1、CAP定理
CAP定理是指在一个分布式系统中,Consistency(数据一致性)、Availability(服务可用性)、Partition tolerance(分区容错性)三者不可兼得
- C 数据一致性Consistency ,也叫数据原子性。系统在执行某项操作后仍处于一致状态。
优点:数据一致,没有数据错误可能
缺点:相对相率降低 - A 服务可用性 Availability,每一个操作总是能够在一定的时间内返回结果。
一定的时间内指的是在可以容忍的范围内返回结果,结果可能成功也可能是失败 - P 分区容错性 Partition-torlerance,在网络分区的情况下,被分隔的节点仍能正常对外提供服务。
三者不可兼得,可以满足其中的两个:
(1)CA放弃P:若想避免分区容错性问题的发生,一种做法是将所有的数据(与事务相关)的放在同一台机器上。
(2)CP放弃A:相对于放弃“分区容错性”来说,其反面就是放弃可用性。一旦遇到分区容错故障,那么受到影响的服务需要等待一定时间,因此等待时间内系统无法对外提供服务。
(3)AP放弃C:放弃一致性,并不是完全放弃数据一致性,而是放弃数据的强一致性,而保留数据最终的一致性。
2.Ribbon----springcloud的RPC底层实现
创建一个新的项目—导入依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<packaging>pom</packaging>
<modules>
<module>appService</module>
<module>appClient</module>
</modules>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.1.10.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>springcloud-first</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>Greenwich.SR4</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<!--springcloud 服务提供者,是通过Http协议对外提供服务的,是使用controller对外提供服务的-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--所有的服务都是客户端提供的 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
提供方:
1.controller – 创建springcloud服务
package com.bjsxt.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 第一个springcloud服务
*/
@RestController
public class FirstServiceController {
@RequestMapping("/first")
public Map<String, String> firstService(Integer id, String name){
System.out.println("id="+id);
System.out.println("name="+name);
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("message","firstService method run.");
return map;
}
}
package com.bjsxt.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
/**
* @ResponBody --将方法的返回值在相对应体中,向客户端输出
* 返回值类型区别:
* 方法返回值类型为string:ResponseBody修改相应头为
* text/html;charset=[spring5.3.x <-> UTF-8 </-> | spring5- <-> ISO-8859-1 </-> | SpringBoot介入的时候,字符集统一为UTF-8]
* 方法返回值类型非String:ResponseBody修改响应头为 -
* application/json;charset=UTF-8
*
* 如果需求明确,返回结果必须是字符串。可以通过RequestMapping注解的属性解决问题。
*/
@Controller
public class SecondServiceController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/second",produces = {"application/json;charset=UTF-8"})
@ResponseBody
public Object secondService(){
return "{\"message\":\"测试返回结果\"}";
// return "{'message','测试返回结果.'}";
}
}
2.创建启动类
package com.bjsxt;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class AppServiceApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(AppServiceApp.class,args);
}
}
3.配置文件
server.port=8080
spring.application.name=first-application-service
eureka.client.service-url.defaultZone=http://eureka1:8762/eureka,http://eureka2:8761/eureka
4.启动
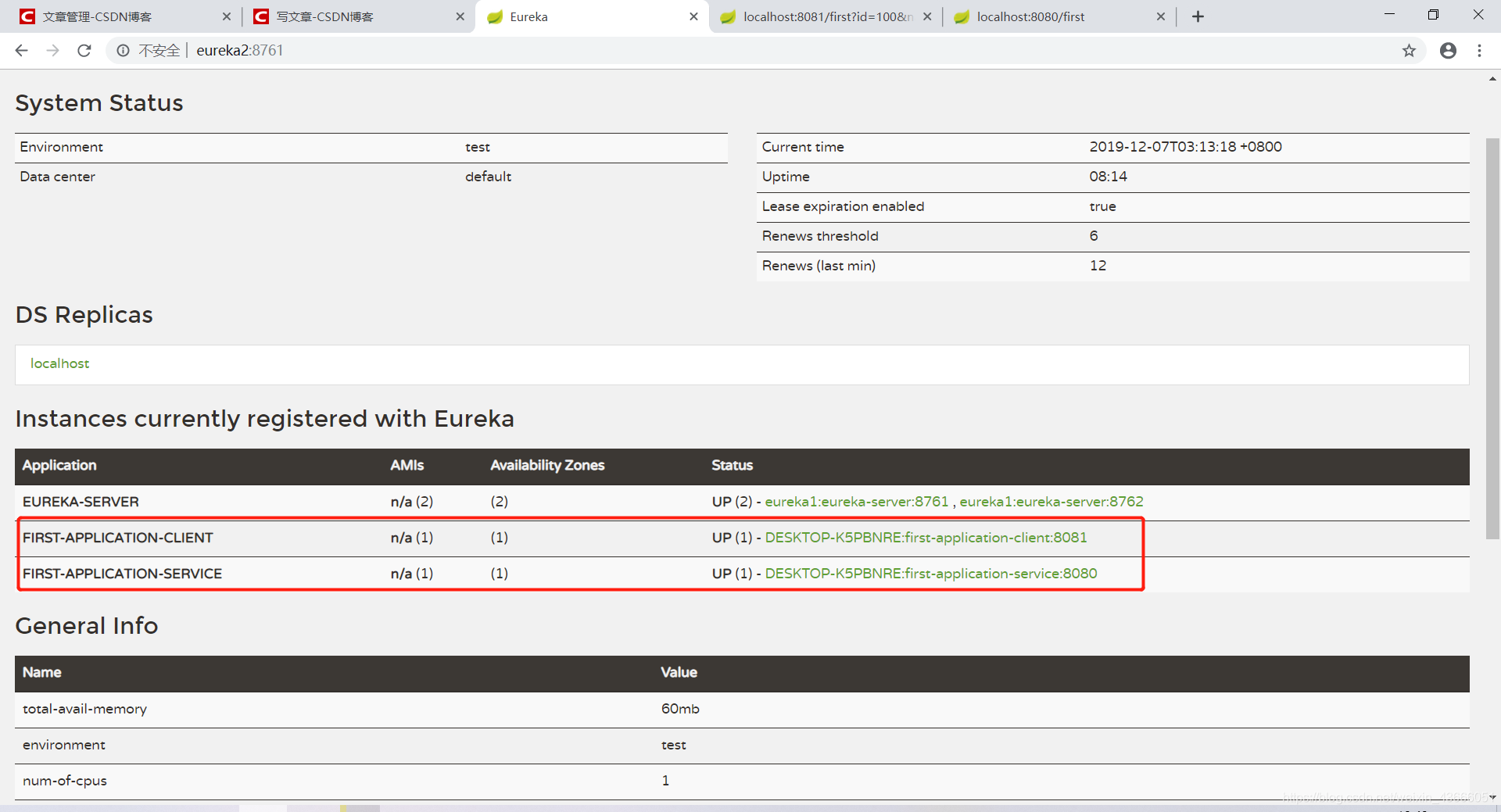
消费方:
1.依赖
2.控制器–单元方法
package com.bjsxt.controller;
import com.bjsxt.service.FirstClientService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class firstClientController {
@Autowired
private FirstClientService service;
@RequestMapping("/second")
public Object second(){
Object rtnValue = service.secondCloudRemoteCall();
return rtnValue;
}
@RequestMapping("/first")
public Object first(Integer id,String name){
Object rtnValue = service.firstCloudRemoteCall(id, name);
System.out.println("remote return value:"+rtnValue);
return rtnValue;
}
}
3.service接口
package com.bjsxt.service;
public interface FirstClientService {
public Object firstCloudRemoteCall(Integer id,String name);
public Object secondCloudRemoteCall();
}
4.service接口的实现类
package com.bjsxt.service.impl;
import com.bjsxt.service.FirstClientService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.ServiceInstance;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalancerClient;
import org.springframework.core.ParameterizedTypeReference;
import org.springframework.http.HttpMethod;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
import java.util.Map;
@Service
public class FirstClientServiceImpl implements FirstClientService {
/**
* 负载均衡客户端,这个客户端和EurekaServer互通
* 可以通过负载均衡客户端,使用服务名称,找你服务的详细信息
*
*/
@Autowired
private LoadBalancerClient loadBalancerClient;
/**
* 远程调用AppService提供的服务,服务名称是:first-application-service
* 要远程调用的服务路径是:/first
* @param id
* @param name
* @return 远程调用服务返回的结果
*/
@Override
public Object firstCloudRemoteCall(Integer id, String name) {
/**
* 通过服务名称找服务实例
* 服务实例包括服务的IP,具体端口,相应的主机名,且包含集群的信息
*/
ServiceInstance instance = loadBalancerClient.choose("first-application-service");
//准备要访问的url
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder("");
builder.append("http://")
.append(instance.getHost())
.append(":")
.append(instance.getPort())
.append("/first?id=")
.append(id)
.append("&name=")
.append(name);
String url = builder.toString();
System.out.println("本次访问的服务地址是:"+url);
//准备一个RestTemplate,发起http请求
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
/**
*
*/
ParameterizedTypeReference<Map<String,String>> type =
new ParameterizedTypeReference<Map<String,String>>() {};
/**
* exchange()方法--发起http请求的方法
* exchange(String url, HttpMethod method, @Nullable HttpEntity<?> requestEntity, ParameterizedTypeReference<T> responseType);
* url----访问地址
* method----请求方式
* entity----请求体
* type----相应类型解析器,会根据解析器配置的泛型类型,提供对应的解析处理能力
*
*/
ResponseEntity<Map<String,String>> responseEntity = restTemplate.exchange(url, HttpMethod.GET, null, type);
//获取相应的具体内容,就是远程调用服务的方法返回值
Map<String, String> rtnValue = responseEntity.getBody();
return rtnValue;
}
@Override
public Object secondCloudRemoteCall() {
ServiceInstance instance = loadBalancerClient.choose("first-application-service");
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder("");
builder.append("http://")
.append(instance.getHost())
.append(":")
.append(instance.getPort())
.append("/second");
String url = builder.toString();
System.out.println("本次访问的服务地址是:"+url);
RestTemplate template = new RestTemplate();
ParameterizedTypeReference<Object> type = new ParameterizedTypeReference<Object>() {};
ResponseEntity<Object> responseEntity = template.exchange(url, HttpMethod.GET, null, type);
Object rtnValue = responseEntity.getBody();
return rtnValue;
}
}
注意:匿名内部类若是抽象类或者接口时,引用类型的泛型传不过来
5.配置文件
package com.bjsxt;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class AppClientApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(AppClientApp.class,args);
}
}
6.启动类
server.port=8081
spring.application.name=first-application-client
eureka.client.service-url.defaultZone=http://eureka1:8762/eureka,http://eureka2:8761/eureka
7.启动

json无限递归的问题:
public class User{
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Role role;
}
public class Role{
private Integer id;
private String name;
private List<User> users;
}
User user = xxService.xxx();
return user;//抛出内存栈溢出错误
{"id":1, "name":"张三", "role":{"id":1, "name":"管理员", "users":[
{"id":1, "name":"张三", "role":{"id":1, "name":"管理员", "users":[
{id":1, "name":"张三", "role":{"id":1, "name":"管理员", "users":[]}}
]}}
]}}
请求穿透问题
Ribbon—支持负载均衡
Ribbon基于http和tcp的客户端
常见的负载均衡策略:
- 轮询策略 (默认)
- 权重轮询 (常用)
- 随机策略 (不推荐)
- 最少并发数策略(在应用在硬件软件环境一致的情况下)
- 在选定的负载均衡策略基础上进行重试机制
- 可用性敏感策略(一般在同区域内服务集群环境中使用)
- 区域敏感性策略(应用在大型的,物理隔离分布式环境中)
举例:
随机策略配置在配置文件中
服务名称.ribbon.NFloadBalancerRuleClassName=com.netflix.loadbalancer.RandomRule
负载均衡:
- 集中式负载均衡 --软件nginx,硬件F5
- 进程内负载均衡–Ribbon
声明式服务调用-Feign—仅在Application Client中使用
1.创建一个新父项目,添加依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<packaging>pom</packaging>
<modules>
<module>serviceapi</module>
<module>feign-provider<







 本文探讨了CAP定理在分布式系统中的权衡,介绍了SpringCloud中的服务提供方开发,重点讲解了Ribbon作为RPC底层实现的负载均衡策略,包括轮询、权重轮询等,并提到了Feign的声明式服务调用。
本文探讨了CAP定理在分布式系统中的权衡,介绍了SpringCloud中的服务提供方开发,重点讲解了Ribbon作为RPC底层实现的负载均衡策略,包括轮询、权重轮询等,并提到了Feign的声明式服务调用。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
















 502
502

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








