CUDA
Heterogeneous Computing(异值计算)
Death of CPU Scaling

Heterogeneous System Architecture (HSA)

GPU(Graphic Processing Unit)
Massively multithreaded manycore chips
-
NVIDIA Tesla products have up to 5120 scalar processors
-
Over 12,000 concurrent threads
-
Over 470 GFOLPS sustained performance
GPGPU(General-Purpose Graphic Processing Unit)
专门用来做计算用的GPU。

Host->CPU Device->GPU
Global Memory:所有的GPU core都能访问的memory。
Shared Memory:一个SM(stream multi-processors)可以访问它自己内部的PBSM(Shared Memory)。
Local Register:每一个core可以访问自己的register。
Stream Multiprocessor

GPU Compute Capability
不同的GPU support不同的功能

Programming Model
什么是CUDA?
CUDA: Compute Unified Device Architecture
CUDA is a compiler and toolkit for programming NVIDIA GPUs
CUDA Program Flow

CUDA = serial program with parallel kernels, all in C CUDA是C程序,它包含串行程序和并行的kernels(也是C程序)。
串行c程序在cpu线程中执行,parallel kernel c 代码在GPU threads中执行。

注意如果CPU与GPU的程序之间有同步的关系,那么就需要有barrier的帮助,将GPU与CPU之间的程序同步化。
CUDA Program Framework
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
__global__ void my_kernel(...) {/*GPU code(parallel)*/
...
}/*__global__代表这段程序将运行在device上*/
int main() {
/*CPU code(serial/parallel(if ptread,openmp,tbb,mpi is used))*/
...
cudaMalloc(...) /*在device上malloc地址空间*/
cudaMemcpy(...)/*将host的数据传递到刚才在device上开辟的地址空间里*/
...
my_kernel<<<nblock,blocksize>>>(...)/*nblock代表block的数量,blocksize代表线程的数量*/
...
cudaMemcpy(...) /*将device的数据传递到刚才在host上开辟的地址空间里*/
...
}
Kernel=Many Concurrent Threads
- 在一定时间内在一台设备中只能执行一个kernel
- 在一个kernel中有许多threads将被执行,每一个thread执行同样的代码,threads执行不同的数据依靠threadID。

- CUDA的thread是physical threads,与CPU上的threads不同,CPU上的threads在做context swtiching的时候,实际上是这样的:因为threads共用register,所以一个thread做完一些计算之后需要找到一个地址空间去存放在做这个thread时register中的内容,只有register的内容放入内存之后,下一个thread才开始在这个core上做计算,;而GPU中的threads,多个threads共用一个core,这也就是为什么gpu中active threads的数量远大于core的数量的原因。为了应对多个threads频繁做context switching时会产生的latency,GPU每一个SM都有很多register set,给每一个线程一个register set,这样就不需要与内存做频繁的数据交换。
Hierarchy(阶级,阶层,层级) of Concurrent Threads

在运行一个kernel的时候,要注意:
-
一个kernel中有许多blocks,一个block中都有从0到N的多个threads,这也就是说,定位threads需要两个数值:block id 和 thread id。
-
一个block中有很多个threads,这些threads都跑在一个SM processor中,但不能把一个SM processor看作是一个真正的SIMD processor,这就是说,**不能认为所有的threads都在运行相同的代码,因为有的thread执行速度快,有的执行速度慢,他们虽然是相同的代码,但是执行的速度不一定是一样的。**如果threads之间是有依赖的,那么就需要barrier了。

上面是一个需要使用barrier的例子,因为scratch[threadID - 1],每次调用的是上一个thread的执行结果。
- 对于不同的block中的代码,是不支持做synchronization的。这是因为如果不同blocks之间做平行,会十分影响GPU的性能。
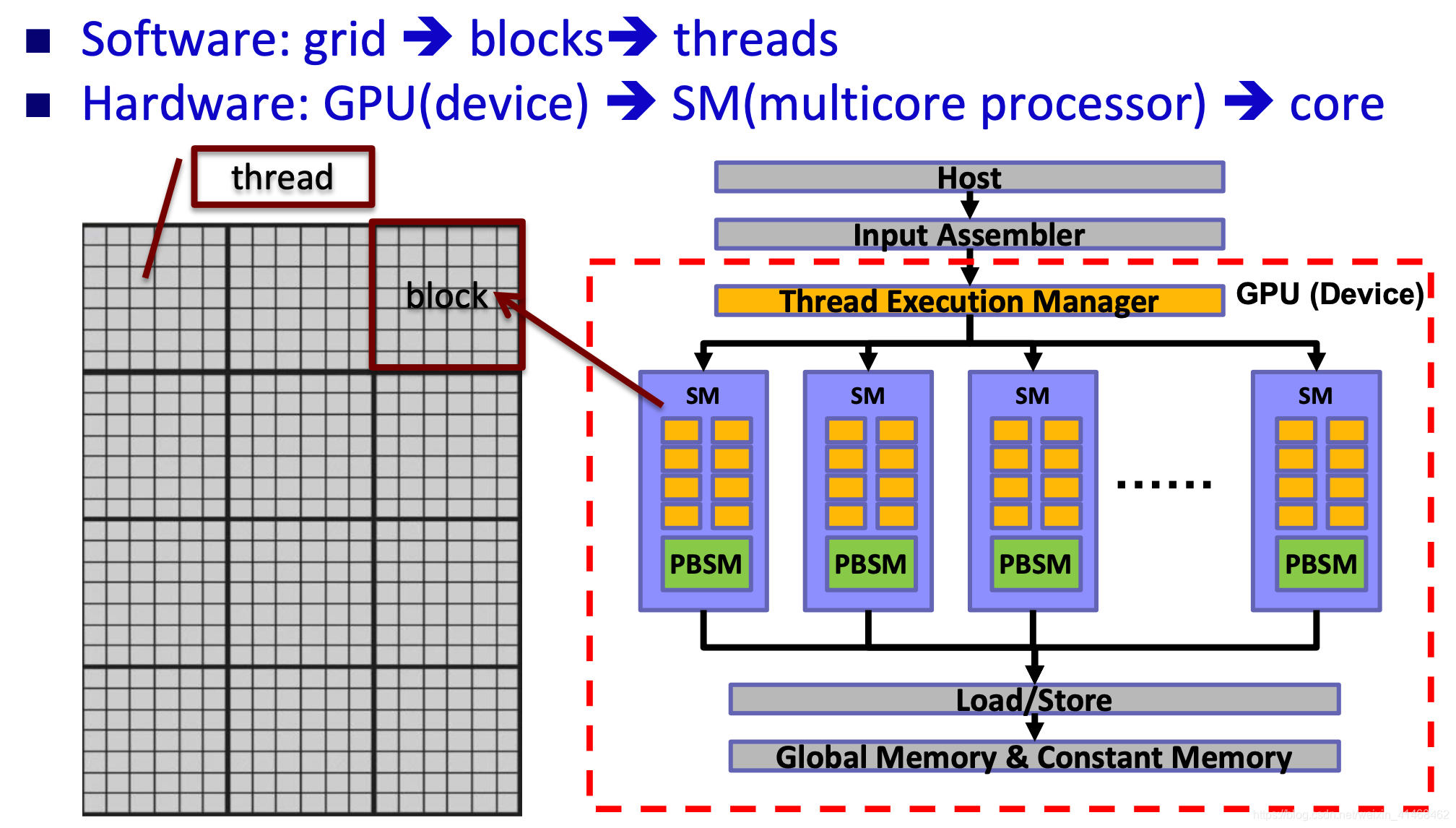
Software Mapping
- 一个kernel运行在一个device(GPU)上,同一个kernel中的block可以mapping到相同的SM processor中,也可以mapping到不同的SM processor中。
- 同一个block中的threads会跑在同一个SM processor中。
- 跨threads之间的沟通通过PBSM,跨block之间的沟通通过Global Memory沟通。
- 对于跨kernels,上一个kernel运行之后的运算结果只要不主动free掉,会被存储在global memory中,下一个kernel来了之后可以直接使用上一个kernel的运算结果。
 ### Block Level Scheduling
### Block Level Scheduling

Thread Level Scheduling - Warp
在一个SM processor中,每32个threads被称为一个warp,每一个warp中的threads是以SIMD的方式执行的,而不同的warp中的threads的执行并不符合SIMD。

也就是说:
-
一个warp中的threads是真正的在被并行执行
-
不同warps或者不同blocks中的threads的并行是逻辑上的(不一定是真正的并行执行)。
-
warp中的threads是同进同出的。例如,如果一个threads做context switching比较慢,那么其他threads会等着这个thread做完,才会往下执行。
-
因此,warp一般不会太高,否则threads同进同出,效能降低很大。
Memory Hierarchy

CUDA Programming Terminology(术语)
-
Host : CPU
-
Device : GPU
-
Kernel : functions executed on GPU
-
Thread : the basic execution unit
-
Block : a group of threads
-
Grid : a group of blocks

Quiz
- What is the difference between the two kernals below?
- my_kernel<<< 1, 100 >>>(A);
- my_kernel<<< 100, 1 >>>(A);
第一个:1个block,100个threads,所以这一百个threads之间可以用shared-memory沟通,也可以使用synchronization来沟通;
第二个:100个block,每个block有一个thread,每一个独立运行,只要有可以使用的资源就可以执行,但是由于执行的单位为32(warp),所以每独立执行一个,有31个资源被浪费掉。
-
Why we have to call
__syncthreads()within a block if there are data dependency between statements?因为不同threads可能处于不同的warp中,一个warp中的thread才是SIMD执行的,而不同的warp中的threads只是逻辑上的并行。如果需要让他们synchronized,就必须有一个barrier,这也是
__syncthreads()的作用。
CUDA Language
-
Kernel launch
kernelFunc<<< nB, nT, nS, Sid >>>(...); //nS and Sid are optional //nB:number of blocks per grid (grid size) //nT:number of threads per block (block size) //nS:shared memory size (in bytes)在kernel执行之前要决定好的大小 //Sid: stream ID, default is 0。kernels之间是synchronize的,但可以使用stream,将kernel拆成许多个stream,让stream之间的数据overlap,相当于pipeline。 -
Build-in device variables(直接可以使用)
threadIdx; blockIdx; blockDim; gridDim -
Intrinsic functions that expose operations in kernel code(在cuda kernel中才可以运行的function)
__syncthreads(); -
Declaration specifier to indicate where things live
__global__ void KernelFunc(...); // kernel function, run on device __device__ void GlobalVar; // variable in device memory __shared__ void SharedVar;// variable in per-block shared memory ,在function里面规定好的size -
Thread and Block IDs
Threadidx;blockidx;blockDim;gridDim
thread和block的索引可以被分割为3个纬度的结构:
//dim3 defined in vector_types.h struct dim3 { x; y; z; }; 例如,
dim3 grid(3, 2); dim3 blk(5, 3); my_kernel<<< grid, blk >>>();

Function Qualifiers
| Function qualifiers | limitations |
|---|---|
__device__ function | 由设备(GPU)执行。只有设备(GPU)才能调用。 |
__global__ function | 由设备(GPU)执行。 只有host(CPU)才能调用 (返回参数一定是void类型的)。 |
__host__ function | 由host(CPU)执行。 只有host(CPU)才能调用。 |
| Functions without qualifiers | 在host(CPU)编译运行。Compiled for the host only. |
__host__ __device__ function | 在host(CPU)和设备(GPU)都可编译运行。Compiled for both the host and the device. |
Variable Type Qualifers
| Variable qualifiers | Limitations |
|---|---|
__device__ var | 1. 存在于设备(GPU)的global memory中 2. lifetime与整个应用相同 3. 在运行过程中,不论是grid中的线程还是来自host的线程都能够访问 |
__constant__ var | 1. 是一个read-only的空间,在initialized后值就不能被改动;2. 优点是速度比__device__ var快(因为constant值不会改变,所以在GP U的架构中可以做cacheing,比如一个block访问了这个constant var,那么就会在这个block对应的SM的缓存中进行存储);3. 存在于constant memory space4. Lifetime 与整个应用相同 5. 在运行过程中,不论是grid中的线程还是来自host的线程都能够访问 |
__shared__ var | 1. 在一个thread block中的shared memory中存在; 2. 和block的lifetime相同;3. 仅同一个block中的线程可以访问 |
Device memory operations
主要包含三个函数:cudaMalloc(), cudaFree(), cudaMemcpy()
-
cudaMalloc(void **devPtr, size_t size)devPtr:返回分配好的设备(GPU)内存空间的地址size:分配的内存空间大小(bytes) -
cudaFree (void *devPtr) -
cudaMemcpy( void *dst, const void *src, size_t count, enum cudaMemcpyKind kind)count:以bytes的大小拷贝cudaMemcpyKind Meaning dst Src cudaMemcpyHostToHost Host->Host host host cudaMemcpyHostToDevice Host->Device device host cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost Device->Host host device cudaMemcpyDeviceToDevice Device->Device device device Program Compilation

Example Code Study
1
__global__ void add(int *a, int *b, int *c)
{ *c = *a + *b;
}
int main(void) {
int a=1, b=2, c; // host copies of a, b, c
int *d_a, *d_b, *d_c; // device copies of a, b, c
// Allocate space for device copies of a, b, c
cudaMalloc((void **)&d_a, sizeof(int));
cudaMalloc((void **)&d_b, sizeof(int));
cudaMalloc((void **)&d_c, sizeof(int));
// Copy inputs to device
cudaMemcpy(d_a,&a,sizeof(int),cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
cudaMemcpy(d_b,&b,sizeof(int),cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
// Launch add() kernel on GPU
add<<<1,1>>>(d_a, d_b, d_c);
// Copy result back to host
cudaMemcpy(&c, d_c, size, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
// Cleanup
cudaFree(d_a); cudaFree(d_b); cudaFree(d_c);
return 0;
}
CPU & GPU Synchronization
Asychronous Functions
大部分的CUDA函数都是Asychronous(异步)的。但一个kernel中的function calls在GPU上会被序列化。
(为什么前面的例子给人的感觉是blocking call呢?因为launch kernel到GPU之后,Host其实就可以做其他的事情了(异步),但是由于存在blocking call cudaMemcpy,因此被同步化。)
-
Kernel launches;
-
特定的异步memory copy函数:
cudaMemcpyAsync,cudaMemsetAsync; -
device与device之间做
cudaMemcpy时; -
小于或等于64kb的H2D
cudaMemcpy; -
cudaEvent functions。
为什么要异步?

可以让没有数据依赖的GPU与CPU函数各做各的。
上例中,为什么不如此更改呢:
void main() {
cudaMemcpy ( /**/, H2D ) ;
kernel2 <<< grid, block>>> () ;
kernel3 <<< grid, block>>> () ;
cpu_method();
cudaMemcpy ( /**/, D2H ) ;
}
因为这样更改,cudaMemcpy串行执行,也就是需要等到cpu_method()做完才会执行,仍然无法做到overlap。
Synchronization between CPU & GPU
CPU和GPU之间的同步:
-
基于Device:
cudaDeviceSynchronize():Block a CPU thread until all issued CUDA calls to a device complete
所有的CPU对某一个device的CUDA calls全部执行完,这个CPU线程才能继续。
-
基于Context:
cudaThreadSynchronize()
Block a CPU thread until all issued CUDA calls from the thread complete只有这个CPU thread launch出去的CUDA calls执行完,这个CPU线程才能继续。
-
基于Stream:
cudaStreamSynchronize(stream-id)
Block a CPU thread until all CUDA calls in stream stream-id complete -
基于Event:
cudaEventSynchronize (event)
Block a CPU thread until event is recorded
如果一个event发生了,那么就block一个CPU线程
2. `cudaStreamWaitEvent (steam-id, event)`
Block a GPU stream until event reports completion
如果某一个stream中的某一个event发生,那么就block一个CPU线程
Device Synchronization Example
void main() {
cudaSetDevice(0);
kernel1 <<< grid, block>>> () ;
kernel2 <<< grid, block>>> () ;
cudaSetDevice(1);//此时切换为了device 1,所以下面cudaDeviceSynchronize();blockCPU直到kernel3做完
kernel3 <<< grid, block>>> () ;
cudaDeviceSynchronize();
cpu_method();
}

Thread Synchronization Example
void main() {
cudaSetDevice(0);
kernel1 <<< grid, block>>> () ;
kernel2 <<< grid, block>>> () ;
cudaSetDevice(1);
kernel3 <<< grid, block>>> () ;
cudaThreadSynchronize();
cpu_method();
}

当这个CPU launch出去的所有的Kernel都做完之后,CPU的这个线程才能继续执行。
CUDA event
-
CUDA event是一个数据类型:
cudaEvent_t -
创建CUDA event:
cudaError_t cudaEventCreate(cudaEvent_t* event)主要记录的是timestamp,是当GPU真的执行完一个Function call的时候记录的时间戳。
这个函数也是被上传到GPU上执行的,但是由于上传到GPU上的函数被序列化执行,所以执行顺序是对的。
-
记录CUDA event:
cudaError_t cudaEventRecord(cudaEvent_t event, cudaStream_t stream = 0) -
cudaEventSynchronize (event):(同步)Wait until the completion of all device work preceding the most recent call to cudaEventRecord()
直到record之后,才能继续执行程序。
Event Synchronization Example
void main() {
cudaSetDevice(0);
kernel1 <<< grid, block>>> () ;
cudaEventRecrod(event);
kernel2 <<< grid, block>>> () ;
cudaSetDevice(1);
kernel3 <<< grid, block>>> () ;
cudaEventSynchronize (event);
cpu_method();
}

直到kernel1做完,才会继续执行程序。因为在kernel1的时候record了event。
Kernel Time Measurement Example
因为大部分call都是异步的,所以不能使用C自带的时间戳(timestamp)计算消耗的时间。
cudaEvent_t start,stop;
cudaEventCreate(&start);
cudaEventCreate(&stop);
cudaEventRecord(start);
kernel<<<block,thread>>>();
cudaEventRecord(stop);
cudaEventSynchronize(stop);//直到stop event被record,才继续执行程序
float time;
cudaEventElapsedTime(&time, start, stop);
Multi-GPU
Multi-GPUs
-
within a node
A single CPU thread, multiple GPU;
Multiple CPU threads belonging to the same process, such as pthread or openMP
-
Multiple GPUs on multiple nodes
Need to go through network API, such as MPI
Single thread multi-GPUs
-
cudaSetDevice():选中哪一个GPU,这之后一直是说的这一个device。// Run independent kernel on each CUDA device int numDevs = 0; cudaGetNumDevices(&numDevs); for (int d = 0; d < numDevs; d++) { cudaSetDevice(d); kernel<<<blocks, threads>>>(args); } -
因为转换与launch kernels都是异步的,所以不会阻塞切换GPU。
cudaSetDevice( 0 ); kernel<<<...>>>(...); cudaSetDevice( 1 ); kernel<<<...>>>(...);Using CUDA with OpenMP
不同CPU线程都给同一个GPU launch kernels,好处是可以最大限度的使用GPU资源,不浪费GPU的计算效能;坏处是GPU的资源也是有限的,如果launch过多的kernel,可能会给不同kernel排序,造成delay(延迟)。
Example: cudaOMP.cu
... cudaGetDeviceCount(&num_gpus); ... omp_set_num_threads(num_gpus); // create as many CPU threads as there are CUDA devices #pragma omp parallel { unsigned int cpu_thread_id = omp_get_thread_num(); unsigned int num_cpu_threads = omp_get_num_threads(); cudaSetDevice(cpu_thread_id); int gpu_id = -1; cudaGetDevice(&gpu_id); printf("CPU thread %d (of %d) uses CUDA device %d\n", ... }Using CUDA with MPI
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){ int rank, size; int A[32]; int i; MPI_Init(&argc, &argv); MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &rank); MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &size); printf(“I am %d of %d\n", rank, size); for(i = 0; i< 32; i++) A[i] = rank+1; launch(A); // a call to launch CUDA kernel MPI_Barrier(MPI_COMM_WORLD); MPI_Finalize(); return 0; }extern "C" void launch(int *A){ int *dA; cudaMalloc((void**)&dA, sizeof(int)*32); cudaMemcpy(dA, A, sizeof(int)*32, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice); kernel<<<1, 32>>>(dA); cudaMemcpy(A, dA, sizeof(int)*32, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost); cudaFree(dA); }Sharing data between GPUs
3种方式:
-
Explicit copies via host
-
Zero-copy shared host array
-
Peer-to-peer memory copy
-
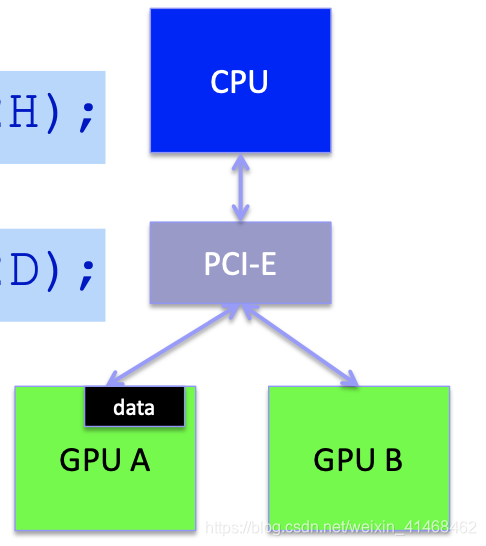
Explicit copies via host
通过CPU将资料从device A传送到device B。
GPU A->PCI-E->CPU(main memory)->PCI-E->GPU B
cudaSetDevice(0);
cudaMemcpy(DM1,HM,n,D2H);
cudaSetDevice(1);
cudaMemcpy(HM,DM2,n,H2D);
Using zero-copy
仍然要通过host传输,但是区别在于所有的资料都存储在CPU的main memory中。缺点是每一次的data存取都必须访问host。
host的main memory中存储这些数据的位置一定要被pinned住(因为OS实际上会随着时间的迁移memory中的数据进行迁移,但是如果要做zero-copy,那么一定要pinned住这块数据区域)

Host Memory Allocation
-
malloc()普通的C语言中的allocate的方式
-
cudaMallocHost(void ** hostPtr,size_t size)- pinned住一块区域,好处是因为没有先去找新的地址的时间,所以存取数据的速度加快
- Used with cudaMemAsync()for async memory copy or CUDA stream,async就是为了不让host管data copy的过程,因为此时pinned住了一块区域,所以可以实现async memory copy而不打扰host(不需要CPU寻找新的地址)
-
cudaHostAlloc(void ** hostPtr,size_t size,unsigned int flags)- Add the flag
cudaHostAllocMappedto allocate pinned host memory for higher cudaMemcpy performance - Add the flag
cudaHostAllocPortableto allocate shared host memory for “Zero copy” - Zero copy 只能使用第三个allocate方法


- Add the flag
Dynamic Parallelism




























 386
386

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








