使用注解的方式相对于使用XML的方式开发方便了许多,其基本原理并无多大变化。
使用XML的开发方式中,我们需要实体类和相对应的XML的映射文件;
使用注解的开发方式中,我们只是把XML映射文件修改成了JAVA接口类,通过创建一个接口,在接口里面定义一系列的操作方法,并在方法之前加上注解。除此之外,和XML配置方式有以下几个不同:
在mybatis-config.xml总配置文件中:映射方式不同,前三个为XML方式,后两个为注解方式
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/cn/bean/Category.xml"/>
<mapper resource="com/cn/bean/Product.xml"/>
<mapper resource="com/cn/bean/Order.xml"/>
<mapper class="com.cn.bean.CategoryMapper"/>
<mapper class="com.cn.bean.ProductMapper"/>
</mappers>
在获取对数据库的操作对象时:
//xml方式 直接使用session对象对数据库进行操作
String resource="mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream=Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory=new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession session=sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//接口方式 需要使用session对象获取接口类对象
String resource="mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream sourceStream=Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory=new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(sourceStream);
SqlSession session=sessionFactory.openSession();
CategoryMapper mapper=session.getMapper(CategoryMapper.class);
注解方式实现CURD:
@Insert("insert into category(name) values(#{name})")
public void addCategory(Category c);
@Select("select * from category")
public List<Category> listCategory();
@Update("update category set name = #{name} where id=#{id}")
public void updateCategory(Category c);
@Delete("delete from category where id = #{id}")
public void deleteCategory(int id);
//使用时直接用接口类对象调用方法即可(有参数需要传入参数)
注解方式实现一对多、多对一、多对多
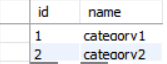
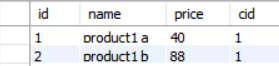
一对多 有如下表关系:
上表为category,下表为product;一个category对应多个product,两者之间的联系在数据库表中通过在product表中增加cid(category id)列实现。
配置CategoryMapper接口(这是接口类,并非实体类)的一对多查询,查询时需要使用ProductMapper接口的条件查询(使用cid查询Product)
//CategoryMapper
@Select("select * from category")
@Results({
@Result(property="id",column="id"),
@Result(property="products",javaType=List.class,column="id",many=@Many(select="com.cn.bean.ProductMapper.listByCategory"))
})
public List<Category> listCategoreWithProduct();
//ProductMapperr
@Select("select * from product where cid = #{cid}")
public List<Product> listByCategory(int cid);
此处注意的地方在于一对多查询的配置方式,首先一个基本的查询查询Category类中的所有基本属性,然后通过配置@Results注解来实现一对多,类似XML中的ResultMap
同样@Results注解也可以用来配置实体类属性和数据库表字段的对应关系,使用@Result标签(property、column);如果属性名称和数据库表中的字段名称相同,可以不加配置,至于一对多的关系,只能通过手动配置实现,如上@Result(property=“products”,javaType=List.class,column=“id”,many=@Many(select=“com.cn.bean.ProductMapper.listByCategory”))
property指示了实体类中的属性,javaType指示类型(可以不写,MyBatis可以自动解析),column指示两者如何关联(即传入many中查询的属性),many指示对应关系通过什么得到,select=“”指示需要使用column中的参数调用com.cn.bean包下的ProductMapper类的listByCategory方法进行查询。
此处需要注意:如果传入的参数为当前表的主键,需要使用@Result配置一下列的对应信息,否则查询结果中会缺少当前表主键的信息。
注解实现多对一
多对一和一对多的实现方式类似,只是在注解的使用上有一点区别:
(Product和Category多对一)
//ProductMapper类
//多对一方法测试
@Select("select * from product")
@Results({
@Result(property="category",column="cid",one=@One(select="com.cn.bean.CategoryMapper.getCategoryById"))
})
public List<Product> listProductsWithCategory();
//CategoryMapper
@Select("select * from category where id = #{id}")
public Category getCategoryById(int id);
注解实现多对多
在使用XML配置多对多的关系的时候我们已经知道,多对多关系通过建立中间表实现,被分解为两个一对多的关系。(订单-订单项-商品,一个订单含有多个订单项,一件商品属于多个订单项;通过订单去查找订单项就是一对多对一(多))。
配置ProductMapper:根据ID获取Product
@Select("select * from product where id= #{id}")
public List<Product> getProductByID(int id);
配置OrderItemMapper:多对一,根据cid获取OrderItem
@Select ("select * from orderItem where oid = #{oid}")
@Results({
@Result(property="product",column="pid",one=@One(select="com.cn.bean.ProductMapper.getProductByID"))
})
public List<OrderItem> getByOrder(int oid);
配置OrderMapper:一对多,调用OrderItemMapper中的方法
@Select("select * from `order`")
@Results({
@Result(property="id", column="id"),
@Result(property="orderItems",javaType=List.class,column="id",many=@Many(select="com.cn.bean.OrderItemMapper.getByOrder"))
})
public List<Order> listOrder();
注解实现动态SQL
使用注解实现动态SQL需要新建获取动态SQL的类,比如为Category类创建动态SQL的获取类:
public class CategoryDynaSQLProvider {
public String select()
{
return new SQL()
.SELECT("*")
.FROM("category")
.WHERE("id = #{id}")
.WHERE("name like concat('%',#{name},'%')")
.toString();
}
}
SQL类中有如下的方法:可以用来拼接SQL语句,动态SQL中的if、where标签等,均可以使用java代码实现。
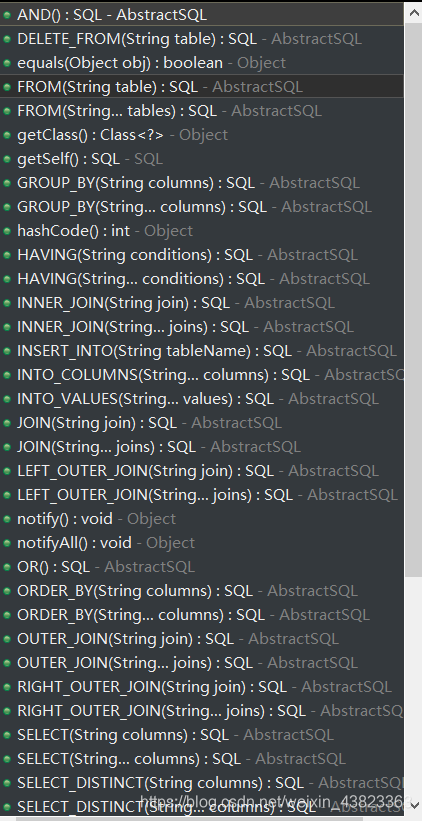
使用方法:在CategoryMapper类中,使用动态SQL语句的标签
@SelectProvider(type=com.cn.dynamicSQL.CategoryDynaSQLProvider.class,method="select")
public List<Category> listCategoryUseDynaSQL();








 博客介绍了MyBatis使用注解方式开发的优势,对比了与XML开发方式的不同。详细阐述了注解方式实现CURD、一对多、多对一、多对多关系的配置方法,以及注解实现动态SQL的方式,包括相关接口配置和SQL拼接类的使用。
博客介绍了MyBatis使用注解方式开发的优势,对比了与XML开发方式的不同。详细阐述了注解方式实现CURD、一对多、多对一、多对多关系的配置方法,以及注解实现动态SQL的方式,包括相关接口配置和SQL拼接类的使用。
















 221
221

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








