神经网络的数学基础
1.数据载入
使用python的Keras库中的手写数字数据集进行实践学习
可以从网上直接下载,下载完了,直接用load载入下载好的数据及就好了:
#from keras.datasets import mnist
#(train_images,train_labels),(test_images,test_labels) = mnist.load_data()
import numpy as np
#这里用load直接load下载好的文件
data = np.load('D:\python\workspace\mnist.npz') # open and read
print(data.keys())
这里下载下来的是.npz文件,关于.npz文件,load其实是一个字典类型的对象,整个数据延迟加载,所以变量空间里是没有显示变量的,是空的
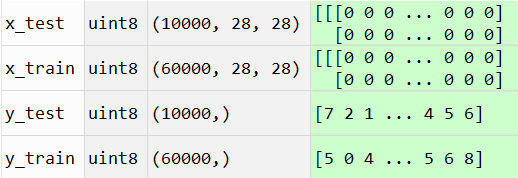
打印出这个字典类型的键值:[‘x_test’, ‘x_train’, ‘y_train’, ‘y_test’]
x_train, y_train = data['x_train'], data['y_train'] # assgian dict values
x_test, y_test = data['x_test'], data['y_test']
data.close() # close the file
这个时候变量空间有值了:
2.网络构建
#构建网络
from keras import models
from keras import layers
network = models.Sequential()
network.add(layers.Dense(512,activation = 'relu',input_shape = (28*28,)))
network.add(layers.Dense(10,activation = 'softmax'))
可能会报错:
softmax() got an unexpected keyword argument ‘axis’
去softmax()函数里面把axis参数删掉就可以了
3.编译步骤,三个参数
#编译步骤
network.compile(optimizer = 'rmsprop',loss = 'categorical_crossentropy',metrics = ['accuracy'])
#compile有三个参数:损失函数,优化器,在训练过程中需要监控的指标
4.数据预处理
#训练数据之前,对数据进行预处理
#每一个28*28的矩阵里面都是灰度值[0,255]之间,我们缩放到[0,1]之间
#训练数据是三维的60000*28*28,我们把28*28作为一个向量,变成60000*784的形状
train_images = x_train.reshape(60000,28*28)
train_images = train_images.astype('float')/255
test_images = x_test.reshape(10000,28*28)#测试数据10000条
test_images = test_images.astype('float32')/255
##准备标签
from keras.utils import to_categorical
train_labels = to_categorical(y_train)
test_labels = to_categorical(y_test)
5.训练过程
##训练过程,fit
network.fit(train_images,train_labels,epochs = 5,batch_size = 128)
这里不能用y_train,一定要用train_labels,即换成独热码之后的,因为神经网络输出为10维的独热码,应该与train_labels这种十维的数进行比较
如果直接用神经网络训练出来的与y_train比较就会报错:
network.fit(train_images,y_train,epochs = 5,batch_size = 128)
ValueError: Error when checking target: expected dense_2 to have shape (10,) but got array with shape (1,)
6.结果
用cpu的tensorflow跑

用gpu的tensorflow跑:
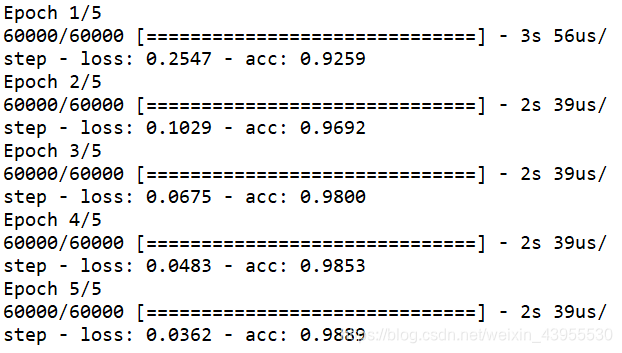
在训练集上,准确度达到了0.989
在测试机上:
test_loss,test_acc = network.evaluate(test_images,test_labels)
10000/10000 [==============================] - 0s 48us/step
print('test_acc:',test_acc)
test_acc: 0.9823
精度达到了0.9823
Code
#from keras.datasets import mnist
#(train_images,train_labels),(test_images,test_labels) = mnist.load_data()
import numpy as np
#为了避免每一次运行程序,那个下载的步骤都要进行一次,这里用load直接load下载好的文件
data = np.load('D:\python\workspace\mnist.npz') # open and read
#print(data.keys())
x_train, y_train = data['x_train'], data['y_train'] # assgian dict values
x_test, y_test = data['x_test'], data['y_test']
data.close() # close the file
#构建网络
from keras import models
from keras import layers
network = models.Sequential()
network.add(layers.Dense(512,activation = 'relu',input_shape = (28*28,)))
network.add(layers.Dense(10,activation = 'softmax'))
#编译步骤
network.compile(optimizer = 'rmsprop',loss = 'categorical_crossentropy',metrics = ['accuracy'])
#compile有三个参数:损失函数,优化器,在训练过程中需要监控的指标
#训练数据之前,对数据进行预处理
#每一个28*28的矩阵里面都是灰度值[0,255]之间,我们缩放到[0,1]之间
#训练数据是三维的60000*28*28,我们把28*28作为一个向量,变成60000*784的形状
train_images = x_train.reshape(60000,28*28)
train_images = train_images.astype('float')/255
test_images = x_test.reshape(10000,28*28)#测试数据10000条
test_images = test_images.astype('float32')/255
##准备标签
from keras.utils import to_categorical
train_labels = to_categorical(y_train)
test_labels = to_categorical(y_test)
##训练过程,fit
network.fit(train_images,train_labels,epochs = 5,batch_size = 128)
#每次处理128个样本,训练集一共60000个样本,每轮要处理469次,epochs = 5,处理五轮,一共就是进行2345次梯度更新
7.数学基础
- 张量(tensor)
- 标量(0D张量)
- 向量(1D张量)
- 矩阵(2D张量)
- 3D张量及多维张量
train_images.ndim#查看张量维数
Out[3]: 2
x_train.ndim
Out[4]: 3
x_train.shape#查看形状
Out[5]: (60000, 28, 28)
x_train.dtype#查看数据类型
Out[6]: dtype('uint8')
-
Numpy中操作张量
- 张量切片
my_slice = x_train[10:100]
- 张量广播
- 张量点积
- 张量变形
train_images = x_train.reshape(60000,28*28)
x = np.zeros((300,200))
x = np.transpose(x)
x.shape
Out[29]: (200, 300)
8.现实生活中数据张量
- 向量数据:2D张量
- 时间序列数据,序列数据:3D张量
- 图像:4D张量
- 视频:5D张量
9.神经网络的引擎
基于梯度的优化,使loss函数达到最小值,让w朝着梯度下降反方向移动
10.动量
解决陷入局部最小点而找不到全局最小点问题,和收敛速度的问题





 本文详细介绍使用Keras库和手写数字数据集构建神经网络的过程,包括数据载入、网络构建、编译、数据预处理、训练及评估。同时探讨神经网络背后的数学原理,如张量概念和梯度优化。
本文详细介绍使用Keras库和手写数字数据集构建神经网络的过程,包括数据载入、网络构建、编译、数据预处理、训练及评估。同时探讨神经网络背后的数学原理,如张量概念和梯度优化。
















 937
937

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








