目录
点
struct Point{
db x, y;
Point(db x, db y): x(x), y(y) {}
bool operator < (const Point &p){
return (x < p.x) || (x == p.x && y < p.y));
}
};
int dcmp(db x){
if(fabs(x) < eps) return 0;
return x < 0? -1: 1;
}
bool operator == (Point a, Point b){ //vector也可用
return dcmp(a.x-b.x) == 0 && dcmp(a.y-b.y) == 0;
}向量
typedef Point Vector;
Vector operator + (Vector a, Vector b){ return Point(a.x+b.x, a.y+b.y);}
Vector operator - (Point a, Point b){ return Vector(a.x-b.x, a.y-b.y);}
Vector operator * (Vector a, db k){ return Vector(a.x*k, a.y*k);} //向量必须为被乘数
Vector operator / (Vector b, db k){ return Vector(a.x/k, a.y/k);}
//inline将函数名为内联函数,不使用栈空间,直接运算,但不能有while,switch等复杂语句
inline db dot(Vector a, Vector b){
return a.x*b.x + a.y*b.y;
}
inline db cross(Vector a, Vector b){
return a.x*b.y - b.x*a.y;
}
db length(Vector a){
return sqrt(dot(a, a));
}
db angle(Vector a, Vector b){
return acos(dot(a, b) / length(a) / length(b));
}点与直线
struct Segment{
Point p1, p2;
};
typedef Segment Line;投射点、对称点
Point project(Line l, Point p){
Point p1 = l.p1, p2 = l.p2;
Vector a = p2 - p1, b = p - p1;
db len_a = dot(a, a); //这里不加sqrt,是因为下面算投影长度时,要除以两次len_a
Vector tmp = a * (dot(a, b) / len_a);
return Point(tmp.x+p1.x, tmp.y+p1.y);
}
Point reflect(Line l, Point p){
Point tmp = project(l, p);
return p + (tmp - p)*2;
}直线关系、共端点线段关系
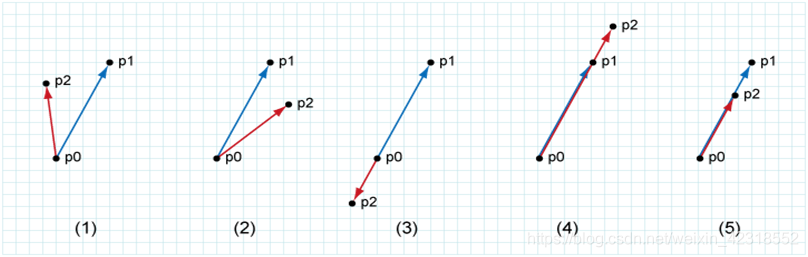
int line_relation(Line l1, Line l2){
Vector a = l1.p2 - l1.p1, b = l2.p2 - l2.p1;
if(cross(a, b) == 0)
return 1;
// puts("parallel");
else if(dot(a, b) == 0)
return 0;
// puts("orthogonal");
else
return -1;
// puts("others");
}
int com_segment_relation(Point p0, Point p1, Point p2){
Vector a = p1-p0, b = p2-p0;
db flag = cross(p1-p0, p2-p0);
if(flag < 0) return 2;
else if(flag > 0) return 1;
else{ //重合
if(a.x*b.x < 0 || a.y*b.y < 0) return 3;
else if(length(a) < length(b)) return 4;
else return 5;
}
}两线段相交及交点
交点:点积求面积再得高,用两个高的比例求得向量比,得交点。
bool segment_intersection(Segment s1, Segment s2){
Point p1 = s1.p1, p2 = s1.p2, p3 = s2.p1, p4 = s2.p2;
if(p2 < p1) swap(p1, p2);
if(p4 < p3) swap(p3, p4);
if(p2 < p3 || p4 < p1)
return false; //同一直线上,最大最小排除
else if(cross(p2-p1, p3-p1)*cross(p2-p1, p4-p1) > 0 || cross(p4-p3, p1-p3)*cross(p4-p3, p2-p3) > 0)
return false;
else
return true;
}
bool onsegment(Segment s, Point p){
return dcmp(cross(s.p2-p, s.p1-p)) == 0 && dcmp(dot(s.p1-p, s.p2-p)) < 0;
}
Point segment_cross_point(Segment s1, Segment s2){
if(!segment_intersection(s1, s2))
exit(0);
Vector a = s1.p2-s1.p1, b1 = s2.p1-s1.p1, b2 = s2.p2-s1.p1;
db len = length(a);
db h1 = fabs(cross(a, b1) / len); //可以省去除len,求t时会消掉
db h2 = fabs(cross(a, b2) / len);
db t = h1 / (h1+h2);
return s2.p1+(s2.p2-s2.p1)*t;
}两直线交点
a*b = |a||b|sin<a,b>, 由此求得比例t
Point line_cross_point(Point P, Vector v, Point Q, Vector w){
if(cross(v, w) == 0)
exit(0);
Vector u = P - Q;
double t = cross(w, u) / cross(v, w);
return P+v*t;
}点线 距离
inline db norm(db x){
return x*x;
}
inline db dist_PtoP(Point p1, Point p2){
return length(p2-p1); //转换为向量模
}
db dist_PtoS(Segment s, Point p){
if(s.p1 == s.p2) return length(p-s.p1);
Vector v1 = s.p2 - s.p1, v2 = p - s.p1, v3 = p - s.p2;
if(dcmp(dot(v1, v2) < 0)) return length(v2);
else if(dcmp(dot(v1, v3) > 0)) return length(v3);
else return fabs(cross(v1, v2)) / length(v1);
}
inline db dist_PtoL(Line l, Point p){
db tmp = cross(l.p2-l.p1, p-l.p1) / length(l.p2-l.p1);
return fabs(tmp);
}
db dist_StoS(Segment s1, Segment s2){
if(segment_intersection(s1.p1, s1.p2, s2.p1, s2.p2))
return 0;
db d1 = dist_PtoS(s2, s1.p1), d2 = dist_PtoS(s2, s1.p2), d3 = dist_PtoS(s1, s2.p1), d4 = dist_PtoS(s1, s2.p2);
return min(min(d1, d2), min(d3, d4));
}
db dist_LtoL(Line l1, Line l2){
if(line_relation(l1, l2) == 1)
return dist_PtoL(l1, l2.p1);
return 0;
}多边形面积
typedef vector<Point> Polygon;
db polygon_area(Polygon &pol){
int sz = pol.size();
db res = 0.0;
for(int i=1; i<sz-1; ++i){ //分为n-1个三角形
res += 0.5*cross(pol[i]-pol[0], pol[i+1]-pol[0]);
}
return fabs(res);
}凸包(基于水平序的Andrew)
另有极角序
不希望有输入点在凸包边上,则<=,否则<
const int maxn = 105;
int convex_hull(Polygon &pol, int n){
sort(pol.begin(), pol.end()); //先x后y
int top = 0;
Point ch[maxn] = {0};
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i){
while(top > 1 && cross(ch[top-1] - ch[top-2], pol[i] - ch[top-1]) < 0) top --;
ch[top ++] = pol[i];
}
int mid = top;
for(int i=n-2; i>=0; --i){
while(top > mid && cross(ch[top-1] - ch[top-2], pol[i] - ch[top-1]) < 0) top --;
ch[top ++] = pol[i];
}
// printf("#%d\n", top);
if(n > 1) top --;
return top;
}点在多边形中:旋转法
int point_in_polygon(Point p, Polygon &pol){
int wn = 0; //winging number
int n = pol.size();
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i){
if(onsegment(Segment(pol[i], pol[(i+1)%n]), p)) return 1;
int k = dcmp(cross(pol[(i+1)%n]-pol[i], p-pol[i]));
int d1 = dcmp(pol[i].y - p.y);
int d2 = dcmp(pol[(i+1)%n].y - p.y);
if(k > 0 && d1 <= 0 && d2 > 0) wn ++;
if(k < 0 && d2 <= 0 && d1 > 0) wn --;
}
if(wn != 0) return 2;
return 0;
}旋转卡壳求多边形直径
https://www.cnblogs.com/xdruid/archive/2012/07/01/2572303.html
db diam_of_ch(Point ch[], int n){
ch[n] = Point(ch[0].x, ch[0].y);
int j = 1;
db res = 0.0;
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i){
while(cross(ch[i+1]-ch[i], ch[j+1]-ch[i]) > cross(ch[i+1]-ch[i], ch[j]-ch[i]))
j = (j+1)%n;
res = max(res, max(length(ch[j]-ch[i]), length(ch[j+1]-ch[i+1])));
}
return res;
}有向直线切割多边形
Polygon convex_cut(Polygon pol, Point A, Point B){
Polygon npol;
int n = pol.size();
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i){
Point C = pol[i], D = pol[(i+1)%n];
if(cross(B-A, C-A) >= 0) npol.push_back(C);
if(cross(B-A, D-C) != 0){
Point ip = line_cross_point(A, B-A, C, D-C);
// printf(" %f %f\n", ip.x, ip.y);
if(onsegment(Segment(C, D), ip)) npol.push_back(ip); //ip == intersection_point
}
}
return npol;
}半平面交
struct DLine{
Point p;
Vector v;
db ang;
DLine() {}
DLine(Point p, Vector v): p(p), v(v) {ang = atan2(v.y, v.x);}
bool operator < (const DLine& l) const{ //极角排序,后面的const 必须有,不然会ce
return ang < l.ang;
}
};
bool OnLeft(DLine l, Point p){
return cross(l.v, p-l.p) > 0;
}
int hpi(DLine* l, int n, Polygon &poly){
sort(l, l+n);
int tail = 0, head = 0;
Point *p = new Point[n];
DLine *nl = new DLine[n];
nl[0] = l[0];
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i){
while(head < tail && !OnLeft(l[i], p[tail-1])) tail --;
while(head < tail && !OnLeft(l[i], p[head])) head ++;
nl[++ tail] = l[i];
if(fabs(cross(nl[tail].v, nl[tail-1].v)) < eps){
tail --;
if(OnLeft(nl[tail], l[i].p)) nl[tail] = l[i]; //同向取内侧,意味这一个点在已加入有向边的内侧,则替换这个有向边
}
if(head < tail) p[tail-1] = line_cross_point(nl[tail].p, nl[tail].v, nl[tail-1].p, nl[tail-1].v);
}
while(head < tail && !OnLeft(nl[head], p[tail-1])) tail --; //删除无用面
if(tail - head <= 1) return 0; //空集
p[tail] = line_cross_point(nl[tail].p, nl[tail].v, nl[head].p, nl[head].v); //末尾直线与起始的交点
int m = 0;
for(int i=head; i<=tail; ++i){
poly.push_back(p[i]);
m ++;
}
return m;
}总代码
#include <iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
#define db double
const db eps = 1e-10;
struct Point{
db x, y;
Point(db x=0, db y=0): x(x), y(y) {} //必须有初始化
bool operator < (const Point& p) const{
return x < p.x || (x == p.x && y < p.y);
}
};
typedef Point Vector;
Vector operator + (Vector a, Vector b){ return Point(a.x+b.x, a.y+b.y);}
Vector operator - (Point a, Point b){ return Vector(a.x-b.x, a.y-b.y);}
Vector operator * (Vector a, db k){ return Vector(a.x*k, a.y*k);}
Vector operator / (Vector a, db k){ return Vector(a.x/k, a.y/k);}
//inline将函数名为内联函数,不使用栈空间,直接运算,但不能有while,switch等复杂语句
inline db dot(Vector a, Vector b){
return a.x*b.x + a.y*b.y;
}
inline db cross(Vector a, Vector b){
return a.x*b.y - b.x*a.y;
}
db length(Vector a){
return sqrt(dot(a, a));
}
db angle(Vector a, Vector b){
return acos(dot(a, b) / length(a) / length(b));
}
int dcmp(db x){ //三态函数,eps间返回0,否则>eps返回1,反之-1
if(fabs(x) < eps) return 0;
return x < 0? -1: 1;
}
bool operator == (Point a, Point b){
return dcmp(a.x-b.x) == 0 && dcmp(a.y-b.y) == 0;
}
struct Segment{
Point p1, p2;
Segment(Point p1=Point(0, 0), Point p2 = Point(0, 0)): p1(p1), p2(p2) {};
};
typedef Segment Line;
typedef vector<Point> Polygon;
Point project(Line l, Point p){
Vector a = l.p2 - l.p1, b = p - l.p1;
db len_a = dot(a, a); //这里不加sqrt,是因为下面算投影长度时,要除以两次len_a
Vector tmp = a * (dot(a, b) / len_a);
return l.p1+tmp;
}
Point reflect(Line l, Point p){
Point tmp = project(l, p);
return p + (tmp - p)*2;
}
int line_relation(Line l1, Line l2){
Vector a = l1.p2 - l1.p1, b = l2.p2 - l2.p1;
if(cross(a, b) == 0)
return 1;
// puts("parallel");
else if(dot(a, b) == 0)
return 0;
// puts("orthogonal");
else
return -1;
// puts("others");
}
int com_segment_relation(Point p0, Point p1, Point p2){
Vector a = p1-p0, b = p2-p0;
db flag = cross(p1-p0, p2-p0);
if(flag < 0) return 2;
else if(flag > 0) return 1;
else{ //重合
if(a.x*b.x < 0 || a.y*b.y < 0) return 3;
else if(length(a) < length(b)) return 4;
else return 5;
}
}
bool segment_intersection(Segment s1, Segment s2){
Point p1 = s1.p1, p2 = s1.p2, p3 = s2.p1, p4 = s2.p2;
if(p2 < p1) swap(p1, p2);
if(p4 < p3) swap(p3, p4);
if(p2 < p3 || p4 < p1)
return 0; //同一直线上,最大最小排除
else if(cross(p2-p1, p3-p1)*cross(p2-p1, p4-p1) > 0 || cross(p4-p3, p1-p3)*cross(p4-p3, p2-p3) > 0)
return 0;
else
return 1;
}
Point segment_cross_point(Segment s1, Segment s2){
if(!segment_intersection(s1, s2))
exit(0);
Vector a = s1.p2-s1.p1, b1 = s2.p1-s1.p1, b2 = s2.p2-s1.p1;
db len = length(a);
db h1 = fabs(cross(a, b1) / len); //可以省去除len,求t时会消掉
db h2 = fabs(cross(a, b2) / len);
db t = h1 / (h1+h2);
return s2.p1+(s2.p2-s2.p1)*t;
}
Point line_cross_point(Point P, Vector v, Point Q, Vector w){
if(cross(v, w) == 0)
exit(0);
Vector u = P - Q;
double t = cross(w, u) / cross(v, w);
return P+v*t;
}
bool onsegment(Segment s, Point p){
return dcmp(cross(s.p2-p, s.p1-p)) == 0 && dcmp(dot(s.p1-p, s.p2-p)) <= 0; //顶点时,dot为0
}
inline db norm(db x){
return x*x;
}
inline db dist_PtoP(Point p1, Point p2){
return length(p2-p1); //转换为向量模
}
db dist_PtoS(Segment s, Point p){
if(s.p1 == s.p2) return length(p-s.p1);
Vector v1 = s.p2 - s.p1, v2 = p - s.p1, v3 = p - s.p2;
if(dcmp(dot(v1, v2) < 0)) return length(v2);
else if(dcmp(dot(v1, v3) > 0)) return length(v3);
else return fabs(cross(v1, v2)) / length(v1);
}
inline db dist_PtoL(Line l, Point p){
db tmp = cross(l.p2-l.p1, p-l.p1) / length(l.p2-l.p1);
return fabs(tmp);
}
db dist_StoS(Segment s1, Segment s2){
if(segment_intersection(s1, s2))
return 0;
db d1 = dist_PtoS(s2, s1.p1), d2 = dist_PtoS(s2, s1.p2), d3 = dist_PtoS(s1, s2.p1), d4 = dist_PtoS(s1, s2.p2);
return min(min(d1, d2), min(d3, d4));
}
db dist_LtoL(Line l1, Line l2){
if(line_relation(l1, l2) == 1)
return dist_PtoL(l1, l2.p1);
return 0;
}
db polygon_area(Polygon &pol){
int sz = pol.size();
db res = 0.0;
for(int i=1; i<sz-1; ++i){ //分为n-1个三角形
res += 0.5*cross(pol[i]-pol[0], pol[i+1]-pol[0]);
}
return fabs(res);
}
const int maxn = 3e4;
Point ch[maxn] = {0};
int convex_hull(Polygon &pol, int n){
sort(pol.begin(), pol.end());
int top = 0;
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i){
while(top > 1 && cross(ch[top-1] - ch[top-2], pol[i] - ch[top-1]) < 0) top --;
ch[top ++] = pol[i];
}
int mid = top;
for(int i=n-2; i>=0; --i){
while(top > mid && cross(ch[top-1] - ch[top-2], pol[i] - ch[top-1]) < 0) top --;
ch[top ++] = pol[i];
}
// printf("#%d\n", top);
if(n > 1) top --;
return top;
}
int point_in_polygon(Point p, Polygon &pol){
int wn = 0; //winging number
int n = pol.size();
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i){
if(onsegment(Segment(pol[i], pol[(i+1)%n]), p)) return 1;
int k = dcmp(cross(pol[(i+1)%n]-pol[i], p-pol[i]));
int d1 = dcmp(pol[i].y - p.y);
int d2 = dcmp(pol[(i+1)%n].y - p.y);
if(k > 0 && d1 <= 0 && d2 > 0) wn ++;
if(k < 0 && d2 <= 0 && d1 > 0) wn --;
}
if(wn != 0) return 2;
return 0;
}
db diam_of_ch(Point* ch, int n){
ch[n] = Point(ch[0].x, ch[0].y);
int j = 1;
db res = 0.0;
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i){
while(cross(ch[i+1]-ch[i], ch[j+1]-ch[i]) > cross(ch[i+1]-ch[i], ch[j]-ch[i]))
j = (j+1)%n;
res = max(res, max(length(ch[j]-ch[i]), length(ch[j+1]-ch[i+1])));
}
return res;
}
Polygon convex_cut(Polygon pol, Point A, Point B){
Polygon npol;
int n = pol.size();
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i){
Point C = pol[i], D = pol[(i+1)%n];
if(cross(B-A, C-A) >= 0) npol.push_back(C);
if(cross(B-A, D-C) != 0){
Point ip = line_cross_point(A, B-A, C, D-C);
// printf(" %f %f\n", ip.x, ip.y);
if(onsegment(Segment(C, D), ip)) npol.push_back(ip); //ip == intersection_point
}
}
return npol;
}
struct DLine{
Point p;
Vector v;
db ang;
DLine() {}
DLine(Point p, Vector v): p(p), v(v) {ang = atan2(v.y, v.x);}
bool operator < (const DLine& l) const{ //极角排序
return ang < l.ang;
}
};
bool OnLeft(DLine l, Point p){
return cross(l.v, p-l.p) > 0;
}
int hpi(DLine* l, int n, Polygon &poly){
sort(l, l+n);
int tail = 0, head = 0;
Point *p = new Point[n];
DLine *nl = new DLine[n];
nl[0] = l[0];
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i){
while(head < tail && !OnLeft(l[i], p[tail-1])) tail --;
while(head < tail && !OnLeft(l[i], p[head])) head ++;
nl[++ tail] = l[i];
if(fabs(cross(nl[tail].v, nl[tail-1].v)) < eps){
tail --;
if(OnLeft(nl[tail], l[i].p)) nl[tail] = l[i]; //同向取内侧,意味这一个点在已加入有向边的内侧,则替换这个有向边
}
if(head < tail) p[tail-1] = line_cross_point(nl[tail].p, nl[tail].v, nl[tail-1].p, nl[tail-1].v);
}
while(head < tail && !OnLeft(nl[head], p[tail-1])) tail --; //删除无用面
if(tail - head <= 1) return 0; //空集
p[tail] = line_cross_point(nl[tail].p, nl[tail].v, nl[head].p, nl[head].v); //末尾直线与起始的交点
int m = 0;
for(int i=head; i<=tail; ++i){
poly.push_back(p[i]);
m ++;
}
return m;
}
DLine l[maxn];
int main()
{
// freopen("data.out", "w", stdout);
Point p1, p2, p3, p4;
int n;
cin >>n;
Polygon poly;
Point p[10] = {Point(0,0), Point(10000, 0), Point(10000, 10000), Point(0, 10000), Point(0,0)};
for(int k=0; k<4; ++k)
l[k] = DLine(p[k], p[k+1] - p[k]);
for(int i=4; i<4+n; ++i){
cin >>p2.x >>p2.y >>p3.x >>p3.y;
l[i] = DLine(p2, p3-p2);
}
int tmp = HalfplaneIntersection(l, n+4, poly);
db ans = polygon_area(poly);
printf("%.1f\n", ans);
return 0;
}








 这篇博客详细介绍了计算几何中的基本概念和操作,包括点、向量、直线的关系,点线距离,多边形的面积以及凸包算法。还讨论了点在多边形中的判断方法,直线切割多边形和半平面交等问题,并提供了相关代码实现。
这篇博客详细介绍了计算几何中的基本概念和操作,包括点、向量、直线的关系,点线距离,多边形的面积以及凸包算法。还讨论了点在多边形中的判断方法,直线切割多边形和半平面交等问题,并提供了相关代码实现。
















 121
121

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








