http://poj.org/problem?id=1753
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |
| Total Submissions: 50937 | Accepted: 21529 |
Description
- Choose any one of the 16 pieces.
- Flip the chosen piece and also all adjacent pieces to the left, to the right, to the top, and to the bottom of the chosen piece (if there are any).
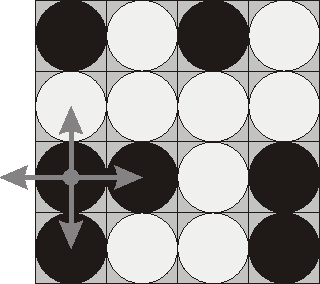 Consider the following position as an example:
Consider the following position as an example:
bwbw
wwww
bbwb
bwwb
Here "b" denotes pieces lying their black side up and "w" denotes pieces lying their white side up. If we choose to flip the 1st piece from the 3rd row (this choice is shown at the picture), then the field will become:
bwbw
bwww
wwwb
wwwb
The goal of the game is to flip either all pieces white side up or all pieces black side up. You are to write a program that will search for the minimum number of rounds needed to achieve this goal.
Input
Output
Sample Input
bwwb bbwb bwwb bwww
Sample Output
4
Source
这题思路相对简单,就是暴力广搜BFS。
只是如果直接无脑干,铁定TLE。
所以就需要 提高计算效率&剪枝。
1.
提高效率相对简单,16个黑白状态也就是16bit,一个int就可以吃下。
翻每一个点的操作也都是固定的计算,例如翻最左上角,其实就是异或一个 1100 1000 0000 0000,也就是0xE400.
以此类推,“翻”的计算量就降下来了。
2.
然后是剪枝,里面有几个话题。
a. 最基本的,翻转过程中,这16个点,每个点至多翻转1次。
那么原状态算是第0层的话,第1层会是16个子节点,为方便描述记为(0,1) (0,2) (0,3)......(0,16)
而到了第2层,(0,1)可以有15个子节点(0,1,2) (0,1,3) ... (0,1,16)
但(0,2)只能有14个子节点(0,2,3) ... (0,2,16)
(0,3) 有13个 (0,3,4) ... (0,3,16)
...
...
(0,15)有1个 (0,15,16)
(0,16)就没有子节点了。
也就是说,每次flip,只允许flip比父节点更靠后的棋子,来保证不会重复。
b. 双向BFS会比单向节省约一半的空间,但中间每轮比较的时间会变成O(m*n)
单向每轮比较的时间是O(2m)
TLE才是死敌,所以用单向就好。
我的写法还是太繁琐了,可以更C一点...
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
class Chess {
public:
int chess;
int filter;
bool history[16];
Chess();
void flip(int pos);
inline bool done();
void input();
void output();
void showHis();
};
Chess::Chess() {
chess = 0;
filter = -1;
memset(history, 0, sizeof(history));
}
void Chess::flip(int pos) {
int tmp;
switch(pos) {
case 0: tmp = 0xC800; break;
/*****
1100
1000
0000
0000
*****/
case 1: tmp = 0xE400; break;
case 2: tmp = 0x7200; break;
case 3: tmp = 0x3100; break;
case 4: tmp = 0x8C80; break;
case 5: tmp = 0x4E40; break;
case 6: tmp = 0x2720; break;
case 7: tmp = 0x1310; break;
case 8: tmp = 0x08C8; break;
case 9: tmp = 0x04E4; break;
case 10:tmp = 0x0272; break;
case 11:tmp = 0x0131; break;
case 12:tmp = 0x008C; break;
case 13:tmp = 0x004E; break;
case 14:tmp = 0x0027; break;
case 15:tmp = 0x0013; break;
}
chess ^= tmp;
filter = pos;
history[pos] = true;
}
bool Chess::done() {
return 0 == chess || 0xFFFF == chess;
}
void Chess::input() {
char c;
int tmp;
for (int i = 0; i < 16; ++i) {
cin >> c;
if ('w'==c) tmp = 1;
else if ('b'==c) tmp = 0;
else exit(-0xBAD);
chess = (chess << 1) + tmp;
}
//printf("%d\n", chess);
}
void Chess::output() {
int tmp = 0xC000;
int w = 15;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < 4; ++j) {
printf("%d", (chess & tmp) >> w);
tmp >>= 1;
--w;
}
printf("\n");
}
}
void Chess::showHis() {
for (int i = 0; i < 16; ++i) {
if (history[i]) {
printf("%d ", i);
}
}
printf("\n");
}
int main() {
/*** worst case ***
Chess dbg;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i) {
dbg.flip(i);
}
dbg.output();
return 0;/**/
Chess c;
c.input();
/* test flip
c.output();
printf("====\n");
c.flip(5);
c.output();
*/
if (c.done()) {
printf("0\n");
return 0;
}
Chess repoSrc[2][13000];
int szSrc[2] = {0, 0};
repoSrc[0][0] = c;
szSrc[0] = 1;
int which = 0;
int step = 0;
while (step < 16) {
for (int i = 0; i < szSrc[which]; ++i) {
for(int f = repoSrc[which][i].filter + 1; f < 16; ++f) {
Chess tmp = repoSrc[which][i];
tmp.flip(f);
//tmp.output();
if (tmp.done()) {
printf("%d\n", step + 1);
//tmp.showHis();
return 0;
}
repoSrc[1-which][szSrc[1-which]++] = tmp;
}
}
//printf("@step%d: szSrc=%d\n", step+1, szSrc[1-which]);
szSrc[which] = 0;
which = 1 - which;
++step;
}
printf("Impossible\n");
return -1;
}
























 90
90

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








