目录
什么是并查集
并查集是一种由孩子指向父亲的树结构,可高效地解决连接问题。它可以非常快速地判断网络中节点间的连接状态,还可用于数学中集合类的实现。
什么时候用并查集?
比如,如下给你一张图,图充满了点,两点间有的连接有的没有连接,问给出任意两点,该两点是否有一条路径可以连接起来。此时就可以用并查集进行相关操作。

内部机制
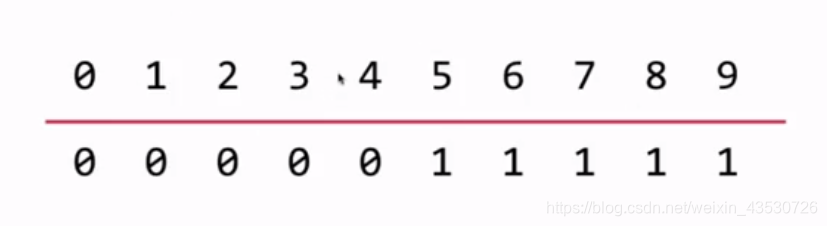
在并查集的内部,我们给每个数据做一个编号,在这里0-9表示10个不同的数据,对每个元素,并查集存储的是一个我们可以称之为它所属于这个集合的parent,比如这里0-4的 parent 为0,5-9的 parent 为1,不同 parent 值可理解为在不同的集合,所以这里的 0-4 和 5-9 是分别属于 0集合 和 1集合 的。
并查集关键操作:
- union() ,将两个元素合并在一起,使它们变成同在一个集合的元素。
- isSameSet(),查看两个元素是否相连(是否同属一个集合)。
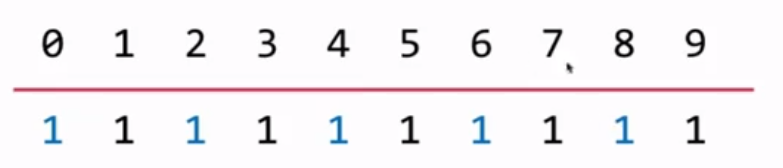
union() 操作图示:

若此时做了 union(1,4)操作,则1所属集合的每个元素和4所属集合的每个元素都连接了起来。所以操作完后 parent 的值都是一样的,都是0或1(自己设定一个值,只要相同就行)。
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 回到目录
Quick-Find
时间复杂度:
- union() :O(n)
- isSameSet():O(1)
- parent 存放每个数据所属集合的编号
public class Main {
static class UnionSet {
private int[] parent;
public UnionSet(int size) {
parent = new int[size];
// 每一个parent[i]指向自己, 表示每一个元素自己自成一个集合
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
parent[i] = i;
}
public int size() {
return parent.length;
}
// 查找过程, 查找元素p所对应的集合编号
private int find(int p) {
if (p < 0 || p >= parent.length)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("p is out of bound.");
return parent[p];
}
//数据之间是否连接
public boolean isSameSet(Integer a, Integer b) {
return find(b) == find(a);
}
// 合并元素p和元素q所属的集合
public void union(int a, int b) {
int aRoot = find(a);
int bRoot = find(b);
if (aRoot == bRoot)
return;
for(int i = 0; i < parent.length; i++)
if (parent[i] == aRoot)
parent[i] = bRoot;
/*也可以写成
if (parent[i] == bRoot)
parent[i] = aRoot;
*/
}
}
}
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 回到目录
Quick-Union(标准情况下的并查集思路)
时间复杂度:
- union() :O(h),h为树的高度
- isSameSet():O(h),h为树的高度
- find()操作, 从当前节点依次往上找到最终的根节点。
- union()操作,找到两个结点的根节点后,将其中一个结点的根节点挂到另一个结点的根节点。
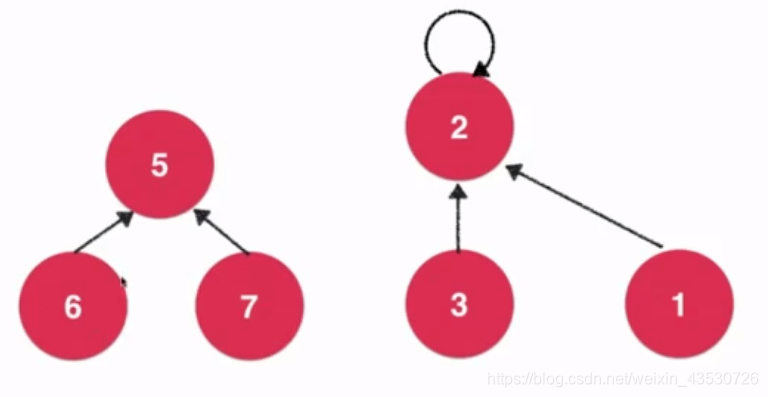
union(6,3) 图示:
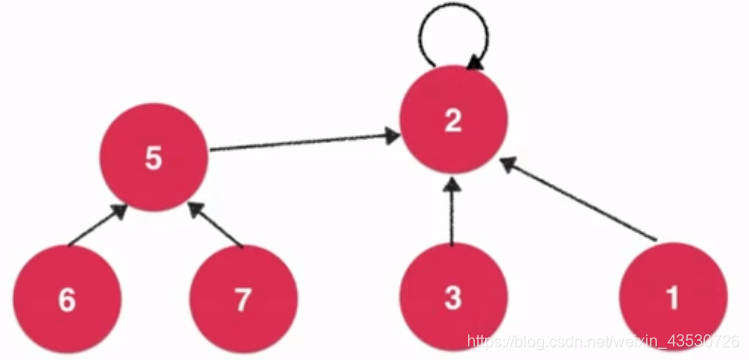
其实比 Quick-Find 就是改了个 find() 的过程。
public class Main {
static class UnionSet {
private int[] parent;
public UnionSet(int size) {
parent = new int[size];
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
parent[i] = i;
}
public int size() {
return parent.length;
}
// 查找过程, 查找元素p所对应的集合编号
private int find(int p) {
if (p < 0 || p >= parent.length)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("p is out of bound.");
while (p != parent[p])
p = parent[p];
return p;
}
public boolean isSameSet(Integer a, Integer b) {
return find(b) == find(a);
}
// 合并元素p和元素q所属的集合
public void union(int a, int b) {
int aRoot = find(a);
int bRoot = find(b);
if (aRoot == bRoot)
return;
parent[aRoot] = bRoot;
}
}
}
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 回到目录
基于size的优化
如果我们依次从0合并到9,那么最终就会形成一棵拥有数组长度的树,这时候我们就要基于 size 对并查集做优化。
优化的方法是:
每一个集合记录一个 size(以i为根的集合中元素个数),在进行 union() 操作的时候,我们将 size 小的(元素少的)挂到 size 大的下面,这样会使得深度稍微小一点。操作完之后记得维护被挂的那个集合的 size()。
其实比 Quick-Union 就是多了个 size数组,然后改了 union() 过程。
public class Main {
static class UnionSet {
private int[] parent;
private int[] sz; // sz[i]表示以i为根的集合中元素个数
public UnionSet(int size) {
parent = new int[size];
sz = new int[size];
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
parent[i] = i;
sz[i] = 1;
}
public int size() {
return parent.length;
}
// 查找过程, 查找元素p所对应的集合编号
private int find(int p) {
if (p < 0 || p >= parent.length)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("p is out of bound.");
while (p != parent[p])
p = parent[p];
return p;
}
public boolean isSameSet(Integer a, Integer b) {
return find(b) == find(a);
}
// 合并元素p和元素q所属的集合
public void union(int a, int b) {
int aRoot = find(a);
int bRoot = find(b);
if (aRoot == bRoot)
return;
if(sz[aRoot] < sz[bRoot]){
parent[aRoot] = bRoot;
sz[bRoot] += sz[aRoot];
}else {
parent[bRoot] = aRoot;
sz[aRoot] += sz[bRoot];
}
}
}
}
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 回到目录
基于rank的优化
现在我们要union(4,2),
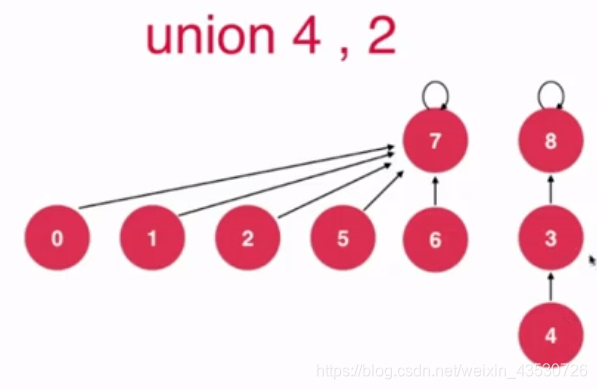
若按照上面的方法,则合并完后会这样:
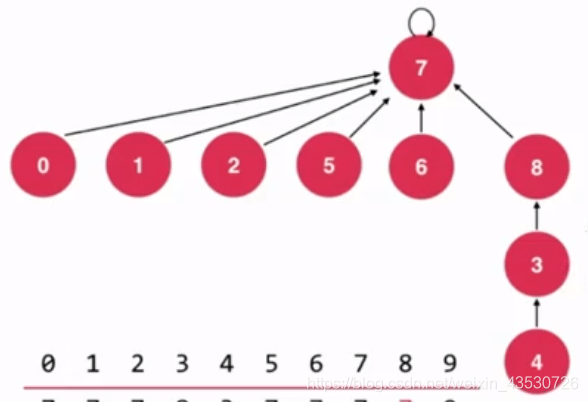
现在的高度为4,但我们可以优化成3的,具体像这样:
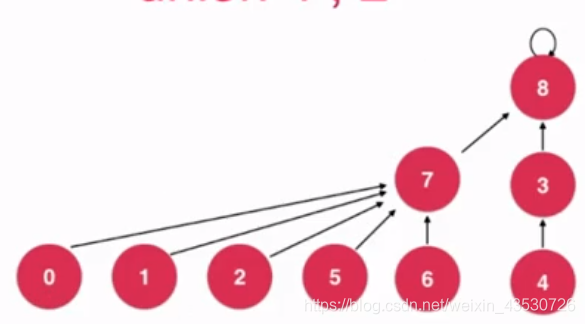
优化的方法:
记录高度 rank,不记录数量 size。
rank[i]表示的是根节点为 i 的树的高度。
其实比 基于size的优化 就是把 size 数组换成了 rank 数组,然后改了 union() 过程。
public class Main {
static class UnionSet {
private int[] parent;
private int[] rank; // rank[i]表示以i为根的集合所表示的树的层数
public UnionSet(int size) {
parent = new int[size];
rank = new int[size];
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
parent[i] = i;
rank[i] = 1;
}
public int size() {
return parent.length;
}
// 查找过程, 查找元素p所对应的集合编号
private int find(int p) {
if (p < 0 || p >= parent.length)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("p is out of bound.");
while (p != parent[p])
p = parent[p];
return p;
}
public boolean isSameSet(Integer a, Integer b) {
return find(b) == find(a);
}
// 合并元素p和元素q所属的集合
public void union(int a, int b) {
int aRoot = find(a);
int bRoot = find(b);
if (aRoot == bRoot)
return;
if(rank[aRoot] < rank[bRoot])
parent[aRoot] = bRoot; // a 挂在 b 下
else if(rank[bRoot] < rank[aRoot])
parent[bRoot] = aRoot;
else { //rank[aRoot] == rank[bRoot]
parent[aRoot] = bRoot; // a 挂在 b 下
rank[bRoot]++; //此时维护rank的值
}
}
}
}
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 回到目录
路径压缩
时间复杂度:
- O(log*n)

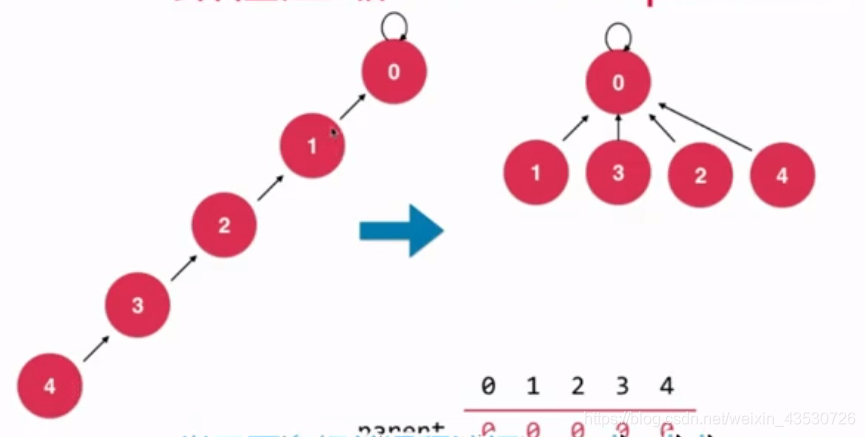
把一棵高树变成一棵矮树 就叫路径压缩,因为对于并查集来说,每一棵子树节点的个数是没有限制的,所以我们应当尽可能地压缩树的高度。
如下图,下面的三个集合是等价的,但是查询的效率是不一样的,越矮的树效率越高。
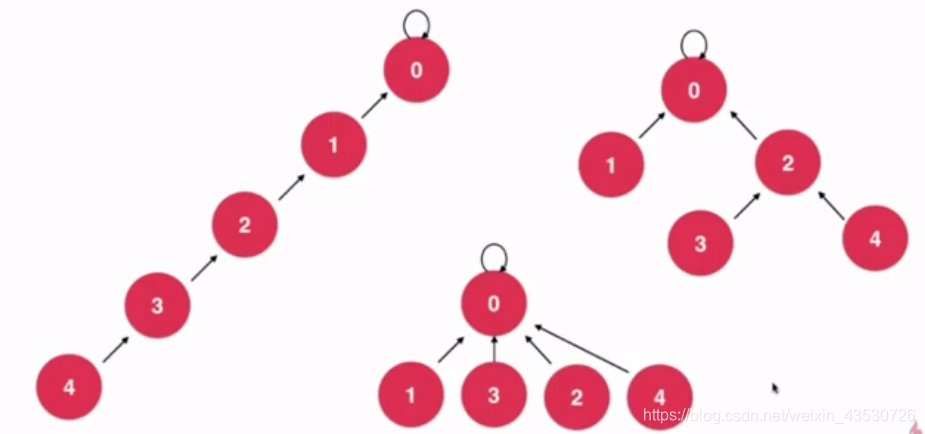
压缩的过程:
发生在 find() 操作的时候,我们让节点接到父节点的父节点上去(即跳过一个节点)
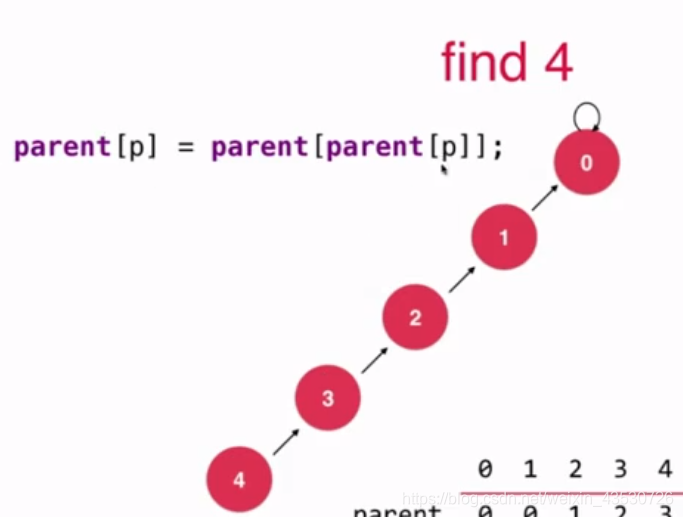
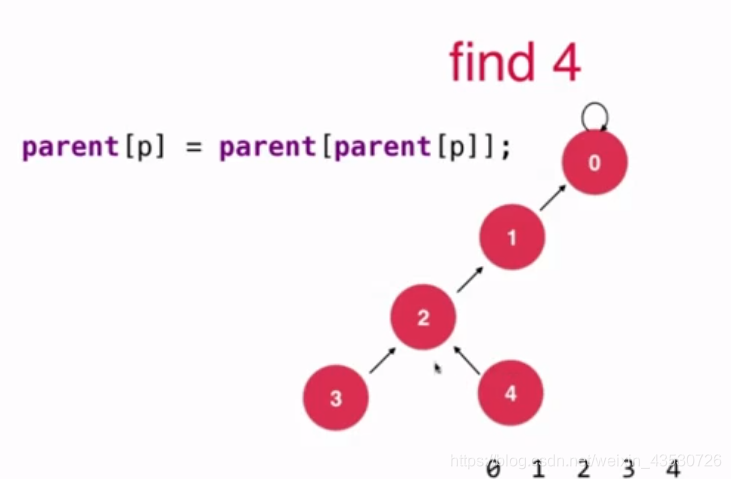
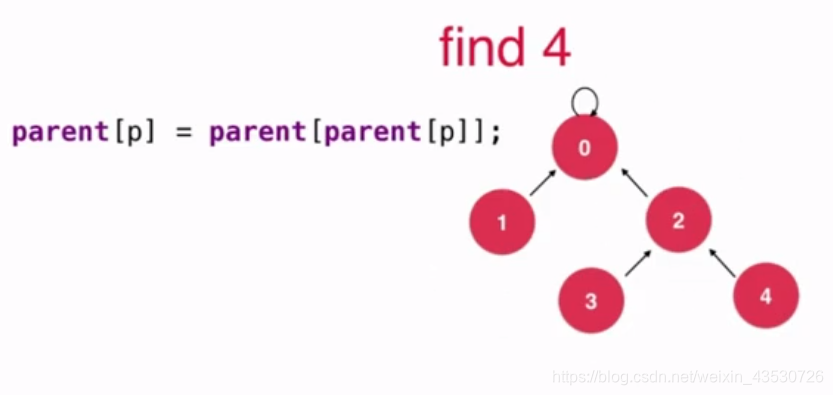
其实比 基于rank的优化 就是把 find() 修改一下,加个 parent[p] = parent[parent[p]]。
public class Main {
static class UnionSet {
private int[] parent;
private int[] rank; // rank[i]表示以i为根的集合所表示的树的层数
public UnionSet(int size) {
parent = new int[size];
rank = new int[size];
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
parent[i] = i;
rank[i] = 1;
}
public int size() {
return parent.length;
}
// 查找过程, 查找元素p所对应的集合编号
private int find(int p) {
if (p < 0 || p >= parent.length)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("p is out of bound.");
while (p != parent[p]) {
parent[p] = parent[parent[p]];
p = parent[p];
}
return p;
}
public boolean isSameSet(Integer a, Integer b) {
return find(b) == find(a);
}
// 合并元素p和元素q所属的集合
public void union(int a, int b) {
int aRoot = find(a);
int bRoot = find(b);
if (aRoot == bRoot)
return;
if(rank[aRoot] < rank[bRoot])
parent[aRoot] = bRoot; // a 挂在 b 下
else if(rank[bRoot] < rank[aRoot])
parent[bRoot] = aRoot;
else { //rank[aRoot] == rank[bRoot]
parent[aRoot] = bRoot; // a 挂在 b 下
rank[bRoot]++; //此时维护rank的值
}
}
}
}
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 回到目录
路径压缩(递归)
我们这次简单粗暴点,让它全部接到第一个根节点。
不过需要注意的是,这个比路径压缩(非递归)性能要差。
其实比 路径压缩(非递归)就是把 find() 修改一下。
public class Main {
static class UnionSet {
private int[] parent;
private int[] rank; // rank[i]表示以i为根的集合所表示的树的层数
public UnionSet(int size) {
parent = new int[size];
rank = new int[size];
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
parent[i] = i;
rank[i] = 1;
}
public int size() {
return parent.length;
}
// 查找过程, 查找元素p所对应的集合编号
private int find(int p){
if(p < 0 || p >= parent.length)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("p is out of bound.");
//这里使用递归,将所有的孩子都直接挂在根下面
if(p != parent[p])
parent[p] = find(parent[p]);
return parent[p];
}
return p;
}
public boolean isSameSet(Integer a, Integer b) {
return find(b) == find(a);
}
// 合并元素p和元素q所属的集合
public void union(int a, int b) {
int aRoot = find(a);
int bRoot = find(b);
if (aRoot == bRoot)
return;
if(rank[aRoot] < rank[bRoot])
parent[aRoot] = bRoot; // a 挂在 b 下
else if(rank[bRoot] < rank[aRoot])
parent[bRoot] = aRoot;
else { //rank[aRoot] == rank[bRoot]
parent[aRoot] = bRoot; // a 挂在 b 下
rank[bRoot]++; //此时维护rank的值
}
}
}
}
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 回到目录





 并查集是一种树形数据结构,用于高效解决集合连接问题。本文介绍了并查集的基本概念、Quick-Find和Quick-Union,以及通过size和rank优化的并查集。还详细讲解了路径压缩及其递归实现,以提高查询效率。
并查集是一种树形数据结构,用于高效解决集合连接问题。本文介绍了并查集的基本概念、Quick-Find和Quick-Union,以及通过size和rank优化的并查集。还详细讲解了路径压缩及其递归实现,以提高查询效率。
















 1056
1056

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








