传送门:Codeforces 519E
A and B are preparing themselves for programming contests.
The University where A and B study is a set of rooms connected by corridors. Overall, the University has n rooms connected by n - 1 corridors so that you can get from any room to any other one by moving along the corridors. The rooms are numbered from 1 to n.
Every day А and B write contests in some rooms of their university, and after each contest they gather together in the same room and discuss problems. A and B want the distance from the rooms where problems are discussed to the rooms where contests are written to be equal. The distance between two rooms is the number of edges on the shortest path between them.
As they write contests in new rooms every day, they asked you to help them find the number of possible rooms to discuss problems for each of the following m days.
Input
The first line contains integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105) — the number of rooms in the University.
The next n - 1 lines describe the corridors. The i-th of these lines (1 ≤ i ≤ n - 1) contains two integers ai and bi (1 ≤ ai, bi ≤ n), showing that the i-th corridor connects rooms ai and bi.
The next line contains integer m (1 ≤ m ≤ 105) — the number of queries.
Next m lines describe the queries. The j-th of these lines (1 ≤ j ≤ m) contains two integers xj and yj (1 ≤ xj, yj ≤ n) that means that on the j-th day A will write the contest in the room xj, B will write in the room yj.
Output
In the i-th (1 ≤ i ≤ m) line print the number of rooms that are equidistant from the rooms where A and B write contest on the i-th day.
Examples
Input
4
1 2
1 3
2 4
1
2 3
Output
1
Input
4
1 2
2 3
2 4
2
1 2
1 3
Output
0
2
Note
in the first sample there is only one room at the same distance from rooms number 2 and 3 — room number 1.
题意:
询问给出一棵无根树上任意两点a,b,求所有点i,到达a,b两点的距离相等的点的数目。
题解:
首先题目给出的是一个无根树,那么我们将无根树转为有根树来做,取1做根节点即可。
到两点距离相等的点,应该是两点之间的中点即其延伸出去的点,如果两点之间没有中点,就特判一下直接输出0即可。
那么接下来的问题就是找中点。
找中点首先得知道两点之间的距离,在树上的两点(a,b)的距离应该等于
D
i
s
=
d
e
e
p
[
a
]
+
d
e
e
p
[
b
]
−
2
∗
d
e
e
p
[
l
c
a
(
a
,
b
)
]
Dis=deep[a]+deep[b]-2*deep[lca(a,b)]
Dis=deep[a]+deep[b]−2∗deep[lca(a,b)] (deep为点的深度,lca为两点的最近公共祖先)
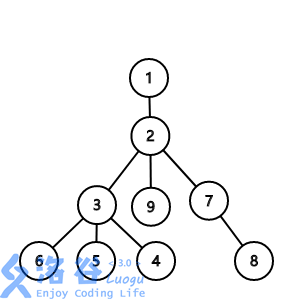
(可以以图中3,8两点之间的距离为例,理解一下距离的计算)
- 如果Dis为奇数,那么一定没有点到达a,b的距离相等,就是我们要特判的情况
Dis为偶数:
- l c a ( a , b ) lca(a,b) lca(a,b)为中点:那么符合的点应该是从lca延伸出去的点(不包括a,b所在子树),那么总数就是: n − s i z e [ l c a 包 含 a 的 子 树 ] − s i z e [ l c a 包 含 b 的 子 树 ] n-size[lca包含a的子树]-size[lca包含b的子树] n−size[lca包含a的子树]−size[lca包含b的子树] (size为子树的大小)
- l c a ( a , b ) lca(a,b) lca(a,b) 不为中点:那么中点在图上一定会更偏向一个点(且一定在两点的最近公共祖先的下方),我们假设更偏向 a ,符合的点应该是中点的子树大小减去包含a的子树的大小,即: s i z e [ 中 点 ] − s i z e [ 中 点 包 含 a 的 子 树 ] size[中点]-size[中点包含a的子树] size[中点]−size[中点包含a的子树]
注:如果两数相等那么符合的点的个数就是n(所有节点数)
AC代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#define ll long long
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
using namespace std;
const int N=110000;
int n,m,k;
int head[N],dep[N],size[N],f[N][21];
struct edge
{
int to,next;
}e[2*N];
void add(int u,int v)
{
e[k].to=v;
e[k].next=head[u];
head[u]=k++;
}
void search(int u,int fa)
{
dep[u]=dep[fa]+1;
size[u]=1;
for(int i=1;(1<<i)<=dep[u];i++)
{
f[u][i]=f[f[u][i-1]][i-1];
}
for(int i=head[u];i!=-1;i=e[i].next)
{
int v=e[i].to;
if(v==fa) continue;
f[v][0]=u;
search(v,u);
size[u]+=size[v];
}
}
int lca(int l,int r)
{
if(dep[l]<dep[r]) swap(l,r);
for(int i=20;i>=0;i--)
{
if(dep[f[l][i]]>=dep[r])
{
l=f[l][i];
}
if(l==r)
{
return l;
}
}
for(int i=20;i>=0;i--)
{
if(f[l][i]!=f[r][i])
{
l=f[l][i];
r=f[r][i];
}
}
return f[l][0];
}
int getc(int res,int k)
{
int x=res;
for(int i=20;i>=0;i--)
{
if(dep[res]-dep[f[x][i]]<=k)
{
x=f[x][i];
}
}
return x;
}
int main()
{
int a,b;
memset(head,-1,sizeof(head));
k=1;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
add(a,b);
add(b,a);
}
search(1,0);
scanf("%d",&m);
while(m--)
{
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
int rt=lca(a,b);
if(a==b)
{
printf("%d\n",n);
continue;
}
int dis=dep[a]+dep[b]-2*dep[rt];
if(dis%2)
{
printf("0\n");
continue;
}
dis/=2;
if(dis==dep[a]-dep[rt])
{
int ra=getc(a,dis-1),rb=getc(b,dis-1);//以lca为根节点,包含a,b的子树的根节点为ra,rb
printf("%d\n",n-size[ra]-size[rb]);
}
else
{
if(dis<dep[a]-dep[rt])//中点偏向a
{
rt=getc(a,dis);//中点
int ra=getc(a,dis-1);
printf("%d\n",size[rt]-size[ra]);
}
else
{
rt=getc(b,dis);
int rb=getc(b,dis-1);
printf("%d\n",size[rt]-size[rb]);
}
}
}
return 0;
}








 本文解析了Codeforces519E竞赛题目,介绍了如何在无根树上找到所有点,这些点到给定两点的距离相等。通过将无根树转化为有根树,利用深度优先搜索和最近公共祖先算法,有效地解决了问题。
本文解析了Codeforces519E竞赛题目,介绍了如何在无根树上找到所有点,这些点到给定两点的距离相等。通过将无根树转化为有根树,利用深度优先搜索和最近公共祖先算法,有效地解决了问题。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








