以下是我的学习笔记,以及总结,如有错误之处请不吝赐教。
本文主要介绍机器学习中的一个分支——概率图模型、相关基础概念以及朴素贝叶斯、隐马尔可夫算法,最后还有相关代码案例。
说到机器学习的起源,可以分为以下几个派别:
- 连接主义:又称为仿生学派(bionicsism)或生理学派(physiologism),其主要原理为神经网络及神经网络间的连接机制与学习算法。比如今天很火的:tensorflow、pytorch、theano、caffe等等。
- 符号主义:又称为逻辑主义(logicism)、心理学派(psychologism)或计算机学派(computerism),其原理主要为物理符号系统(即符号操作系统)假设和有限合理性原理。
- 统计学派:利用经典的统计学习理论为代表,具体有SVM等统计学习理论。
- 概率图模型:相比于其他学习算法的优势在于可以利用图结构来将已知信息带入到知识网络中。主要代表有朴素贝叶斯、隐马尔可夫等等。
基本概念:
贝叶斯公式:下面这是最简单的贝叶斯公式:

复杂的形式可以写成:
贝叶斯网络:
是一种模拟人类推理过程中因果关系的不确定定处理模型,其网络结构是一个有向无环图(directed acyclic graph)。
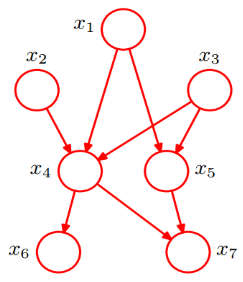
全概率公式:
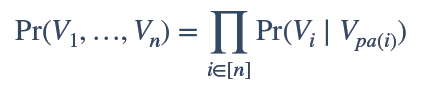
我们利用上图可以将原本联合概率公式P(x1,x2,x3,x4,x5,x6,x7),由原来的复杂形式,转换为简单的条件概率公式相乘,从而将原来的复杂度降到n次复杂,大大简化计算量:
例:
![]()
同时我们可以根据给定联合概率时,求得单个条件概率的值。
马尔科夫链:因安德烈·马尔可夫(A.A.Markov,1856-1922)得名,是指数学中具有马尔可夫性质的离散事件随机过程。在给定当前知识或信息的情况下,过去(即当前以前的历史状态)对于预测将来(即当前以后的未来状态)是无关的。其中每个状态的转移只依赖于之前的n个状态,这个过程被称为1个n阶的模型,其中n是影响转移状态的数目。
最简单的马尔科夫过程就是一阶过程,每一个状态的转移只依赖于其之前的那一个状态,用数学表达式表示如下:
![]()
隐马尔可夫模型(Hidden Markov Model) :包含一个隐藏的马尔科夫过程和一个与这个隐藏马尔科夫过程概率相关的并且可以观察到的状态集合。它是一种统计模型,用来描述一个含有隐含未知参数的马尔可夫过程。该模型克服了前后马尔科夫链前后关系缺失带来的困扰,因此可以观察的参数中确定该过程的隐含参数,然后利用这些参数来作进一步的分析。
条件独立(conditional independence):我们都知道独立分布的概率可以表示为:
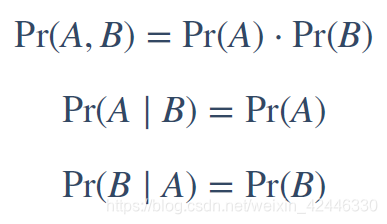
那么条件独立公式就是:
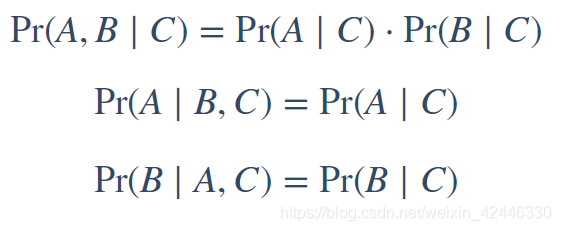
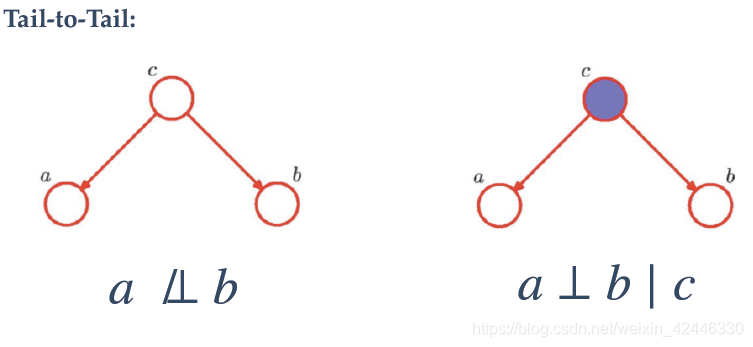
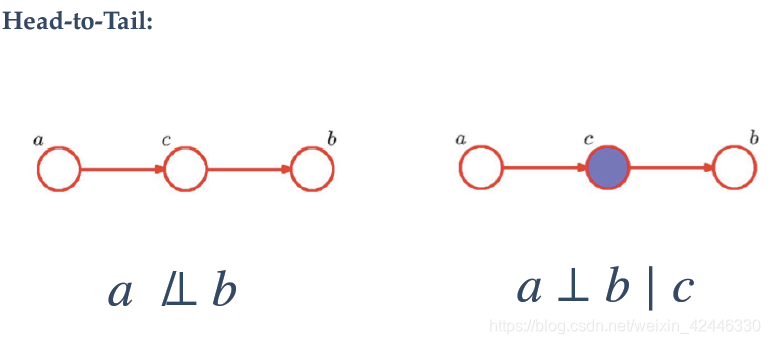
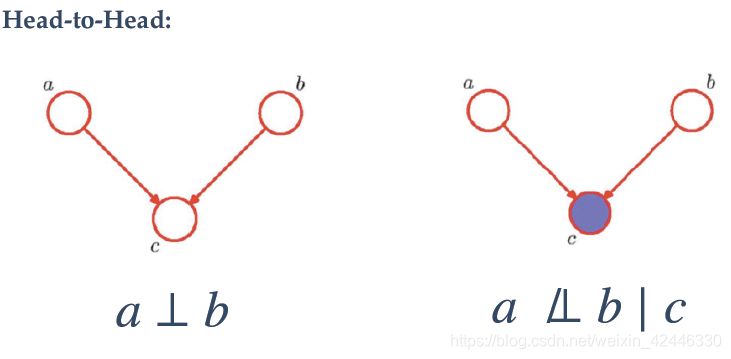
我们也可以根据图的形式来表示:图中表示独立条件,
表示不独立。
应用算法:
隐马尔科夫链(HMM):
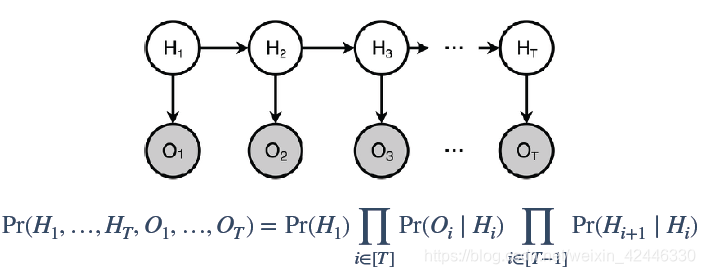
隐马尔科夫链主要有以下四种解法:
- 遍历算法;
- Forward Algorithm,向前算法,或者Backward Algo,向后算法;
- Viterbi Algo,维特比算法;
- Baum-Welch Algo,鲍姆-韦尔奇算法。
遍历算法:该算法时间复杂度为2T。
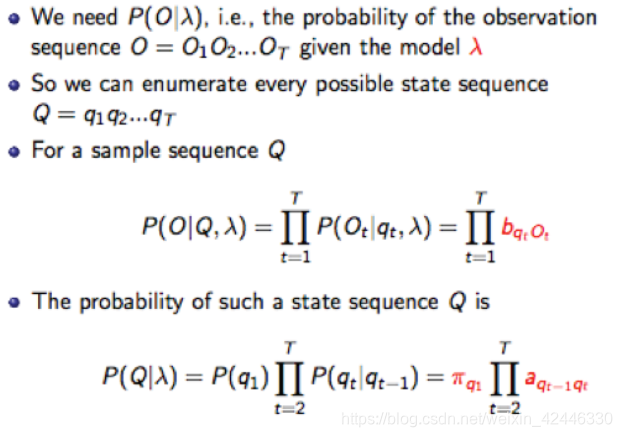
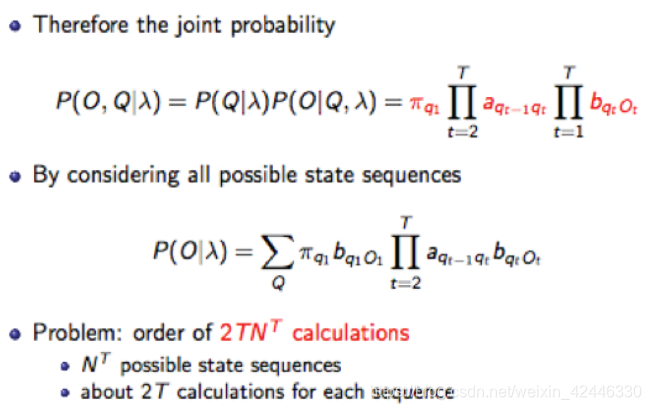
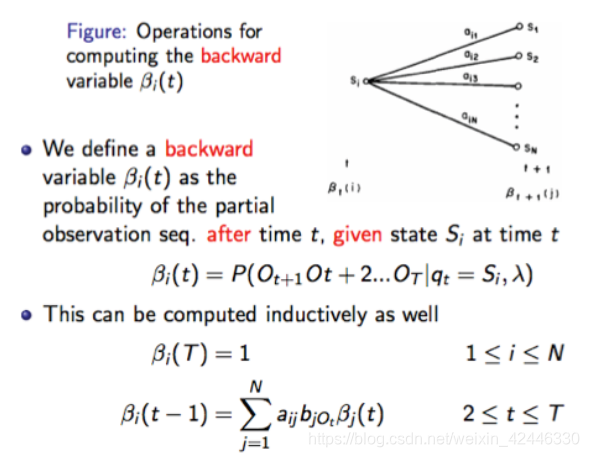
前项、后项算法:该算法时间复杂度为。
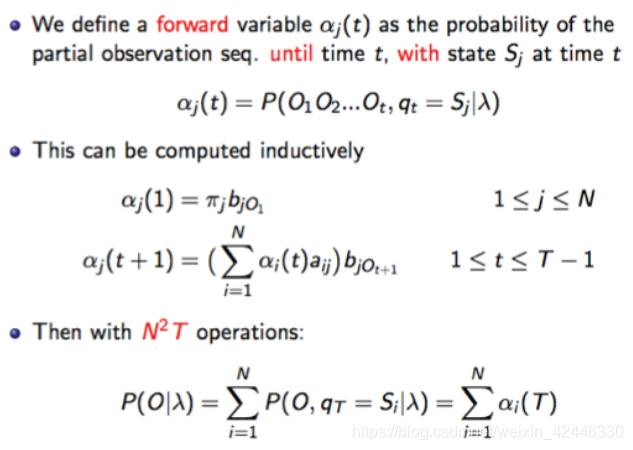
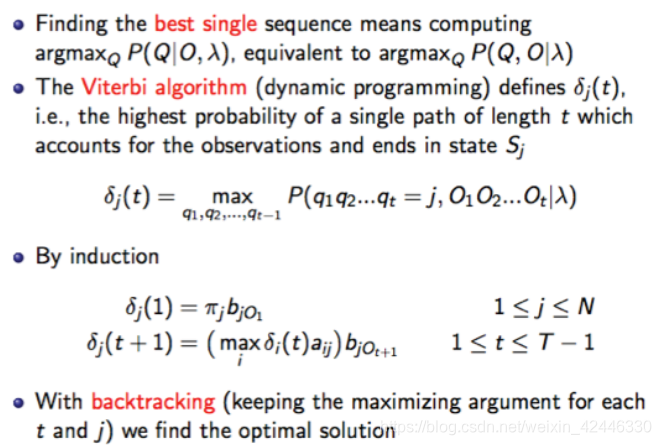
Vierbi算法:
算法实践:欢迎关注我的github,HMM_viterbi词性标注
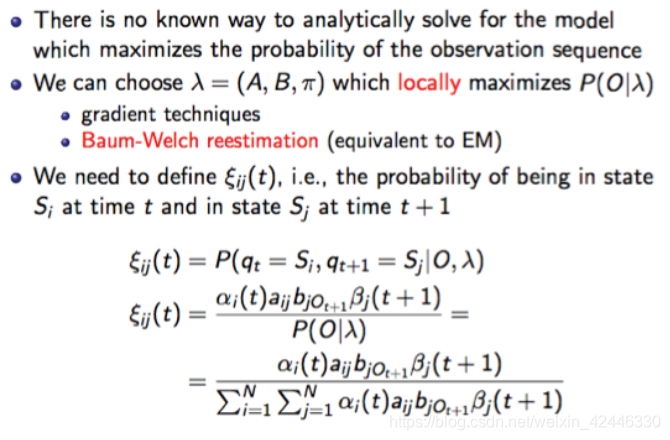
(Baum-Welch Algo)鲍姆-韦尔奇算法:这个算法也属于EM算法的一种。
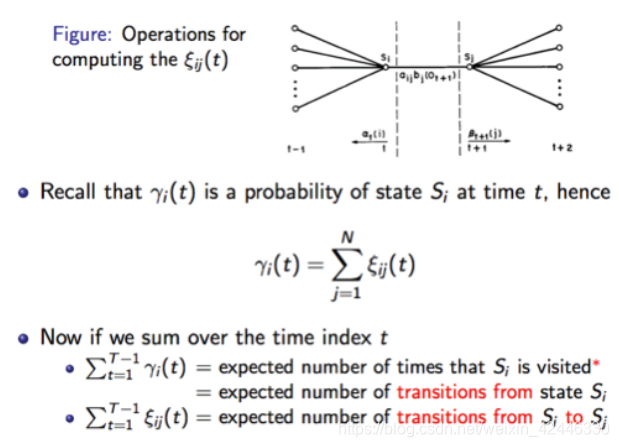
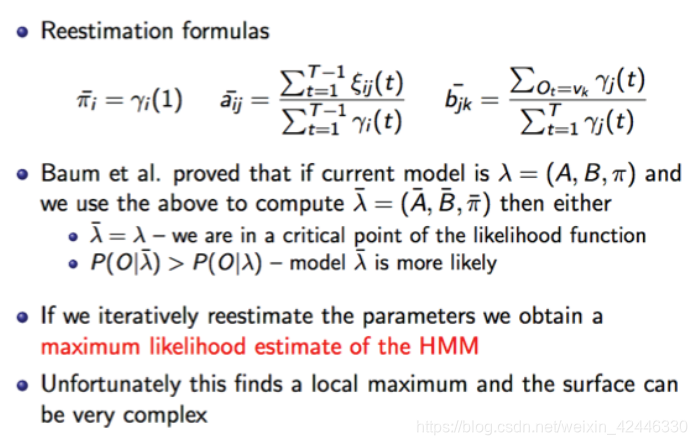
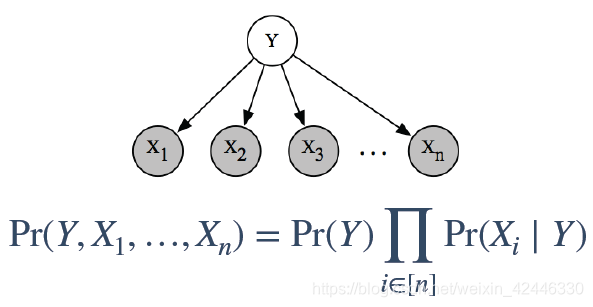
朴素贝叶斯(naive bayes)算法:
核心代码:
#定义先验概率
def prior(vd,normal):
for i in range(len(normal)):
for j in range(vd):
normal_count_dict[j]=normal_count_dict.get(j,0)+normal.content[i][j]
#计算vd各特征向量出现的次数,即,求content各特征向量count按列累加的结果
for j in range(vd):
normal_count_prob[j]=(normal_count_dict.get(j,0)+1)/(len(normal)+2)
#计算vd各特征向量出现的概率(拉普拉斯平滑)
#定义后验概率
def posterior():
for i in range(X_test_array.shape[0]):
for j in range(X_test_array.shape[1]):
if X_test_array[i][j]!=0:
Px_spam[i]=Px_spam.get(i,1)*spam_count_prob.get(j)
#计算vd条件下,各测试样本的后验概率
Px_normal[i]=Px_normal.get(i,1)*normal_count_prob.get(j)
#计算normal条件下,各测试样本的后验概率
test_classify[i]=Py0*Px_normal.get(i,0),Py1*Px_spam.get(i,0)
#后验概率P(Y|X)=P(Y)*P(X|Y)/P(X)
简单介绍了隐马尔可夫即朴素贝叶斯相关概念及相关代码实现,后续会继续更新,To be continue......





 本文深入探讨概率图模型,包括其在机器学习领域的地位与作用,重点解析朴素贝叶斯与隐马尔可夫模型的基本原理及应用。通过实例代码展示算法实践,适合初学者与进阶者学习。
本文深入探讨概率图模型,包括其在机器学习领域的地位与作用,重点解析朴素贝叶斯与隐马尔可夫模型的基本原理及应用。通过实例代码展示算法实践,适合初学者与进阶者学习。
















 772
772

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








