我们从最简单的例子开始看起来
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
List<FlowRule> rules=new ArrayList<>(); // 定义限流规则集合
FlowRule rule=new FlowRule(); // 定义限流规则
rule.setResource("helloSentinel"); // 定义限流资源
rule.setGrade(RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS); // 定义限流规则类型
rule.setCount(1); // 定义QPS阈值 每秒最多通过的请求个数
/
FlowRule flowRule2=new FlowRule(); // 定义限流规则
flowRule2.setResource("helloSentinelV2"); // 定义限流资源
flowRule2.setGrade(RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS); // 定义限流规则类型
flowRule2.setCount(1); // 定义QPS阈值 每秒最多通过的请求个数
/
rules.add(rule); // 添加规则到集合
rules.add(flowRule2); // 添加规则到集合
FlowRuleManager.loadRules(rules); // 加载规则集合
log.info("start init");
}
定义流控规则
/
methodV1
@GetMapping("/helloSentinel")
public String helloSentinel() {
Entry entry = null;
try {
/受保护的资源
entry = SphU.entry("helloSentinel");
// 业务方法
myService.doinit();
return "ok";
} catch (BlockException e) {
log.info("helloSentinel方法被限流了");
return "helloSentinel方法被限流了";
} finally {
if(entry!=null){
entry.exit();
}
}
}
methodV2
@GetMapping("/helloSentinelV2")
@SentinelResource(value = "helloSentinelV2",blockHandler ="testHelloSentinelV2BlockMethod")
public String helloSentinelV2() {
myService.doinit();
return "ok";
}
public String testHelloSentinelV2BlockMethod(BlockException e){
return "testHelloSentinelV";
}
我们看看上面的代码 主要就是methodV1,
我们提前声明资源 并且标注资源的qps什么的,比如说QPS 为1
在methodV1 中我们使用
entry = SphU.entry("helloSentinel"); 对我们的资源进行保护, 然后执行我们的业务逻辑
如果有异常了代表qps 超过了
在methodV2 中我们直接使用 @SentinelResource 注解
@SentinelResource 注解底层用的aop
SentinelResourceAspect 我们看下这个类

这里使用了aop来处理的SentinelResource,主要用了aop的环绕通知
// 核心逻辑还是这样
entry = SphU.entry(resourceName, resourceType, entryType, pjp.getArgs());
我们点进去看这里
private Entry entryWithPriority(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args)
throws BlockException {
Context context = ContextUtil.getContext();
if (context instanceof NullContext) {
// The {@link NullContext} indicates that the amount of context has exceeded the threshold,
// so here init the entry only. No rule checking will be done.
return new CtEntry(resourceWrapper, null, context);
}
if (context == null) {
// Using default context.
context = InternalContextUtil.internalEnter(Constants.CONTEXT_DEFAULT_NAME);
}
// Global switch is close, no rule checking will do.
if (!Constants.ON) {
return new CtEntry(resourceWrapper, null, context);
}
主要看这里 这里用了构建者模式 构建了 ProcessorSlotChain
/ 基于资源创建了一个 ProcessorSlot<Object> chain
ProcessorSlot<Object> chain = lookProcessChain(resourceWrapper);
/*
* Means amount of resources (slot chain) exceeds {@link Constants.MAX_SLOT_CHAIN_SIZE},
* so no rule checking will be done.
*/
if (chain == null) {
return new CtEntry(resourceWrapper, null, context);
}
Entry e = new CtEntry(resourceWrapper, chain, context);
try {
chain.entry(context, resourceWrapper, null, count, prioritized, args);
} catch (BlockException e1) {
e.exit(count, args);
throw e1;
} catch (Throwable e1) {
// This should not happen, unless there are errors existing in Sentinel internal.
RecordLog.info("Sentinel unexpected exception", e1);
}
return e;
}
这不就是单例的双层锁么 然后吧这个放在缓存了
ProcessorSlot<Object> lookProcessChain(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper) {
ProcessorSlotChain chain = chainMap.get(resourceWrapper);
if (chain == null) {
synchronized (LOCK) {
chain = chainMap.get(resourceWrapper);
if (chain == null) {
// Entry size limit.
if (chainMap.size() >= Constants.MAX_SLOT_CHAIN_SIZE) {
return null;
}
主要看这里 这里用了builder模式,做了个初始化
chain = SlotChainProvider.newSlotChain();
Map<ResourceWrapper, ProcessorSlotChain> newMap = new HashMap<ResourceWrapper, ProcessorSlotChain>(
chainMap.size() + 1);
newMap.putAll(chainMap);
newMap.put(resourceWrapper, chain);
chainMap = newMap;
}
}
}
return chain;
}
这里主要构建了一个这样的数据结构DefaultProcessorSlotChain

接下来我们看下这个代码 我拿到这个chain 链条就开始做些事情
chain.entry(context, resourceWrapper, null, count, prioritized, args);

他就会调用第一个的chain的entry 然后就像filter一样 依次往下调用
通过 entry 方法执行当前的业务逻辑
通过 fireEntry();方法就可以调用下一个
这里的链条的调用的 就像filter过滤一样,吧每个chain 的entry 轮询调用一遍
sentinel 主要看限流 熔断 降级
chain.addLast(new NodeSelectorSlot());
chain.addLast(new ClusterBuilderSlot());
chain.addLast(new LogSlot());
chain.addLast(new StatisticSlot());
chain.addLast(new AuthoritySlot());
chain.addLast(new SystemSlot());
chain.addLast(new FlowSlot());
chain.addLast(new DegradeSlot());
也就是说sentinle 的dashboard 上面的逻辑全部在这些slot上
StatisticSlot 我们主要看这个 这个slot是用来计数用的,是用来统计指标的
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count,
boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {
try {
// Do some checking.
fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
// Request passed, add thread count and pass count.
node.increaseThreadNum();
node.addPassRequest(count);
if (context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode() != null) {
// Add count for origin node.
context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode().increaseThreadNum();
context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode().addPassRequest(count);
}
if (resourceWrapper.getEntryType() == EntryType.IN) {
// Add count for global inbound entry node for global statistics.
Constants.ENTRY_NODE.increaseThreadNum();
Constants.ENTRY_NODE.addPassRequest(count);
}
// Handle pass event with registered entry callback handlers.
for (ProcessorSlotEntryCallback<DefaultNode> handler : StatisticSlotCallbackRegistry.getEntryCallbacks()) {
handler.onPass(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, args);
}
} catch (PriorityWaitException ex) {
node.increaseThreadNum();
if (context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode() != null) {
// Add count for origin node.
context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode().increaseThreadNum();
}
if (resourceWrapper.getEntryType() == EntryType.IN) {
// Add count for global inbound entry node for global statistics.
Constants.ENTRY_NODE.increaseThreadNum();
}
// Handle pass event with registered entry callback handlers.
for (ProcessorSlotEntryCallback<DefaultNode> handler : StatisticSlotCallbackRegistry.getEntryCallbacks()) {
handler.onPass(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, args);
}
} catch (BlockException e) {
// Blocked, set block exception to current entry.
context.getCurEntry().setError(e);
// Add block count.
node.increaseBlockQps(count);
if (context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode() != null) {
context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode().increaseBlockQps(count);
}
if (resourceWrapper.getEntryType() == EntryType.IN) {
// Add count for global inbound entry node for global statistics.
Constants.ENTRY_NODE.increaseBlockQps(count);
}
// Handle block event with registered entry callback handlers.
for (ProcessorSlotEntryCallback<DefaultNode> handler : StatisticSlotCallbackRegistry.getEntryCallbacks()) {
handler.onBlocked(e, context, resourceWrapper, node, count, args);
}
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
// Unexpected error, set error to current entry.
context.getCurEntry().setError(e);
// This should not happen.
node.increaseExceptionQps(count);
if (context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode() != null) {
context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode().increaseExceptionQps(count);
}
if (resourceWrapper.getEntryType() == EntryType.IN) {
Constants.ENTRY_NODE.increaseExceptionQps(count);
}
throw e;
}
}
他是先调用往下一个solt的传递方法 再执行的业务逻辑
执行solt 的传递方法 如果成功没有异常的话
/ 正常情况下 则增加当前线程数以及请求通过数据
node.increaseThreadNum();
node.addPassRequest(count);
异常 增加被规则限流的数据
node.increaseBlockQps(count);
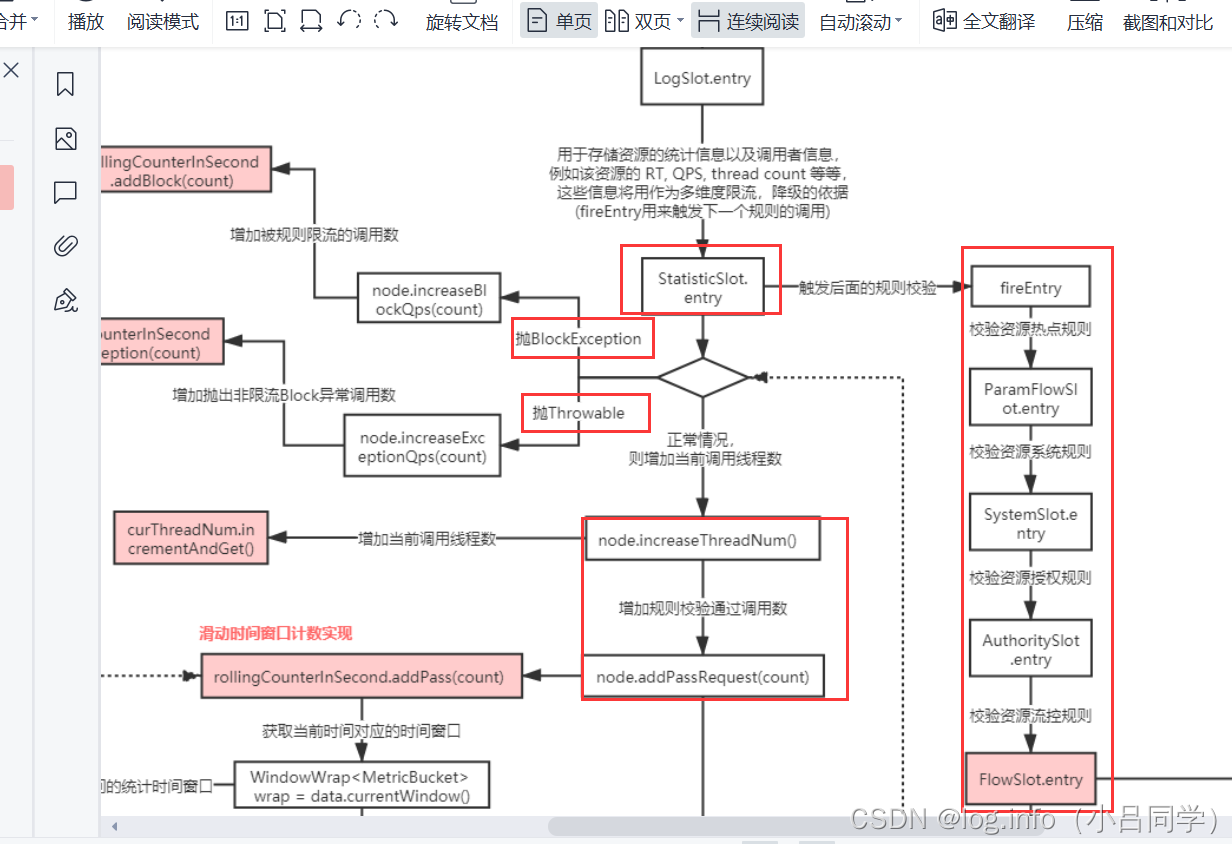
意思是 正常情况下
把我们的链条都通过了也没有报错
我线程数加1 并且 通过一个请求数qps+1
如果出现异常的话 我异常的qps+1
这个solt 主要是做统计用的数据的指标统计的
然后我们再看他具体限流 逻辑 flowSlot
/// 这个就是具体的限流 流控 有关的slot
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count,
boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {
checkFlow(resourceWrapper, context, node, count, prioritized);
fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
}
/// 这里的大概意思 就是我通过sentinel 页面输入的各种流控规则 我都可以从内存中拿得到
然后我遍历每一个规则 看当前是否匹配 如果不匹配的话我就抛异常 抛异常让StatisticSlot 抓到异常然后qps 什么的指标加1
针对每一个规则都要判断一下 可能基于这个资源做了很多规则
如果没有通过 被限流了,后面的链条不会执行的
Collection<FlowRule> rules = ruleProvider.apply(resource.getName());
if (rules != null) {
for (FlowRule rule : rules) {
if (!canPassCheck(rule, context, node, count, prioritized)) {
throw new FlowException(rule.getLimitApp(), rule);
}
}
}
FlowRule 我们来看下这个Rule中的有什么字段
/**
* The threshold type of flow control (0: thread count, 1: QPS).
*/
private int grade = RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS;
这个字段不就是sentinel的dashboard中的 是否是qps 么?
总之这个类就是页面的传过来的参数

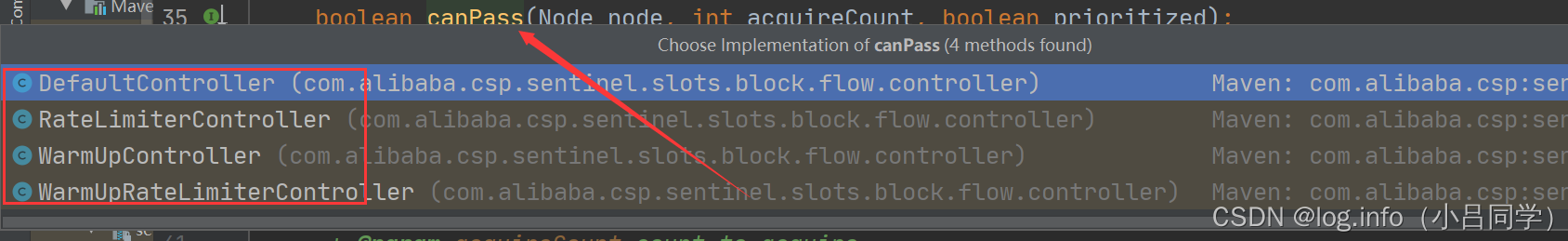

这里就用了各种限流算法 比如说滑动窗口,令牌桶,漏斗算法
什么的
他sentinel这边的核心架构就是和他刚开始的 methodV1一样 try catch 中间有很多限流算法
如果各种策略都通过的话 线程数+1 通过请求数+1,如果不通过的话的
就抛异常 被捕获然后异常qps+1
我们看下他的流控指标是怎么加入的
rollingCounterInSecond.addPass(count);
// 这个叫做统计中心
private transient volatile Metric rollingCounterInSecond = new ArrayMetric(SampleCountProperty.SAMPLE_COUNT,
IntervalProperty.INTERVAL);
我们以后怎么 统计我们系统的各种压测指标qps, 除了压测工具一样
完全可以实现一个统计中心统计我系统的各种异常数 异常比例
看他的构造函数
public LeapArray(int sampleCount, int intervalInMs) {
AssertUtil.isTrue(sampleCount > 0, "bucket count is invalid: " + sampleCount);
AssertUtil.isTrue(intervalInMs > 0, "total time interval of the sliding window should be positive");
AssertUtil.isTrue(intervalInMs % sampleCount == 0, "time span needs to be evenly divided");
this.windowLengthInMs = intervalInMs / sampleCount;
this.intervalInMs = intervalInMs;
this.sampleCount = sampleCount;
/ 主要看这里
this.array = new AtomicReferenceArray<>(sampleCount);
}

这里就初始化了1个数组,有2个位置, 然后我们再看下
WindowWrap<MetricBucket> wrap = data.currentWindow();
wrap.value().addPass(count);
data.currentWindow(); 这个当前窗口是怎么拿到的
// 我们看下这个currentWindow 怎么做的
public WindowWrap<T> currentWindow(long timeMillis) {
if (timeMillis < 0) {
return null;
}
// 根据当前时间 计算我应该处于数组的那个位置
int idx = calculateTimeIdx(timeMillis);
// 根据当前时间 我的这个位置的开始坐标
long windowStart = calculateWindowStart(timeMillis);
while (true) {
// 我拿到当前的 桶
WindowWrap<T> old = array.get(idx);
if (old == null) {
// 代表程序刚运行没有 我创建一个放进去 利用cas
WindowWrap<T> window = new WindowWrap<T>(windowLengthInMs, windowStart, newEmptyBucket(timeMillis));
if (array.compareAndSet(idx, null, window)) {
return window;
} else {
Thread.yield();
}
} else if (windowStart == old.windowStart()) {
// 如果 我此时这个请求的开始位置 计算出来和你桶的开始位置一致 我就再当前这个桶中 做各种统计指标的加1
return old;
} else if (windowStart > old.windowStart()) {
// 如果大于的话 我就 做替换 将原有的做置空处理
if (updateLock.tryLock()) {
try {
return resetWindowTo(old, windowStart);
} finally {
updateLock.unlock();
}
} else {
Thread.yield();
}
} else if (windowStart < old.windowStart()) {
return new WindowWrap<T>(windowLengthInMs, windowStart, newEmptyBucket(timeMillis));
}
}
}
// 这里主要运用了滑动时间算法根据时间的推移 我拿到 属于我的桶
然后对桶的qps 各种指标进行增加,
之后 在 FlowSlot 这些solt 就会拿到对应的桶 用来做比较 和你的阈值做比较
如果限流了 就会抛异常
我们看下限流算法 他这边主要就是用了限流算法
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/CrankZ/article/details/115152054
我们看下这里的限流算法







 本文详细解读了Sentinel的限流规则配置、AOP应用及核心组件如ProcessorSlotChain的工作原理,重点介绍了QPS限流算法和统计模块。通过实例分析,展示了如何在实际项目中使用Sentinel实现流量控制和指标监控。
本文详细解读了Sentinel的限流规则配置、AOP应用及核心组件如ProcessorSlotChain的工作原理,重点介绍了QPS限流算法和统计模块。通过实例分析,展示了如何在实际项目中使用Sentinel实现流量控制和指标监控。
















 1207
1207

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








