前言
基于JDK1.8源码解析List集合类中的ArrayList,LinkedList以及Vector和ArrayList的比较。
先说一下各个List集合类最重要的知识点以及集合类间的区别:
ArrayList:
- 底层是数组;
- 线程不安全;
- 每次扩容后的容量都是原来容量的1.5倍(向下取整),扩容的实现需要调用底层由C/C++编写的native方法;
- 增删时,需要数组的拷贝复制,调用底层由C/C++编写的native方法;
LinkedList:
- 底层是链表;
- 线程不安全;
- 不需要扩容;
- LinkedList的增删其实就是链表中添加或者删除结点;
Vector(一般很少使用):
- 底层是数组;
- 线程安全;
- 每次扩容后的容量都是原来容量的1倍;
- 增删的底层原理与ArrayList相同;
这里主要总结ArrayList(底层是数组,线程不安全)与LinkedList(底层是链表,线程不安全),以及Vector(底层是数组,线程安全)与ArrayList的区别。
1、ArrayList解析
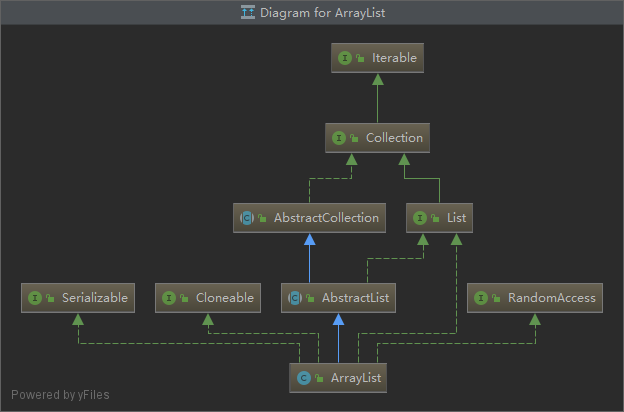
ArrayList关系图
1.1 ArrayList文件顶部注解
一般源码的精髓都集中在文件最上方的总览注解中,因此,在阅读源码时,阅读总览注解非常重要(原谅我英语渣)。
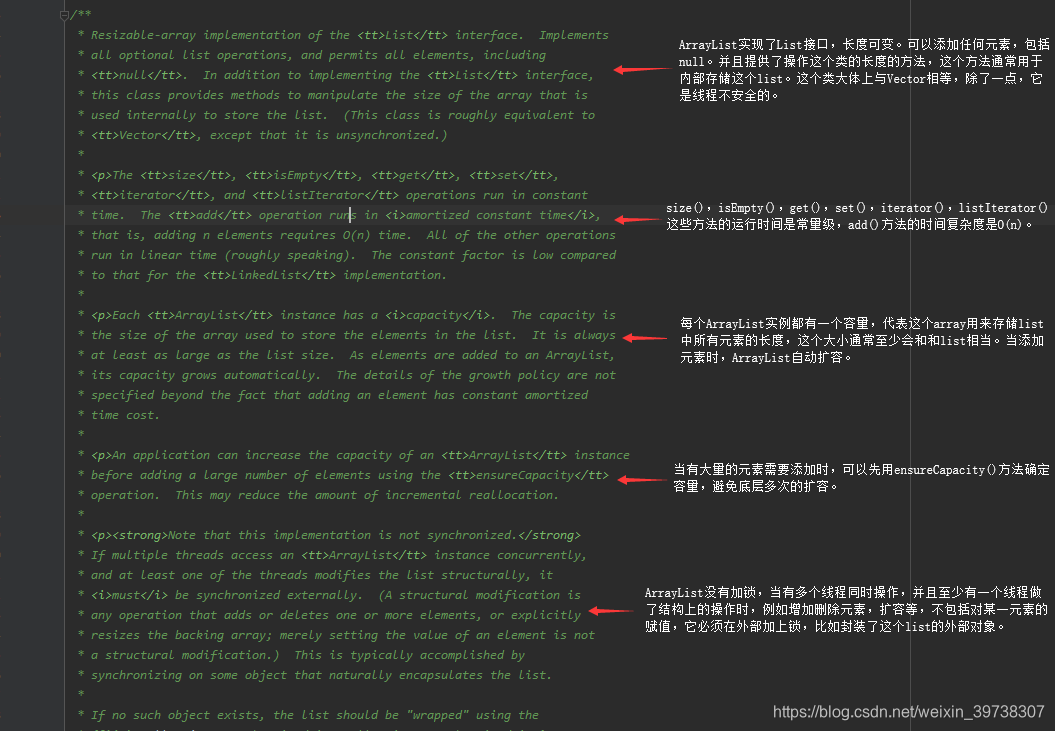
通过注解我们可以提取出以下几点重要信息:
- ArrayList是一个可以存储任何对象元素(包括null)的长度可变数组;
- ArrayList底层是一个Object数组,封装了基本的增删改查等操作,并且利用底层的arrayCopy()实现了动态扩容;
- 除了add()方法的时间复杂度是O(n)之外,其他方法例如get()、set()、size()等时间复杂度都是常量级。如果不考虑底层内存拷贝的耗时,其实add()方法如果不指定下标,默认插到尾部,时间复杂度依旧是常量级;
- 如果单次添加的数据过大的话,可以调用ArrayList的ensureCapacity()方法直接给ArrayList开辟一块内存容量,避免中间扩容时多次的内存拷贝造成不必要的时间浪费;
- ArrayList和Vector类似但是本身线程不安全,如果要对结构做修改,例如增删元素等,在多线程环境下必须加锁,但是也可以通过Collections.synchronizedList()包装成一个线程安全的容器;
- ArrayList还引入了快速失败机制,关于快速失败机制:https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/weixin_39738307/article/details/106100118;
1.2 ArrayList的成员变量
先来看一下ArrayList的几个成员变量。
private static final long serialVersionUID = 8683452581122892189L;
/**
* Default initial capacity.
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for empty instances.
*/
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for default sized empty instances. We
* distinguish this from EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA to know how much to inflate when
* first element is added.
*/
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* The array buffer into which the elements of the ArrayList are stored.
* The capacity of the ArrayList is the length of this array buffer. Any
* empty ArrayList with elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
* will be expanded to DEFAULT_CAPACITY when the first element is added.
*/
transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
/**
* The size of the ArrayList (the number of elements it contains).
*
* @serial
*/
private int size;结合注解,可以知道:
- serialVersionUID:序列化时为了保持版本的兼容性;
- DEFAULT_CAPACITY:初始化时的默认容量,默认为10;
- EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA:静态不可变的Object空数组,所有的容量设置为0的list都共享这个空的Object空数组;
- DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA:默认的数组,所有没有在初始化时指定容量大小的ArrayList。在第一次插入元素时,如果elementData数组是被赋值为DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA,那么就会被扩容至默认大小10;如果是被赋值为EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA,那按照原来的扩容方式扩容;
- elementData:ArrayList中用来存储数据的Object数组,基本上增删扩容等操作都是围绕着这个Object数组展开的。并且ArrayList的size是这个数组的元素个数。如果没有在初始化的时候指定ArrayList的容量,这个数组一开始是空的,只有当插入了第一个元素之后才会扩容至默认的初试容量;
- size:Object数组中的元素个数。
除此之外还有一个MAX_ARRAY_SIZE,静态final的整型变量,数值是最大整数-8,限定可分配的最大数量,防止ArrayList分配的过大导致OutOfmemoryError。
1.3 构造方法
ArrayList提供了三种方式的构造器,可以构造一个默认初始容量为10的空列表、构造一个指定初始容量的空列表以及构造一个包含指定collection的元素的列表,这些元素按照该collection的迭代器返回的顺序排列的。

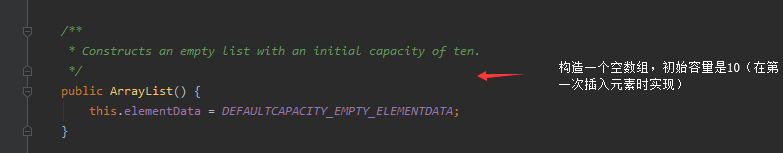
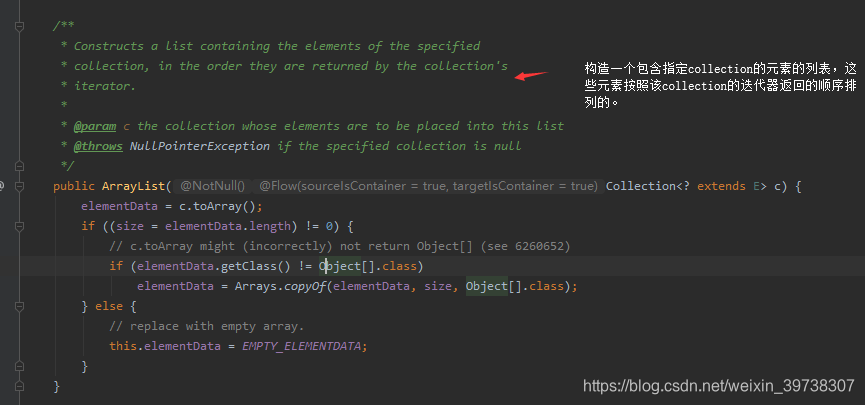
其中比较常用的是无参构造器。结合上面的分析,使用无参构造器和使用指定容量的构造器并且指定容量为0的时候,ArrayList会将存储数据的Object设置为一个空的指定数组。
1.4 插入方法
ArrayList的插入方法有两种,可以指定插入位置,或者不指定,插在数组尾。
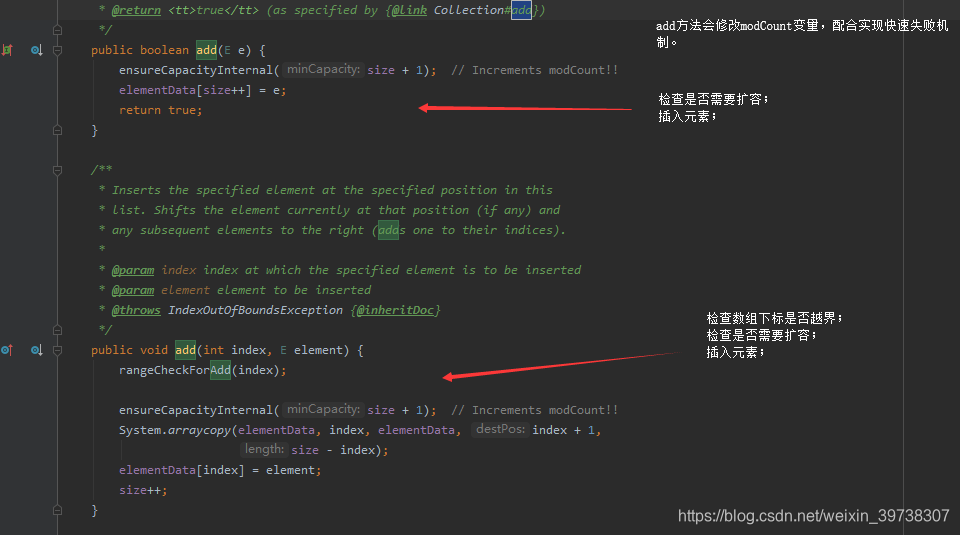
Add(E e):
这个函数看起来比较简单,先是调用了ensureCapacityInternal方法,然后把元素放在数组的下标为size的位置(数组中最后一个元素的后面一个位置),size再自增。
先来看看ensureCapacityInternal方法做了什么。
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity));
}这个函数的方法的代码只有一行,接着看看calculateCapacity和ensureExplicitCapacity方法的实现。
calculateCapacity:
private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
return minCapacity;
}结合上面对成员变量的解读,可以知道,如果elementData数组等于DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA,也就是说elementData现在被赋值为一个指定的空数组,那么就返回DEFAULT_CAPACITY(10)和minCapacity(size+1)中的最大值(对于还没插入过元素的无参构造器构造生成的ArrayList就是返回10,至于为什么会有这样一个比较过程,感兴趣的可以自行扩展阅读)。
ensureExplicitCapacity:
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}如果元素的个数超过了数组的长度,就调用扩容方法。
modCount变量是用于快速失败机制:https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/weixin_39738307/article/details/106100118;
其中grow方法就是ArrayList中核心的扩容方法了。
/**
* Increases the capacity to ensure that it can hold at least the
* number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}需要注意的是"int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);"。这行代码说明扩容是原来容量的1.5倍向下取整。
其中,Arrays.copyOf()调用的是由C++编写的arraycpoy()本地方法。
到这里可以知道Add(E e)的流程可以概括为:
- 检查是否需要扩容,如果需要扩容的话底层调用扩容方法进行扩容;
- modCount+1,用于实现快速失败机制;
- 在数组尾端添加元素。
add(int index, E element):
再返回开头的add方法源码,并且结合之前分析的Add(E e)调用的方法,可以看出
- 检查下标是否合法;
- 检查是否需要扩容;
- 调用arraycpoy()方法,将要插入的位置上的元素以及之后的元素往后挪;
- 插入元素到指定坐标;
1.5 get方法
获取指定下标的值。
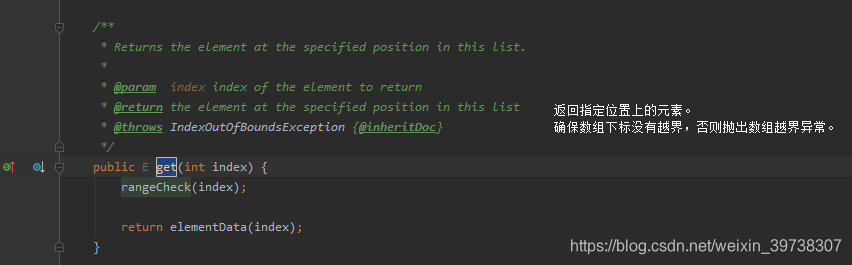
步骤:
- 检查坐标
- 返回对应坐标的元素
1.6 set方法
设置指定下标的值。
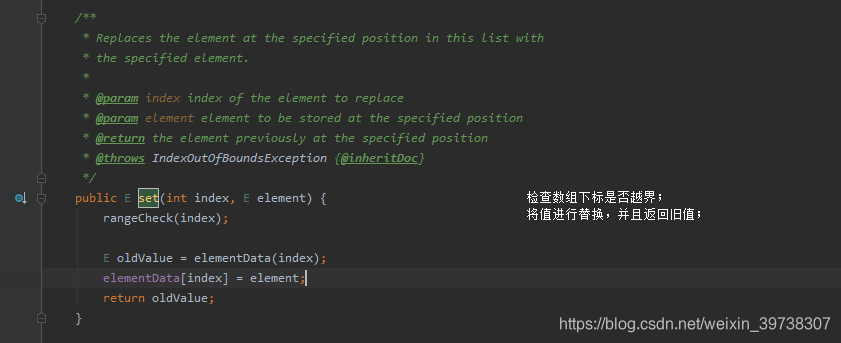
步骤:
- 检查坐标
- 替换对应坐标上的值
- 返回旧值
1.7 remove方法
remove(int index)
删除指定下标的元素。
/**
* Removes the element at the specified position in this list.
* Shifts any subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their
* indices).
*
* @param index the index of the element to be removed
* @return the element that was removed from the list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
return oldValue;
}步骤:
- 检查下标;
- 设置快速失败机制的参数;
- 通过调用底层的arraycopy方法将删除元素后面的所有元素全部左移一位;
- 将最后一个位置的引用设置为null,配合GC清理;
- 返回旧值。
remove(Object o)
删除第一个与传入参数相同的元素。
/**
* Removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this list,
* if it is present. If the list does not contain the element, it is
* unchanged. More formally, removes the element with the lowest index
* <tt>i</tt> such that
* <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>
* (if such an element exists). Returns <tt>true</tt> if this list
* contained the specified element (or equivalently, if this list
* changed as a result of the call).
*
* @param o element to be removed from this list, if present
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this list contained the specified element
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (elementData[index] == null) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
} else {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}通过注解可以知道, 删除第一个与指定对象相同的元素(如果存在的话);如果不存在的话,就不改变这个list。
这里调用了fastRemove方法,看看它的实现。
/*
* Private remove method that skips bounds checking and does not
* return the value removed.
*/
private void fastRemove(int index) {
modCount++;
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
}可以看出也是一个配合实现快速失败机制的方法。
步骤:
- 遍历数组,找到与传入对象相同的第一个元素(ArrayList也可以存储null,如果传入的是null的话,判断用==);
- 设置快速失败机制的参数;
- 通过调用底层的arraycopy方法将删除元素后面的所有元素全部左移一位;
- 将最后一个位置的引用设置为null,配合GC清理;
- 删除成功则返回true,否则返回false。
2、ArrayList与Vector的区别
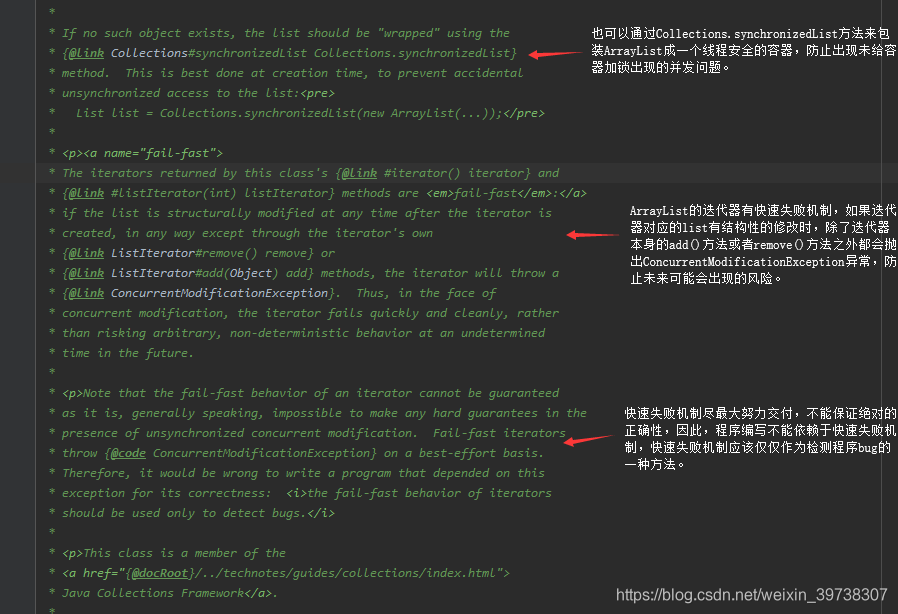
Vector是一个比较老的集合类了,现在开发基本不用,在不要求线程安全的情况下一般多用ArrayList,如果要求线程安全可以使用别的方法,例如Collections.synchronizedList()方法包装ArrayList,或者使用JUC包下的CopyOnWriteArrayList来代替。因此对Vector只要稍作了解即可,比如Vector和ArrayList的区别。
- Vector的底层也是数组,从ArrayList源码文件最上方的总览注释上面可以得知,ArrayList和Vector最大的区别在于Vector是线程安全,而ArrayList是线程不安全的;
- ArrayList默认扩容是1.5倍,Vector扩容是1倍。
3、LinkedList解析
在平时的开发过程中,虽然一般ArrayList用的比较多,但是LinkedList也是需要学习的,在一些特殊的场景中也会用到。LinkedList的分析相对于ArrayList会简单一些。
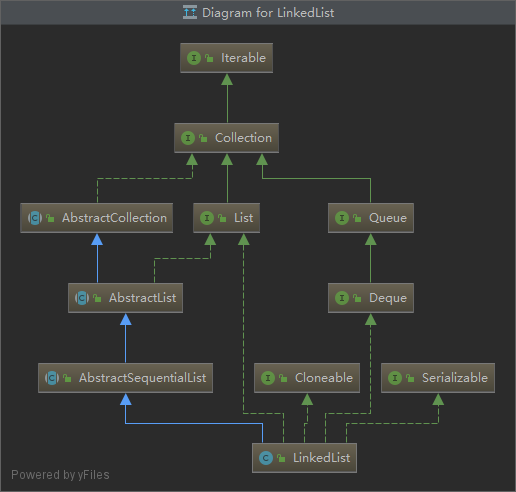
LinkedList实现了Deque接口,因此可以像操作队列和栈一样操作LinkedList。
3.1 LinkedList文件顶部注解
老样子,还是先通读一遍类文件顶部的注释。
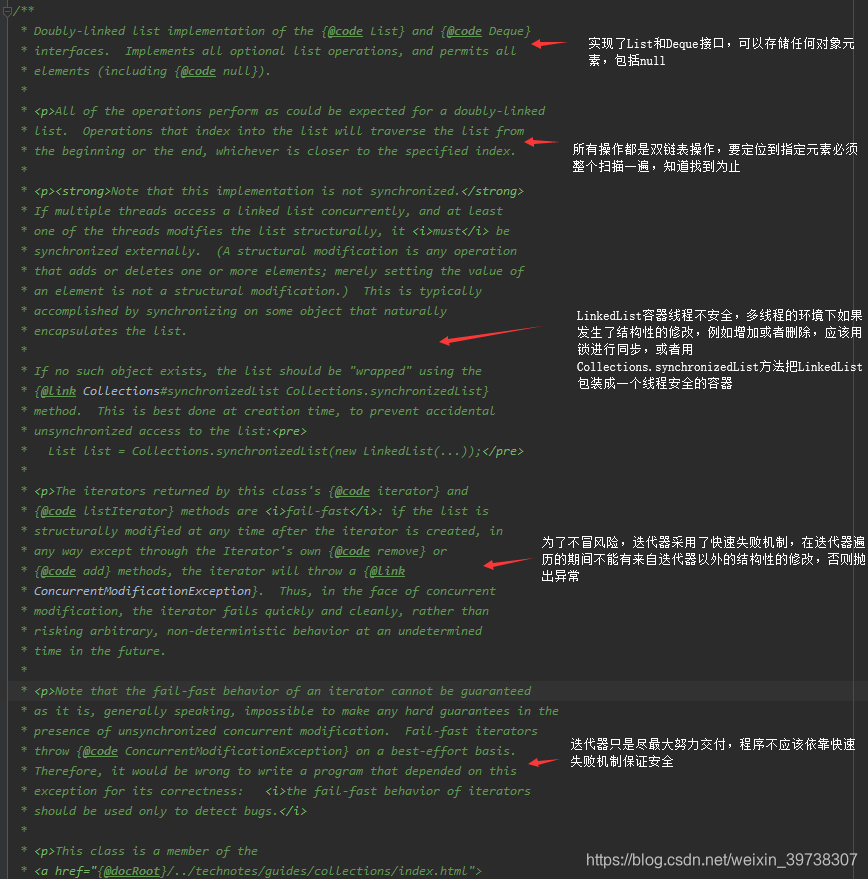
补充:关于快速失败机制:https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/weixin_39738307/article/details/106100118;
3.2 LinkedList的成员变量
transient int size = 0;
/**
* Pointer to first node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (first.prev == null && first.item != null)
*/
transient Node<E> first;
/**
* Pointer to last node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (last.next == null && last.item != null)
*/
transient Node<E> last;- size:LinkedList中的元素个数;
- first:链表头结点;
- last:链表尾结点;
3.3 构造方法
无参构造器:

构造一个包含指定collection的元素的列表,这些元素按照该collection的迭代器返回的顺序排列的:
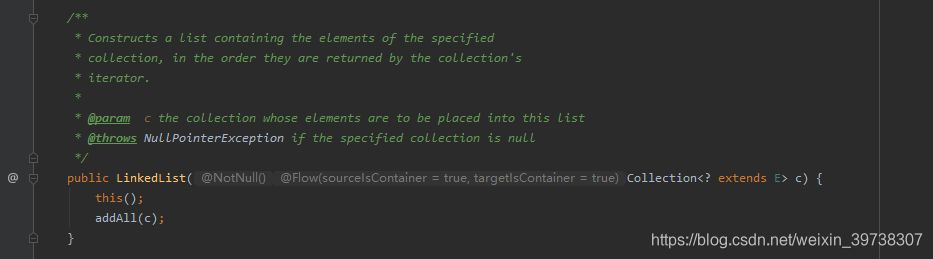
一般无参构造器用的比较多。
3.4 get方法
/**
* Returns the element at the specified position in this list.
*
* @param index index of the element to return
* @return the element at the specified position in this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E get(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return node(index).item;
}先看一下"checkElementIndex(index)"做了什么:
private void checkElementIndex(int index) {
if (!isElementIndex(index))
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}继续跟踪:
/**
* Tells if the argument is the index of an existing element.
*/
private boolean isElementIndex(int index) {
return index >= 0 && index < size;
}可以知道, "checkElementIndex(index)"对传入的下标做合法性判断。
再看看"node(index)":
/**
* Returns the (non-null) Node at the specified element index.
*/
Node<E> node(int index) {
// assert isElementIndex(index);
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}这个方法根据下标在头结点和尾结点中选取较近的一个结点,然后遍历直到找到对应下标的元素。
可以看到get方法做了两件事:
- 检验传入的下标的合法性;
- 根据下标选择头结点或者尾结点,并从选取的结点开始遍历直到找到对应下标的元素并返回。
3.5 add方法
add(int index, E element):
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this list.
* Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and any
* subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).
*
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
if (index == size)
linkLast(element);
else
linkBefore(element, node(index));
}添加元素到链表的指定位置。
跟踪checkPositionIndex(index):
private void checkPositionIndex(int index) {
if (!isPositionIndex(index))
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}继续跟踪 isPositionIndex(index):
private boolean isPositionIndex(int index) {
return index >= 0 && index <= size;
}可以看到,checkPositionIndex函数是对下标做检查,如果下标不合法就抛出异常(但是,为啥一个同样的函数要写两遍?) 。
其中if-else调用的两个函数:
/**
* Links e as last element.
*/
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}插入到链表尾。
/**
* Inserts element e before non-null Node succ.
*/
void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) {
// assert succ != null;
final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
succ.prev = newNode;
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}插入到指定结点之前。
所以步骤可以概括为:
- 下标检查;
- 插入元素到指定位置。
add(E e):
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #addLast}.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}添加元素到链表尾。
3.6 set方法
/**
* Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with the
* specified element.
*
* @param index index of the element to replace
* @param element element to be stored at the specified position
* @return the element previously at the specified position
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E set(int index, E element) {
checkElementIndex(index);
Node<E> x = node(index);
E oldVal = x.item;
x.item = element;
return oldVal;
}结合之前分析过的,可以概括出步骤为:
- 检查下标;
- 替换指定位置为新值;
- 返回旧值。
3.7 remove方法
remove(int index):
/**
* Removes the element at the specified position in this list. Shifts any
* subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their indices).
* Returns the element that was removed from the list.
*
* @param index the index of the element to be removed
* @return the element previously at the specified position
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E remove(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return unlink(node(index));
}删除指定位置上的元素。node方法在之前已经分析过了,先看看unlink方法:
/**
* Unlinks non-null node x.
*/
E unlink(Node<E> x) {
// assert x != null;
final E element = x.item;
final Node<E> next = x.next;
final Node<E> prev = x.prev;
if (prev == null) {
first = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
}
if (next == null) {
last = prev;
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}可以看出,unlink方法其实是将传入的结点移出链表,同时那个结点的前后两个结点再进行连接。把结点里对元素对象的引用设置为null,如果外部也没有引用指向那个元素对象,那GC就自然会帮我们回收啦~
步骤可以概括为:
- 检查下标;
- 删除结点;
- 返回删除的结点的元素。
remove(Object o):
/**
* Removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this list,
* if it is present. If this list does not contain the element, it is
* unchanged. More formally, removes the element with the lowest index
* {@code i} such that
* <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>
* (if such an element exists). Returns {@code true} if this list
* contained the specified element (or equivalently, if this list
* changed as a result of the call).
*
* @param o element to be removed from this list, if present
* @return {@code true} if this list contained the specified element
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item)) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}删除LinkedList中第一个与传入对象相同的元素 ,如果没有就不做修改。
结合前面已经分析过的,步骤可以概括为:
- 遍历结点找到对应的元素,如果找不到返回false;
- 删除找到的结点。
4、总结
要点总结:
- ArrayList底层是数组,初始容量默认为10,每次扩容为原容量的1.5倍(向下取整);
- ArrayList基于动态数组实现,扩容的底层通过JNI调用JVM里由C/C++编写的native方法实现,可概括为申请一块新的内存存放新数组,再把原数组的数据拷贝到新内存中;
- ArrayList和LinkedList都不是线程安全,底层存储元素的是一个Object数组,能存放任何元素包括null;
- ArrayList和LinkedList都实现了快速失败机制;
- 删除元素是不会减少容量,存储数组最后一个空出来的位置的引用会变成null,减少容量要调用trimToSize();
- Vector线程安全,增删操作都用synchronized实现同步,但是效率有损失,并且每次扩容都是100%的比率增长,比较消耗内存,目前已经过时。可以用JUC包下的CopyOnWriteArrayList容器代替或者用Collections的方法包装ArrayList(例:List list = Collections.synchronizedList(new Array List<>());)保证线程安全。Vector初始容量为10,每次以一倍的比率扩容,扩容的底层实现与ArrayList相同;
- LinkedList的底层是一个双向链表,查找和增删时间复杂度均为O(n),增删在大部分情况下优于ArrayList(不是绝对,例如一直在末尾删除,ArrayList不需要移动数组,时间复杂度是常量级),查询在大部分情况下不如ArrayList(不是绝对,例如查询的是首个元素);
- 增删多的情况一般用LinkedList。
参考资料
- JDK1.8源码





 本文深入剖析了Java集合框架中的ArrayList、LinkedList及Vector的特点与区别,详细解释了它们的底层实现,如数组与链表的运用,以及扩容、增删查改等操作的原理。
本文深入剖析了Java集合框架中的ArrayList、LinkedList及Vector的特点与区别,详细解释了它们的底层实现,如数组与链表的运用,以及扩容、增删查改等操作的原理。
















 533
533

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








