文章目录
[一] 简介:
一个基于已链接节点的、范围任意的 BlockingQueue 。此队列按 FIFO(先进先出)排序元素。队列的头部 是在队列中时间最长的元素。队列的尾部 是在队列中时间最短的元素。新元素插入到队列的尾部,并且队列获取操作会获得位于队列头部的元素。链接队列的吞吐量通常要高于基于数组的队列,但是在大多数并发应用程序中,其可预知的性能要低。
可选的容量范围构造方法参数作为防止队列过度扩展的一种方法。如果未指定容量,则它等于 Integer.MAX_VALUE 。除非插入节点会使队列超出容量,否则每次插入后会动态地创建链接节点。
此类及其迭代器实现 Collection 和 Iterator 接口的所有可选 方法。
此类是 Java Collections Framework 的成员。
[二] 架构
UML
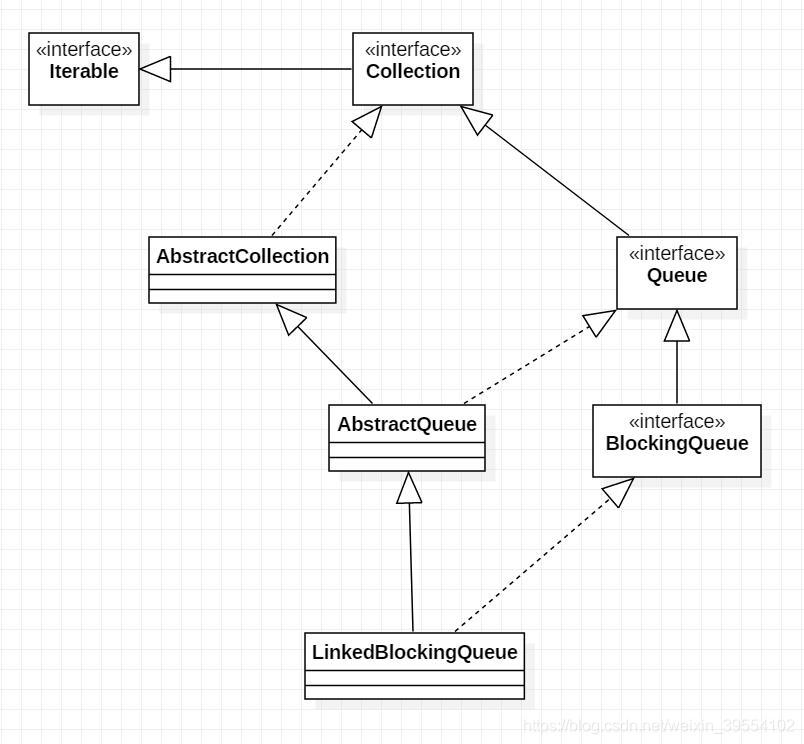
public class LinkedBlockingQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E>
implements BlockingQueue<E>, java.io.Serializable {
}
存储元素的数据节点 Node
/**
* 链接列表节点类
*/
static class Node<E> {
E item;
/**
* 其中一个:
* - 真正的后继节点
* - 这个节点,意思是后继节点是head.next
* - null,意味着没有后继节点(这是最后一个节点)
*/
Node<E> next;
Node(E x) {
item = x;
}
}
[三] 字段属性
/** 容量限制,如果没有,则最大为Integer.MAX_VALUE */
private final int capacity;
/** 当前的元素数量 */
private final AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(0);
/** 链表的头指针 */
private transient Node<E> head;
/** 链表的为指针*/
private transient Node<E> last;
/** 锁持有 take, poll, etc */
private final ReentrantLock takeLock = new ReentrantLock();
/** 等待队列获取*/
private final Condition notEmpty = takeLock.newCondition();
/** 锁持有 put, offer, etc */
private final ReentrantLock putLock = new ReentrantLock();
/** 等待队列放入 */
private final Condition notFull = putLock.newCondition();
[四]构造方法
创建一个容量为 Integer.MAX_VALUE 的 LinkedBlockingQueue。
public LinkedBlockingQueue() {
this(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
创建一个具有给定(固定)容量的 LinkedBlockingQueue。
public LinkedBlockingQueue(int capacity) {
if (capacity <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.capacity = capacity;
last = head = new Node<E>(null);
}
创建一个容量是 Integer.MAX_VALUE 的 LinkedBlockingQueue,最初包含给定 collection 的元素,元素按该 collection 迭代器的遍历顺序添加。
public LinkedBlockingQueue(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;
putLock.lock(); // Never contended, but necessary for visibility
try {
int n = 0;
for (E e : c) {
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (n == capacity)
throw new IllegalStateException("Queue full");
enqueue(e);
++n;
}
count.set(n);
} finally {
putLock.unlock();
}
}
[五] 核心方法
offer(E) 插入元素到尾部
将指定元素插入到此队列的尾部(如果立即可行且不会超出此队列的容量),在成功时返回 true,如果此队列已满,则返回 false。
public boolean offer(E e) {
if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
if (count.get() == capacity)
return false;
int c = -1;
final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;
putLock.lock();
try {
if (count.get() < capacity) {
enqueue(e);
c = count.getAndIncrement();
if (c + 1 < capacity)
notFull.signal();
}
} finally {
putLock.unlock();
}
if (c == 0)
signalNotEmpty();
return c >= 0;
}
enqueue(E)
创建一个新节点, 链接到链表的尾部
private void enqueue(E x) {
// assert putLock.isHeldByCurrentThread();
last = last.next = new Node<E>(x);
}
signalNotEmpty()
发出等待的信号。 仅来自put / offer(通常不会锁定takeLock)。
private void signalNotEmpty() {
final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;
takeLock.lock();
try {
notEmpty.signal();
} finally {
takeLock.unlock();
}
}
poll() 查看头元素
public E poll() {
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
if (count.get() == 0)
return null;
E x = null;
int c = -1;
final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;
takeLock.lock();
try {
if (count.get() > 0) {
x = dequeue();
c = count.getAndDecrement();
if (c > 1)
notEmpty.signal();
}
} finally {
takeLock.unlock();
}
if (c == capacity)
signalNotFull();
return x;
}
dequeue()
从队列头部删除节点。
private E dequeue() {
// assert takeLock.isHeldByCurrentThread();
Node<E> h = head;
Node<E> first = h.next;
h.next = h; // help GC
head = first;
E x = first.item;
first.item = null;
return x;
}
signalNotFull()
发出等待信号。 仅从take / poll调用。
private void signalNotFull() {
final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;
putLock.lock();
try {
notFull.signal();
} finally {
putLock.unlock();
}
}
peek() 移除头元素
public E peek() {
if (count.get() == 0)
return null;
final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;
takeLock.lock();
try {
Node<E> first = head.next;
if (first == null)
return null;
else
return first.item;
} finally {
takeLock.unlock();
}
}
[六] BlockingQueue 方法(阻塞)
put(E) 放入元素
将指定元素插入到此队列的尾部,如有必要,则等待空间变得可用。
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int c = -1;
final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
putLock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count.get() == capacity) {
notFull.await();
}
enqueue(e);
c = count.getAndIncrement();
if (c + 1 < capacity)
notFull.signal();
} finally {
putLock.unlock();
}
if (c == 0)
signalNotEmpty();
}
take() 取出元素
获取并移除此队列的头部,在元素变得可用之前一直等待(如果有必要)。
public E take() throws InterruptedException {
E x;
int c = -1;
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;
takeLock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count.get() == 0) {
notEmpty.await();
}
x = dequeue();
c = count.getAndDecrement();
if (c > 1)
notEmpty.signal();
} finally {
takeLock.unlock();
}
if (c == capacity)
signalNotFull();
return x;
}
offer(E , long, TimeUnit) 放入元素
将指定元素插入到此队列的尾部,如有必要,则等待指定的时间以使空间变得可用。
public boolean offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
int c = -1;
final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
putLock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count.get() == capacity) {
if (nanos <= 0)
return false;
nanos = notFull.awaitNanos(nanos);
}
enqueue(e);
c = count.getAndIncrement();
if (c + 1 < capacity)
notFull.signal();
} finally {
putLock.unlock();
}
if (c == 0)
signalNotEmpty();
return true;
}
poll(long, TimeUnit) 移除元素
获取并移除此队列的头部,在指定的等待时间前等待可用的元素(如果有必要)。
public E poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
E x = null;
int c = -1;
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;
takeLock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count.get() == 0) {
if (nanos <= 0)
return null;
nanos = notEmpty.awaitNanos(nanos);
}
x = dequeue();
c = count.getAndDecrement();
if (c > 1)
notEmpty.signal();
} finally {
takeLock.unlock();
}
if (c == capacity)
signalNotFull();
return x;
}
[七] 迭代器 iterator()
迭代器的内部实现 Itr
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
/*
* Basic weakly-consistent iterator. At all times hold the next
* item to hand out so that if hasNext() reports true, we will
* still have it to return even if lost race with a take etc.
*/
private Node<E> current; // 当前节点
private Node<E> lastRet; // 最后返回的节点
private E currentElement; // 当前元素
Itr() {
fullyLock();
try {
current = head.next;
if (current != null)
currentElement = current.item;
} finally {
fullyUnlock();
}
}
}
/**
* Lock to prevent both puts and takes.
*/
void fullyLock() {
putLock.lock();
takeLock.lock();
}
/**
* Unlock to allow both puts and takes.
*/
void fullyUnlock() {
takeLock.unlock();
putLock.unlock();
}
hasNext()
public boolean hasNext() {
return current != null;
}
next()
public E next() {
fullyLock();
try {
if (current == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
E x = currentElement;
lastRet = current;
current = nextNode(current);
currentElement = (current == null) ? null : current.item;
return x;
} finally {
fullyUnlock();
}
}
nextNode(Node p)
返回p的下一个实时后继,如果不是,则返回null。
与其他遍历方法不同,迭代器需要同时处理:
- 出列节点(p.next == p)
- (可能是多个)内部删除的节点 (p.item == null)
private Node<E> nextNode(Node<E> p) {
for (; ;) {
Node s = p.next;
if (s == p)
return head.next;
if (s == null || s.item != null)
return s;
p = s;
}
}
remove()
移除上一次指向 next() 方法返回的元素
public void remove() {
if (lastRet == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
fullyLock();
try {
Node<E> node = lastRet;
lastRet = null;
for (Node<E> trail = head, p = trail.next;
p != null;
trail = p, p = p.next) {
if (p == node) {
unlink(p, trail);
break;
}
}
} finally {
fullyUnlock();
}
}










 本文深入解析了Java中LinkedBlockingQueue的实现原理,包括其架构、字段属性、构造方法及核心方法,如offer、poll、peek等。此外,还详细介绍了其作为BlockingQueue的阻塞方法,如put、take、offer和poll的带时间限制版本。最后,文章提供了迭代器的内部实现细节。
本文深入解析了Java中LinkedBlockingQueue的实现原理,包括其架构、字段属性、构造方法及核心方法,如offer、poll、peek等。此外,还详细介绍了其作为BlockingQueue的阻塞方法,如put、take、offer和poll的带时间限制版本。最后,文章提供了迭代器的内部实现细节。
















 573
573

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








