一、照相机标定
标定照相机是指计算出该照相机的内参数,在我们的例子中,是指计算矩阵K,如果你的应用要求高精度,那么可以扩展照相机模型,使其包含径向畸变和其他条件。对于大多数应用来说,简单的照相机模型已经足够。标定照相机的标准方法是,拍摄多幅平面棋盘模式的图像,然后进行处理计算。
照相机的测量值写入辅助函数中,图像大小为:2592*1936像素:
def my_calibration(sz):
row, col = sz
fx = 2555*col/2592
fy = 2586*row/1936
K = diag([fx, fy, 1])
K[0, 2] = 0.5*col
K[1, 2] = 0.5*row
return K
二、以平面和标记物进行姿态评估:
如果图像中包含平面状的标记物,并且已经对照相机进行了标定,那么我们可以计算出照相机的姿态,这里的标记物体可以为任何平坦的物体。下面我们借助图一和图二提取图像的sift特征,然后使用RANSAC算法稳健地估计单应性矩阵:


运行代码找出特征,并映射在另一张照片中:
sift.process_image('book_frontal.JPG', 'im0.sift')
l0, d0 = sift.read_features_from_file('im0.sift')
sift.process_image('book_perspective.bmp', 'im1.sift')
l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file('im1.sift')
# match features and estimate homography
matches = sift.match_twosided(d0, d1)
ndx = matches.nonzero()[0]
fp = homography.make_homog(l0[ndx, :2].T)
ndx2 = [int(matches[i]) for i in ndx]
tp = homography.make_homog(l1[ndx2, :2].T)
model = homography.RansacModel()
H, inliers = homography.H_from_ransac(fp, tp, model)
运行结果为:
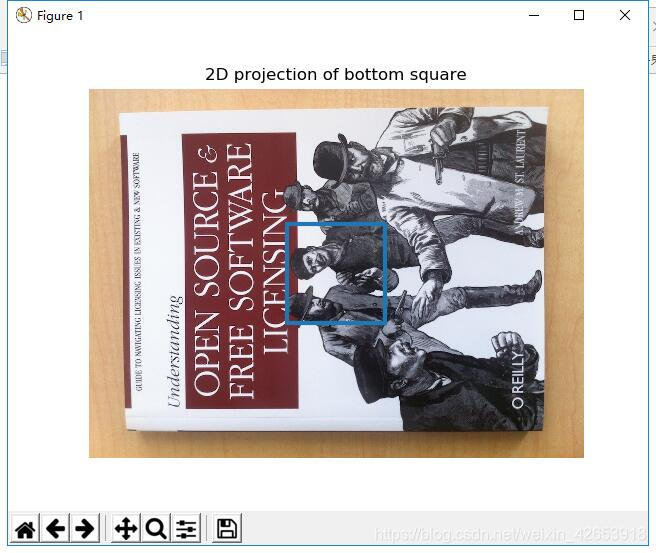
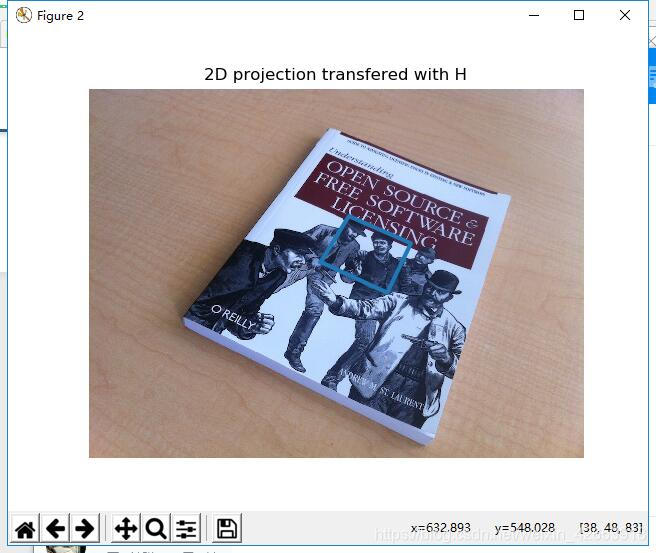
下面我们定义相应的三维坐标系,使其标定物体在X-Y平面上,原点在标记物的某位置上。可以使用下面的函数来产生立方体的点:
def cube_points(c, wid): # 绘制立方体的一各点列表
""" Creates a list of points for plotting
a cube with plot. (the first 5 points are
the bottom square, some sides repeated). """
p = []
# 底部
p.







 本文详细介绍了使用Python进行相机标定的过程,包括计算相机内参矩阵和姿态评估。通过SIFT特征匹配和RANSAC算法估计单应性矩阵,计算相机姿态。同时,利用PyOpenGL在图像中放置虚拟物体,如茶壶,实现图像增强效果。还提供了PyOpenGL的下载和安装指南。
本文详细介绍了使用Python进行相机标定的过程,包括计算相机内参矩阵和姿态评估。通过SIFT特征匹配和RANSAC算法估计单应性矩阵,计算相机姿态。同时,利用PyOpenGL在图像中放置虚拟物体,如茶壶,实现图像增强效果。还提供了PyOpenGL的下载和安装指南。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
















 5692
5692

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








