V)
if len(np.unique(route)) == N:
route.append(route[0])
dis = calc_distance(route)
if dis < best_distance:
H_path = []
best_distance = dis
best_route = route
[H_path.append((route[i], route[i + 1])) for i in range(len(route) - 1)]
print('第{}次迭代找到的次优解距离为:{},能量为:{},路径为:'.format(n, best_distance, energys[n]))
[print(chr(97 + v), end=',' if i < len(best_route) - 1 else '\n') for i, v in enumerate(best_route)]
if len(H_path) > 0:
draw_H_and_E(citys, H_path, energys)
else:
print('没有找到最优解')
跑通打卡√
实验10 卷积神经网络分类MNIST数据集
import tensorflow as tf
import datetime
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist
def weight_variable(shape):
initial = tf.random.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=0.1)
return tf.Variable(initial)
def bias_variable(shape):
initial = tf.constant(0.1, shape=shape)
return tf.Variable(initial)
def conv2d(x, W):
return tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
def max_pool(x):
return tf.nn.max_pool2d(x, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
x_train, x_test = x_train / 255.0, x_test / 255.0
y_train = tf.one_hot(y_train, 10)
y_test = tf.one_hot(y_test, 10)
x_train = x_train[..., tf.newaxis]
x_test = x_test[..., tf.newaxis]
model = tf.keras.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(32, (5, 5), activation='relu', padding='same', input_shape=(28, 28, 1)),
tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2), padding='same'),
tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(64, (5, 5), activation='relu', padding='same'),
tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2), padding='same'),
tf.keras.layers.Flatten(),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(1024, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.5),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10)
])
loss_fn = tf.keras.losses.CategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True)
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss=loss_fn, metrics=['accuracy'])
starttime = datetime.datetime.now()
print("start: " + str(starttime))
model.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs=5, batch_size=100)
test_loss, test_acc = model.evaluate(x_test, y_test, verbose=2)
print('\nTest accuracy:', test_acc)
跑通打卡√
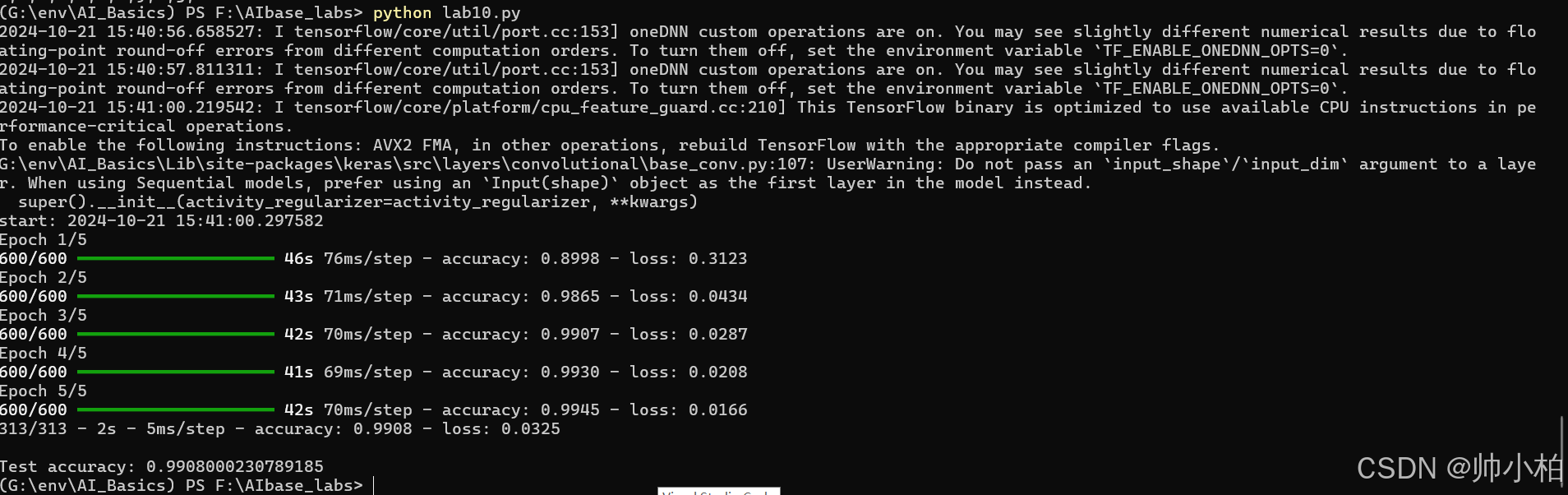
实验11 胶囊网络分类
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
from tensorflow.keras.utils import to_categorical
from tqdm import tqdm
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Conv2D, Dense, Reshape
class CapsLayer(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, epsilon, iter_routing, num_outputs, vec_len, with_routing=True, layer_type='FC'):
super(CapsLayer, self).__init__()
self.epsilon = epsilon
self.iter_routing = iter_routing
self.num_outputs = num_outputs
self.vec_len = vec_len
self.with_routing = with_routing
self.layer_type = layer_type
def build(self, input_shape):
if self.layer_type == 'FC':
self.W = self.add_weight(
shape=(1, input_shape[1], self.num_outputs * self.vec_len, input_shape[3], input_shape[4]),
initializer=tf.random_normal_initializer(stddev=0.01),
trainable=True)
def call(self, inputs, kernel_size=None, stride=None):
if self.layer_type == 'CONV':
capsules = Conv2D(self.num_outputs * self.vec_len, kernel_size, stride, padding="VALID")(inputs)
capsules = Reshape((-1, capsules.shape[-1] // self.vec_len, self.vec_len, 1))(capsules)
capsules = self.squash(capsules)
return capsules
elif self.layer_type == 'FC':
inputs = tf.reshape(inputs, shape=(-1, inputs.shape[1], 1, inputs.shape[-2], 1))
b_IJ = tf.zeros([1, inputs.shape[1], self.num_outputs, 1, 1], dtype=tf.float32)
capsules = self.routing(inputs, b_IJ)
return tf.squeeze(capsules, axis=1)
def routing(self, inputs, b_IJ):
input_shape = inputs.get_shape()
inputs = tf.tile(inputs, [1, 1, self.num_outputs * self.vec_len, 1, 1])
u_hat = tf.reduce_sum(self.W * inputs, axis=3, keepdims=True)
u_hat = tf.reshape(u_hat, shape=[-1, input_shape[1], self.num_outputs, self.vec_len, 1])
u_hat_stopped = tf.stop_gradient(u_hat)
for r_iter in range(self.iter_routing):
c_IJ = tf.nn.softmax(b_IJ, axis=2)
if r_iter == self.iter_routing - 1:
s_J = tf.multiply(c_IJ, u_hat)
s_J = tf.reduce_sum(s_J, axis=1, keepdims=True)
v_J = self.squash(s_J)
else:
s_J = tf.multiply(c_IJ, u_hat_stopped)
s_J = tf.reduce_sum(s_J, axis=1, keepdims=True)
v_J = self.squash(s_J)
v_J_tiled = tf.tile(v_J, [1, input_shape[1], 1, 1, 1])
u_produce_v = tf.matmul(u_hat_stopped, v_J_tiled, transpose_a=True)
b_IJ += tf.reduce_sum(u_produce_v, axis=0, keepdims=True)
return v_J
def squash(self, vector):
vec_squared_norm = tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(vector), -2, keepdims=True)
scalar_factor = vec_squared_norm / (1 + vec_squared_norm) / tf.sqrt(vec_squared_norm + self.epsilon)
return scalar_factor * vector
class Capsnet(tf.keras.Model):
def __init__(self, image_size, num_classes, lambda_val, m_plus, m_minus, epsilon, iter_routing, num_outputs_decode, num_dims_decode):
super(Capsnet, self).__init__()
self.image_size = image_size
self.lambda_val = lambda_val
self.m_plus = m_plus
self.m_minus = m_minus
self.epsilon = epsilon
self.iter_routing = iter_routing
self.num_outputs_layer_conv2d = 256
self.num_outputs_layer_PrimaryCaps = 32
self.num_dims_layer_PrimaryCaps = 8
self.num_outputs_decode = num_outputs_decode
self.num_dims_decode = num_dims_decode
self.conv1 = Conv2D(self.num_outputs_layer_conv2d, kernel_size=9, strides=1, padding='VALID')
self.primaryCaps = CapsLayer(self.epsilon, self.iter_routing, num_outputs=self.num_outputs_layer_PrimaryCaps, vec_len=self.num_dims_layer_PrimaryCaps, with_routing=False, layer_type='CONV')
self.digitCaps = CapsLayer(self.epsilon, self.iter_routing, num_outputs=self.num_outputs_decode, vec_len=self.num_dims_decode, with_routing=True, layer_type='FC')
self.fc1 = Dense(512)
self.fc2 = Dense(1024)
self.decoder = Dense(image_size * image_size, activation='sigmoid')
def call(self, inputs, training=None):
x, y = inputs
conv1 = self.conv1(x)
caps1 = self.primaryCaps(conv1, kernel_size=9, stride=2)
caps2 = self.digitCaps(caps1)
v_length = tf.sqrt(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(caps2), axis=2, keepdims=True) + self.epsilon)
# 打印形状以调试
tf.print("caps2 shape:", tf.shape(caps2))
tf.print("y shape:", tf.shape(y))
batch_size = tf.shape(x)[0]
y = tf.reshape(y, (batch_size, self.num_outputs_decode, 1))
# 确保维度匹配
masked_v = tf.matmul(tf.squeeze(caps2, axis=2), y, transpose_a=True)
vector_j = tf.reshape(masked_v, shape=(-1, self.num_dims_decode))
fc1_output = self.fc1(vector_j)
fc2_output = self.fc2(fc1_output)
decoded = self.decoder(fc2_output)
max_l = tf.square(tf.maximum(0., self.m_plus - v_length))
max_r = tf.square(tf.maximum(0., v_length - self.m_minus))
max_l_out = tf.reshape(max_l, shape=(-1, self.num_outputs_decode))
max_r_out = tf.reshape(max_r, shape=(-1, self.num_outputs_decode))
label_onehot_out = tf.squeeze(y, axis=2)
L_c = label_onehot_out * max_l_out + self.lambda_val * (1 - label_onehot_out) * max_r_out
margin_loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(L_c, axis=1))
reconstruction_err = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(decoded - tf.reshape(x, shape=(-1, self.image_size * self.image_size))))
return margin_loss + 0.0005 * reconstruction_err, v_length
class RunMain():
def __init__(self, image_size=28, num_classes=10, batch_size=32, lambda_val=0.5, m_plus=0.9, m_minus=0.1, epsilon=1e-9, iter_routing=3, num_outputs_decode=10, num_dims_decode=16):
self.image_size = image_size
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.lambda_val = lambda_val
self.m_plus = m_plus
self.m_minus = m_minus
self.epsilon = epsilon
self.iter_routing = iter_routing
self.num_outputs_decode = num_outputs_decode
self.num_dims_decode = num_dims_decode
self.capsnet_model = Capsnet(self.image_size, self.num_classes, self.lambda_val, self.m_plus, self.m_minus, self.epsilon, self.iter_routing, self.num_outputs_decode, self.num_dims_decode)
(self.train_images, self.train_labels), (self.test_images, self.test_labels) = tf.keras.datasets.mnist.load_data()
self.train_images = self.train_images / 255.0
self.test_images = self.test_images / 255.0
self.train_labels = to_categorical(self.train_labels, num_classes)
self.test_labels = to_categorical(self.test_labels, num_classes)
def train(self, iteration):
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam()
for step in tqdm(range(iteration), total=iteration, ncols=70, leave=False, unit='b'):
idx = np.random.choice(len(self.train_images), self.batch_size, replace=False)
image, labels = self.train_images[idx], self.train_labels[idx]
image = np.expand_dims(image, axis=-1)
labels = np.expand_dims(labels, axis=-1)
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
loss, _ = self.capsnet_model((image, labels), training=True)
grads = tape.gradient(loss, self.capsnet_model.trainable_variables)
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, self.capsnet_model.trainable_variables))
if step % 100 == 0:
print('step {}: loss = {:3.4f}'.format(step, loss))
def predict(self):
steps_per_epoch = len(self.test_images) // self.batch_size
correct = 0
num_samples = steps_per_epoch * self.batch_size
for test_step in range(steps_per_epoch):
idx = np.random.choice(len(self.test_images), self.batch_size, replace=False)
image, labels = self.test_images[idx], self.test_labels[idx]
image = np.expand_dims(image, axis=-1)
v_length = self.capsnet_model((image, labels), training=False)[1]
prediction = np.argmax(np.squeeze(v_length), axis=1)
correct += np.sum(prediction == np.argmax(labels, axis=1))
acc = correct / num_samples
print('test accuracy = {}'.format(acc))
if __name__ == "__main__":
ram_better = RunMain()
ram_better.train(200)
ram_better.predict()
跑通打卡失败×
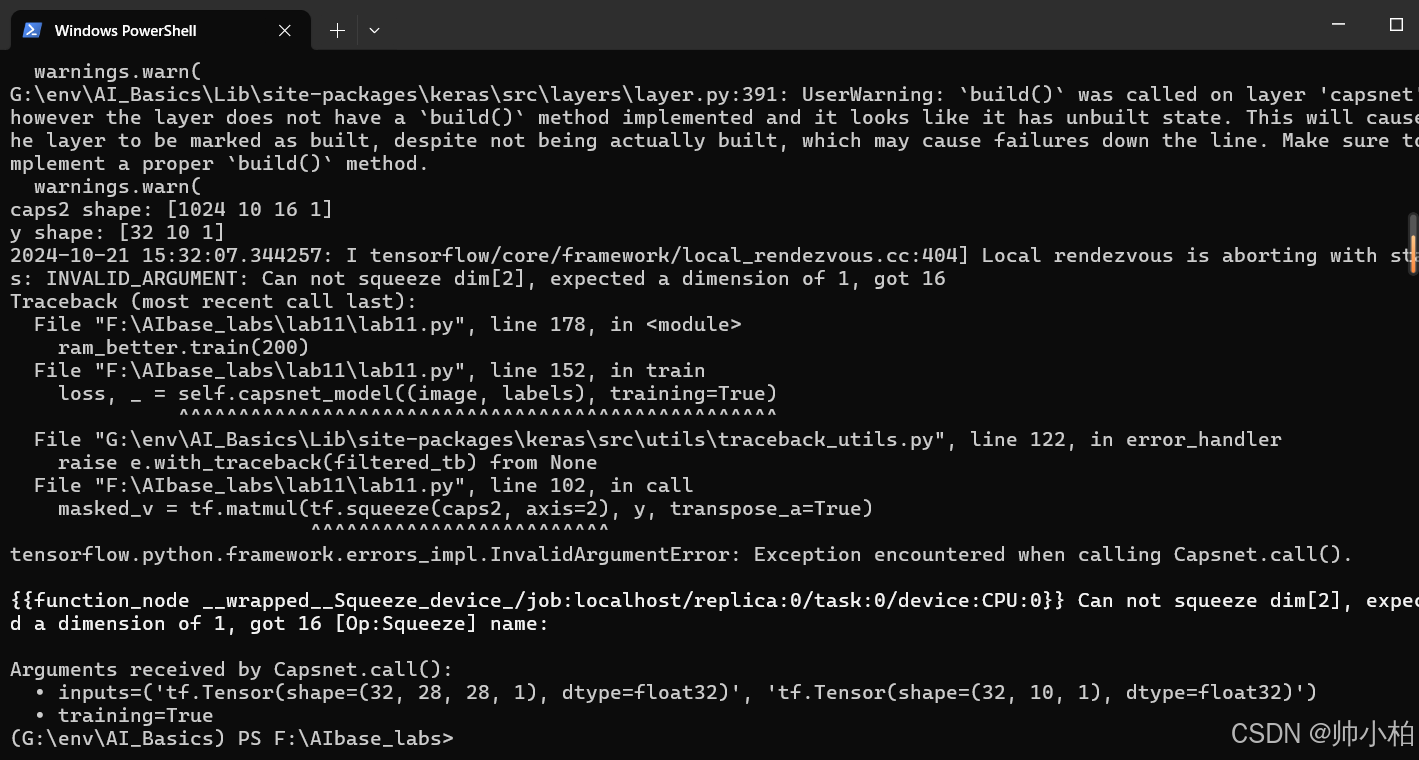
实验12 用生成对抗网络生成数字图像
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Concatenate
from tensorflow.keras.models import Model
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.gridspec as gridspec
import os
# 数据准备
mnist = tf.keras.datasets.mnist
(X_train, y_train), (_, _) = mnist.load_data()
X_train = X_train / 255.0
X_train = X_train.reshape(-1, 784)
y_train = tf.keras.utils.to_categorical(y_train, 10)
# 超参数
batch_size = 64
z_dim = 100
epochs = 100000
# 数据集
train_dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((X_train, y_train)).shuffle(10000).batch(batch_size)
# 生成器
class Generator(Model):
def __init__(self):
super(Generator, self).__init__()
self.dense1 = Dense(128, activation='relu')
self.dense2 = Dense(784, activation='sigmoid')
def call(self, z, y):
inputs = Concatenate(axis=1)([z, y])
x = self.dense1(inputs)
return self.dense2(x)
# 判别器
class Discriminator(Model):
def __init__(self):
super(Discriminator, self).__init__()
self.dense1 = Dense(128, activation='relu')
self.dense2 = Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')
def call(self, x, y):
inputs = Concatenate(axis=1)([x, y])
x = self.dense1(inputs)
return self.dense2(x)
def sample_Z(m, n):
return np.random.uniform(-1., 1., size=[m, n])
# 损失和优化器
cross_entropy = tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy(from_logits=False)
generator = Generator()
discriminator = Discriminator()
g_optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(1e-4)
d_optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(1e-4)
@tf.function
def train_step(x, y):
batch_size = tf.shape(x)[0]
batch_size = tf.cast(batch_size, tf.int32) # 转换为整数
z = sample_Z(batch_size, z_dim).astype(np.float32)
with tf.GradientTape() as tape_g, tf.GradientTape() as tape_d:
# 生成器前向传播
x_fake = generator(z, y)
# 判别器前向传播
d_real = discriminator(x, y)
d_fake = discriminator(x_fake, y)
# 损失计算
d_loss = cross_entropy(tf.ones_like(d_real), d_real) + cross_entropy(tf.zeros_like(d_fake), d_fake)
g_loss = cross_entropy(tf.ones_like(d_fake), d_fake)
# 计算梯度并更新
grads_g = tape_g.gradient(g_loss, generator.trainable_variables)
grads_d = tape_d.gradient(d_loss, discriminator.trainable_variables)
g_optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads_g, generator.trainable_variables))
d_optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads_d, discriminator.trainable_variables))
return d_loss, g_loss
def plot(samples, epoch):
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(4, 4))
gs = gridspec.GridSpec(4, 4)
gs.update(wspace=0.05, hspace=0.05)
for i, sample in enumerate(samples):
ax = plt.subplot(gs[i])
plt.axis('off')
ax.set_xticklabels([])
ax.set_yticklabels([])
ax.set_aspect('equal')
plt.imshow(sample.reshape(28, 28), cmap='Greys_r')
plt.savefig('out/epoch_{}.png'.format(str(epoch).zfill(3)), bbox_inches='tight')
plt.close(fig)
# 创建输出目录
if not os.path.exists('out/'):
os.makedirs('out/')
# 训练循环
for epoch in range(epochs):
for x_batch, y_batch in train_dataset:
d_loss, g_loss = train_step(x_batch, y_batch)
if epoch % 1000 == 0:
z_sample = sample_Z(16, z_dim).astype(np.float32)
y_sample = np.zeros(shape=[16, 10])
y_sample[:, 4] = 1
samples = generator(z_sample, y_sample).numpy()
plot(samples, epoch)
print('Epoch: {}, D loss: {:.4f}, G loss: {:.4f}'.format(epoch, d_loss, g_loss))
跑通打卡失败×
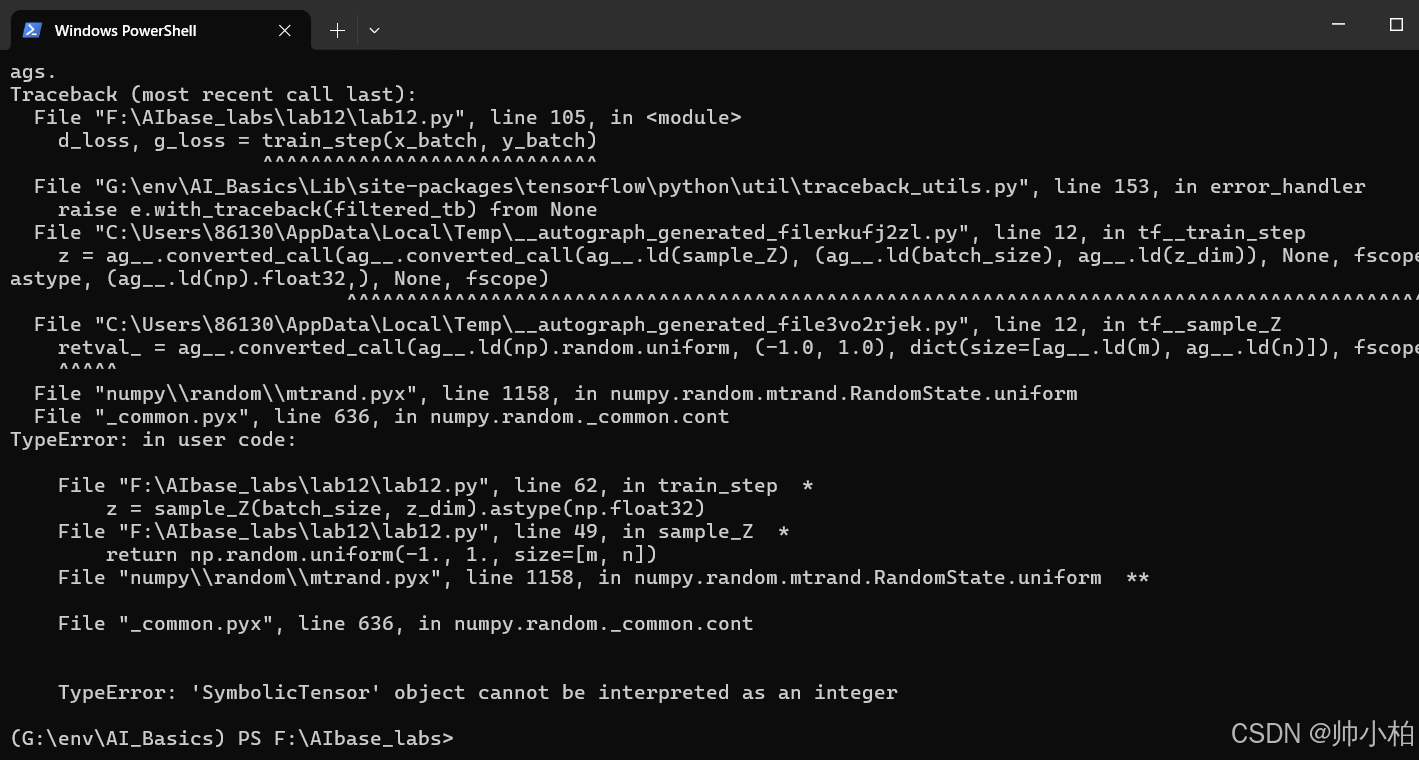



























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










