文章目录
1.Pytorch 和 Tensorflow区别
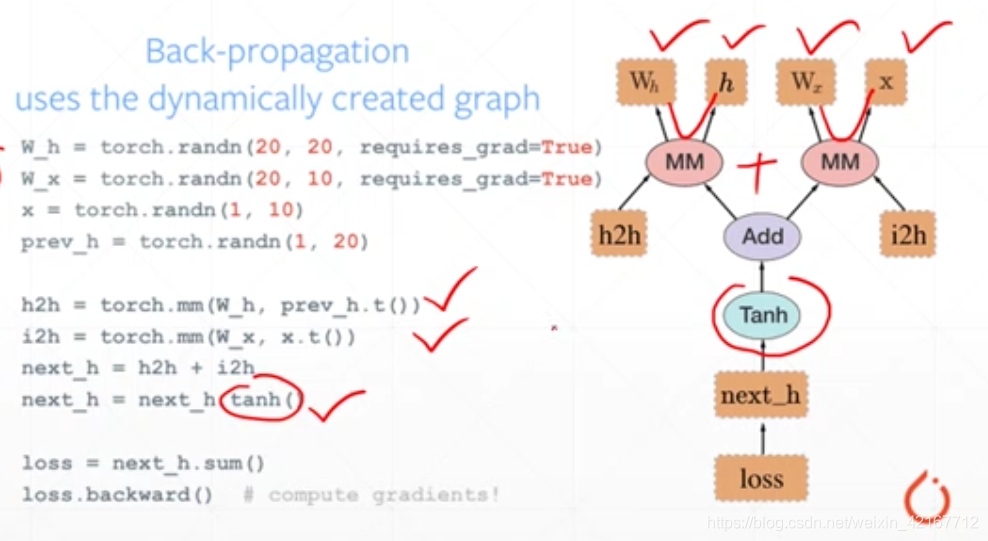
Pytorch 是动态图,你一旦用代码将神经网络架构搭建起来。那么就可以直接运行
Tensorflow是静态图,用代码将神经网络架构写出来后,还要专门写一段运行的代码


2.利用GPU进行加速运算
import torch
import time
print(torch.__version__)
print(torch.cuda.is_available())
# print('hello, world.')
a = torch.randn(10000, 1000)
b = torch.randn(1000, 2000)
#a矩阵乘以b矩阵在CPU上的运算时间
t0 = time.time()
c = torch.matmul(a, b)# 2维*2维 就是矩阵点乘
t1 = time.time()
print(a.device, t1 - t0, c.norm(2)) #计算时间 c.norm(2)的意思是对c向量求L2范数。范数就是用来计算出一个向量的大小,好用于比较
device = torch.device('cuda') #调用cuda
a = a.to(device) #将矩阵a和b搬到GPU上
b = b.to(device)
#计算GPU上计算所用的时间
t0 = time.time()
c = torch.matmul(a, b)
t2 = time.time()
print(a.device, t2 - t0, c.norm(2))
3.Pytorch提供的自动求导功能
import torch
from torch import autograd
x = torch.tensor(1.) #把x当作是样本的值,通过导数求得参数a,b,c的梯度分别是多少
a = torch.tensor(1., requires_grad=True) # 对a进行求导
b = torch.tensor(2., requires_grad=True) #对b进行求导
c = torch.tensor(3., requires_grad=True) #对c进行求导
y = a**2 * x + b * x 







 本文对比了Pytorch与Tensorflow的区别,强调Pytorch的动态图特性和GPU加速。介绍了Pytorch的自动求导功能,常用网络层,以及在回归任务中的目标损失函数。通过MINST数据集的实战,展示了模型训练过程。
本文对比了Pytorch与Tensorflow的区别,强调Pytorch的动态图特性和GPU加速。介绍了Pytorch的自动求导功能,常用网络层,以及在回归任务中的目标损失函数。通过MINST数据集的实战,展示了模型训练过程。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 480
480

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








