第10章





10.4 命名空间namespace SALES如果在头文件中定义,类实现的文件里面也要将函数包含在头文件里面,成员函数加const修饰,void showSales() const;,不允许修改成员函数的值
main
using namespace std;
using namespace SALES;
int main(){
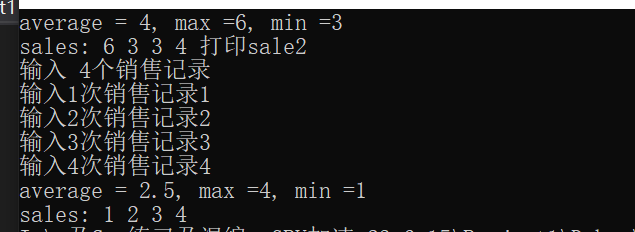
double arr[] = {6,3, 3, 4};
Sales sale1 = Sales(arr, QUARTERS);
sale1.showSales();
cout << "打印sale2" << endl;
Sales sale2 = Sales();
sale2.setSales();
sale2.showSales();
//cout << "打印sale2" << endl;
//setSales(sale2);
//showSales(sale2);
return 0;
}
Sales .h
#pragma once
namespace SALES
{
const int QUARTERS = 4;
class Sales {
public:
Sales(const double ar[], int n);
Sales();
void setSales();
~Sales();
void showSales() const;
double getMin(const double ar[]) const;
double getMax(const double ar[]) const;
double getAverage(const double ar[]) const;
private:
double sales[QUARTERS];
double average;
double max;
double min;
};
}
Sales .cpp
#include "Sales.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
namespace SALES
{
Sales::Sales( const double ar[], int n)
{
average = getAverage(ar);
min = getMin(ar);
max = getMax(ar);
for (unsigned i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
sales[i] = ar[i];
}
}
Sales::Sales()
{
sales[QUARTERS] = { 0 };
average = 0;
max = 0;
min = 0;
}
void Sales::setSales()
{
cout << "输入 " << QUARTERS << "个销售记录" << endl;
int counter = 0;
double array[QUARTERS] = { 0 };
while (counter < QUARTERS) {
cout << "输入" << counter + 1 << "次销售记录";
cin >> array[counter];
sales[counter] = array[counter];
counter++;
}
average = getAverage(array);
min = getMin(array);
max = getMax(array);
}
Sales::~Sales()
{
}
void Sales::showSales() const
{
cout << "average = " << average <<
", max =" << max <<
", min =" << min << endl;
cout << "sales: ";
for (int i = 0; i < QUARTERS; i++) {
cout << sales[i] << " ";
}
}
double Sales::getMin(const double ar[]) const
{
double min = ar[0];
for (int i = 1; i < QUARTERS; i++) {
if (min > ar[i]) {
min = ar[i];
}
}
return min;
}
double Sales::getMax(const double ar[]) const
{
double max = ar[0];
for (int i = 1; i < QUARTERS; i++) {
if (max < ar[i]) {
max = ar[i];
}
}
return max;
}
double Sales::getAverage(const double ar[]) const
{
double aver = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < QUARTERS; i++) {
aver += ar[i];
}
return aver / QUARTERS;
}
}
10.6 定义成员函数内不允许修改值 void showMove() const;
using namespace std;
class TMove
{
private:
double m_x;
double m_y;
public:
TMove(double a = 0, double b = 0);
~TMove();
void showMove() const;
TMove add(const TMove& m) const;
void reset(double a = 0, double b = 0);
};
TMove::~TMove() {
}
TMove::TMove(double a, double b)
{
m_x = a;
m_y = b;
}
void TMove::showMove() const
{
cout << " ----- 显示" << endl;
cout << " m_x = " << m_x << ", m_y = " << m_y << endl;
}
TMove TMove::add(const TMove& m) const
{
/*m_x += m.m_x;
m_y += m.m_y;*/
return TMove(m_x + m.m_x, m_y + m.m_y);
}
void TMove::reset(double a, double b)
{
m_x = a;
m_y = b;
}
int main() {
TMove ar1(1, 2), ar2(2, 2);
ar1.showMove();
ar2.showMove();
TMove ar3 = ar1.add(ar2);
ar3.showMove();
return 0;
}
10.7 成员变量定义char类型的字符串数组,char* name_test;和char name[mk_size];是等价的,作为函数形参的时候,都是使用char* _tempname接收,但是在赋值的时候不一样,使用char* name_test;,对应的拷贝需要先分配内存空间,再进行拷贝,而char name[mk_size];不需要分配内存空间
//char* name_test;
name_test = new char[mk_size];
strcpy_s(name_test, mk_size, _tempname);
//char name[mk_size];
strcpy_s(name, mk_size, _tempname);
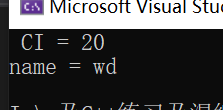
using namespace std;
const int len = 19;
class Plorg {
public:
Plorg(const char* name = "Plorga", int ci = 0);
~Plorg();
void show() const;
private:
static const unsigned mk_size = 20;
char name[mk_size];
char *name_test;
int CI;
};
Plorg::Plorg(const char* _tempname, int ci)
{
CI = ci;
strcpy_s(name, mk_size, _tempname);
//name_test = new char[mk_size];
//strcpy_s(name_test, mk_size, _tempname);
}
Plorg::~Plorg()
{
}
void Plorg::show() const
{
cout << " CI = " << CI << endl;
cout << "name = " << name << endl;
}
int main() {
Plorg plor("wd",20);
plor.show();
return 0;
}
10.8 void visit(void (*pf) (Item& item));函数,遍历 MyList 的数组 arr,一共 m_size 个有效元素。每个元素传给 函数pf,pf(arr[i]),对每个元素执行你传进来的函数。这是一个 函数指针,pf 是它的名字。它指向一个“接受 Item& 引用参数,返回 void”的函数。static void show(MyList::Item& item)满足这个要求,所以void visit(void (*pf) (Item& item));函数将会调用show`函数
- 知识点2:
typedef int Item;定义了变量类型的别名
static void show(MyList::Item& item)
{
cout << item << ' ';
}
void MyList::visit(void (*pf) (Item& item))
{
for (unsigned i = 0; i < m_size; ++i) {
pf(arr[i]);
}
}
#include <iostream>
#include <exception>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <array>
#include "string"
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
class MyList {
public:
typedef int Item;
MyList(const Item arr[] = NULL, unsigned int n =0);
~MyList();
bool isFull() const;
bool isEmpty() const;
bool append(const Item& item);
void visit(void (*pf) (Item& item));
private:
static const unsigned int maxLen = 4;
unsigned int m_size;
int arr[maxLen];
};
static void show(MyList::Item& item)
{
cout << item << ' ';
}
void MyList::visit(void (*pf) (Item& item))
{
for (unsigned i = 0; i < m_size; ++i) {
pf(arr[i]);
}
}
MyList::MyList(const Item arr[], unsigned int n)
{
if (NULL == arr) {
m_size = 0;
return;
}
m_size = maxLen < n ? maxLen : n;
for (int i = 0; i < maxLen; i++) {
this->arr[i] = arr[i];
}
}
MyList::~MyList()
{
}
bool MyList::isFull() const
{
return (maxLen == m_size);
}
bool MyList::isEmpty() const
{
return (0 == m_size);
}
bool MyList::append(const Item& item)
{
if (isFull()) {
return false;
}
arr[m_size++] = item;
}
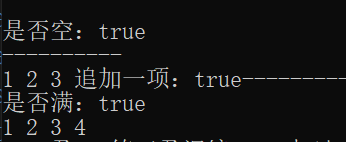
int main() {
MyList listOne;
listOne.visit(show);
cout << endl;
cout << "是否空:" << boolalpha << listOne.isEmpty() << endl;
cout << "----------" << endl;
MyList::Item arr[] = {1,2,3};
MyList lisTwo(arr,3);
lisTwo.visit(show);
cout << "追加一项:" <<lisTwo.append(4);
cout << "----------" << endl;
cout << "是否满:" << boolalpha << lisTwo.isFull() << endl;
lisTwo.visit(show);
return 0;
}
第11章




11.1 运算符重载 ,返回本身时要传指针; 字符串作为函数变量,形参表示void Vector::showVtec(const char* name)
Vector operator+ (const Vector& rvalue) const;
Vector& operator+= (const Vector& rvalue);
Vector operator- (const Vector& rvalue) const;
Vector& Vector::operator+=(const Vector& rvalue)
{
*this = *this + rvalue;
return (*this);
}

#pragma once
class Vector
{
public:
explicit Vector(double x = 0, double y = 0); // (x, y) OR (length, angle)
void reset(double x = 0, double y = 0);
double getX() const;
double getY() const;
double getLength() const;
Vector operator+ (const Vector& rvalue) const;
Vector& operator+= (const Vector& rvalue);
Vector operator- (const Vector& rvalue) const;
void showVtec();
// ======================================
private:
double m_x; // 直角坐标的X坐标
double m_y; // 直角坐标的Y坐标
};
#include "Vector.h"
#include <cmath>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
Vector::Vector(double x, double y)
{
m_x = x;
m_y = y;
}
void Vector::reset(double x, double y)
{
m_x = x;
m_y = y;
}
double Vector::getX() const
{
return m_x;
}
double Vector::getY() const
{
return m_y;
}
double Vector::getLength() const
{
return sqrt(m_x* m_x + m_y* m_y);
}
Vector Vector::operator+(const Vector& rvalue) const
{
return Vector(rvalue.m_x + this->m_x, rvalue.m_y + this->m_y);
}
Vector& Vector::operator+=(const Vector& rvalue)
{
*this = *this + rvalue;
return (*this);
}
Vector Vector::operator-(const Vector& rvalue) const
{
return Vector(this->m_x - rvalue.m_x, this->m_y- rvalue.m_y);
}
void Vector::showVtec()
{
cout << "(" << m_x << "," << m_y << ")" << endl;
}
int main() {
Vector vet1(1, 2);
Vector vet2(3, 4);
Vector vet3(0, 0);
vet3 = vet1 + vet2;
vet1.showVtec("vet1");
vet2.showVtec("vet2");
vet3.showVtec("vet1 + vet2 = vet3");
vet3.reset();
vet3 = vet1 - vet2;
vet3.showVtec("vet1 - vet2 = vet3");
vet3 += vet1;
vet1.showVtec("vet1");
vet3.showVtec("vet3 += vet1 :");
return 0;
}
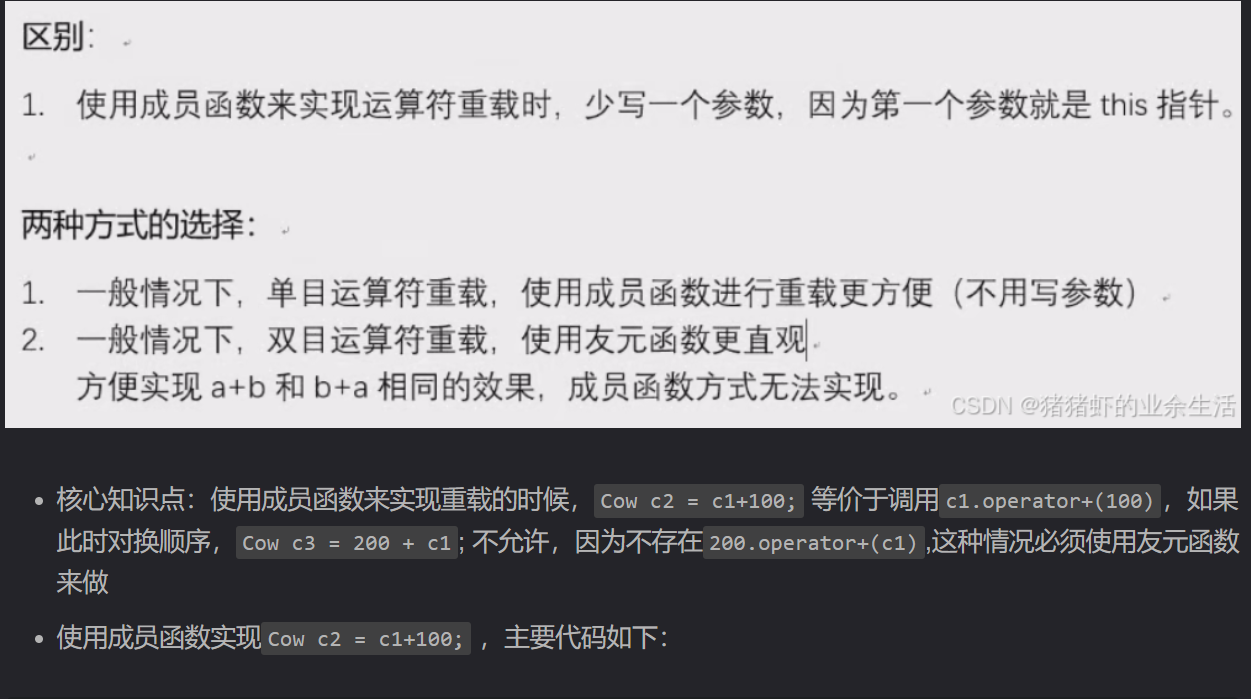
11.4 友元函数实现运算符重载:知识点:什么时候使用友元函数,什么时候使用成员函数来实现重载
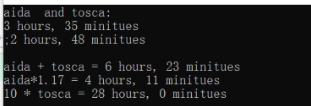
11.4.1 修改前
#include <iostream>
#include <exception>
#include <stdexcept>
#include "string"
#include <fstream>
#include<conio.h>
#include<Windows.h>
#include <graphics.h>
#include "myTime.h"
using namespace std;
int main() {
myTime aida(3,35);
myTime tosca(2,48);
myTime temp;
cout << "aida and tosca:" << endl;
cout << aida << ";" << tosca << endl;
temp = aida + tosca;
cout << "aida + tosca = " << temp;
temp = aida*1.17;
cout << "aida*1.17 = " << temp;
temp = 10 * tosca;
cout << "10 * tosca = " << temp;
return 0;
}
------------------------------------------------
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
class myTime
{
private:
int hours;
int minutes;
public:
myTime();
myTime(int h, int m = 0);
void AddMin(int m);
void AddHr(int h);
void Reset(int h, int m);
myTime operator + (const myTime &t) const;
myTime operator - (const myTime &t) const;
myTime operator * (double mult) const;
friend myTime operator*(double m, const myTime &t) { return t * m; };
friend std::ostream &operator << (std::ostream &os, const myTime &t);
};
------------------------------------------------
#include "myTime.h"
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
myTime::myTime()
{
hours = 0;
minutes = 0;
}
myTime::myTime(int h, int m)
{
hours = h;
minutes = m;
}
void myTime::AddMin(int m)
{
minutes += m;
hours += minutes / 60;
minutes = minutes & 60;
}
void myTime::AddHr(int h)
{
hours += h;
}
void myTime::Reset(int h, int m)
{
hours = h;
minutes = m;
}
myTime myTime::operator+(const myTime & t) const
{
myTime sum;
sum.minutes = this->minutes + t.minutes;
sum.hours = this->hours + t.hours + sum.minutes / 60;
sum.minutes = sum.minutes % 60;
return sum;
}
myTime myTime::operator-(const myTime & t) const
{
myTime diff;
int tot1, tot2;
tot1 = t.minutes + 60 * t.hours;
tot2 = this->minutes + this->hours * 60;
diff.minutes = (tot2 - tot1)%60;
diff.hours = (tot2 - tot1) / 60;
return diff;
}
myTime myTime::operator*(double mult) const
{
myTime tm;
long totalMinute = this->hours * 60 * mult + this->minutes * mult;
tm.hours = totalMinute / 60;
tm.minutes = totalMinute % 60;
return tm;
}
std::ostream & operator<<(std::ostream & os, const myTime & t)
{
os << t.hours << " hours, " << t.minutes << " minitues" << endl;
return os;
// TODO: 在此处插入 return 语句
}
11.4.2 全都使用友元函数来实现
- 下面成员函数的实现和友元函数实现效果是一样的
myTime operator + (const myTime &t) const;
myTime operator - (const myTime &t) const;
friend myTime operator+(const myTime &t1, const myTime &t2);
friend myTime operator-(const myTime &t1, const myTime &t2);
myTime operator+(const myTime & t1, const myTime & t2)
{
myTime sum;
sum.minutes = t1.minutes + t2.minutes;
sum.hours = t1.hours + t2.hours + sum.minutes / 60;
sum.minutes = sum.minutes % 60;
return sum;
}
myTime operator-(const myTime & t1, const myTime & t2)
{
myTime diff;
int tot1, tot2;
tot1 = t1.minutes + 60 * t1.hours;
tot2 = t2.minutes + t2.hours * 60;
diff.minutes = (tot2 - tot1) % 60;
diff.hours = (tot2 - tot1) / 60;
return diff;
}
第12章







12.1 深拷贝和浅拷贝问题; char name[20]; 和 char* hobby;两者赋值的不同
12.1.1 Cow(const Cow &c); //拷贝构造函数; 如果不定义拷贝构造函数而使用了拷贝功能,c++会自动生成一个拷贝函数,实现的是浅拷贝。如果只是普通的数据类型是没有关系的,但是如果是指针,就会出现问题,以下列案例为例:
Cow::Cow(const Cow& c)
{
strcpy_s(name, c.name);
this->hobby = new char[20];
strcpy_s(this->hobby, 20, c.hobby);
this->weight = c.weight;
}
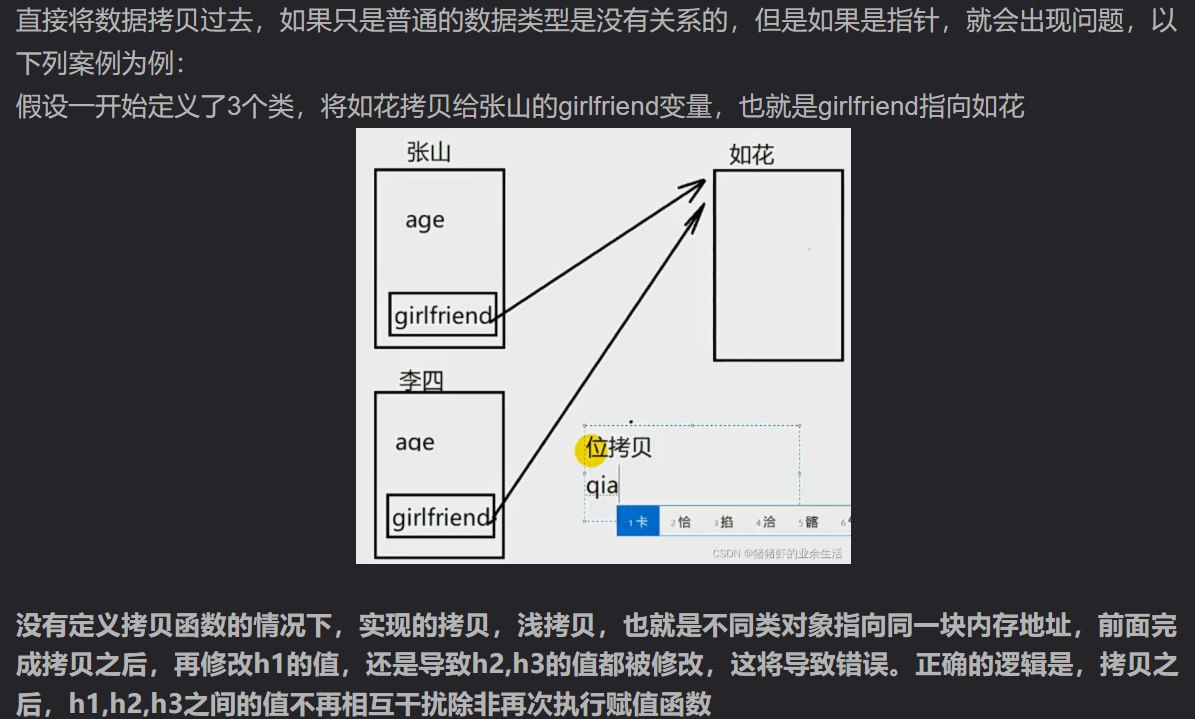
12.1.2 拷贝构造函数和赋值运算符重载Cow& operator= (const Cow& c); 的区别,功能相似(都是实现对象的拷贝,但它们的使用场景不同,拷贝构造函数当 新对象被创建 并用另一个同类对象初始化时调用Cow c1; Cow c2 = c1;或者Cow c2(c1);赋值运算符当 已存在的对象 被另一个同类对象赋值时调用Cow c3; c3 = c1;
12.1.3 当前类变量里面有动态分配指针的char* hobby, 赋值的时候要先new分配内存才能进行使用,即使实现了 operator=,如果没有拷贝构造函数,以下代码会 调用编译器生成的默认拷贝构造函数(浅拷贝),导致内存问题。 如果只实现拷贝构造函数, 因为 Cow 类中有 动态分配的 char* hobby,默认的拷贝构造函数会直接复制指针(浅拷贝),也会出问题。因此此处要求拷贝构造和赋值运算符重载同时实现
Cow c1("Alice", "Swimming", 120.0);
Cow c2 = c1; // 调用拷贝构造函数,而非 operator=
12.1.4 char name[20];和 char* hobby;使用总结前者了可以直接使用strcpy_s进行赋值strcpy_s(name, c.name),后者需要先对要使用的变量分配空间,然后再拷贝
Cow& Cow::operator= (const Cow& c) {
strcpy_s(name, c.name);
this->hobby = new char[20];
strcpy_s(this->hobby,20, c.hobby);
this->weight = c.weight;
return *this;
}
12.1.5 对于char *hobby 成员变量,需要在析构函数里面进行内存释放delete [] hobby;
12.1.6 完整代码
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include "string"
#include<Windows.h>
#include <array>
using namespace std;
class Cow {
private:
char name[20];
char* hobby;
double weight;
public:
Cow();
Cow(const char *nm, const char *hobby, double weight);
Cow(const Cow &c); //拷贝构造函数
~Cow();
Cow& operator= (const Cow& c); //赋值运算符重载
Cow operator+ (const Cow& c); //+号运算符重载
bool operator>(const Cow& c); //关系运算符重载
void ShowCow() const;
};
Cow& Cow::operator= (const Cow& c) {
strcpy_s(name, c.name);
this->hobby = new char[20];
strcpy_s(this->hobby,strlen(c.hobby)+1, c.hobby);
this->weight = c.weight;
return *this;
}
Cow Cow::operator+(const Cow& c)
{
this->weight = c.weight + this->weight;
return Cow(this->name, this->hobby, this->weight);
}
bool Cow::operator>(const Cow& c)
{
if (this->weight > c.weight) return true;
return false;
}
void Cow::ShowCow() const
{
cout << this->name << ", " << this->hobby << ", " << this->weight << endl;
}
Cow::Cow() {
//name = "NoBody";
strcpy_s(name, "NoBody");
hobby = new char[20];
strcpy_s(name, "none");
weight = 200;
}
Cow::Cow(const char* nm, const char* ho, double wei)
{
strcpy_s(name, nm);
hobby = new char[20];
strcpy_s(hobby,20, ho);
weight = wei;
}
Cow::Cow(const Cow& c)
{
strcpy_s(name, c.name);
this->hobby = new char[20];
strcpy_s(this->hobby, 20, c.hobby);
this->weight = c.weight;
}
Cow::~Cow()
{
delete [] hobby;
}
int main(void) {
Cow cow1("wang", "drink", 20);
Cow cow2("zheng", "play", 21);
cow1.ShowCow();
cow2.ShowCow();
Cow cow3;
cow3 = cow1;
cow3.ShowCow();
cow3 = cow1 + cow2;
cow3.ShowCow();
return 0;
}
12.2 各种重载的应用
12.2.1 知识点1:拷贝构造函数MyString (const MyString& s);和赋值运算符重载MyString& operator = (const MyString& s);的区别:返回值不一样,新的对象被创建 调用拷贝构造函数,对已经存在的对象赋值,调用赋值构造函数
- 新对象被创建
MyString s1("and I am a c++ student"); //新的对象被创建,调用拷贝构造函数
MyString s2 = "Please enter your name: "; //新的对象被创建,调用拷贝构造函数
- 对已经存在的对象赋值,调用赋值构造函数
s2 = s2 + s1;
s1 = "red"; //调用赋值运算符重载
s2 = "My name is " + s3;
//拷贝构造函数
MyString::MyString(const MyString& s)
{
this->str = s.str;
}
MyString& MyString::operator=(const MyString& s)
{
this->str = s.str;
// TODO: 在此处插入 return 语句
return *this;
}
12.2.2 知识点2:实现 s2 = s2 + s1; ,实现s2 = "My name is " + s3;以及实现s2 = s3 + "My name is ";三者之间的区别和联系,三者都是实现+运算符重载,"My name is "属于char*类型
MyString operator+(const char *s);只能处理MyString + const char*MyString operator+(const MyString &s);只能处理MyString +MyStringMyString operator+(const char* s1, const MyString& s2);全局函数实现 const char* + MyString,但是需要注意的是全局函数非成员函数,s2无法直接访问类里面的变量中,因此需要额外定义一个函数来获取要处理的东西s2.getString()
MyString operator+(const char* s1, const MyString& s2)
{
//return MyString(s1+ s2); //全局函数而非成员函数,s2无法直接访问类里面的变量
return MyString(s1 + s2.getString());
}
12.2.3 知识点3:char *类型的字符串和string类型的字符串可以直接相加实现字符串的拼接
12.2.4 知识点4:遍历string类型的字符串并对其字符进行修改for (char& ch : str)
for (char& ch : str) { // 使用引用直接修改 str
ch = static_cast<char>(tolower(static_cast<unsigned char>(ch)));
}
或者
for (char &ch : str) {
if (isalpha(ch)) {
ch = (char)toupper(ch);
}
}
12.2.5 知识点5:返回引用的作用,可以直接对值进行修改并返回被修改的值,MyString& Stringlow();可以通过MyString ans = ”ssf"; ans.Stringlow(); 直接进行调用,返回引用,表示修改当前对象,但是如果MyString Stringlow();不返回引用,就无法这样调用,这种方式,在函数里面创建了一个新的对象,但 ans.Stringlow(); 只是调用函数,没有接收返回值,所以 ans 本身不会改变。ans = ans.Stringlow() 将返回值赋给 ans
12.2.6 知识点6:getline函数接收输入有空格的数据,输入运算符和输出运算符重载,一个是ostream,一个是istream,接收输入时,只能接收到空格以前的数据is >> s.str;return is;,如果要接收空格以后的数据std::getline(is, s.str);
friend ostream& operator <<(ostream& os, const MyString& s); //输出符重载
friend istream& operator >>(istream& is, MyString& s); //输入符重载
code
#pragma once
#include "string"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class MyString
{
public:
MyString();
~MyString();
MyString(const string s);
MyString (const MyString& s); //拷贝构造函数
MyString& operator = (const MyString& s); //赋值运算符重载
MyString(const char* s); //构造函数
MyString operator+(const char *s); //只能处理MyString + const char*,不能处理const char* + MyString
MyString operator+(const MyString &s);
MyString& Stringlow();
MyString& Stringbig();
friend ostream& operator <<(ostream& os, const MyString& s); //输出符重载
friend istream& operator >>(istream& is, MyString& s); //输入符重载
bool operator == (const MyString &s); //关系运算符重载
string getString()const;
int has(const char c);
private:
string str;
};
//定义全局函数实现 const char* + MyString
MyString operator+(const char* s1, const MyString& s2);
#include "MyString.h"
MyString::MyString()
{
}
MyString::~MyString()
{
}
MyString::MyString(const string s)
{
this->str = s;
}
//拷贝构造函数
MyString::MyString(const MyString& s)
{
this->str = s.str;
}
MyString& MyString::operator=(const MyString& s)
{
this->str = s.str;
// TODO: 在此处插入 return 语句
return *this;
}
//如何将char *类型的数据直接赋值给string类型的数据
MyString::MyString(const char* s)
{
this->str = s;
}
MyString MyString::operator+(const char* s)
{
return MyString(s + this->str);
}
MyString MyString::operator+(const MyString& s)
{
return MyString(this->str + s.str);
}
MyString& MyString::Stringlow()
{
string temp = "";
for (char& ch : str) { // 使用引用直接修改 str
ch = static_cast<char>(tolower(static_cast<unsigned char>(ch)));
}
return *this;
}
MyString& MyString::Stringbig()
{
string temp = "";
temp.reserve(str.length()); // 预分配空间提高效率
//for (char ch : str) {
// temp += static_cast<char>(toupper(static_cast<unsigned char>(ch)));
// // 处理所有字符,不仅仅是字母,因为tolower对非字母字符是透明的
//}
//for (char& ch : str) { // 使用引用直接修改 str
// ch = static_cast<char>(toupper(static_cast<unsigned char>(ch)));
//}
for (char &ch : str) {
if (isalpha(ch)) {
ch = (char)toupper(ch);
}
}
return *this;
}
bool MyString::operator==(const MyString& s)
{
return this->str == s.str;
}
string MyString::getString() const
{
return string(str);
}
int MyString::has(const char c)
{
int len = 0;
for (char ch : str) {
if (ch == c) {
len++;
}
}
return len;
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const MyString& s)
{
os << s.str;
return os;
// TODO: 在此处插入 return 语句
}
istream& operator>>(istream& is, MyString& s)
{
//is >> s.str;
std::getline(is, s.str);
return is;
// TODO: 在此处插入 return 语句
}
MyString operator+(const char* s1, const MyString& s2)
{
//return MyString(s1+ s2); //全局函数而非成员函数,s2无法直接访问类里面的变量
return MyString(s1 + s2.getString());
}
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include "string"
#include<Windows.h>
#include <array>
#include "MyString.h"
using namespace std;
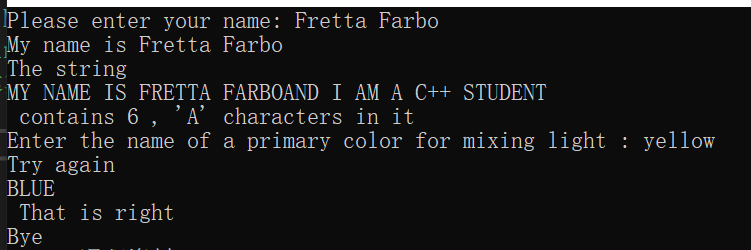
int main(void) {
MyString s1("and I am a c++ student"); //新的对象被创建,调用拷贝构造函数
MyString s2 = "Please enter your name: "; //新的对象被创建,调用拷贝构造函数
//MyString s2 = "Please enter your name"; 里面 "Please enter your name"是const char *类型
MyString s3;
cout << s2;
cin >> s3;
s2 = "My name is " + s3;
cout << s2 << " \n";
s2 = s2 + s1;
s2.Stringbig();
cout << "The string\n" << s2 << "\n contains " << s2.has('A') << " , 'A' characters in it \n";
s1 = "red"; //调用赋值运算符重载
MyString rgb[3] = { MyString(s1),MyString("green"),MyString("blue")};
cout << "Enter the name of a primary color for mixing light : ";
MyString ans;
bool success = false;
while (cin >> ans) {
//MyString Stringlow();这种方式,在函数里面创建了一个新的对象,但 ans.Stringlow(); 只是调用函数,没有接收返回值,所以 ans 本身不会改变。ans = ans.Stringlow() 将返回值赋给 ans
ans.Stringlow(); // MyString& MyString::Stringlow() // 返回引用,表示修改当前对象
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
if (ans == rgb[i]) {
cout << " That is right \n";
success = true;
break;
}
}
if (success)
break;
else
cout << "Try again\n";
}
cout << "Bye";
return 0;
}
第13章 类继承



13.1 多态
13.1.1 知识点1:纯虚函数和虚函数的区别是什么:虚函数和 纯虚函数都用于实现 多态,虚函数用virtual声明,但是有函数体,也就是基类会实现这个函数,派生类可以重写他,但是不是必须的,但允许派生类自定义行为时使用; 纯虚函数也用virtual,virtual void show() = 0; // 纯虚函数(无实现),基类 只定义接口,强制派生类必须实现时使用,使用了纯虚函数的类就是抽象类,基类不能对函数进行实现
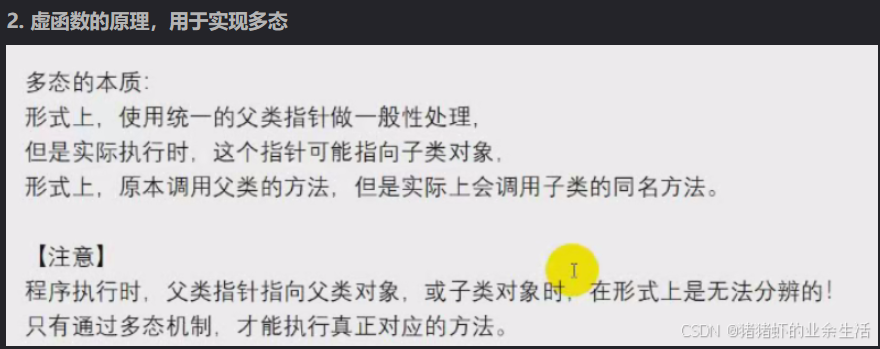
13.1.2 知识点2:多态的作用,基类和派生类,父类和子类有同名函数,但是功能不一样,但是同时,子类又继承了父类,就会导致调用的错误,想调用子类的同名函数,但是在某些情况下,会错误调用父类的同名函数。上述问题的解决方案就是在父类里面使用虚基类,只需要在父类的同名函数前面加上virtual关键字即可,子类的同名函数可加可不加,虚函数的作用,就是为了用于实现多态
13.1.3 派生类重写基类的函数时候,可以加上override关键字,防止函数名写错,只需要在函数声明的时候用override,函数实现的时候不需要加这个关键字
13.1.4 实际开发过程中,如果某一个类作为基类,推荐是对该类的析构函数都加上virtual关键字
13.1.5 多态实现的三个条件:必须是公有继承class Classic: public Cd ;必须是通过基类的指针或引用 指向派生类对象 访问派生类方法Cd* pcd = &c1;pcd = &c2; ;基类的方法必须是虚函数,且完成了虚函数的重写
13.1.6 多态和继承之间的区别,1.继承关系中,并不要求基类方法一定是虚函数。而多态时,要求基类方法必须是虚函数。2.多态的实现要求必须是公有继承。3.多态:子类重写父类的方法,使得子类具有不同的实现。且运行时,根据实际创建的对象动态决定使用哪个方法
virtual ~Cd();
virtual void Report() const;
virtual Cd& operator= (const Cd& d);
13.1.7 多数情况会沿用基类的变量,在基类的成员变量基础上添加一些新的变量,那么对已有的变量,派生类该如何初始化。 Classic::Classic(const char* w, const char* s1, const char* s2, int n, double x):Cd(s1, s2, n, x) {},而不能Classic::Classic(const char* w, const char* s1, const char* s2, int n, double x):Cd(performers,label, selections, playtime) 。这些成员变量属于基类,派生类构造函数无权直接访问基类私有成员,通过参数 s1, s2, n, x 直接传递给基类构造函数 Cd(s1, s2, n, x)。
- 基类
Cd(const char* s1, const char* s2, int n, double x);,基类里面同时定义了多个变量,基类的构造函数对变量进行初始化
char performers[50];
char label[20];
int selections;
double playtime;
Cd::Cd(const char* s1, const char* s2, int n, double x)
{
strcpy_s(performers, sizeof(performers), s1);
strcpy_s(label, sizeof(label), s2);
this->selections = n;
this->playtime = x;
}
- 派生类:只定义了一个成员变量
char worker[50];,其余变量继承于基类,其构造函数Classic(const char* w, const char* s1, const char* s2, int n, double x);
对基类的成员函数,Classic::Classic(const char* w, const char* s1, const char* s2, int n, double x):Cd(s1, s2, n, x) {},而不能Classic::Classic(const char* w, const char* s1, const char* s2, int n, double x):Cd(performers,label, selections, playtime) 。这些成员变量属于基类,派生类构造函数无权直接访问基类私有成员
Classic::Classic(const char* w, const char* s1, const char* s2, int n, double x):
Cd(s1, s2, n, x)
{
strcpy_s(this->worker, sizeof(this->worker), w);
}
13.1.8 派生类不能直接访问基类的私有成员变量和私有成员函数。派生类如何访问基类的成员变量,不能直接就调用performers 等基类的成员变量,而是Cd::Report()进行打印
void Classic::Report() const
{
//std::cout << performers << ", " << this->label << " , selections = " <<
// selections << " , playtime = " << playtime << std::endl;
std::cout << "worker " << worker << " ";
Cd::Report();
}
code
- 基类
#pragma once
class Cd
{
private:
char performers[50];
char label[20];
int selections;
double playtime;
public:
Cd(const char* s1, const char* s2, int n, double x);
Cd(const Cd& d);
Cd();
virtual ~Cd();
virtual void Report() const;
virtual Cd& operator= (const Cd& d);
};
#include "Cd.h"
#include "string"
#include <iostream>
Cd::Cd(const char* s1, const char* s2, int n, double x)
{
strcpy_s(performers, sizeof(performers), s1);
strcpy_s(label, sizeof(label), s2);
this->selections = n;
this->playtime = x;
}
Cd::Cd(const Cd& d)
{
strcpy_s(performers, strlen(d.performers) + 1, d.performers);
strcpy_s(label, strlen(d.label) + 1, d.label);
selections = d.selections;
playtime = d.playtime;
}
Cd::Cd()
{
//因为数组名 performers 是一个常量指针,不能直接赋值。
//this->performers = '';
memset(performers, 0, sizeof(performers)); // 全部初始化为 '\0'
memset(label, 0, sizeof(label)); // 全部初始化为 '\0'
selections = 0;
playtime = 0;
}
Cd::~Cd()
{
}
void Cd::Report() const
{
std::cout << this->performers << ", " << this->label << " , selections = " << selections << " , playtime = " << playtime << std::endl;
}
Cd& Cd::operator=(const Cd& d)
{
// TODO: 在此处插入 return 语句
strcpy_s(performers, strlen(d.performers) + 1, d.performers);
strcpy_s(label, strlen(d.label) + 1, d.label);
selections = d.selections;
playtime = d.playtime;
return *this;
}
- 派生类
#pragma once
#include "Cd.h"
class Classic: public Cd
{
private:
char worker[50];
public:
Classic();
Classic(const char* w, const char* s1, const char* s2, int n, double x);
~Classic();
void Report() const;
};
#include "Classic.h"
#include "string"
#include <iostream>
Classic::Classic()
{
memset(worker, 0, sizeof(worker));
}
Classic::Classic(const char* w, const char* s1, const char* s2, int n, double x):
Cd(s1, s2, n, x)
//Cd(performers,label, selections, playtime) 这些成员变量属于基类,派生类构造函数无权直接访问基类私有成员。
//通过参数 s1, s2, n, x 直接传递给基类构造函数 Cd(s1, s2, n, x)。
{
strcpy_s(this->worker, sizeof(this->worker), w);
}
Classic::~Classic()
{
}
void Classic::Report() const
{
//std::cout << performers << ", " << this->label << " , selections = " <<
// selections << " , playtime = " << playtime << std::endl;
std::cout << "worker " << worker << " ";
Cd::Report();
}
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include "string"
#include<Windows.h>
#include <array>
#include "Classic.h"
using namespace std;
void Bravo(const Cd &disk) {
disk.Report();
}
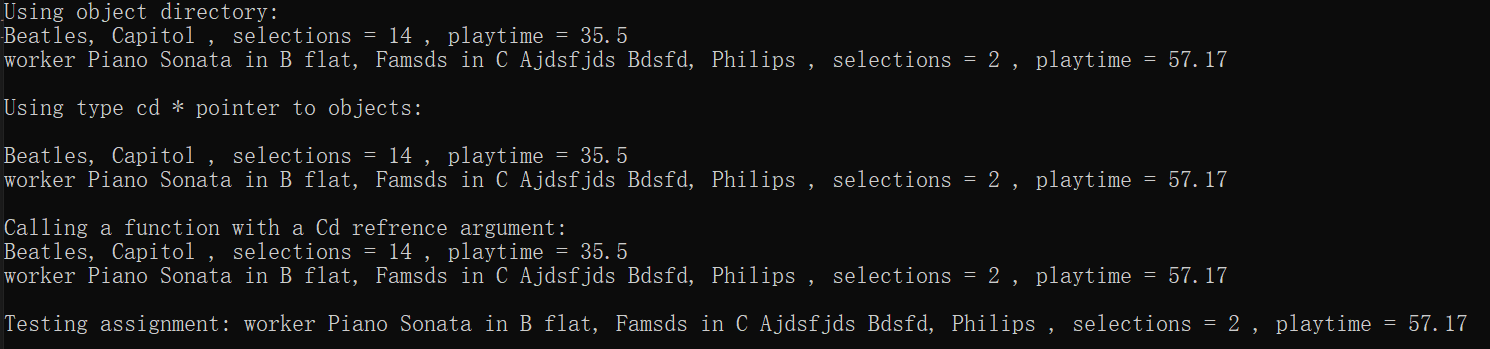
int main(void) {
Cd c1("Beatles", "Capitol", 14, 35.5); //基类
Classic c2 = Classic("Piano Sonata in B flat, Famsds in C", "Ajdsfjds Bdsfd", "Philips",2, 57.17); //派生类
Cd* pcd = &c1;
cout << "Using object directory:\n";
c1.Report();
c2.Report();
cout << endl;
cout << "Using type cd * pointer to objects:\n";
cout << endl;
pcd->Report();
pcd = &c2;
pcd->Report();
cout << endl;
cout << "Calling a function with a Cd refrence argument:\n";
Bravo(c1);
Bravo(c2);
cout << endl;
cout << "Testing assignment: ";
Classic copy;
copy = c2;
copy.Report();
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
13.2 char performers[50];和char * performers;作为成员变量初始化数组的差异,前者直接拷贝strcpy_s(this->worker, sizeof(this->worker), w);,后者需要先分配内存再拷贝
unsigned str_len = strlen(s1);
performers = new char[str_len+1];
strcpy_s(performers, str_len + 1, s1);
13.2.1 封装空间分配函数
static char *newPtr(const char* s) {
unsigned str_len = strlen(s);
char *array = new char[str_len + 1];
strcpy_s(array, str_len + 1, s);
return array;
}
code
#pragma once
class Cd
{
private:
char * performers;
char *label;
int selections;
double playtime;
public:
Cd(const char* s1, const char* s2, int n, double x);
Cd(const Cd& d);
Cd();
virtual ~Cd();
virtual void Report() const;
virtual Cd& operator= (const Cd& d);
};
#include "Cd.h"
#include "string"
#include <iostream>
static char *newPtr(const char* s) {
unsigned str_len = strlen(s);
char *array = new char[str_len + 1];
strcpy_s(array, str_len + 1, s);
return array;
}
Cd::Cd(const char* s1, const char* s2, int n, double x)
{
// 检查空指针
if (s1 == nullptr) s1 = "";
if (s2 == nullptr) s2 = "";
unsigned str_len = strlen(s1);
performers = new char[str_len+1];
strcpy_s(performers, str_len + 1, s1);
label = newPtr(s2);
this->selections = n;
this->playtime = x;
}
Cd::Cd(const Cd& d)
{
performers = newPtr(d.performers);
label = newPtr(d.label);
selections = d.selections;
playtime = d.playtime;
}
Cd::Cd()
{
}
Cd::~Cd()
{
delete[] performers;
delete[] label;
}
void Cd::Report() const
{
std::cout << this->performers << ", " << this->label << " , selections = " << selections << " , playtime = " << playtime << std::endl;
}
Cd& Cd::operator=(const Cd& d)
{
// TODO: 在此处插入 return 语句
performers = newPtr(d.performers);
label = newPtr(d.label);
selections = d.selections;
playtime = d.playtime;
return *this;
}
13.4 多态
13.4.1 基类定义 Port(const char *br = "none", const char* st = "none", int b = 0);,派生类VintagePort(const char *br,int b, const char *n, int y);,基类的有个参数在派生类里面没有使用,在派生类里面该如何定义
VintagePort::VintagePort(const char* br, int b, const char* n, int y):Port(br,"none", b)
{
this->nickname = ptrSize(n);
this->year = y;
}
- 基类
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Port
{
private:
char* brand;
char style[20];
int bottles;
public:
Port(const char *br = "none", const char* st = "none", int b = 0);
Port(const Port& p);
virtual ~Port(){delete[] brand; }
Port& operator=(Port& p);
Port& operator+=(int b);
Port& operator-=(int b);
int BottleCount() const { return bottles; };
virtual void Show() const;
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const Port& p);
};
#include "Port.h"
#include "string"
#include <fstream>
static char* ptrZoom(const char *s) {
int len = strlen(s);
char* str = new char[len+1];
strcpy_s(str, len + 1, s);
return str;
}
Port::Port(const char* br, const char* st, int b)
{
this->brand = ptrZoom(br);
int len = strlen(st);
strcpy_s(this->style, len + 1, st);
this->bottles = b;
}
Port::Port(const Port& p)
{
this->brand = ptrZoom(p.brand);
int len = strlen(p.style);
strcpy_s(this->style, len + 1, p.style);
this->bottles = p.bottles;
}
Port& Port::operator=(Port& p)
{
this->brand = ptrZoom(p.brand);
int len = strlen(p.style);
strcpy_s(this->style, len + 1, p.style);
this->bottles = p.bottles;
return *this;
}
Port& Port::operator+=(int b)
{
this->bottles += b;
return *this;
}
Port& Port::operator-=(int b)
{
this->bottles -= b;
return *this;
}
void Port::Show() const
{
cout << "Brand :" << this->brand << "\n";
cout << "Kind :" << style << "\n";
cout << "Bottles :" << this->bottles << "\n";
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const Port& p)
{
os << p.brand << ", " << p.style << ", " << p.bottles << endl;
// TODO: 在此处插入 return 语句
return os;
}
- 派生类
#pragma once
#include "Port.h"
class VintagePort:public Port
{
private:
char* nickname;
int year;
public:
VintagePort();
VintagePort(const char *br,int b, const char *n, int y);
VintagePort(const VintagePort& vp);
~VintagePort() { delete[] nickname; }
VintagePort& operator=(const VintagePort& vp);
void Show() const;
friend ostream& operator <<(ostream& os, const VintagePort& vp);
};
#include "VintagePort.h"
static char *ptrSize(const char* s) {
unsigned str_len = strlen(s);
char* str = new char[str_len+1];
strcpy_s(str, str_len + 1, s);
return str;
}
VintagePort::VintagePort()
{
const char *str = " ";
nickname = ptrSize(str);
year = 0;
}
VintagePort::VintagePort(const char* br, int b, const char* n, int y):Port(br,"none", b)
{
this->nickname = ptrSize(n);
this->year = y;
}
VintagePort::VintagePort(const VintagePort& vp)
{
this->nickname = ptrSize(vp.nickname);
this->year = vp.year;
}
VintagePort& VintagePort::operator=(const VintagePort& vp)
{
this->nickname = ptrSize(vp.nickname);
this->year = vp.year;
return *this;
}
void VintagePort::Show() const
{
cout << "nickname = " << this->nickname << ",year = " << this->year << endl;
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const VintagePort& vp)
{
os << "nickname = " << vp.nickname << ",year = " << vp.year << endl;
return os;
}
#include <array>
#include "Port.h"
#include "VintagePort.h"
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
Port port1("gallo", "tawny", 20);
cout << port1 << endl << endl;
VintagePort vp("gallo", 24, "nice", 16);
VintagePort vp2(vp);
cout << vp2 << endl << endl;
VintagePort vp3;
vp3 = vp;
cout << vp3 << endl << endl;
Port* p_port;
p_port = &port1;
p_port->Show();
cout << endl;
p_port = &vp;
p_port->Show();
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
























 8万+
8万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








