斐波那契序列:
- 规则:当前这个数值,等于其当前两位数值的和,示例如:1 1 2 3 5 8 13
- 实现方法:递归实现
- 递归实现的要点:
终止条件
循环主体 - 具体代码实现:
//------斐波那契------------
class FiberTest{
public static int fiber (int location){
if (location<1){
return -1;
}
if (location == 1 || location == 2 ){
return 1;
}
else{
return fiber(location-1)+fiber(-2);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(fiber(-100));
System.out.println(fiber(1));
System.out.println(fiber(2));
System.out.println(fiber(5));
System.out.println(fiber(7));
}
}

---------阶乘------------
class FacTest{
public static long fac (int n){
if (n < 1){
return -1;
}
if (n == 1){
return 1;
}
else {
return n*fac(n-1);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
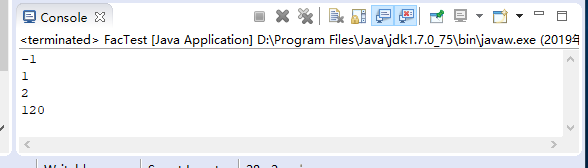
System.out.println(fac(-3));
System.out.println(fac(1));
System.out.println(fac(2));
System.out.println(fac(5));
}
}
```
//------阶乘的阶乘---------
class FacFacTest{
public static long fac(int n){
if (n<1){
return -1;
}
if(n == 1){
return 1;
}
else {
return n*fac(n - 1);
}
}
public static long facFac(int n){
if(n < 1){
return -1;
}
if (n == 1 ) {
return 1;
}
else {
return fac(n)*facFac(n - 1);
}
}
public static void main (String[] args){
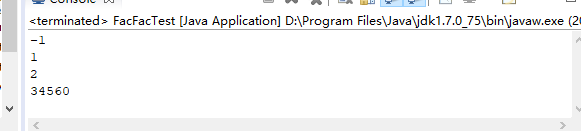
System.out.println(facFac(-3));
System.out.println(facFac(1));
System.out.println(facFac(2));
System.out.println(facFac(5));
}
}











 本文介绍了如何使用Java语言通过递归方法实现斐波那契序列、阶乘及阶乘的阶乘。斐波那契序列遵循每个数是前两个数之和的规则,递归实现需设定终止条件和递归主体。具体代码实现虽未展示,但读者可期待详细步骤和逻辑解析。
本文介绍了如何使用Java语言通过递归方法实现斐波那契序列、阶乘及阶乘的阶乘。斐波那契序列遵循每个数是前两个数之和的规则,递归实现需设定终止条件和递归主体。具体代码实现虽未展示,但读者可期待详细步骤和逻辑解析。
















 1111
1111

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








