Reward
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 14966 Accepted Submission(s): 4795
Problem Description
Dandelion's uncle is a boss of a factory. As the spring festival is coming , he wants to distribute rewards to his workers. Now he has a trouble about how to distribute the rewards.
The workers will compare their rewards ,and some one may have demands of the distributing of rewards ,just like a's reward should more than b's.Dandelion's unclue wants to fulfill all the demands, of course ,he wants to use the least money.Every work's reward will be at least 888 , because it's a lucky number.
Input
One line with two integers n and m ,stands for the number of works and the number of demands .(n<=10000,m<=20000)
then m lines ,each line contains two integers a and b ,stands for a's reward should be more than b's.
Output
For every case ,print the least money dandelion 's uncle needs to distribute .If it's impossible to fulfill all the works' demands ,print -1.
Sample Input
2 1 1 2 2 2 1 2 2 1
Sample Output
1777 -1
题目大意 : 输入一张有向图, U, V表示U希望得到的工资比V要大,每个人最少给888,求最少要花多少钱。
思路 : 第一次写这道题是两周前,读完题以后第一反应就是反向建图,然后正常拓扑排序花费逐次 + 1, 反向建图倒是没错,因为按照从小到大的顺序增加奖励,但是逐次花费 + 1是不对的,如图所示
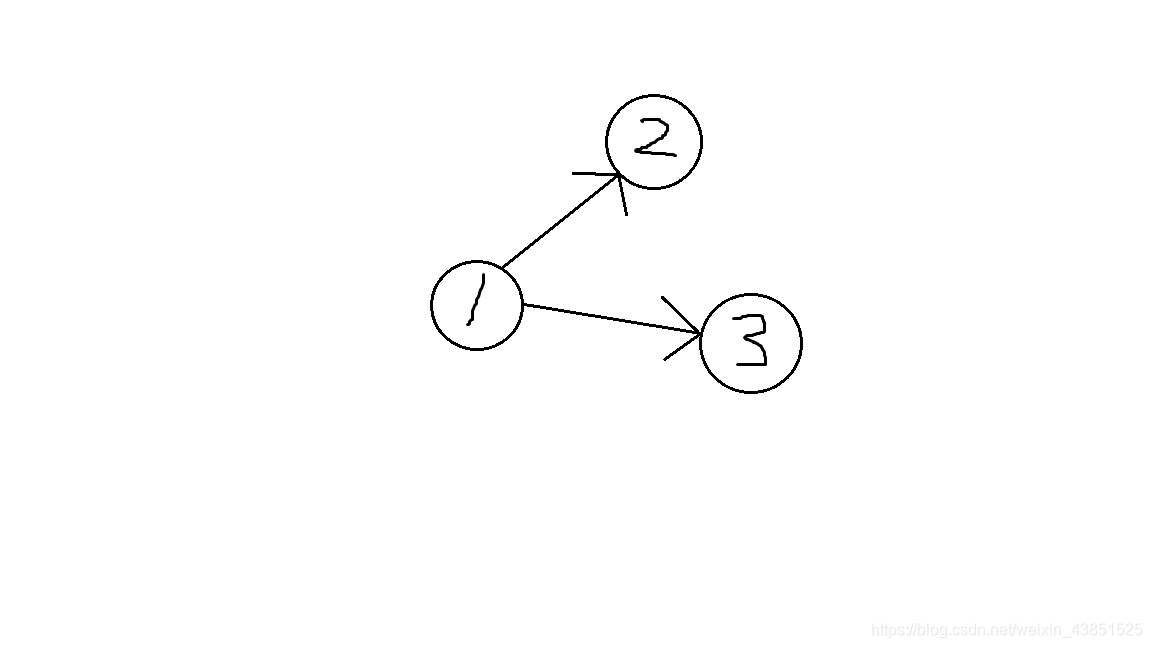
如果奖励逐次 + 1的话,这个图会是888 + 889 + 890,可事实上, 2和3之间并没有什么联系,所以2 和 3的奖励是可以一样的,正确的应该是888 + 889 + 889。所以我想用dfs来解决,这样就可以依次 + 1了,到头了再回溯回来,但是如果图不连通的话复杂度会不会太大了呢?
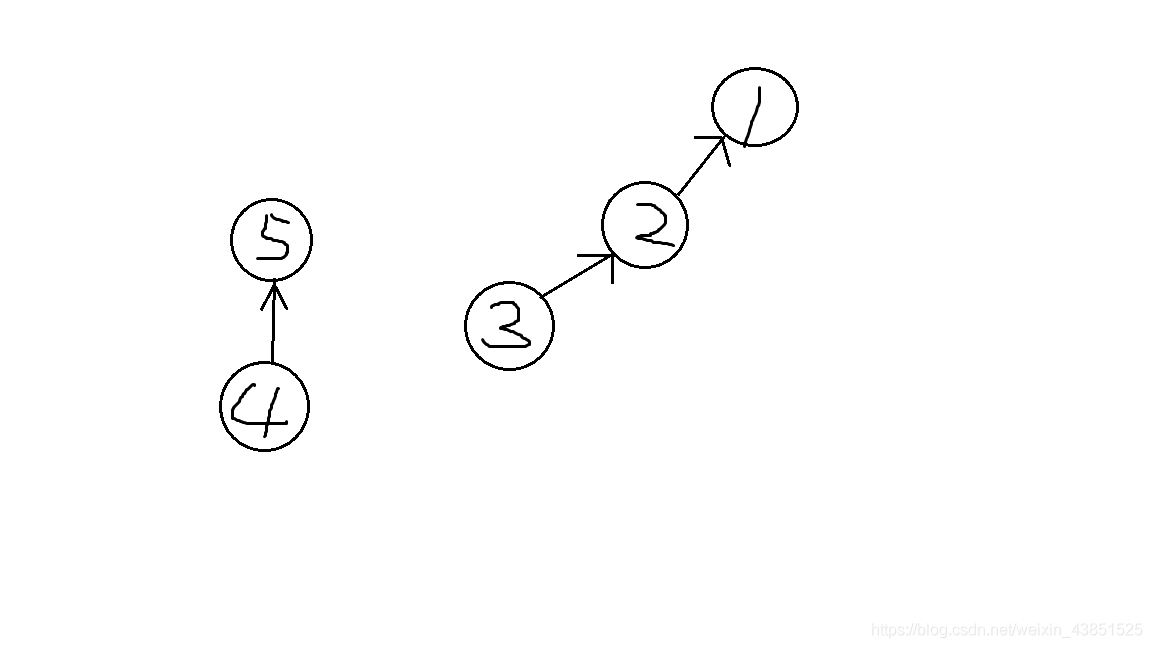
如果图不连通,可能要用到并查集,还得以该连通块的父节点为头存一张新图,就算写完了也不一定能保证会不会TLE。想了一会发现,拓扑排序一定是一棵树,每个点的奖励一定是上一个点的奖励 + 1,如此以来,这两个问题都迎刃而解了
AC代码 :
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1e5 + 5;
struct node
{
int v, next;
}e[maxn];
int head[maxn], dp[maxn], in[maxn], n, m, cnt, sum;
void init() {
memset (e, 0, sizeof(e));
memset (in, 0, sizeof(in));
memset (dp, 0, sizeof(dp));
memset (head, -1, sizeof(head));
sum = cnt = 0;
}
void add (int from, int to) {
e[++cnt].v = to;
e[cnt].next = head[from];
head[from] = cnt;
}
void topsort() {
queue <int> q;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (!in[i]) q.push(i), dp[i] = 888; //初始化
}
int ans = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
ans++;
sum += dp[u];
for (int i = head[u]; i != -1; i = e[i].next) {
int v = e[i].v;
in[v]--;
dp[v] = dp[u] + 1; //下一个节点的奖励值是上一个的 + 1
if (!in[v]) q.push(v);
}
}
if (ans != n) cout << -1 << endl;
else cout << sum << endl;
}
int main()
{
while (cin >> n >> m) {
init();
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int ui, vi;
cin >> ui >> vi;
add (vi, ui);
in[ui]++;
}
topsort();
}
return 0;
}








 本文探讨了一个工厂老板在春节前夕如何合理分配奖金的问题,确保每位员工的奖金满足特定条件且总成本最低。通过构建有向图并运用拓扑排序算法,实现了有效解决此问题的方法。
本文探讨了一个工厂老板在春节前夕如何合理分配奖金的问题,确保每位员工的奖金满足特定条件且总成本最低。通过构建有向图并运用拓扑排序算法,实现了有效解决此问题的方法。
















 267
267

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








