一、事件监听
监听原生组件的事件采用链式调用,注册事件必须采用箭头函数的写法。
Column(){
TextInput({placeholder: '请输入用户名'}).margin({bottom: 20})
.onChange((value)=>{
promptAction.showToast({message: value})
})
.onSubmit(()=>{
AlertDialog.show({message: '登录失败' })
})
Button('登录').width('100%')
.onClick(()=>{
promptAction.showDialog({message: '登录成功'})
})
}.height('100%')
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.padding({left: 20, right: 20})

对输入框注册onChange事件(输入框内容改变触发),对输入框注册onSubmit事件(提交输入框信息时触发),对按钮注册onClick事件(点击按钮触发)
二、组件状态
@State装饰的变量,或称为状态变量,一旦变量拥有了状态属性,就可以触发其直接绑定UI组件的刷新。当状态改变时,UI会发生对应的渲染改变,从而实现实时刷新页面。
2.1 简单数据
当@State装饰的数据是简单数据时,数据只要发生改变就会重新渲染UI。
@State username:string = ""
@State password:string = ""
login(){
if (this.username == "admin" && this.password == "123456") {
AlertDialog.show({message: '登录成功'})
return
}
promptAction.showToast({message: '登录失败'})
}
build() {
Row(){
Column({space: 20}){
TextInput({placeholder: '请输入用户名', text: this.username})
.onChange((value)=>{
this.username = value
})
TextInput({placeholder: '请输入密码', text: this.password})
.onChange((value)=>{
this.password = value
}).type(InputType.Password)
Button('登录').width('100%')
.onClick(()=>{
this.login()
})
}.width('100%').padding({left: 20, right: 20})
}.height('100%')
}

将username和password作为状态变量,实时刷新UI。
2.2 复杂数据
当数据是复杂数据时(比如对象),对象自身或自身属性改变时才能监测到,再下一层则无法监测到。
@Entry
@Component
struct InfoCase {
@State p:IPersonModel = new IPersonModel({
name: '小李',
age: 20,
sex: '男',
address: {
province: '四川',
city: '成都',
area: '武侯'
}
})
build() {
Column({space: 10}){
Row({space: 15}){
Text('姓名:')
TextInput({text: this.p.name}).layoutWeight(1)
.onChange(value=>{
this.p.name = value
})
}.padding(10)
Row({space: 15}){
Text('年龄:')
TextInput({text: this.p.age.toString()}).layoutWeight(1)
.onChange(value=>{
this.p.age = parseInt(value)
})
}.padding(10)
Row({space: 15}){
Text('性别:')
Select([{value: '男'},{value: '女'}])
.layoutWeight(1)
.value(this.p.sex)
.onSelect((index:number, value: string)=>{
this.p.sex = value as '男'|'女'
})
}.padding(10)
Row({space: 15}){
Text('地址:')
TextInput({text: this.p.address.province}).layoutWeight(1)
.onChange((value)=>{
this.p.address.province = value
})
TextInput({text: this.p.address.city}).layoutWeight(1)
.onChange((value)=>{
this.p.address.city = value
})
TextInput({text: this.p.address.area}).layoutWeight(1)
.onChange((value)=>{
this.p.address.area = value
})
}.padding(10)
Row({space: 10}){
Button('修改姓名')
.onClick(()=>{
this.p.name = '老李'
})
Button('修改年龄')
.onClick(()=>{
this.p.age = 35
})
Button('修改地址')
.onClick(()=>{
// 自身属性的属性不能直接修改
this.p.address.province = '重庆'
// 需要修改自身的属性
this.p.address = new IAddressModel(this.p.address)
})
}
}.padding(10)
}
}
interface IAddress{
province: string
city: string
area: string
}
interface IPerson {
name: string
age: number
sex: '男'|'女'
address: IAddress
}
export class IAddressModel implements IAddress{
province: string = ''
city: string = ''
area: string = ''
constructor(model: IAddress) {
this.province = model.province
this.city = model.city
this.area = model.area
}
}
export class IPersonModel implements IPerson{
name: string = ''
age: number = 0
sex: "男" | "女" = '男'
address: IAddress = new IAddressModel({} as IAddress)
constructor(model: IPerson) {
this.name = model.name
this.age = model.age
this.sex = model.sex
this.address = model.address
}
}
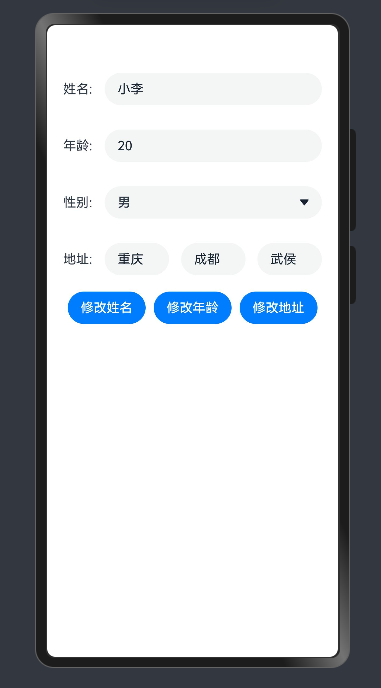
修改复杂对象时,直接修改对象本身和对象的属性是能直接渲染到ui,但修改对象属性中的对象属性时则不能,需要new一个新对象进行修改。
























 1012
1012

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








