Generate matrices A, with random Gaussian entries, B, a Toeplitz matrix, where A ∈ Rn×m and B ∈ Rm×m,for n = 200, m = 500.
import numpy as np
import scipy.linalg
mu, sigma = 0, 0.1
n = 200
m = 500
A = np.random.normal(mu, sigma, size=(n, m))
c = [i for i in range(m+1)]
B = scipy.linalg.toeplitz(c,c)
Exercise 9.1: Matrix operations
Calculate A + A, AA⊤, A⊤A and AB. Write a function that computes A(B − λI) for any λ.
print("A + A:")
print(A + A)
print("A·A⊤:")
print(np.dot(A,A.T))
print("A⊤A:")
print(np.dot(A.T,A))
print("AB:")
print(np.dot(A,B))
def compute_func(A,B,λ):
print("A(B − λI):")
print(np.dot(A,B-λ*(np.eye(m, k=0))))
compute_func(A,B,2.0)Exercise 9.2: Solving a linear system
Generate a vector b with m entries and solve Bx = b.
b = np.array([1 for i in range(m)])
x = np.linalg.solve(B, b)
print(x)Exercise 9.3: Norms
Compute the Frobenius norm of A: ∥A∥F and the infinity norm of B: ∥B∥∞. Also find the largest andsmallest singular values of B.
print("the Frobenius norm of A:")
print(np.linalg.norm(A,'fro'))
print("the infinity norm of B:")
print(np.linalg.norm(B,np.inf))
print("the largest singular values:")
print(np.linalg.norm(A,2))
print("the smallest singular values:")
print(np.linalg.norm(A,-2))Exercise 9.4: Power iteration
Generate a matrix Z, n × n, with Gaussian entries, and use the power iteration to find the largesteigenvalue and corresponding eigenvector of Z. How many iterations are needed till convergence?
Optional: use the time.clock() method to compare computation time when varying n.
Z = np.random.normal(mu,sigma,size=(n,n))
x = np.array([0 for i in range(n)])
y = np.array([1 for i in range(n)])
tmp = 0
tmp1 = 100
num = 0
begin = time.clock()
while(abs(tmp1 - tmp)>0.0000001):
x = np.dot(Z,y)
tmp1 = tmp
tmp = np.linalg.norm(x,2)
y = x/tmp
num += 1
end = time.clock()
print(end-begin)
print("the largest eigenvalue:", tmp)
print("the corresponding eigenvector:", y)
print("The number of iterations:", num)Exercise 9.5: Singular values
Generate an n × n matrix, denoted by C, where each entry is 1 with probability p and 0 otherwise. Usethe linear algebra library of Scipy to compute the singular values of C. What can you say about therelationship between n, p and the largest singular value?
x = 0
def Singular_values(n, p):
C = []
for i in range(n):
C1 = []
for j in range(n):
if np.random.random() <= p:
C1.append(1)
else:
C1.append(0)
C.append(C1)
C = np.mat(C)
x = scipy.linalg.svdvals(C)
return np.max(x)
for n in [10*(i + 1) for i in range(10)]:
for p in [0.1*(i + 1) for i in range(9)]:
print( str(Singular_values(n, p))+ " ",end='')
print("")result:
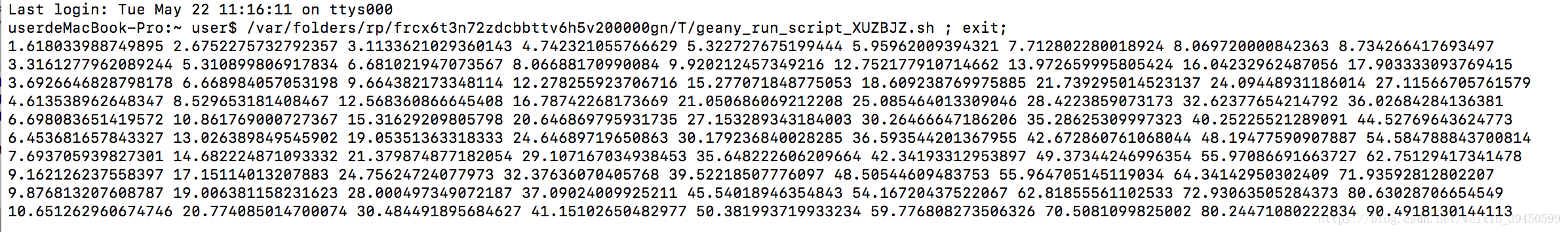
横坐标为p,纵坐标为n。由输出结果得出,奇异值随n的增长而增长,随p的增长而增长。
Exercise 9.6: Nearest neighbor
Write a function that takes a value z and an array A and finds the element in A that is closest to z. Thefunction should return the closest value, not index.
Hint: Use the built-in functionality of Numpy rather than writing code to find this value manually. Inparticular, use brackets and argmin.

def find_closest(A, z):
C = np.abs(A-z)
idx = np.argmin(C)
return A[idx // A[0].size][idx % A[0].size]
A = np.random.rand(n, n)
print(A)
print(find_closest(A, 1))






















 355
355

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








