一、文件支持中文三步曲
1.1解决方法
python 2中
1文件声明为:#encoding=utf-8
或者
#_*_coding:UTF-8_*_
2 文件格式保存为:utf-8
3 所有中文前面加u, 如 print u"今天的天气"
python 3
1文件格式保存为utf-8
2 文件声明可加#encoding=utf-8 ,也可以不加
3 中文前面可以加u,也可以不加
实例:
#encoding=gbk
s="中国"
print (s)
1保存为ANSI,文件名为1.py
2 文件头声明#encoding=gbk
3 中文前面不加u,加u也可以
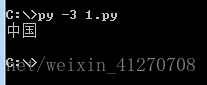
备注:文件声明utf-8,文件保存为utf-8;文件声明gbk,文件保存为ANSI
二、编码格式
2.1编码格式
ASCII编码:256个字符
gbk编码:支持生僻字,范围更广
gb2312编码:包含所有中文
ANSI编码:操作系统默认编码
Unicode编码:全球所有字符编码
2.2 存储编码
UTF—8编码:把一个汉字或者其他字符,保存为1-3个字节
完全兼容acsii码的256个字符
UTF-16:保存为2个字节,2种表述法,大小尾
UTF-32:保存为4个字节,很占内存
以上两个好处,在于一个字符长度固定
备注:unicode编码,UTF-8存储
2.3 chardet的使用
导入包 :py -2 –m pip install chardet
py -3 –m pip install chardet
实例:
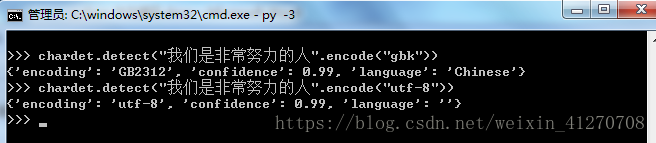
import chardet
chardet.detect("我们是非常努力的人".encode("gbk"))
chardet.detect("我们是非常努力的人".encode("utf-8"))
2.4 decode与encode的应用
2.4.1 python 2中的应用
py2:文件保存为utf-8,文件第一行声明为utf-8
#encoding=utf-8
#str1.decode() 默认是:ascii
str1="中国" 类型:str
print type(str1)
print type(str1.decode("utf-8"))
print str1.decode("utf-8")==u"我们"
print type(str1.decode("utf-8").encode("utf-8")),str1.decode("utf-8").encode("utf-8")==str1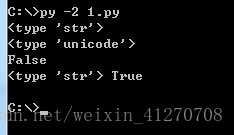
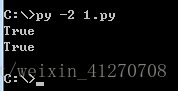
py2:文件保存为ANSI格式,文件第一行声明为gbk
str1="我们" 类型:str
#str1.decode() 默认是:ascii
str1.decode("gbk")==u"我们"
str1.decode("gbk").encode("gbk")== str1
总结:
1)py2的str类型等价于py3的bytes类型
eg:str类型:s=”中国”
unicode类型:s=u”中国”
2)py3的str类型等价于py2的unicode类型
eg:str类型:s=”中国”
bytes类型:s=”中国”.encode(“utf-8”)
3)encode 不管是py2还是py3,只能对unicode对象来用
在py2:将unicode类型的对象,转换为str类型
在py3: 将str类型的对象,转换为了bytes类
2.4.2 综合练习
练习一:
py2 :声明str类型变量和unicode变量
将unicode变量变为2个str变量(gbk,utf-8各一次)
将utf-8编码的str类型,转换为gbk
#encoding=gbk
import chardet
print (chardet.detect(u"中国的天气".encode("gbk")))
print (chardet.detect(u"中国的天气".encode("utf-8")))
print (chardet.detect("中国的天气".decode("gbk").encode("gbk")))

练习二:
#encoding=gbk
s="今天的天气"
byteString = "今天的天气".encode("gbk")
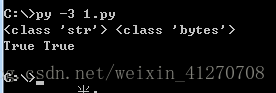
print(type(s),type(byteString))
print (isinstance(s,str),isinstance(s.encode("gbk"),bytes))
2.4.3字符转换过程
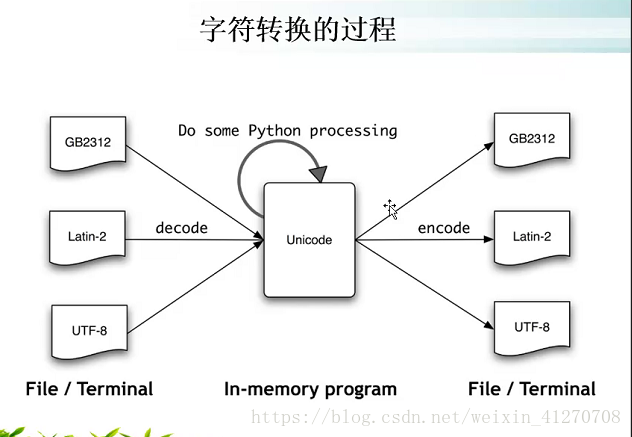
Unicode:在内存中使用,只能用encode
bytes:在文件存储和网络数据传输中使用,只能用decode
实例一:
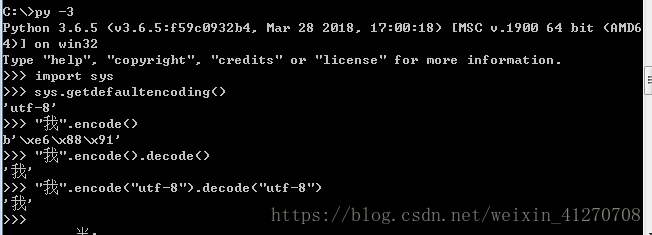
python3
import sys
sys.getdefaultencoding()
"我".encode()
"我".encode().decode()
"我".encode("utf-8").decode("utf-8")
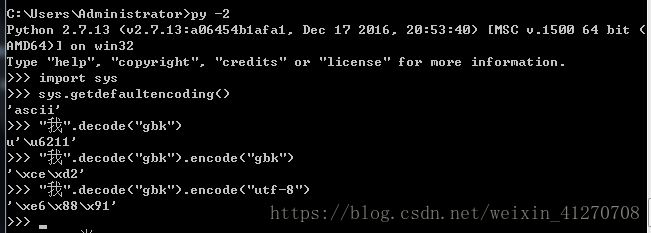
python 2
import sys
sys.getdefaultencoding()
"我".decode("gbk")
"我".decode("gbk").encode("gbk")
"我".decode("gbk").encode("utf-8")
2.4.4 文件中三种编码互转
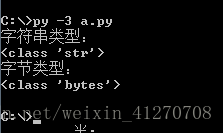
fp1=open("e://a.txt","r",encoding="gbk")
info1=fp1.read()
print("字符串类型:")
print(type(info1))
print("字节类型:")
print(type(info1.encode("utf-8")))#编码为utf-8格式字节类型数据
fp2=open("e://b.txt","w",encoding="utf-8")
fp2.write(info1)
fp1.close()
fp2.close()





















 1005
1005

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








