
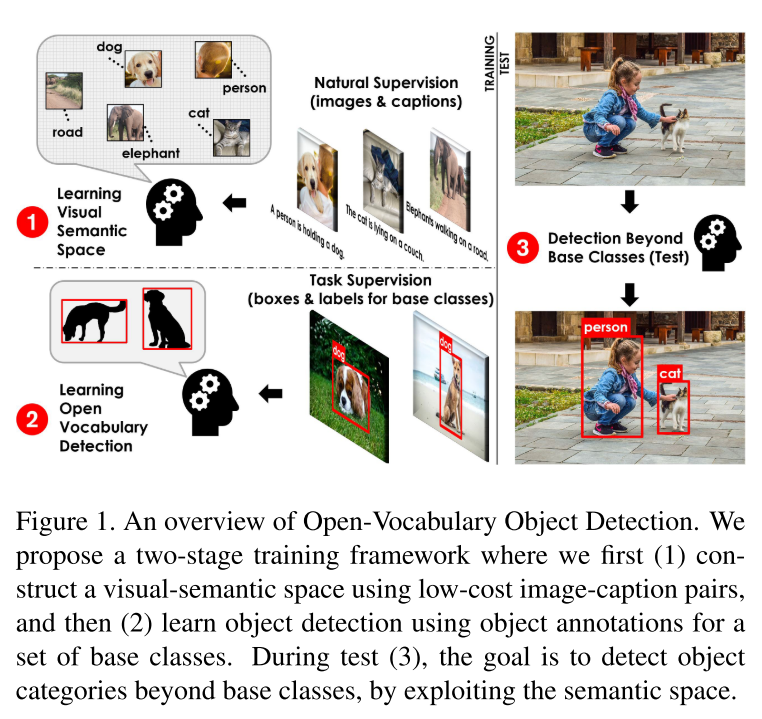
1. Motivation
-
Despite the remarkable accuracy of deep neural networks in object detection, they are costly to train and scale due to supervision requirements.
-
Weakly supervised and zero-shot learning techniques have been explored to scale object detectors to more categories with less supervision, but they have not been as successful and widely adopted as supervised models.
-
To address the task of OVD, we propose a novel method based on Faster R-CNN [32], which is first pretrained on an image-caption dataset, and then fine-tuned on a bounding box dataset.
-
More specifically, we train a model that takes an image and detects any object within a given target vocabulary VT.
-
To train such a model, we use an image-caption dataset covering a large variety of words denoted as $V_C $as well as a much smaller dataset with localized object annotations from a set of base classes VBV_BVB.
2. Contribution
-
In this paper, we put forth a novel formulation of the object detection problem, namely open- vocabulary object detection, which is more general, more practical, and more effective than weakly supervised and zero-shot approaches.
-
Meanwhile, objects with bounding box annotation can be detected almost as accurately as supervised methods, which is significantly better than weakly supervised baselines.
-
Accordingly, we establish a new state ofthe art for scalable object detection.
-
We name this framework Open Vocabulary Object Detection(OVD).
3. Method
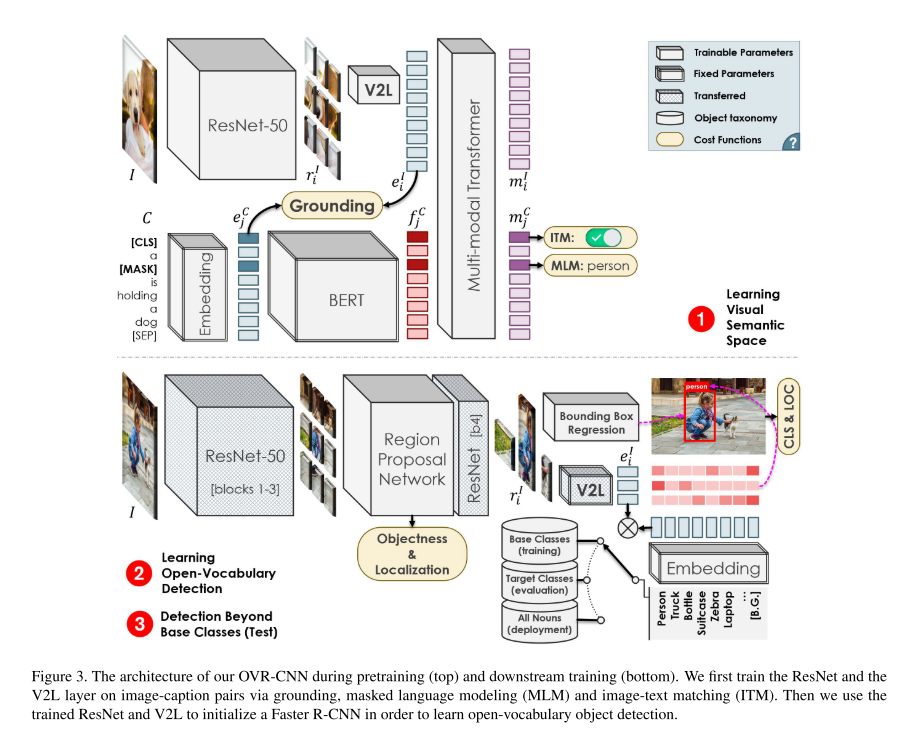
图3为OVR-CNN的framework,基于Faster R-CNN,但是是在zero-shot的形式上训练得到的目标检测器。
确切来说,用base classes VBV_BVB训练,用target classesVTV_TVT测试。
为了提升精度,本文的核心思想是通过一个更大的词汇库VCV_CVC来预训练一个visual backbone,从而学习丰富的语义空间信息。
在第二个阶段中,使用训练好的ResNet以及V2L 2个模型来初始化Faster R-CNN,从而实现开放词汇的目标检测。
3.1. Learning a visual-semantic space Object
为了解决使用固定的embedding matrix替代classifier weights来训练pretrain base classes embedding而产生overfitting的问题,本文提出了V2L layer。使用的数据不只是base classes。
-
To prevent overfitting, we propose to learn the aforementioned Vision to Language (V2L) projection layer along with the CNN backbone during pretraining, where the data is not limited to a small set of base classes.
-
We use a main (grounding) task as well as a set of auxiliary self-supervision tasks to learn a robust CNN backbone and V2L layer.
作者使用PixelBERT,input为了image-caption,将image输入viusal backbone(ResNet-50),将caption输入language backbone(pretrained BERT),联合产生token embedding,然后将token embedding 输入到multi-model transformer中来提取multi-model embedding。
对于visual backbone,利用ResNet-50,提取输入I的特征,得到W/32×H/32W/32 \times H/32W/32×H/32的feature map,本文定义为W/32×H/32W/32 \times H/32








 该研究提出了一种新颖的开放词汇目标检测方法,通过预训练和微调,使得模型能检测到词汇表中的任何对象,同时在有边界框注释的对象检测上表现几乎与监督方法相当,建立了可扩展目标检测的新标准。该方法结合了图像标题数据集和少量基础类别数据,通过学习视觉语义空间提高准确性。
该研究提出了一种新颖的开放词汇目标检测方法,通过预训练和微调,使得模型能检测到词汇表中的任何对象,同时在有边界框注释的对象检测上表现几乎与监督方法相当,建立了可扩展目标检测的新标准。该方法结合了图像标题数据集和少量基础类别数据,通过学习视觉语义空间提高准确性。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
















 1178
1178

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








