前言
TreeMap的基本概念:
- TreeMap集合是基于红黑树(Red-Black tree)的 NavigableMap实现。该集合最重要的特点就是可排序,该映射根据其键的自然顺序进行排序,或者根据创建映射时提供的 Comparator 进行排序,具体取决于使用的构造方法。这句话是什么意思呢?就是说TreeMap可以对添加进来的元素进行排序,可以按照默认的排序方式,也可以自己指定排序方式。
- 根据上一条,我们要想使用TreeMap存储并排序我们自定义的类(如User类),那么必须自己定义比较机制:一种方式是User类去实现java.lang.Comparable接口,并实现其compareTo()方法。另一种方式是写一个类(如MyCompatator)去实现java.util.Comparator接口,并实现compare()方法,然后将MyCompatator类实例对象作为TreeMap的构造方法参数进行传参(当然也可以使用匿名内部类),这些比较方法是怎么被调用的将在源码中讲解。
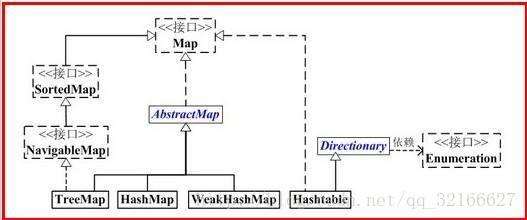
- Map集合体系类图。
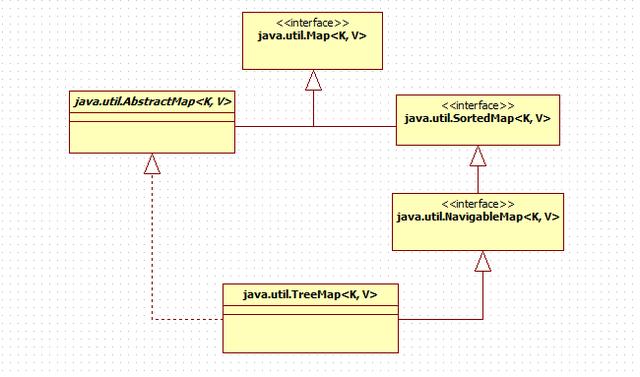
- TreeMap继承类图
- SortedMap接口
public interface SortedMap extends Map { // 返回排序数据所用的Comparator Comparator super K> comparator(); // 返回在[fromKey, toKey)之间的数据 SortedMap subMap(K fromKey, K toKey); // 返回从第一个元素到toKey之间的数据 SortedMap headMap(K toKey); // 返回从fromKey到末尾之间的数据 SortedMap tailMap(K fromKey); //返回第一个数据的key K firstKey(); //返回最后一个数据的key K lastKey();}- NavigableMap接口
public interface NavigableMap extends SortedMap { //返回原map中小于且最接近key的键值对(不包含等于) Map.Entry lowerEntry(K key); //返回小于且最接近key的键(不包含等于) K lowerKey(K key); //返回小于且最接近key的键值对(包含等于) Map.Entry floorEntry(K key); //返回最接近的大于key的键(包含等于) K floorKey(K key); //返回最接近的大于等于key的键值对 Map.Entry ceilingEntry(K key); //返回最接近的大于等于key的键 K ceilingKey(K key); //返回最接近的大于key的键值对 Map.Entry higherEntry(K key); //返回最接近的大于key的键 K higherKey(K key); //返回最小的Entry Map.Entry firstEntry(); //返回最大的Entry Map.Entry lastEntry(); //删除并返回最小的Entry Map.Entry pollFirstEntry(); //删除并返回最大的Entry Map.Entry pollLastEntry(); //返回一个与原map反向顺序的视图,仍然是同一个map,操作会互相影响 NavigableMap descendingMap(); //返回一个所有key键的视图 NavigableSet navigableKeySet(); //返回一个所有key键的视图,顺序是逆序 NavigableSet descendingKeySet(); //返回fromKey到toKey的map视图,通过fromInclusive与toInclusive控制是否包含 NavigableMap subMap(K fromKey, boolean fromInclusive, K toKey, boolean toInclusive); //返回小于toKey的键值对的视图(inclusive为true代表包含等于) NavigableMap headMap(K toKey, boolean inclusive); //返回大于fromKey的键值对视图(inclusive为true代表包含等于) NavigableMap tailMap(K fromKey, boolean inclusive); //范围 [fromKey, toKey) 的视图 SortedMap subMap(K fromKey, K toKey); //小于toKey的map视图 SortedMap headMap(K toKey); //大于等于fromKey的map视图 SortedMap tailMap(K fromKey);}正文
TreeMap源码分析
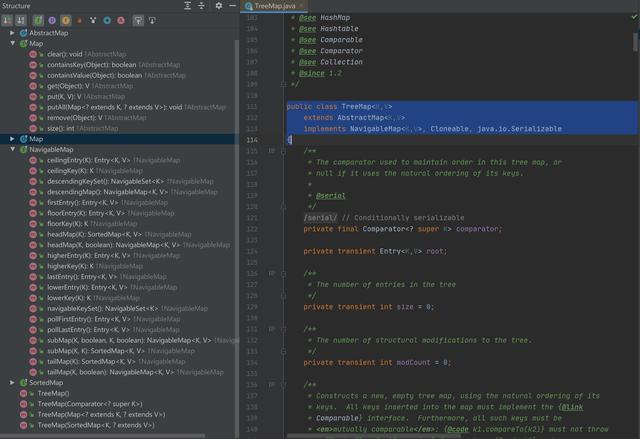
1,类名及类成员变量
public class TreeMap extends AbstractMap implements NavigableMap, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable{ // 比较器对象 private final Comparator super K> comparator; // 根节点 private transient Entry root; // 集合大小 private transient int size = 0; // 树结构被修改的次数 private transient int modCount = 0; // 静态内部类用来表示节点类型 static final class Entry implements Map.Entry { K key; // 键 V value; // 值 Entry left; // 指向左子树的引用(指针) Entry right; // 指向右子树的引用(指针) Entry parent; // 指向父节点的引用(指针) boolean color = BLACK; // }}2,类构造方法
public TreeMap() { // 1,无参构造方法 comparator = null; // 默认比较机制 } public TreeMap(Comparator super K> comparator) { // 2,自定义比较器的构造方法 this.comparator = comparator; } public TreeMap(Map extends K, ? extends V> m) { // 3,构造已知Map对象为TreeMap comparator = null; // 默认比较机制 putAll(m); } public TreeMap(SortedMap m) { // 4,构造已知的SortedMap对象为TreeMap comparator = m.comparator(); // 使用已知对象的构造器 try { buildFromSorted(m.size(), m.entrySet().iterator(), null, null); } catch (java.io.IOException cannotHappen) { } catch (ClassNotFoundException cannotHappen) { } }3,put()方法详解
public V put(K key, V value) { Entry t = root; // 获取根节点 // 如果根节点为空,则该元素置为根节点 if (t == null) { compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check root = new Entry<>(key, value, null); size = 1; // 集合大小为1 modCount++; // 结构修改次数自增 return null; } int cmp; Entry parent; Comparator super K> cpr = comparator; // 比较器对象 // 如果比较器对象不为空,也就是自定义了比较器 if (cpr != null) { do { // 循环比较并确定元素应插入的位置(也就是找到该元素的父节点) parent = t; // t就是root // 调用比较器对象的compare()方法,该方法返回一个整数 cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key); if (cmp < 0) // 待插入元素的key"小于"当前位置元素的key,则查询左子树 t = t.left; else if (cmp > 0) // 待插入元素的key"大于"当前位置元素的key,则查询右子树 t = t.right; else // "相等"则替换其value。 return t.setValue(value); } while (t != null); } // 如果比较器对象为空,使用默认的比较机制 else { if (key == null) throw new NullPointerException(); @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Comparable super K> k = (Comparable super K>) key; // 取出比较器对象 do { // 同样是循环比较并确定元素应插入的位置(也就是找到该元素的父节点) parent = t; cmp = k.compareTo(t.key); // 同样调用比较方法并返回一个整数 if (cmp < 0) // 待插入元素的key"小于"当前位置元素的key,则查询左子树 t = t.left; else if (cmp > 0) // 待插入元素的key"大于"当前位置元素的key,则查询右子树 t = t.right; else // "相等"则替换其value。 return t.setValue(value); } while (t != null); } Entry e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent); // 根据key找到父节点后新建一个节点 if (cmp < 0) // 根据比较的结果来确定放在左子树还是右子树 parent.left = e; else parent.right = e; fixAfterInsertion(e); size++; // 集合大小+1 modCount++; // 集合结构被修改次数+1 return null; }3.1,自定义比较器的使用。说了这么多关于比较器的内容,不上手试试这么能行?
- 先来看下面这段代码
package com.jimmy.map;import java.util.Map;import java.util.Map.Entry;import java.util.Set;import java.util.TreeMap;public class TreeMapDemo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { Map map = new TreeMap<>(); map.put("ddd", "444"); map.put("ccc", "333"); map.put("bbb", "222"); map.put("aaa", "111"); Set> entrySet = map.entrySet(); for (Entry each : entrySet) { System.out.println(each.getKey()+"::"+each.getValue()); } }}输出结果如下,结果是排序过的,为什么呢?那是因为String类实现了Comparable接口并实现了compareTo()方法,该方法按字典顺序比较两个字符串,请自行查看其实现。
aaa::111bbb::222ccc::333ddd::444- 下面我们写个自定义User类,使用2种方式将类对象按照age字段从小到大排序。
方式1,User实现Comparable接口并实现了compareTo()方法
User类
package com.jimmy.domain;public class User implements Comparable{ private String username; private int age; public User(String username, int age) { this.username = username; this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "User [username=" + username + ", age=" + age + "]"; } @Override public int compareTo(User user) { int temp = this.age - user.age; return temp == 0 ? this.username.compareTo(user.username) : temp; } }测试代码
package com.jimmy.map;import java.util.Map;import java.util.Map.Entry;import java.util.Set;import java.util.TreeMap;import com.jimmy.domain.User;public class TreeMapDemo1 { public static void main(String[] args) { Map map = new TreeMap<>(); map.put(new User("jimmy1", 30), "hello"); map.put(new User("jimmy2", 30), "hello"); map.put(new User("jimmy", 22), "hello"); map.put(new User("jimmy", 20), "hello"); Set> entrySet = map.entrySet(); for (Entry each : entrySet) { System.out.println(each.getKey()+"::"+each.getValue()); } }}输出结果如下,首先按age排序,若年龄相等则再按username的字母表顺序排序。
User [username=jimmy, age=20]::helloUser [username=jimmy, age=22]::helloUser [username=jimmy1, age=30]::helloUser [username=jimmy2, age=30]::hello方式2,写一个类实现java.util.Comparator接口,并将该类对象传递给TreeMap的构造方法。这种方式将实体类和比较机制解耦合,可以写很多个不同的比较器对象。
实体类
package com.jimmy.domain;public class User3 { // User对象不再实现任何接口 private String username; private int age; public User3(String username, int age) { super(); this.username = username; this.age = age; } public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "User3 [username=" + username + ", age=" + age + "]"; }}比较器类
package com.jimmy.map;import java.util.Comparator;import com.jimmy.domain.User3;public class TreeMapComparator implements Comparator{ // 比较器类 @Override public int compare(User3 o1, User3 o2) { int temp = o1.getAge() - o2.getAge(); return temp == 0 ? o1.getUsername().compareTo(o2.getUsername()) : temp; }}测试代码
package com.jimmy.map;import java.util.Map;import java.util.Set;import java.util.TreeMap;import java.util.Map.Entry;import com.jimmy.domain.User3;public class TreeMapDemo3 { public static void main(String[] args) { Map map = new TreeMap<>(new TreeMapComparator()); map.put(new User3("jimmy1", 30), "hello"); map.put(new User3("jimmy2", 30), "hello"); map.put(new User3("jimmy", 22), "hello"); map.put(new User3("jimmy", 20), "hello"); Set> entrySet = map.entrySet(); for (Entry each : entrySet) { System.out.println(each.getKey()+"::"+each.getValue()); } }}输出结果如下,跟上面的相同。
User3 [username=jimmy, age=20]::helloUser3 [username=jimmy, age=22]::helloUser3 [username=jimmy1, age=30]::helloUser3 [username=jimmy2, age=30]::hello当然,我们还可以不写比较器类,而是使用匿名内部类的形式来写比较器。
package com.jimmy.map;import java.util.Comparator;import java.util.Map;import java.util.Set;import java.util.TreeMap;import java.util.Map.Entry;import com.jimmy.domain.User3;public class TreeMapDemo4 { public static void main(String[] args) { Map map = new TreeMap<>(new Comparator() { @Override public int compare(User3 o1, User3 o2) { int temp = o1.getAge() - o2.getAge(); return temp == 0 ? o1.getUsername().compareTo(o2.getUsername()) : temp; } }); map.put(new User3("jimmy1", 30), "hello"); map.put(new User3("jimmy2", 30), "hello"); map.put(new User3("jimmy", 22), "hello"); map.put(new User3("jimmy", 20), "hello"); Set> entrySet = map.entrySet(); for (Entry each : entrySet) { System.out.println(each.getKey()+"::"+each.getValue()); } }}4,一般以getEntry()方法为基础的获取元素的方法,其中包括containsKey(),get(),remove()等。
final Entry getEntry(Object key) { // 如果有自定义比较器对象,就按照自定义规则遍历二叉树 if (comparator != null) return getEntryUsingComparator(key); if (key == null) throw new NullPointerException(); @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Comparable super K> k = (Comparable super K>) key; Entry p = root; while (p != null) { // 按照默认比较规则遍历二叉树 int cmp = k.compareTo(p.key); if (cmp < 0) p = p.left; else if (cmp > 0) p = p.right; else return p; } return null; }5,一般以getFirstEntry(),getLastEntry()为基础的获取头和尾元素的方法,其中包括:firstKey(),lastKey();firstEntry(),lastEntry();pollFirstEntry(),pollLastEntry();
final Entry getFirstEntry() { // 获取第一个元素也就是最小的元素,一直遍历左子树 Entry p = root; if (p != null) while (p.left != null) p = p.left; return p; } final Entry getLastEntry() { // 获取最后个元素也就是最大的元素,一直遍历右子树 Entry p = root; if (p != null) while (p.right != null) p = p.right; return p; }6,keySet()和entrySet()方法,在讲HashMap的时候已经讲过了,Map没有迭代器,要将Map转化为Set,用Set的迭代器才能进行元素迭代。
使用案例
1,SortedMap接口的使用
static void testSortedMap(){ SortedMap map = new TreeMap() ;// 通过子类实例化接口对象 map.put("D、baidu","http://www.baidu.com/") ; map.put("A、alibaba","www.alibaba.com") ; map.put("C、tencent","www.tencent.cn") ; map.put("B、csdn","www.csdn.cn") ; System.out.println("第一个元素的内容的key:" + map.firstKey() + " 对应的值:" + map.get(map.firstKey())); System.out.println("最后一个元素的内容的key:" + map.lastKey() + " 对应的值:" + map.get(map.lastKey())) ; System.out.println("返回小于指定范围的集合:") ; for(Map.Entry me:map.headMap("B、csdn").entrySet()){ System.out.println("|- " + me.getKey() + " --> " + me.getValue()) ; } System.out.println("返回大于指定范围的集合:") ; for(Map.Entry me:map.tailMap("B、csdn").entrySet()){ System.out.println("|- " + me.getKey() + " --> " + me.getValue()) ; } System.out.println("部分集合:") ; for(Map.Entry me:map.subMap("A、alibaba","C、tencent").entrySet()){ System.out.println("|- " + me.getKey() + " --> " + me.getValue()) ; } }输出结果:
第一个元素的内容的key:A、alibaba 对应的值:www.alibaba.com最后一个元素的内容的key:D、baidu 对应的值:http://www.baidu.com/返回小于指定范围的集合:|- A、alibaba --> www.alibaba.com返回大于指定范围的集合:|- B、csdn ---> www.csdn.cn|- C、tencent ---> www.tencent.cn|- D、baidu ---> http://www.baidu.com/部分集合:|- A、alibaba ---> www.alibaba.com|- B、csdn ---> www.csdn.cn2,自然排序和自定义比较器
static void testTreeMap(){ //使用自然排序 TreeMap map = new TreeMap<>(); map.put("ddd", "444"); map.put("ccc", "333"); map.put("bbb", "222"); map.put("aaa", "111"); System.out.println("自然顺序-----------------------------------------"); Set> entrySet = map.entrySet(); for (Map.Entry each : entrySet) { System.out.println(each.getKey()+"::"+each.getValue()); } //自定义比较器 TreeMap map1 = new TreeMap<>((t1,t2)->t2.compareTo(t1)); map1.put("ddd", "444"); map1.put("ccc", "333"); map1.put("bbb", "222"); map1.put("aaa", "111"); System.out.println("倒序-----------------------------------------"); Set> entrySet1 = map1.entrySet(); for (Map.Entry each : entrySet1) { System.out.println(each.getKey()+"::"+each.getValue()); } }输出结果:
自然顺序-----------------------------------------aaa::111bbb::222ccc::333ddd::444倒序-----------------------------------------ddd::444ccc::333bbb::222aaa::1113,NavigableMap接口的使用
static void testNavigableMap(){ // SortedMap接收TreeMap的实例 NavigableMap navigatorTreeMap = new TreeMap<>(); // 增加元素 navigatorTreeMap.put("aa", 11); navigatorTreeMap.put("bb", 22); navigatorTreeMap.put("cc", 33); navigatorTreeMap.put("dd", 44); navigatorTreeMap.put("ee", 55); navigatorTreeMap.put("ff", 55); navigatorTreeMap.put("gg", 55); // 7个元素:7 System.out.println(navigatorTreeMap.size()); // 返回大于等于cc的最小键:cc System.out.println(navigatorTreeMap.ceilingKey("cc")); // 返回一个键-值映射关系,它与大于等于cc的最小键关联:cc=33 System.out.println(navigatorTreeMap.ceilingEntry("c")); // 返回逆序视图:{gg=55, ff=55, ee=55, dd=44, cc=33, bb=22, aa=11} System.out.println(navigatorTreeMap.descendingMap()); // 最小键:aa System.out.println(navigatorTreeMap.firstKey()); // 最小键对应的k-v键值对:aa=11 System.out.println(navigatorTreeMap.firstEntry()); // 返回一个键-值映射关系,它与小于等于给定键的最大键关联:bb=22 System.out.println(navigatorTreeMap.floorEntry("c")); // 返回小于等于cc的最大键:cc System.out.println(navigatorTreeMap.floorKey("cc")); // 返回此映射的部分视图,其键值严格小于bb:{aa=11} System.out.println(navigatorTreeMap.headMap("bb")); // 同上小于等于(true):{aa=11, bb=22} System.out.println(navigatorTreeMap.headMap("bb", true)); // 返回一个键-值映射关系,它与小于等于给定键的最大键关联:cc=33 System.out.println(navigatorTreeMap.higherEntry("c")); // 返回小于等于cc的最大键:dd System.out.println(navigatorTreeMap.higherKey("cc")); // 返回一个键-值映射关系,它与小于等于给定键的最大键关联:gg=55 System.out.println(navigatorTreeMap.lastEntry()); // 返回小于等于cc的最大键:gg System.out.println(navigatorTreeMap.lastKey()); // 返回一个键-值映射关系,它与小于等于给定键的最大键关联:bb=22 System.out.println(navigatorTreeMap.lowerEntry("c")); // 返回严格小于cc的最大键:bb System.out.println(navigatorTreeMap.lowerKey("cc")); // 移除并返回与此映射中的最小键关联的键-值映射关系:aa=11 System.out.println(navigatorTreeMap.pollFirstEntry()); // 移除并返回与此映射中的最大键关联的键-值映射关系:gg=55 System.out.println(navigatorTreeMap.pollLastEntry()); // 返回此映射中所包含键的,NavigableSet 视图。:[bb, cc, dd, ee, ff] System.out.println(navigatorTreeMap.navigableKeySet()); // 返回部分视图,true表示包括当前元素键值对:{bb=22, cc=33, dd=44} System.out.println(navigatorTreeMap.subMap("aa", true, "dd", true)); // 返回部分视图包括前面的元素,不包括后面的:{bb=22, cc=33} System.out.println(navigatorTreeMap.subMap("bb", "dd")); // 返回元素大于cc的元素映射视图,包括cc://{cc=33, dd=44, ee=55, ff=55} System.out.println(navigatorTreeMap.tailMap("cc")); // 返回元素大于等于cc的元素映射视图:{dd=44, ee=55, ff=55} System.out.println(navigatorTreeMap.tailMap("cc", false)); // 返回此映射中所包含映射关系的逆序:{ff=55, ee=55, dd=44, cc=33, bb=22}视图 System.out.println(navigatorTreeMap.descendingMap()); // 返回此映射中所包含键的逆序,NavigableSet视图:[ff, ee, dd, cc, bb] System.out.println(navigatorTreeMap.descendingKeySet()); }输出结果:
7cccc=33{gg=55, ff=55, ee=55, dd=44, cc=33, bb=22, aa=11}aaaa=11bb=22cc{aa=11}{aa=11, bb=22}cc=33ddgg=55ggbb=22bbaa=11gg=55[bb, cc, dd, ee, ff]{bb=22, cc=33, dd=44}{bb=22, cc=33}{cc=33, dd=44, ee=55, ff=55}{dd=44, ee=55, ff=55}{ff=55, ee=55, dd=44, cc=33, bb=22}[ff, ee, dd, cc, bb]总结
TreeMap继承了Map的性质,同时其树结构又可以进行元素排序,用处很大。
----------------------------------------------
转载自:https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/qq_32166627/article/details/72773293























 962
962

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








