History of Machine Translation
Before Neural networks, machine translation is performed by statistic machine translation:
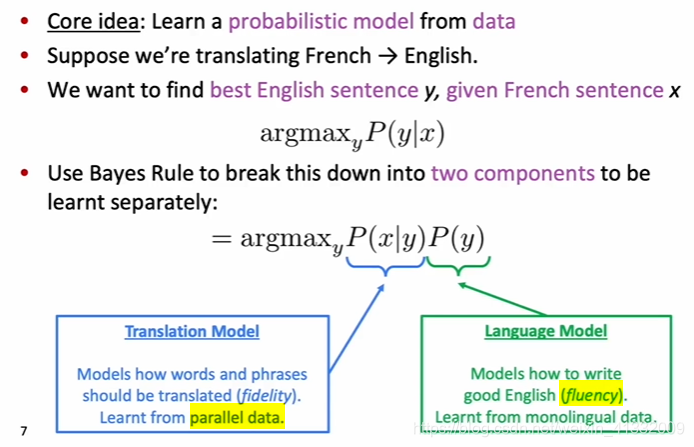
translation model and language model are trained separately
train the translation model:


what is alignment?
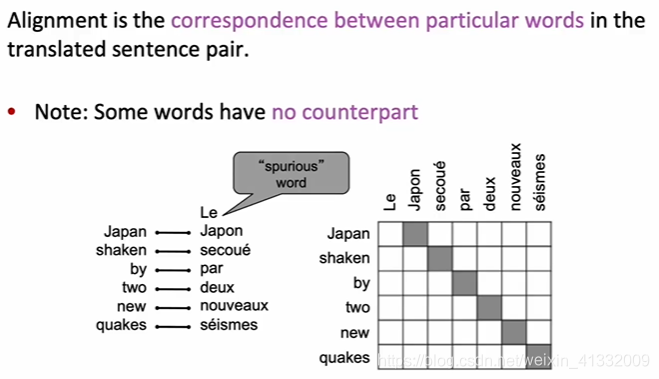
alignment can be many-to-one:
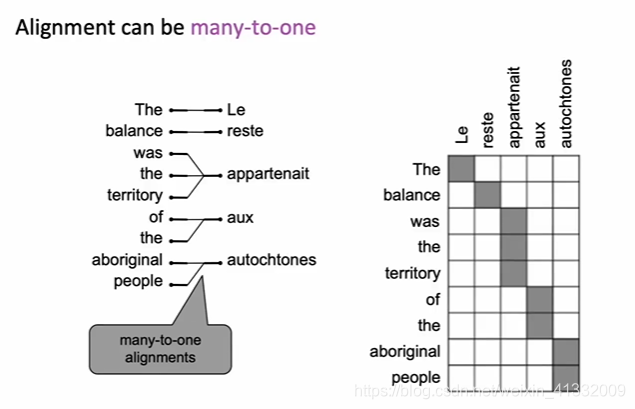
or, one-to-many:
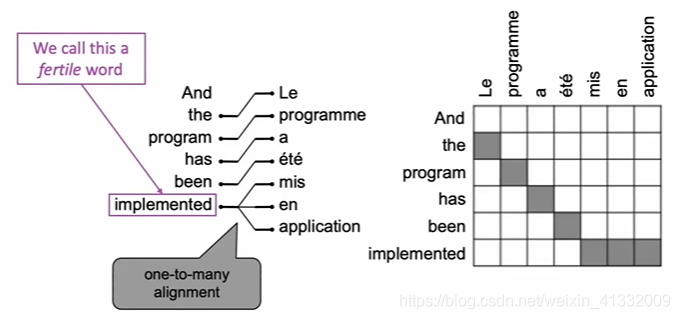
or many-to-many(phrase level):
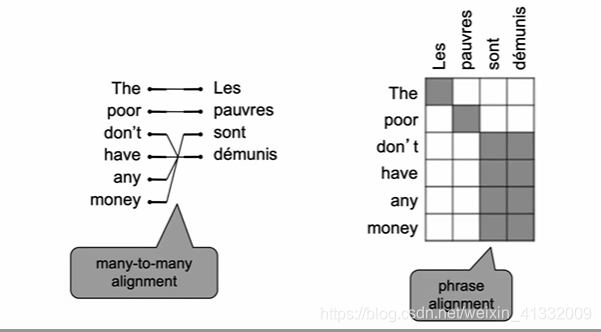
Learning alignment for Statistic Machine Translation:

how to decode for SMT
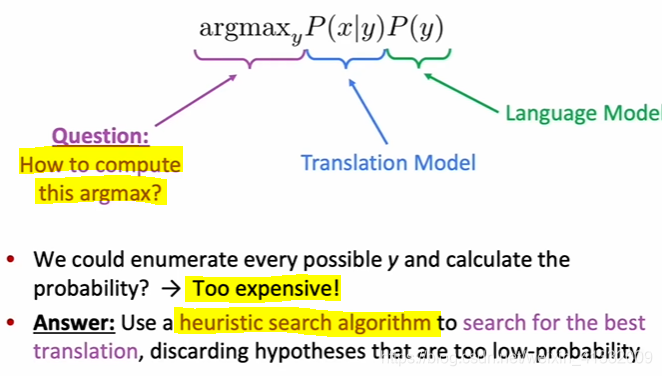
decoding: finding the best sentence in target language.
heuristic search: prune the tree to discard some hypotheses with low-probability
Statistical Machine Learning is too complex, with many seperated subcomponents, lots of feature engineering, and lots of human effort.
Neural Machine Translation (2014)
Seq2Seq
1. testing the seq2seq model:
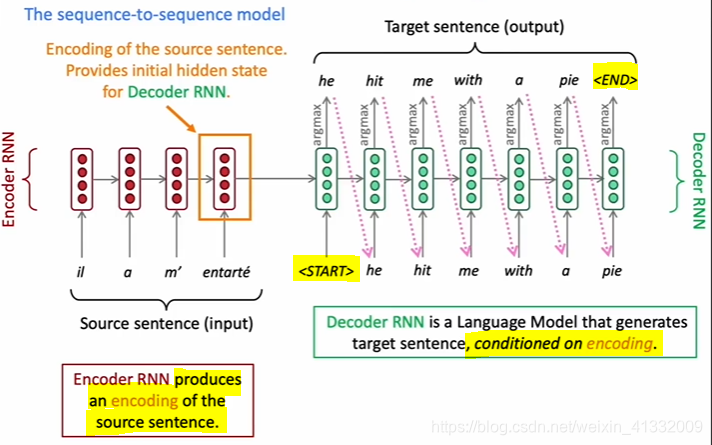
The encoder/decoder RNN can be any type of RNN, e.g. vanilla RNN, LSTM, bidirectional RNN, multi-layer RNN ...
The decoder RNN takes <START> as input, and generate a probability distribution that can be translated to a target word with argmax.

1.1 greedy decoding:
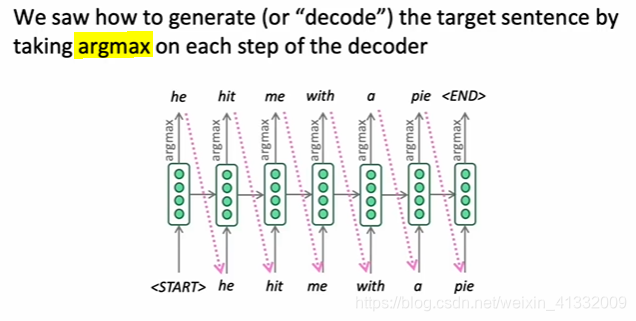
the problem: no way to back-track -- local minimia
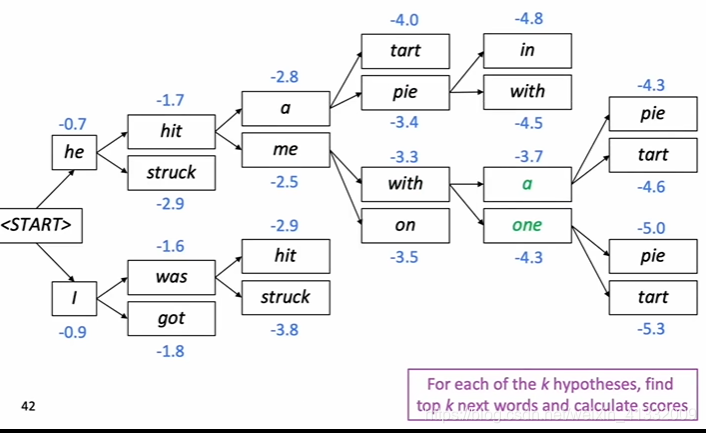
1.2 beam search decoding:

beam search example:
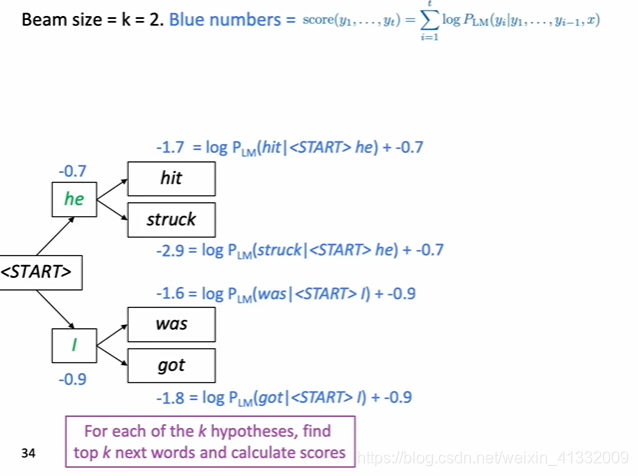 ------->
-------> 
------> 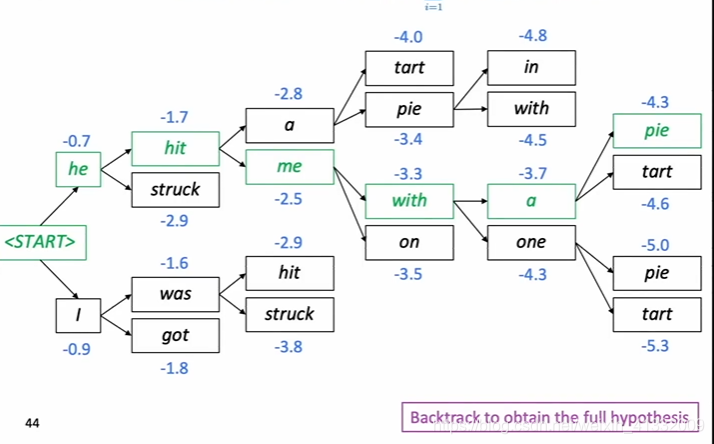
the stop criteria for beam search:

choose the best hypothesis after beam search:

2. training the seq2seq model:
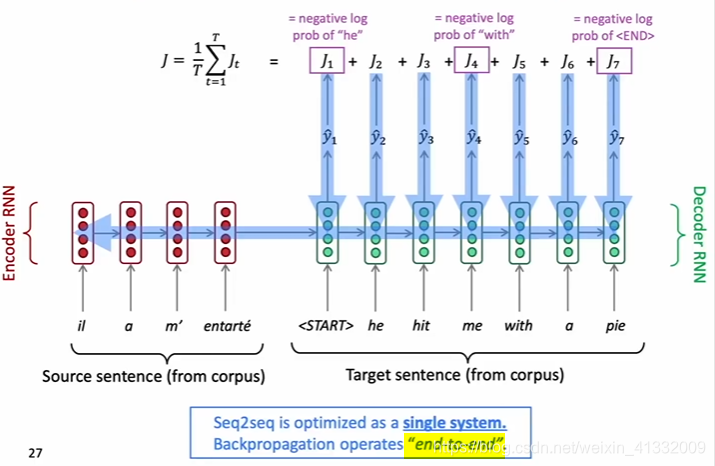
Feed the encoder/decoder RNN with word-embedding of source/target language words.
the decoder RNN produces the probability distribution of words in every position
the loss is the entropy loss of probability distribution and the ground truth word (one-hot)
3. seq2seq can also be used for:

Evaluate Machine Translation
BLEU(Bilingual Evaluation Understudy)

Difficulties in Machine Translation
- Out-of-vocabulary words (<unk>)
- Domain mismatch between training and testing data (if you train the NMT on wikipedia and then test it on people on twitter chatting)
- Maintaining context over longer text
- low-resource language pairs (like Thai-Eng)
- NMT picks up biases in the training data
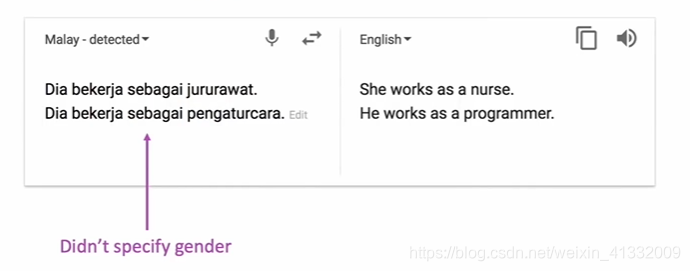
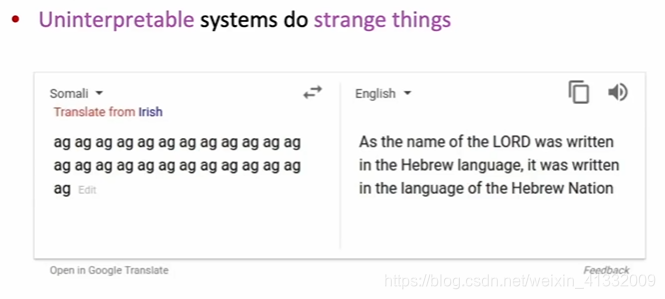
(this is because the parallel text of Somali-Eng is based on the Bible, the NMT just produce random text using language model)
Attention
the vanilla RNN:
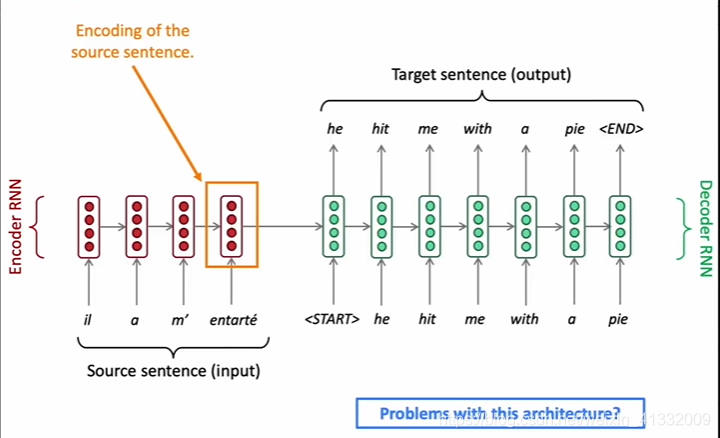
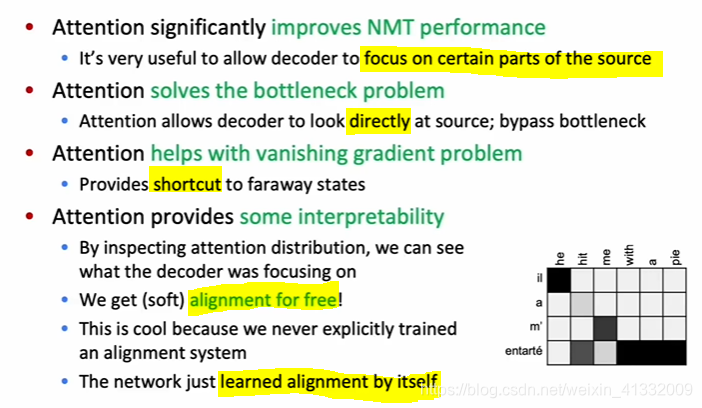
the orange box is the encoding of the whole source sentence, it need to capture all the information of the source sentence ---> information bottleneck! (too much pressure on this single vector to be a good representation of the source sentence.)
the target sentence just have one input, i.e. the orange box, so it does not provide location information.

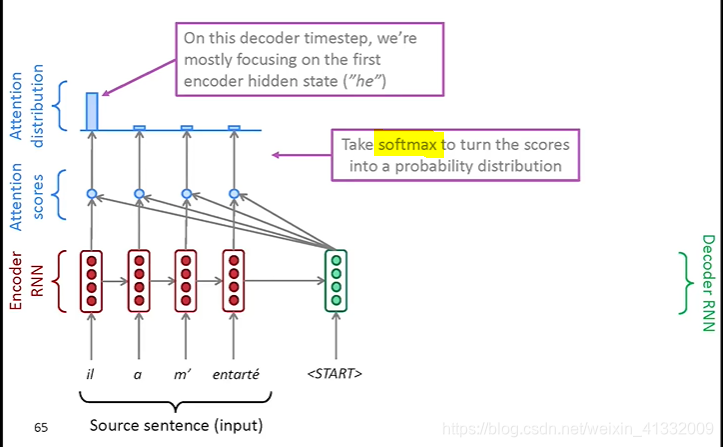
an example of attention:
 --->
--->
(a) (b)
 ---->
----> 
(c) (d)
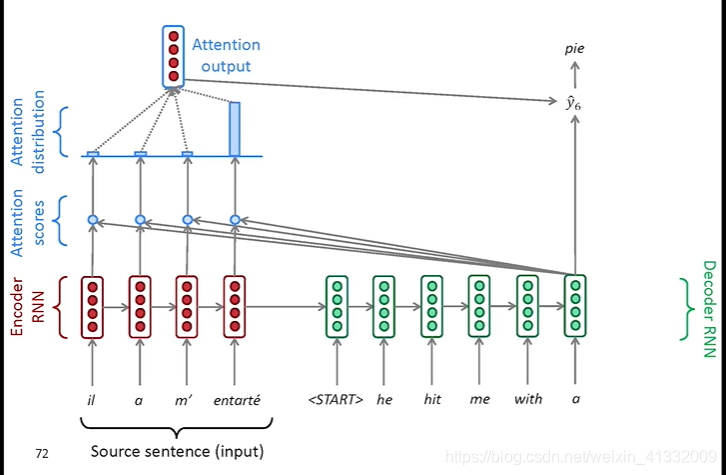
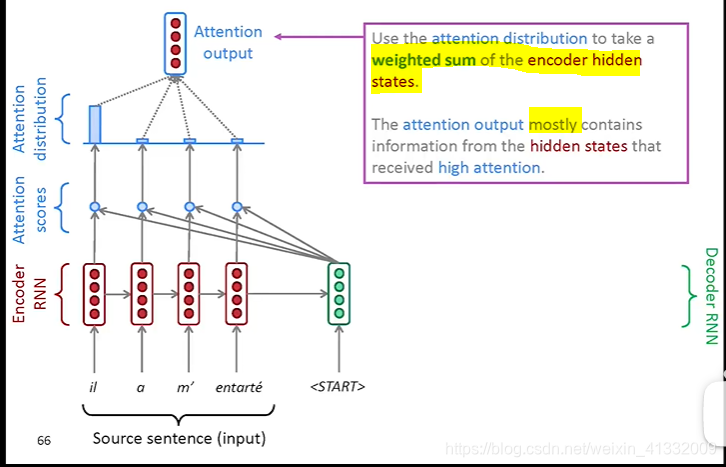
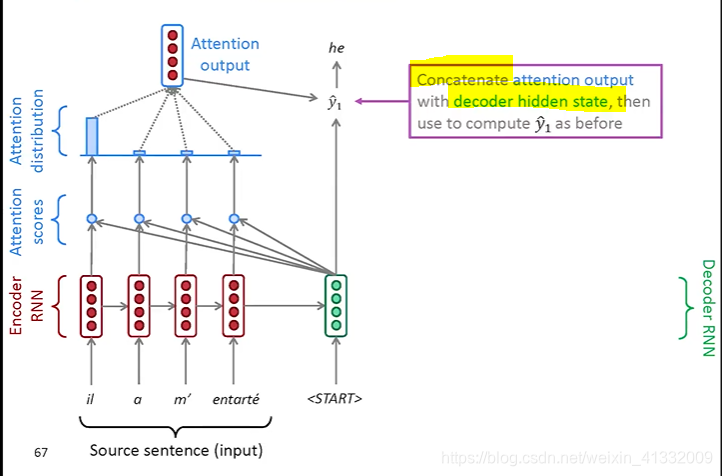
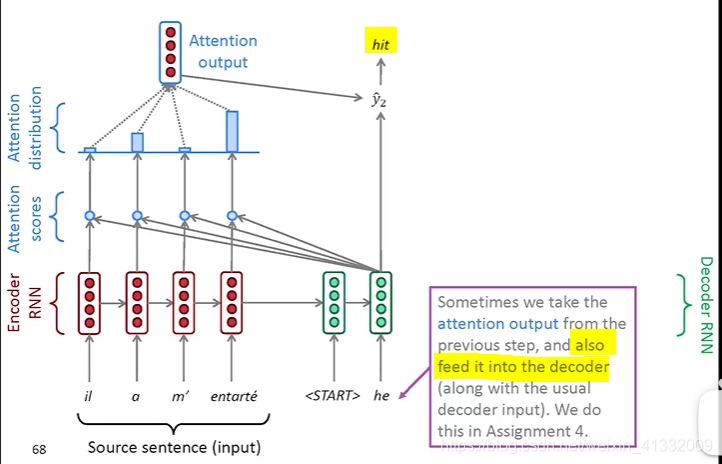
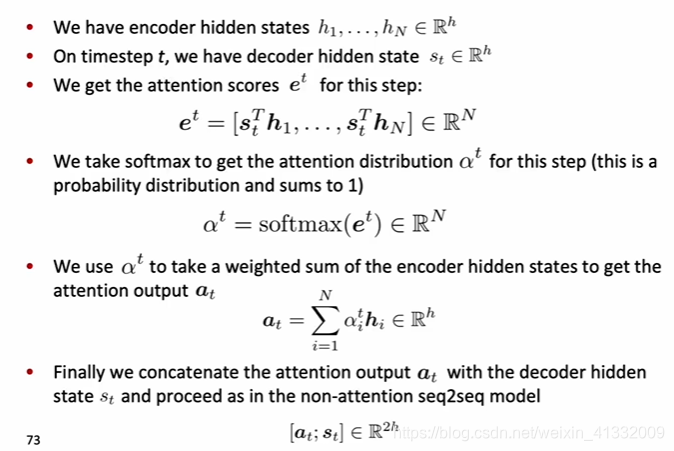
(a). We use the decoder hidden state
to perform dot product with every encoder hidden states
, and it gives a set of scores. Using softmax to turn this set of scores to probability distribution (0~1)
math equation for attention:
Advantage of Attention:




 本文概述了机器翻译的历史,从统计机器翻译中的模型训练、对齐方法到神经机器翻译(NMT)的Seq2Seq模型,重点介绍了注意力机制如何解决信息瓶颈问题。探讨了BLEU评估标准,并讨论了NMT面临的挑战,如OOV词、领域不匹配等。
本文概述了机器翻译的历史,从统计机器翻译中的模型训练、对齐方法到神经机器翻译(NMT)的Seq2Seq模型,重点介绍了注意力机制如何解决信息瓶颈问题。探讨了BLEU评估标准,并讨论了NMT面临的挑战,如OOV词、领域不匹配等。
















 1590
1590

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








