Introduction to Java
Essentials
Hello World
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello world!");
}
}
/*
1. All code in Java must be part of a class
2. We delimit the beginning and end of segment of code using { and }
3. All statements in Java must end in a semi-colon
4. For code to run we need public static void main(String[] args)
*/
Running a Java Program (In terminal)
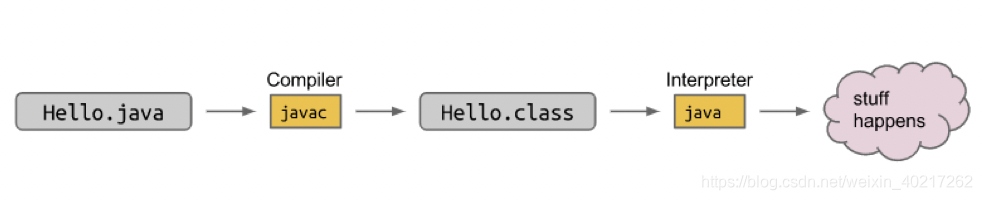
The most common way to execute a Java program is to run it though a sequence of two programs.
- Java compiler; $ javac HelloWorld.java
- Java interpreter; $ java HelloWorld
Variables and Loops
public class HelloNumbers {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 0;
while (x < 10) {
System.out.println(x);
x = x + 1;
}
// We cannot do these following statements in Java
// x = "horse";
// String x = "horse";
}
}
/*
1. Before Java variables can be used, they must be declared.
2. Java variables must have a specific type
3. Java variables can never change
4. Types are verified before the code even runs!!!
*/
Static Typing
One of the most important features of Java is that all variables and expressions have so-called static type.Java variables can contain values of that type, and only that type. Furthermore, the type of a variable can never change.
Advantages of static typing
- The compiler ensures that all types are compatible, making it easier for the programmer to debug their code.
- Since the code is guaranteed to be free of type errors, users of your compiled programs will never run into type errors.
- Every variable, parameter, and function has a declared type, making it easier for a programmer to understand and reason about code.
disadvantages: - Code is more verbose
- Code is less general. (There is a way around this in Java – generics)
String h = 5 + "horse";
// This one will succeed
// Since java is strongly typed, if you tell it h is a string, it can concatenate the the elements and give you a string
int h = 5 + "horse";
// When h is an int, it can't concatenate a number and a string and give you a number.
System.out.println(5 + "horse"); // 5horse
System.out.println(5 + " "); // 5
System.out.println(5 + "10"); // 510
System.out.println(5 + 10); // 15
- 动态类型语言:在运行期进行类型检查的语言,也就是在编写代码的时候可以不指定变量的数据类型,比如Python和Ruby
- 静态类型语言:它的数据类型是在编译期进行检查的,也就是说变量在使用前要声明变量的数据类型,这样的好处是把类型检查放在编译期,提前检查可能出现的类型错误,典型代表C/C++和Java
- 强类型语言,一个变量不经过强制转换,它永远是这个数据类型,不允许隐式的类型转换。举个例子:如果你定义了一个double类型变量a,不经过强制类型转换那么程序int b = a无法通过编译。典型代表是Java。e.g. int a = 5.3 // fail
- 弱类型语言:它与强类型语言定义相反,允许编译器进行隐式的类型转换,典型代表C/C++
Defining Functions in Java
In java, all code is part of a class, we must define functions so that they belong to some class
public class LargeDemo {
public static int larger(int x, int y) {
if (x > y) {
return x;
}
return y;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(larger(2, 4));
}
}
/*
1. Functions must be declared as part of a class in Java. In Java, all functions are methods.
2. All parameters of a function must have a declared type and the return value of the function must have a declared type.
3. Functions in Java return only one value!
*/
- Writing the code self-documenting that’s readable
- javadoc
Code Style, Comments, Javadoc
- Consistent style (spacing, variable naming, brace style, etc)
Size (lines that are not too wide, source files that are not too long) - Descriptive naming (variables, functions, classes), e.g. variables or functions with names like year or getUserName instead of x or f.
- Avoidance of repetitive code: You should almost never have two significant blocks of code that are nearly identical except for a few changes.
- Comments where appropriate. Line comments in Java use the // delimiter. Block (a.k.a. multi-line comments) comments use /* and */.
https://sp19.datastructur.es/materials/guides/style-guide.html
Objects
Defining and Using Class
Elements in a class
- Instance variables/ non-static variables
- Static Methods and Non-static Methods
- Constructors
Terminologies in Class
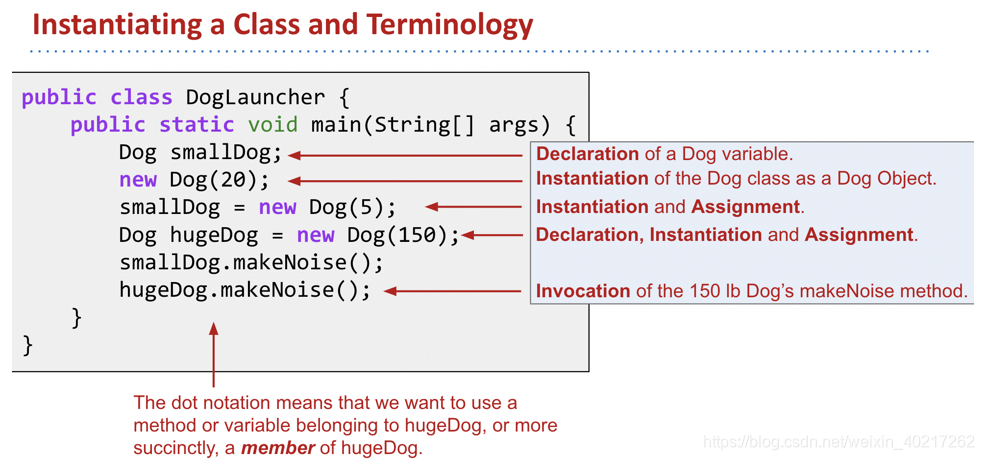
- An Object in Java is an instance of any class.
- The Dog class has its own variables, also known as instance variables or non-static variables. These must be declared inside the class, unlike languages like Python or Matlab, where new variables can be added at runtime.
- The method that we created in the Dog class did not have the static keyword. We call such methods instance methods or non-static methods.
- To call the makeNoise method, we had to first instantiate a Dog using the new keyword, and then make a specific Dog bark. In other words, we called d.makeNoise() instead of Dog.makeNoise()
- Once an object has been instantiated, it can be assigned to a declared variable of the appropriate type, e.g. d = new Dog();
- Variables and methods of a class are also called members of a class.
- Members of a class are accessed using dot notation.

Static vs. Non-Static Methods
1. Static Method
public class Dog {
public static void makeNoise() {
System.out.println("Bark!");
}
}
// We cannot: $ java Dog, because there is no main method
// To actually run the class, we'd either need to add a main method to the Dog class, as we saw in chapter 1.1.
//Or we could create a separate DogLauncher class that runs methods from the Dog class.
public class DogLauncher {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog.makeNoise();
}
}
// $ java DogLauncher
A class that uses another class is sometimes called a “client” of that class, i.e. DogLauncher is a client of Dog.
Neither of the two techniques is better: Adding a main method to Dog may be better in some situations, and creating a client class like DogLauncher may be better in others.
2. Non-Static Methods, Instance Variables and Object Instantiation
In fact, not all dogs will make noise in the way mentioned before. So, we can create different classes to represent different dogs, e.g. TinyDog class, BigDog class and with a specific static method.
– But, classes can be instantiated, and instances can hold data.
public class Dog {
public int weightInPounds;
public void makeNoise() {
if (weightInPounds < 10) {
System.out.println("yipyipyip!");
} else if (weightInPounds < 30) {
System.out.println("bark. bark.");
} else {
System.out.println("woof!");
}
}
}
public class DogLauncher {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog d;
d = new Dog();
d.weightInPounds = 20;
d.makeNoise();
}
}
Arrays of Objects
Dog[] dogs = new Dog[2]; // No Dog objects are created in that statement
// just like constructing two dog houses that are currently empty
dogs[0] = new Dog(8);
“new” is used in two different ways:
- Once to create an array that can hold two Dog objects;
- Twice to create each actual Dog
Static vs. Non-static (Class Methods vs. Instance Methods)
Java allows us to define two types of methods:
1. Class methods, a.k.a. static methods
Static methods are actions that are taken by the class itself
2. Instance methods, a.k.a non-static methods
Instance methods are actions that can be taken only by specific instance of a class
Both are useful in different circumstances:
// Math class provides a sqrt method, which is static
int x = Math.sqrt(100);
// But if sqrt had been an instance method, we would have to create a Math instance first.
Sometimes, it makes sense to have a class with both instance methods and static methods, like comparator()
Key differences between static and non-static (a.k.a instance) method:
- Static methods are invoked using the class name, e.g. Dog.makeNoise();
- Instance methods are invoked using an instance name, e.g. maya.makeNoise();
- Static methods can’t access instance variables, because there is no “me”
Why static method? - Some classes are never instantiated. For example, Math.
- Sometimes, classes may have a mix of static and non-static methods
Static variable
It is occasionally useful for classes to have static variables. These are properties inherent to the class itself, rather than the instance.
All objects will have the same properties
But if you have a static variable for a class, just use the class name rather than using the instance variable name.
A class may have a mix of static and non-static members - A variable or method defined in a class is also called a member of that class
- Static members are accessed using class name, e.g. Dog.binomen
- Non-static members cannot be invoked using class name
- Static members, you should really really strive to use class name
- Static methods must access instance variable via a specific instance
public static void main(String[] args)
- public: So far, all of our methods start with this keyword.
- static: It is a static method, not associated with any particular instance.
- void: It has no return type.
- main: This is the name of the method.
- String[] args: This is a parameter that is passed to the main method.
Since main is called by the Java interpreter itself rather than another Java class, it is the interpreter’s job to supply these arguments. They refer usually to the command line arguments.





 本文介绍了Java编程的基础知识,包括HelloWorld程序、变量与循环、函数定义、静态类型的优势与劣势、自文档化的代码编写、类的定义与使用、静态与实例方法的区别以及数组对象的概念。深入探讨了Java的特性,如静态类型、强类型语言的特点,并对比了动态类型语言。
本文介绍了Java编程的基础知识,包括HelloWorld程序、变量与循环、函数定义、静态类型的优势与劣势、自文档化的代码编写、类的定义与使用、静态与实例方法的区别以及数组对象的概念。深入探讨了Java的特性,如静态类型、强类型语言的特点,并对比了动态类型语言。
















 236
236

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








