该系列博客衍生于我所参与的一个校企合作项目,作为该项目的一名成员,我无法公开项目的代码,文中出现的所有代码以及流程图均与原项目不同,包括代码的语言选择、通讯的流程图、通讯协议等。
原项目中的实现功能如下:
- 在 Linux 上使用 ROS 的收发机制来实现通讯模块与无人驾驶模块的数据传输;
- 在推耙机与中控室之间主要使用基于 TCP 协议的自定义数据帧的形式来进行数据传输,采用 Python 实现。
而本系列博客的最终需求是在两台不同主机之间使用基于 TCP 协议的自定义数据帧的形式来进行数据传输。代码采用的是基于 Java 的通讯实现。 下面是学习的过程:
目录:
1 需求分析
需求:实现客户端正常连接服务器端之后,客户端可以通过向服务器端发送具体指令来获得服务器端的相应数据。其中,指令所代表的含义规定如下:
| 指令 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| 1818 | 请求实验室人员的数量 |
| 1819 | 请求服务器中实验室人员的平均补贴 |
| …… | …… |
| 0000 | 退出与服务器的连接 |
1.1 绘制流程图
依据需求,通过画出对应的流程图来理清自己的思路,然后根据流程图写出相应代码。

2 基本概念
2.1 TCP 的报文协议
TCP 的报文协议与 Socket 数据包协议是两个概念,一个是更加底层,一个是上层的 Socket 的自定义数据帧。
TCP 的报文协议一般在底层优化的时候用到,其大致内容如下:
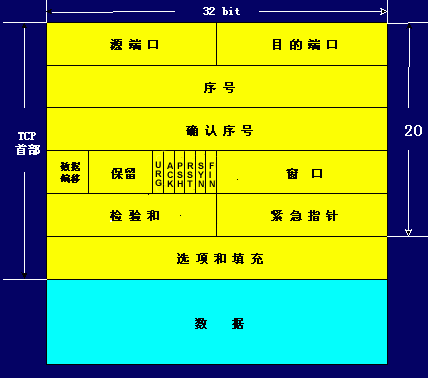
感兴趣的朋友可以阅读这篇博客,讲的比较清楚。【传送门】
2.2 基于 Socket 的自定义数据帧
这一层协议是我们常用的。
在实际工作中,当对方主机接收到我们的数据时,一方面需要校验该段数据是否是指定主机发出的;另一方面,则要保证该数据是完整的。
比如我们使用如下 Socket 的自定义数据帧来传输,其中的校验码则是为了保证该段数据是否是指定主机发出的;消息体长度则是为了保证对方可以完整地接收数据。

2.3 位运算
如上一节所示,自定义数据帧中每一块内容的长度是用 byte,即字节来定义的,同时两台主机的 Socket 传输内容实际上是使用 byte[] ,即字节数组的方式。所以我们必须要掌握 int 型与 byte[] 型的转换方式。
2.3.1 int 型到 byte[] 型的转换
/**
* int到byte[]
* @param i 输入待转换的int
* @return 返回的对应的byte[]
*/
public static byte[] intToByteArray(int i) {
byte[] result = new byte[4];
//由高位到低位
result[0] = (byte)((i >> 24) & 0xFF);
result[1] = (byte)((i >> 16) & 0xFF);
result[2] = (byte)((i >> 8) & 0xFF);
result[3] = (byte)(i & 0xFF);
return result;
}
2.3.2 byte[] 型到 int 型的转换:
/**
* byte[]转int
* @param bytes 指定的byte[]
* @return int型的值
*/
public static int byteArrayToInt(byte[] bytes) {
return (bytes[3] & 0xFF) |
(bytes[2] & 0xFF) << 8 |
(bytes[1] & 0xFF) << 16 |
(bytes[0] & 0xFF) << 24;
}
在计算机中,“位”才是最小单位,1byte(字节)= 8 bit(位),更多关于位运算的知识,可以参考这篇博客。【传送门】
3 代码实现
为了更好的说明代码中每一步代表的含义,我将代码的解释说明注释在了代码中,如果我有写得不清楚的地方可以评论或者私信我,我会第一时间回复。
3.1 客户端代码
import java.io.*;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Client {
public static <Int> void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//连接服务器
// 127.0.0.1 指代的是本地电脑的 IP 地址
Socket s = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 5612);
System.out.println("已连接到服务器5612端口,准备向服务器发送指令。");
//获取输出流
OutputStream out = s.getOutputStream();
while(true){
//服务端开始输入指令
System.out.println("请输入指令:");
System.out.println("1819:请求服务器中实验室人员的数量");
System.out.println("1820:请求服务器中实验室人员的平均补贴");
System.out.println("0000:退出与服务器的连接");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int instruction=scanner.nextInt();
if(instruction != 1819 && instruction != 1820 && instruction != 0000){
System.out.println("输入的指令有误,请重新输入");
continue;
}
// 如果客户端不选择主动退出
if (instruction!=0000) {
//将int型指令转化为byte[]
byte[] instructionArr = intToByteArray(instruction);
//将byte[]指令按照Socket数据包协议编码成新的数组
byte[] sendSocketArr = encode(instructionArr);
//开始在输出流中发送数据
out.write(sendSocketArr, 0, sendSocketArr.length);
System.out.println("指令已经按照协议编码好发送给服务器端,等待服务器端数据返回");
/下面就是为了接收服务器端返回的数据//
InputStream in = s.getInputStream();
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(in);
//卧槽,用BufferedInputStream代替了InputStream,问题就解决了。
byte[] bs = new byte[1024 * 100];
bis.read(bs);
// 将接收到的字节数据的前几位打印出来,看看是否正确
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(Arrays.copyOfRange(bs, 0, 16)));
//首先确定校验符
//提取出指定校验符的指定位置
byte[] checkCharacterArr = subBytes(bs, 2, 4);
//将字节数组转化为int类型
int checkCharacter = byteArrayToInt(checkCharacterArr);
//根据校验符判断该Socket数据包是否是我们的数据包
if (checkCharacter == 888) {
//同理,从数据包中得到消息体的长度
byte[] lengthMsgArr = subBytes(bs, 6, 4);
//将字节数组转化为int类型
int lengthMsg = byteArrayToInt(lengthMsgArr);
System.out.println("消息体长度"+lengthMsg);
//当知道数据包中消息体的长度后,便可以根据长度来解析出Socket的消息体
byte[] destMsg = subBytes(bs, 10, lengthMsg);
//按照Socket协议解码之后的数据
switch (instruction) {
case 1819:
int speed = byteArrayToInt(destMsg);
System.out.printf("此时,实验室人员的数量有 %d 人\n", speed);
break;
case 1820:
int volume=byteArrayToInt(destMsg);
System.out.printf("实验室人员的平均补贴为 %d 元\n",volume);
break;
default:
break;
}
System.out.println("数据接收完毕。\n");
}
}
else{
System.out.println("退出连接");
break;
}
}
//关闭通道
out.close();
s.close();
}
/**
* 用于Socket数据包的解码,该方法并没有编写完成,比如若校验错误,则返回{-1,-1};
*开始解析数据包,不考虑粘包的情况。目前先假设数据包格式为:消息头(包头+校验符+消息体长度)+消息体。
*假设包头为:head[0]+head[1] 其中内容如下。校验码为int型的888,消息体长度为int型(取值范围为-2147483648到+-2147483648),消息体为byte[]
*这样的话消息头总共占有10(2字节+int型的4字节+int型的4字节)字节,消息体则放在消息头后面
* @param msg 整个Socket数据包
* @return 返回消息体
*/
public static byte[] decodeMsg(byte[] msg){
//首先确定校验符
//提取出指定校验符的指定位置
byte[] checkCharacterArr=subBytes(msg,2, 4);
//将字节数组转化为int类型
int checkCharacter=byteArrayToInt(checkCharacterArr);
//根据校验符判断该Socket数据包是否是我们的数据包
// if (checkCharacter==888) {
//同理,从数据包中得到消息体的长度
byte[] lengthMsgArr = subBytes(msg, 6, 4);
//将字节数组转化为int类型
int lengthMsg = byteArrayToInt(lengthMsgArr);
//当知道数据包中消息体的长度后,便可以根据长度来解析出Socket的消息体
byte[] destMsg = subBytes(msg, 10, lengthMsg);
return destMsg;
// }else{
// return new byte[]{-1, -1};
// }
}
/**
* Socket数据包协议
* @param fileArr 输入的指令或者数据,要求为字节数组型
* @return 根据Socket数据包协议编码的字节数组
*/
public static byte[] encode(byte[] fileArr){
byte[] head1 = new byte[2];
head1[0] = (byte) 0;
head1[1] = (byte) 1;
byte[] head2 = intToByteArray(888);
byte[] head3 = intToByteArray(fileArr.length);
//head是包的标识符
byte[] head = byteConcat(head1, head2, head3);
byte[] data = byteMerger(head, fileArr);
return data;
}
/**
* int到byte[]
* @param i 输入待转换的int
* @return 返回的对应的byte[]
*/
public static byte[] intToByteArray(int i) {
byte[] result = new byte[4];
//由高位到低位
result[0] = (byte)((i >> 24) & 0xFF);
result[1] = (byte)((i >> 16) & 0xFF);
result[2] = (byte)((i >> 8) & 0xFF);
result[3] = (byte)(i & 0xFF);
return result;
}
/**
* byte[]转int
* @param bytes 指定的byte[]
* @return int型的值
*/
public static int byteArrayToInt(byte[] bytes) {
return (bytes[3] & 0xFF) |
(bytes[2] & 0xFF) << 8 |
(bytes[1] & 0xFF) << 16 |
(bytes[0] & 0xFF) << 24;
}
public static byte[] byteConcat(byte[] bt1, byte[] bt2, byte[] bt3) {
byte[] bt4 = new byte[bt1.length + bt2.length + bt3.length];
int len = 0;
System.arraycopy(bt1, 0, bt4, 0, bt1.length);
len += bt1.length;
System.arraycopy(bt2, 0, bt4, len, bt2.length);
len += bt2.length;
System.arraycopy(bt3, 0, bt4, len, bt3.length);
return bt4;
}
public static byte[] byteMerger(byte[] bt1, byte[] bt2) {
byte[] bt3 = new byte[bt1.length + bt2.length];
System.arraycopy(bt1, 0, bt3, 0, bt1.length);
System.arraycopy(bt2, 0, bt3, bt1.length, bt2.length);
return bt3;
}
/**
* 利用System.arraycopy的方法在字节数组中截取指定长度数组
* @param src
* @param begin
* @param count
* @return
*/
public static byte[] subBytes(byte[] src, int begin, int count) {
byte[] bs = new byte[count];
System.arraycopy(src, begin, bs, 0, count);
return bs;
}
}
3.2 服务器端代码
import java.io.*;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//服务器开始监听5612端口
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(5612);
System.out.println("服务端已启动,正在监听5612端口...");
//等待客户端连接
Socket s = serverSocket.accept();
//获取输入流:服务器指令。指令的大小利用一个1024的数组肯定是可以存储的
InputStream in = s.getInputStream();
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(in);
while(true){
//一样的字节数组缓冲操作,将IO流中的数据放到buf数组中
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int length = bis.read(buf);
if (length!=-1){
//解析数据包,得到服务器的请求
//首先确定校验符
//提取出指定校验符的指定位置
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(buf));
byte[] checkCharacterArr = subBytes(buf, 2, 4);
//将字节数组转化为int类型
int checkCharacter = byteArrayToInt(checkCharacterArr);
//根据校验符判断该Socket数据包是否是我们的数据包
if (checkCharacter == 888) {
//同理,从数据包中得到消息体的长度
byte[] lengthMsgArr = subBytes(buf, 6, 4);
//将字节数组转化为int类型
int lengthMsg = byteArrayToInt(lengthMsgArr);
//当知道数据包中消息体的长度后,便可以根据长度来解析出Socket的消息体
byte[] destMsgArr = subBytes(buf, 10, lengthMsg);
int destMsg = byteArrayToInt(destMsgArr);
//哈哈哈,原来在switch之前定义,就可以使用这个变量
byte[] sendSocketArr = null;
switch (destMsg) {
case 1819:
byte[] fileArr1819 = intToByteArray(18);
System.out.println("数据正在编码中……");
sendSocketArr = encodeMsg(fileArr1819);
break;
case 1820:
byte [] fileArr1820=intToByteArray(400);
System.out.println("数据正在编码中……");
sendSocketArr=encodeMsg(fileArr1820);
break;
default:
break;
}
OutputStream out = s.getOutputStream();
System.out.println("开始发送……");
out.write(sendSocketArr, 0, sendSocketArr.length);
// 将发送到的字节数据的前几位打印出来,并与客户端接收的数据做一个对比,看看是否正确
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(Arrays.copyOfRange(sendSocketArr, 0, 16)));
System.out.println("发送完毕。\n");
}
}else{
break;
}
}
//关闭资源。io流关闭的同时socket也会关闭,或者用什么方法隔离开。
in.close();
s.close();
serverSocket.close();
}
/**
* 用于Socket数据包的解码,该方法并没有编写完成,比如若校验错误,则返回{-1,-1};
*开始解析数据包,不考虑粘包的情况。目前先假设数据包格式为:消息头(包头+校验符+消息体长度)+消息体。
*假设包头为:head[0]+head[1] 其中内容如下。校验码为int型的888,消息体长度为int型(取值范围为-2147483648到+-2147483648),消息体为byte[]
*这样的话消息头总共占有10(2字节+int型的4字节+int型的4字节)字节,消息体则放在消息头后面
* @param msg 整个Socket数据包
* @return 返回消息体
*/
public static byte[] decodeMsg(byte[] msg){
//首先确定校验符
//提取出指定校验符的指定位置
byte[] checkCharacterArr=subBytes(msg,2, 4);
//将字节数组转化为int类型
int checkCharacter=byteArrayToInt(checkCharacterArr);
//根据校验符判断该Socket数据包是否是我们的数据包
// if (checkCharacter==888) {
//同理,从数据包中得到消息体的长度
byte[] lengthMsgArr = subBytes(msg, 6, 4);
//将字节数组转化为int类型
int lengthMsg = byteArrayToInt(lengthMsgArr);
//当知道数据包中消息体的长度后,便可以根据长度来解析出Socket的消息体
byte[] destMsg = subBytes(msg, 10, lengthMsg);
return destMsg;
// }else{
// return new byte[]{-1, -1};
// }
}
/**
* Socket数据包协议
* @param fileArr 输入的指令或者数据,要求为字节数组型
* @return 根据Socket数据包协议编码的字节数组
*/
public static byte[] encodeMsg(byte[] fileArr){
byte[] head1 = new byte[2];
head1[0] = (byte) 0;
head1[1] = (byte) 1;
byte[] head2 = intToByteArray(888);
byte[] head3 = intToByteArray(fileArr.length);
//head是包的标识符
byte[] head = byteConcat(head1, head2, head3);
byte[] data = byteMerger(head, fileArr);
return data;
}
public static byte[] byteConcat(byte[] bt1, byte[] bt2, byte[] bt3) {
byte[] bt4 = new byte[bt1.length + bt2.length + bt3.length];
int len = 0;
System.arraycopy(bt1, 0, bt4, 0, bt1.length);
len += bt1.length;
System.arraycopy(bt2, 0, bt4, len, bt2.length);
len += bt2.length;
System.arraycopy(bt3, 0, bt4, len, bt3.length);
return bt4;
}
/**
* byte[]转int
* @param bytes 指定的byte[]
* @return int型的值
*/
public static int byteArrayToInt(byte[] bytes) {
return (bytes[3] & 0xFF) |
(bytes[2] & 0xFF) << 8 |
(bytes[1] & 0xFF) << 16 |
(bytes[0] & 0xFF) << 24;
}
/**
* int到byte[]
* @param i 输入待转换的int
* @return 返回的对应的byte[]
*/
public static byte[] intToByteArray(int i) {
byte[] result = new byte[4];
//由高位到低位
result[0] = (byte)((i >> 24) & 0xFF);
result[1] = (byte)((i >> 16) & 0xFF);
result[2] = (byte)((i >> 8) & 0xFF);
result[3] = (byte)(i & 0xFF);
return result;
}
public static byte[] byteMerger(byte[] bt1, byte[] bt2) {
byte[] bt3 = new byte[bt1.length + bt2.length];
System.arraycopy(bt1, 0, bt3, 0, bt1.length);
System.arraycopy(bt2, 0, bt3, bt1.length, bt2.length);
return bt3;
}
/**
* 1.图片转为字节数组
* 图片到程序FileInputStream
* 程序到数组 ByteArrayOutputStream
*/
public static byte[] fileToByteArray(String FilePath){
//1.创建源与目的的
File src=new File(FilePath);
//在字节数组输出的时候是不需要源的。
byte[] dest=null;
//2.选择流,选择文件输入流
//方便在finally中使用,设置为全局变量
InputStream is=null;
ByteArrayOutputStream os=null;
try {
is=new FileInputStream(src);
os=new ByteArrayOutputStream();
//3.操作,读文件
//10k,创建读取数据时的缓冲,每次读取的字节个数。
byte[] flush=new byte[1024*10];
//接受长度;
int len=-1;
while((len=is.read(flush))!=-1) {
//表示当还没有到文件的末尾时
//字符数组-->字符串,即是解码。将文件内容写出字节数组
os.write(flush,0,len);
}
os.flush();
return os.toByteArray();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//4.释放资源
try {
//表示当文打开时,才需要通知操作系统关闭
if(is!=null) {
is.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* 利用System.arraycopy的方法在字节数组中截取指定长度数组
* @param src
* @param begin
* @param count
* @return
*/
public static byte[] subBytes(byte[] src, int begin, int count) {
byte[] bs = new byte[count];
System.arraycopy(src, begin, bs, 0, count);
return bs;
}
}
3.3 客户端的 Console 测试
客户端的 Console 测试如下:
已连接到服务器5612端口,准备向服务器发送指令。
请输入指令:
1819:请求服务器中实验室人员的数量
1820:请求服务器中实验室人员的平均补贴
0000:退出与服务器的连接
1819
指令已经按照协议编码好发送给服务器端,等待服务器端数据返回
[0, 1, 0, 0, 3, 120, 0, 0, 0, 4, 0, 0, 0, 18, 0, 0]
消息体长度4
此时,实验室人员的数量有 18 人
数据接收完毕。
请输入指令:
1819:请求服务器中实验室人员的数量
1820:请求服务器中实验室人员的平均补贴
0000:退出与服务器的连接
1820
指令已经按照协议编码好发送给服务器端,等待服务器端数据返回
[0, 1, 0, 0, 3, 120, 0, 0, 0, 4, 0, 0, 1, -112, 0, 0]
消息体长度4
实验室人员的平均补贴为 400 元
数据接收完毕。
请输入指令:
1819:请求服务器中实验室人员的数量
1820:请求服务器中实验室人员的平均补贴
0000:退出与服务器的连接
1818
输入的指令有误,请重新输入
请输入指令:
1819:请求服务器中实验室人员的数量
1820:请求服务器中实验室人员的平均补贴
0000:退出与服务器的连接
0000
退出连接
Process finished with exit code 0








 本文介绍了如何在TCP协议基础上构建自定义的Socket数据帧进行短数据传输,详细阐述了TCP报文协议、基于Socket的自定义数据帧及位运算的相关知识,并提供了Java代码实现客户端和服务器端的通讯。内容包括需求分析、基本概念、代码实现等部分,旨在帮助读者理解TCP数据传输的自定义帧设计和实现。
本文介绍了如何在TCP协议基础上构建自定义的Socket数据帧进行短数据传输,详细阐述了TCP报文协议、基于Socket的自定义数据帧及位运算的相关知识,并提供了Java代码实现客户端和服务器端的通讯。内容包括需求分析、基本概念、代码实现等部分,旨在帮助读者理解TCP数据传输的自定义帧设计和实现。

















 858
858

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








