1、准备工作
mysql 8.0.27版本
CREATE TABLE `t_student` (
`id` bigint NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`age` int DEFAULT NULL,
`name` varchar(255) COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `idx_age` (`age`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=38 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_general_ci;
INSERT INTO `t_student` (`id`, `age`) VALUES (5, 10);
INSERT INTO `t_student` (`id`, `age`) VALUES (10, 15);
INSERT INTO `t_student` (`id`, `age`) VALUES (15, 60);
INSERT INTO `t_student` (`id`, `age`) VALUES (20, 50);
INSERT INTO `t_student` (`id`, `age`) VALUES (25, 40);
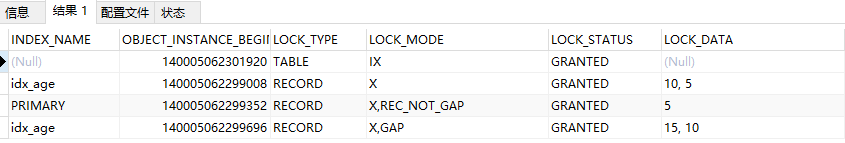
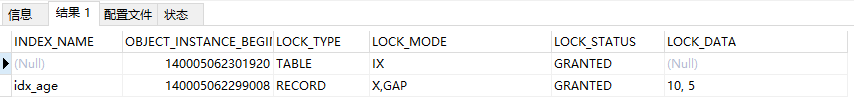
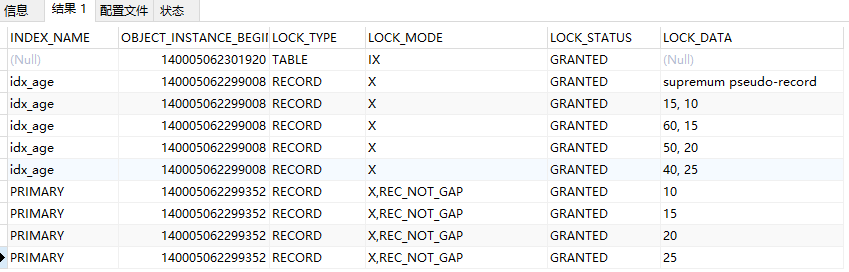
select * from performance_schema.data_locks; --查询锁信息
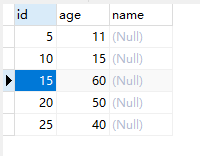
存在主键索引范围【5,25】
supremum是临界最大值
间隙锁:(-supremum,5)(5,10)(10,15)...(25,+supremum)
next-key:(-supremum,5】(5,10】(10,15】...(25,+supremum】
age索引和主键有关,(id,age)--->>((5,11),(10,15)】...((25,40),(+supremum,+supremum)】,为了方便以下记为(11,15】...(40,+supremum)
2、前引结论
1、加锁基本单位是next-key lock,前开后闭
2、访问到数据才会加锁,数据不存在就往后继续访问
3、等值查询:给唯一索引加锁,数据存在next-key lock退化为行锁,数据不存在next-key lock退化为间隙锁
4、某些例子让人头大,不明嚼栗,需要结合explain分析(结合索引下推,自己实践)
- 对于锁定读,如果一条二级索引记录不符合索引条件的下推中的条件,即使隔离级别不大于RC,也不会释放该记录上的锁
以下主要实践行锁,其他锁实践结论较简单,这里不做实验。
3、行锁实践
锁的使用主要和mysql隔离级别、数据是否存在有关 ,本次采用RR级别
主要是对唯一索引、普通索引做的等值查询和范围查询
唯一索引
等值查询
|
步骤(数据存在) |
事务A |
事务B |
|
1 |
begin; | |
|
2 |
select * from t_student where id = 10 for update; | |
|
3 |
id = 10的数据存在,用到记录锁 |
insert into t_student(id, age) values (2,7); -- 不阻塞 |
|
commit; |
|
步骤(数据不存在) |
事务A |
事务B |
|
1 |
begin; | |
|
2 |
select * from t_student where id = 9 for update; | |
|
3 |
id = 9 的数据不存在,用到(5,10)间隙锁 |
insert into t_student(id, age) values (6,0); -- 阻塞 |
|
4 |
insert into t_student(id, age) values (3,0); insert into t_student(id, age) values (11,0); update t_student set age = 11 where id = 10; update t_student set age = 6 where id = 5; -- 不阻塞 | |
|
5 |
commit; | |
|
1 |
begin; | |
|
2 |
select age from t_student where id = -1 for update; | |
|
3 |
(-∞,5)被锁定
|
insert into t_student(id, age) values (4,0); -- 阻塞 update t_student set age = 0 where id = 5; -- 不阻塞 |
|
4 |
commit; | |
|
1 |
begin; | |
|
2 |
select age from t_student where id = 444 for update; | |
|
3 |
(25,+∞)被锁定
|
insert into t_student(id, age) values (26,0); -- 阻塞 update t_student set age = 0 where id = 25; -- 不阻塞 |
|
4 |
范围查询(需要查看explain计划)
|
步骤 |
事务A |
事务B |
|
1 |
begin; | |
|
2 |
select * from t_student where id >= 6 for update; | |
|
3 |
id = 6 的数据不存在,用到(5,10]临建锁,(10,+maximum)临建锁 |
insert into t_student(id, age) values (6,7); -- 阻塞 |
|
4 |
update t_student set age = 0 where id = 10; -- 阻塞 | |
|
5 |
update t_student set age = 0 where id = 5; -- 不阻塞 | |
|
6 |
commit; |
普通索引
等值查询
不能确定唯一性,即使定位到记录,也是会向后查询,直到查询到不为该值的记录,从而间隙锁锁定该值的区间
|
步骤(数据存在,会对该主键加行锁) |
事务A |
事务B |
|
1 |
begin; | |
|
2 |
select id from t_student where age = 10 for update; | |
|
3 |
|
insert into t_student(id, age) values (-7, 18); -- 不阻塞 insert into t_student(age) values (14); -- 阻塞 |
|
commit; |
|
步骤(数据不存在) |
事务A |
事务B |
|
1 |
begin; | |
|
2 |
select id from t_student where age = 6 for update; | |
|
3 |
age = 6的数据不存在(-∞,10)间隙锁
age在锁范围需要看id |
insert into t_student(id, age) values (6, 10); -- 不阻塞 insert into t_student(id, age) values (6, 5); -- 阻塞 |
|
commit; |
范围查询(需要查看explain计划)
|
步骤 |
事务A |
事务B |
|
1 |
begin; | |
|
2 |
select * from t_student where age >= 12 for update; | |
|
3 |
age = 12 的数据不存在,用到(12,15]临建锁,(15,+maximum)临建锁,对应主键行锁
|
insert into t_student(id, age) values (6,20); -- 阻塞 |
|
4 |
update t_student set age = 0 where id = 10; -- 阻塞 | |
|
5 |
update t_student set age = 0 where id = 5; -- 不阻塞 | |
|
6 |
commit; |
最后留下一个问题:
select id from t_student where id >= 5 for update; 会加哪种锁呢?








 本文通过具体实例演示了MySQL中行锁的工作原理,特别是在重复读隔离级别下,针对唯一索引和普通索引进行等值查询及范围查询时的加锁行为。
本文通过具体实例演示了MySQL中行锁的工作原理,特别是在重复读隔离级别下,针对唯一索引和普通索引进行等值查询及范围查询时的加锁行为。
















 1302
1302

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








